Ratabulus ventralis, Imamura & Gomon, 2010
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.24199/j.mmv.2010.67.03 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10879374 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/4A057A6D-335F-7049-30A0-FD5AFD31FDA2 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Ratabulus ventralis |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Ratabulus ventralis View in CoL sp. nov.
New English name: Longfin flathead
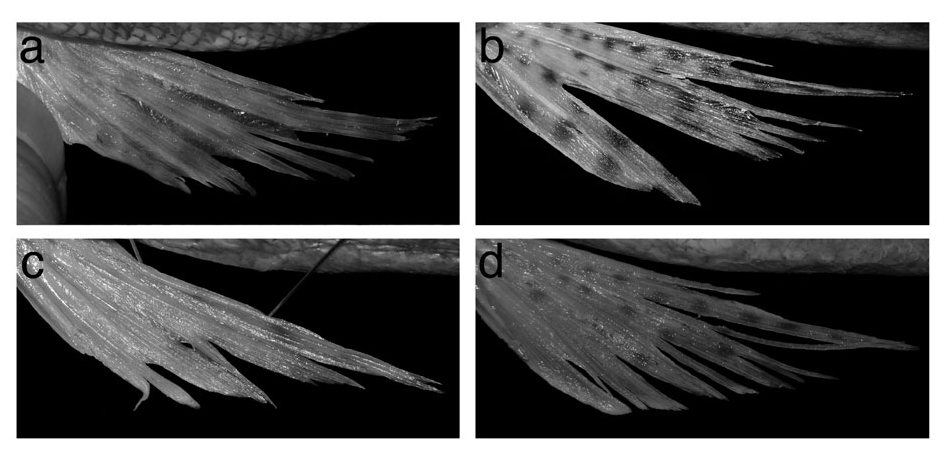
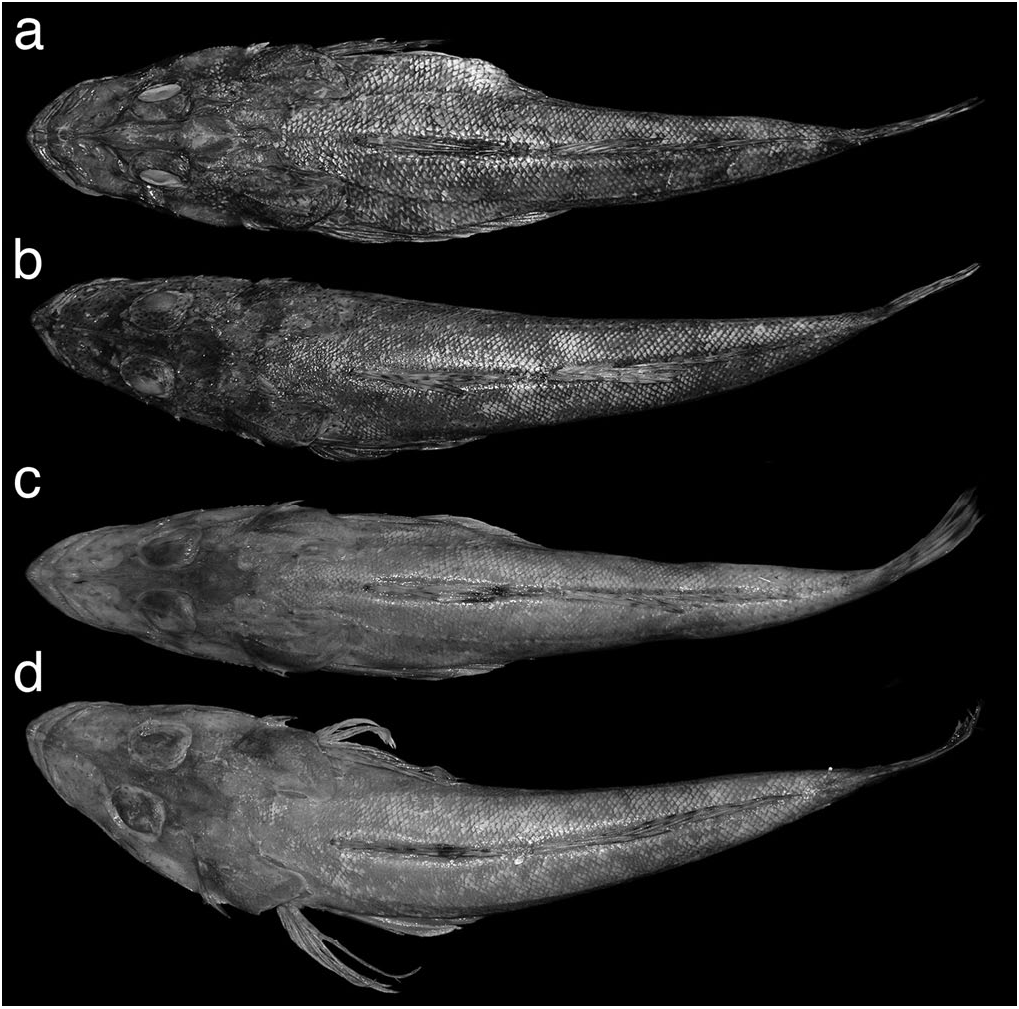
( Figures 2d View Figure 2 , 3d View Figure 3 , 4d View Figure 4 , 5d View Figure 5 , 6d View Figure 6 )
Ratabulus diversidens View in CoL (nec McCulloch, 1914): Paxton et al., 1989: 470 (list and distribution, off Brisbane) (in part); Knapp, 1999: 2410 (description, Coral Sea) (in part); Hoese et al., 2006: 944 (list and distribution, off Brisbane) (in part).
Holotype. CSIRO H6116-02 View Materials , 304 mm SL, east of Townsville , Queensland (18°39.3'S, 148°03.4'E – 18°36.4'S, 147°59.5'E), 244–248 m, 8 December 1985, FRV Soela. GoogleMaps
Paratypes. Eleven specimens (172–328 mm SL) from Queensland, northeastern Australia. AMS I.25804-019, 278 mm SL, just north of Townsville (17°51'S, 147°01'E), 260 m, 9 January 1986 GoogleMaps , FRV Soela; AMS I.25823-002, 328 mm SL, north of Townsville (17°58'S, 147°02'E), 260 m, 16 January 1986 GoogleMaps , FRV Soela; AMS I.25832-007- 006, 284 mm SL, north of Townsville (17°58'S, 147°03'E), 260 m, 19 January 1986 GoogleMaps , FRV Soela; CSIRO H690-03 View Materials , 232 mm SL, Swain Reefs (21°31'S, 152°58'E), 247 m, 20 November 1985 GoogleMaps , FRV Soela; QM