Heliogomphus chaoi Karube, 2004
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.5318.1.4 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:8B66C25D-87F5-499C-9052-65FF731FF284 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8158267 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/486087AF-0677-FFEB-FF42-FD71B5BBEFD6 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Heliogomphus chaoi Karube, 2004 |
| status |
|
Heliogomphus chaoi Karube, 2004 View in CoL
( Figs. 1–5 View FIGURE 1 View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 View FIGURE 4 View FIGURE 5 )
Specimens examined. 1♁, Giang Ly Ranger Station (12.1805 N, 108.6873 E, altitude 1516 m), Bidoup Nui Ba National Park, Lam Dong Province, Vietnam, 12.vi.2022, Q. T. Phan leg.; 1♁ (reared from larva), Hoa Trung (16.0950 N, 108.0491 E, altitude 191 m), Hoa Lien Commune , Hoa Vang District, Danang City, Vietnam, 13.iii.2021 GoogleMaps , Q. T. Phan leg.; 1♁, 3 last stadium larvae (1♁, 2♀♀), same location, 10.vi.2021 GoogleMaps ; 1 ♁, Ta Dung National Park (11.8716 N, 107.9824 E, altitude 598 m), Dak Nong Province, Vietnam, 15.v.2020 GoogleMaps , Q. T. Phan leg.; 2♁♁, Khe Gia Trang (14.4231 N, 107.7284 E, altitude 629 m), Chu Mom Ray National Park , Kon Tum Province, Vietnam, 12.vi.2019 GoogleMaps , Q. T. Phan leg.; 1♁, Chu Yang Sin National Park (12.4270 N, 108.3679 E, altitude 1033 m), Krong Mar Commune, Krong Bong District, Dak Lak Province, Vietnam, 06.v.2018 GoogleMaps , Q. T. Phan leg.; 2♁♁, Khe Giua (15.2566 N, 107.7378 E, altitude 775 m), Song Thanh National Park , Quang Nam Province, Vietnam, 25.vi.2018 GoogleMaps , Q.P. Ngo leg.; 2♀♀, same location and collector, 18.v.2019 GoogleMaps .
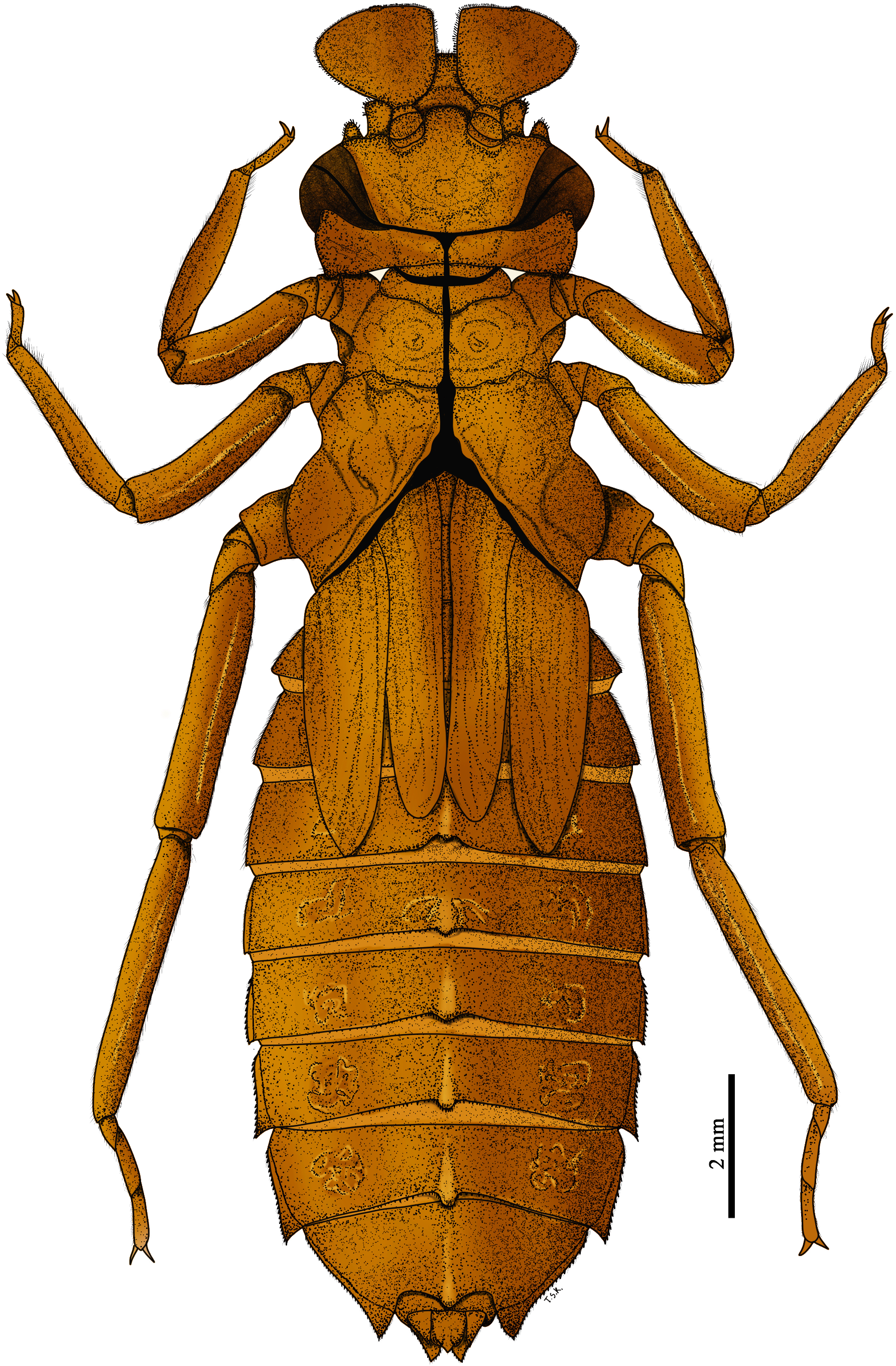
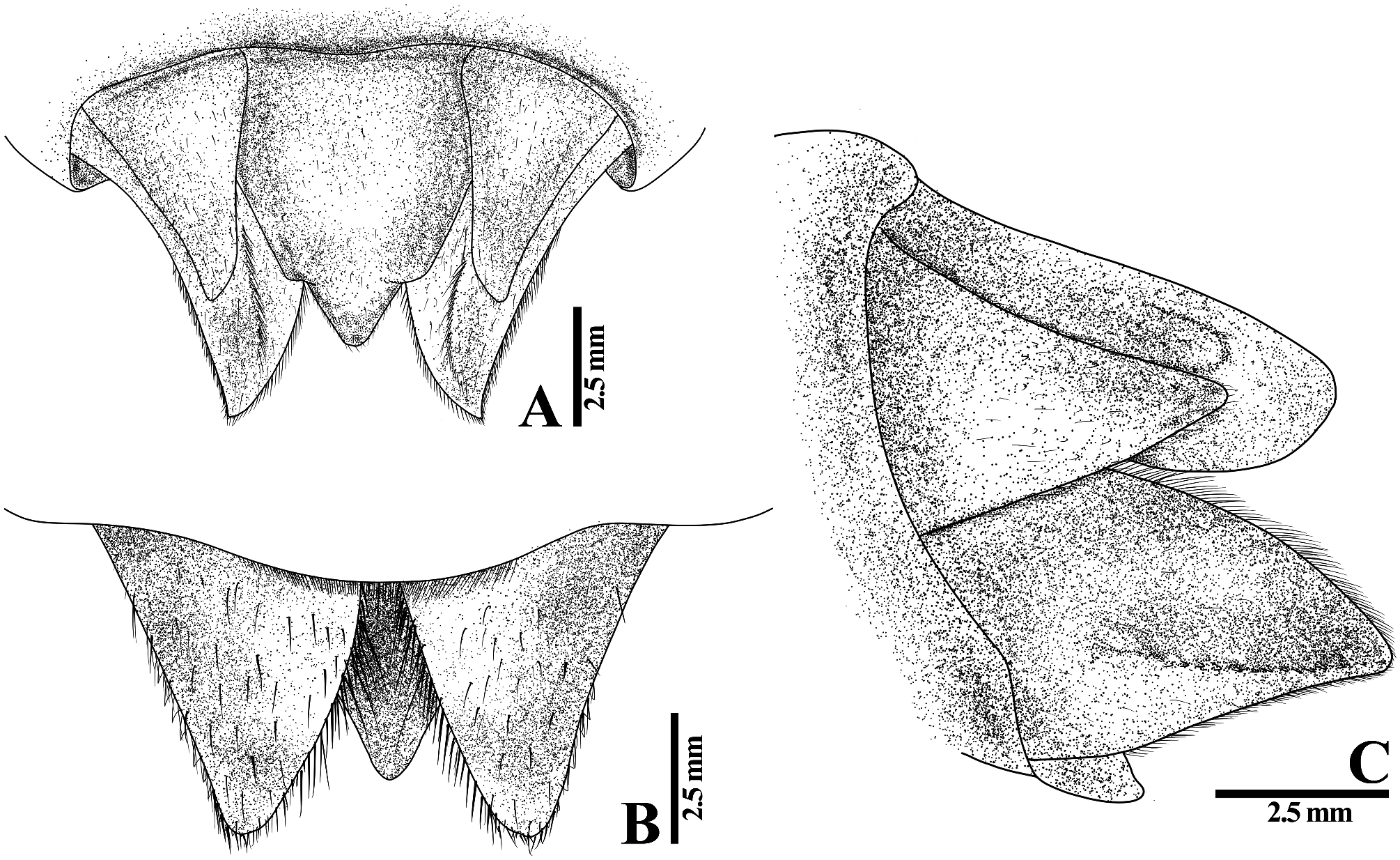
Description of larva. General appearance and colour pattern as shown in ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 ).