I. 18546, 284 mm SL, off Swain Reefs (22.54°S, 152.12°E – 22.59°S, 152.12°E), 347–384 m, 3 October 1980 GoogleMaps ; QM I. 19276, 255 mm SL, east of Capricorn Group (23.11°S, 153.00°E – 23.01°S, 152.55°E), 366–392 m, 20 September 1980 GoogleMaps ; QM I. 20934, 254 mm SL, east of Swain Reefs (22.03°S, 153.05°E), 170 m, 28 August 1983 GoogleMaps ; QM I. 20939, 316 mm SL, east of Bunker Group (23.59°S, 152.51°E), 340 m, 27 August 1983 GoogleMaps ; QM I. 21624, 221 mm SL, southeast of Swain Reefs (22.4°S, 153.35°E), 310 m, 6 September 1983 GoogleMaps ; QM I. 23088, 260 mm SL, off Swain Reefs (20.49°S, 151.52°E), 288 m, 20 September 1986 GoogleMaps ; QM I. 34327, 172 mm SL, east of Noosa (26.25°S, 153.4°E), 119–120 m, 19 July 2002 GoogleMaps .
Diagnosis. A species of Ratabulus with 91–104 anteroventrally slanted oblique scale rows above lateral line; snout length 30.9– 32.4% HL, markedly decreasing proportionally with growth; pectoral fin length 15.8–18.6% SL; pelvic fin length 26.2– 28.2% SL; nasal bone with tubercles; dorsal surface of head with small, round, brown spots, body without dark spots; pelvic fin with small brown spots.
Description. Dorsal fin rays I + VIII + I-11 (I + VII or VIII + I-11, or I + IX + 0-11, VII in one, IX in one); anal fin rays 12; pectoral fin rays 2 + 11 + 7 = 20 (2 + 10 or 11 + 6–9 = 19–21); pelvic fin rays I, 5; branched caudal fin rays 13 (12 or 13); scales in lateral line 55 (52–55), anterior four (3–5) scales with spine; posteroventrally slanted oblique scale rows above lateral line 83 (71–76); anteroventrally slanted oblique scale rows above lateral line 98 (91–104); gill rakers 1 + 7 = 8 (1 + 7 or 8 = 8 or 9).