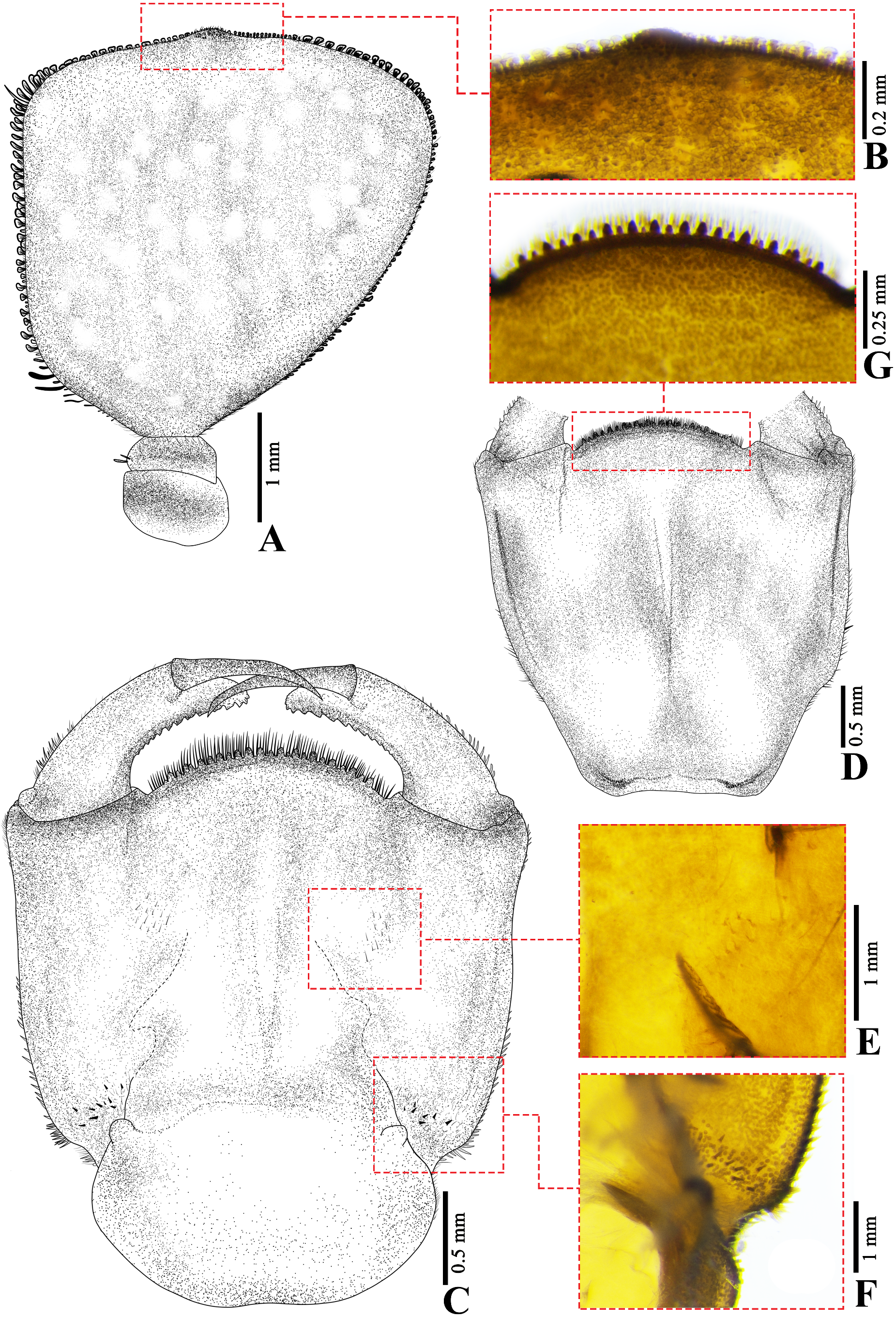
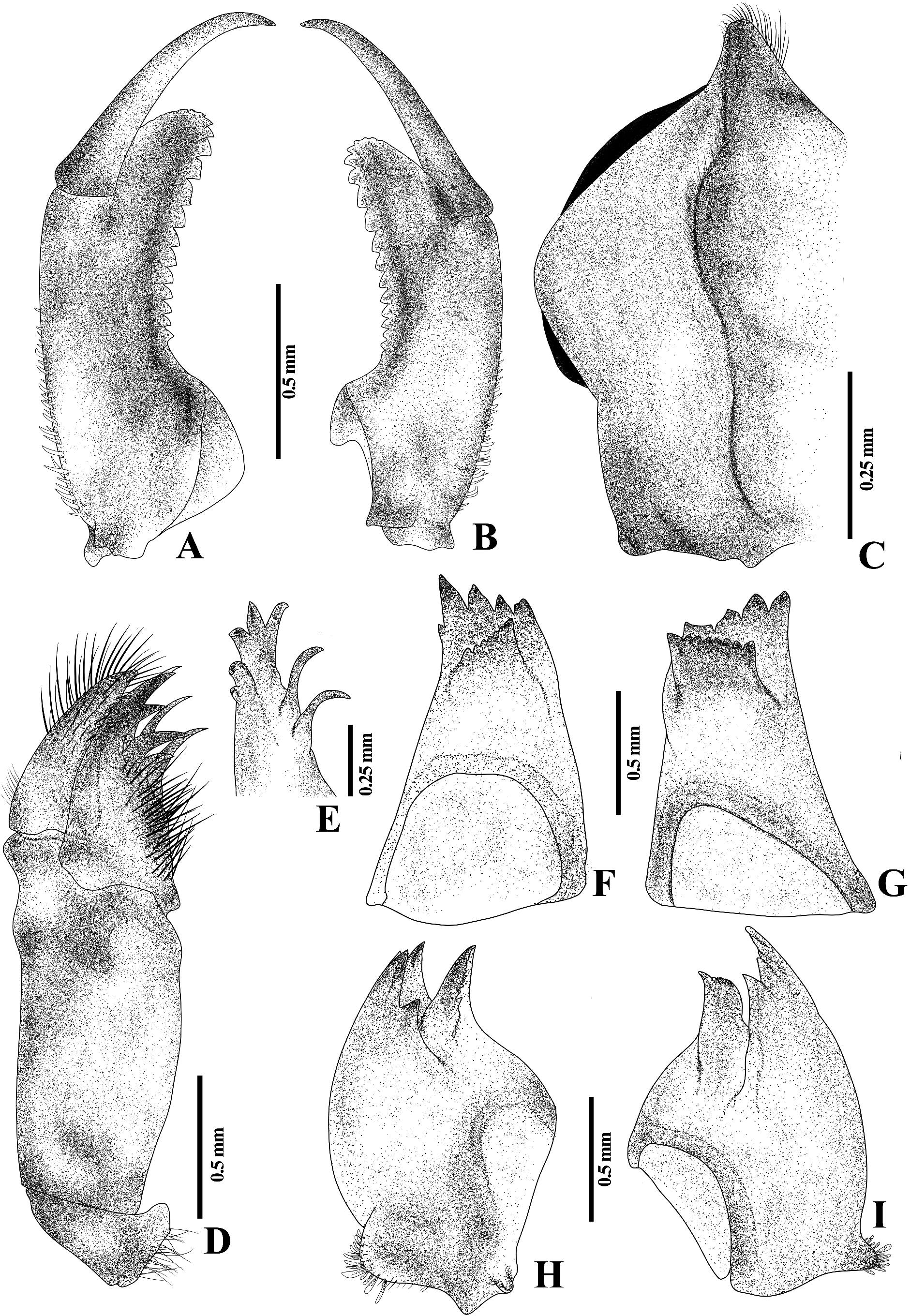
Head. Flat in dorsal view, smooth squashed pentagonal in outline; antennae ( Fig. 2A View FIGURE 2 ), 4-segmented, with scattered SLS, A1 and A2 small, cylindrical, scattered SLS, A3 enlarged, rectangular, plate-shaped, with scattered distinct SLS and BLS along margin, A4 ( Fig. 2B View FIGURE 2 ) vestigial, forming a small protuberance; labrum fan-shaped, dorsally with a ridge on the middle dividing it into two steps, with sparse long SS on distal margin and covered SLS, in ventral view with fine, small SS along distal margin and scattered SPS on basal half; clypeus with scattered SLS, distal end almost round; frons with scattered SLS, antefrons almost rectangular, postfrons protruding anteriorly and rounded on distal end ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 ). Compound eyes broad and rounded protruding laterally; occiput with scattered SLS, lateral margins slightly