See table 1 for selected proportional measurements. Head length 2.7 (2.4–2.6) in SL. Snout rather robust, its length 3.2 in HL (3.1–3.2 in HL, slightly decreasing proportionally with growth, fig. 9). Iris lappet broad and simple both dorsally and ventrally (fig. 5d). Interorbital width 13.9 (12.5–16.7) in HL. Nasal bone without distinct spines, but with tubercles (fig. 4d). Lachrymal with three anterolaterally directed spines on left side, right side partly damaged (2–5, with short serrations posterior to spines in some paratypes). Single preocular spine in front of eye, its base with tubercles (with small spines in several paratypes). Suborbital ridge roughly serrated by many small to large spines; anteriormost (preorbital) spine small. Supraorbital ridge serrated except anteriorly. Single postocular spine present. Pterotic with serrated ridge ending in strong spine. Parietal with single spine, lacking spines posteriorly (with small spines or tubercles in many paratypes). Supratemporal with smooth ridge (with serrated ridge in many paratypes) ending in spine. Posttemporal with one spine (usually with 1–3, rarely with serrated ridge ending in one spine). Preopercle with two (two or three) spines; upper longer, not reaching posterior margin of opercle, with one small spine on base laterally. Ridge of lower opercular spine without serrations (with weak serrations or with spine in some paratypes). Posterior end of maxilla reaching just beyond anterior margin of eye. Front of upper jaw with short canines (with conical teeth in some paratypes) anteriorly, followed by long and slender canines; middle and posterior parts of jaw with villiform teeth, one or two inner rows (innermost row) having small, slender conical teeth. Lower jaw with narrow tooth band of small conical teeth anteriorly, teeth smaller posteriorly, followed by villiform teeth; innermost row with short to moderately long (short to long and slender) canines. Palatine with moderately broad tooth band; anterior part with moderately long (short to moderately long) canines laterally, and long, slender (moderately long to long and slender) canines mesially; posterior part with moderately long to long conical teeth. Vomer with about three (about 3–5) tooth rows medially; short canines anteriorly, followed by long, slender canines. Posterior margin of caudal fin slightly concave (mostly straight in some paratypes); caudal fin length 6.0 (5.3–6.0) in SL. Pectoral fin length 5.8 (5.4–6.3) in SL. Posterior tip of pelvic fin reaching second (third to fourth) anal fin ray; pelvic fin length 3.7 (3.5–3.8) in SL.
Color in alcohol. Head and body pale brown dorsally, pale yellowish ventrally; dorsal surface of head with small, round, brown spots; body without spots and bands dorsally; side below lateral line with one pale grayish longitudinal stripe (grayish stripe formed by continuous series of spots in some paratypes). First dorsal fin with one blackish submarginal stripe, base clear anteriorly with small scattered black spots; second dorsal fin with brown (dark brown in some paratypes) spots. Anal fin pale. Caudal fin with several black longitudinal narrow stripes and spots posteriorly; upper part of caudal fin with several brown spots. Pectoral and pelvic fins with small brown spots (fig. 6d).
Distribution. Northeastern Australia from Townsville (17°51'S) to Noosa, Queensland (26.25°S), at depths of at least 120–366 m (fig. 1).
Etymology. The specific name ventralis from Latin, meaning ‘of the belly’, refers to this species’ characteristic long pelvic fin.
Remarks. R. ventralis is most similar to R. diversidens , from which it can be distinguished as discussed in ‘Remarks’ in the above treatment of the latter. This species is poorly represented in museum collections and has been mostly overlooked in the literature. It has been considered by authors, which have treated specimens, as simply northern records of R. diversidens .
| CSIRO |
Australian National Fish Collection |
| QM |
Queensland Museum |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Ratabulus ventralis
| Imamura, Hisashi & Gomon, Martin F. 2010 |
Ratabulus diversidens
| Hoese, D. F. & Bray, D. J. & Paxton, J. R. & Allen, G. R. 2006: 944 |
| Knapp, L. W. 1999: 2410 |
| Paxton, J. R. & Hoese, D. F. & Allen, G. R. & Hanley, J. E. 1989: 470 |