convergent; postocular lobes broadly rounded, with distinct protuberances, with BLS and intermingled short SS and long SS. Prementum ( Fig. 2C, D View FIGURE 2 ) subquadrate, as long as wide, lateral margins convex and convergent basally, scattered BLS on dorsal and ventral view, in dorsal view with clusters of small spinose premental setae ( Fig. 2E View FIGURE 2 ) and clusters of distinct SPS on laterobasal margin ( Fig. 2F View FIGURE 2 ), lateral margin with row of distinct SPS and SS along basal half. Ligula ( Fig. 2G View FIGURE 2 ) convex, distal margin with row of 22–24 short, rounded, subquadrate teeth, with fringe of very fine, close-set SS along the margin; labial palps ( Fig. 3A, B View FIGURE 3 ) outer margin with scattered SS and SPS, serrations along inner margin and distal margin, distal end rounded, with distinct sharp end tooth, movable hook slender, about 1.15 times length of labial palp, acuminate, bent inwards. Genae ( Fig. 3C View FIGURE 3 ) forming a bilobed, large ridge, with two distinct protuberances (anterior protuberance pointing anteriorly, posterior protuberance pointing ventrally), with long SS at the middle of its ridge. Maxilla: ( Fig. 3D, E View FIGURE 3 ) galeolacinia with seven teeth, three dorsal teeth of approximately the same size; one apical tooth largest, three ventral teeth of different size. Mandibles ( Fig. 3F–I View FIGURE 3 ) with formula: L 1+1’234 0 a(m1–6)b / R 1+1’ 234 y a(m1–6)b, a>b in both mandibles, asymmetrical.
Thorax. Narrower than head, prothorax almost saddle-shaped; pronotum broadly rounded not projecting laterally, with two crescent-shaped ridges. Wing sheaths parallel, covering SLS, reaching abdominal segment S4; anterior and posterior wing sheaths reaching half of abdominal S4 to anterior margin of abdominal S5. Legs flattened. Forelegs shortest and hind legs longest; hind legs reaching posterior margin of S8–middle of S9. Tarsal formula 2–2–3.
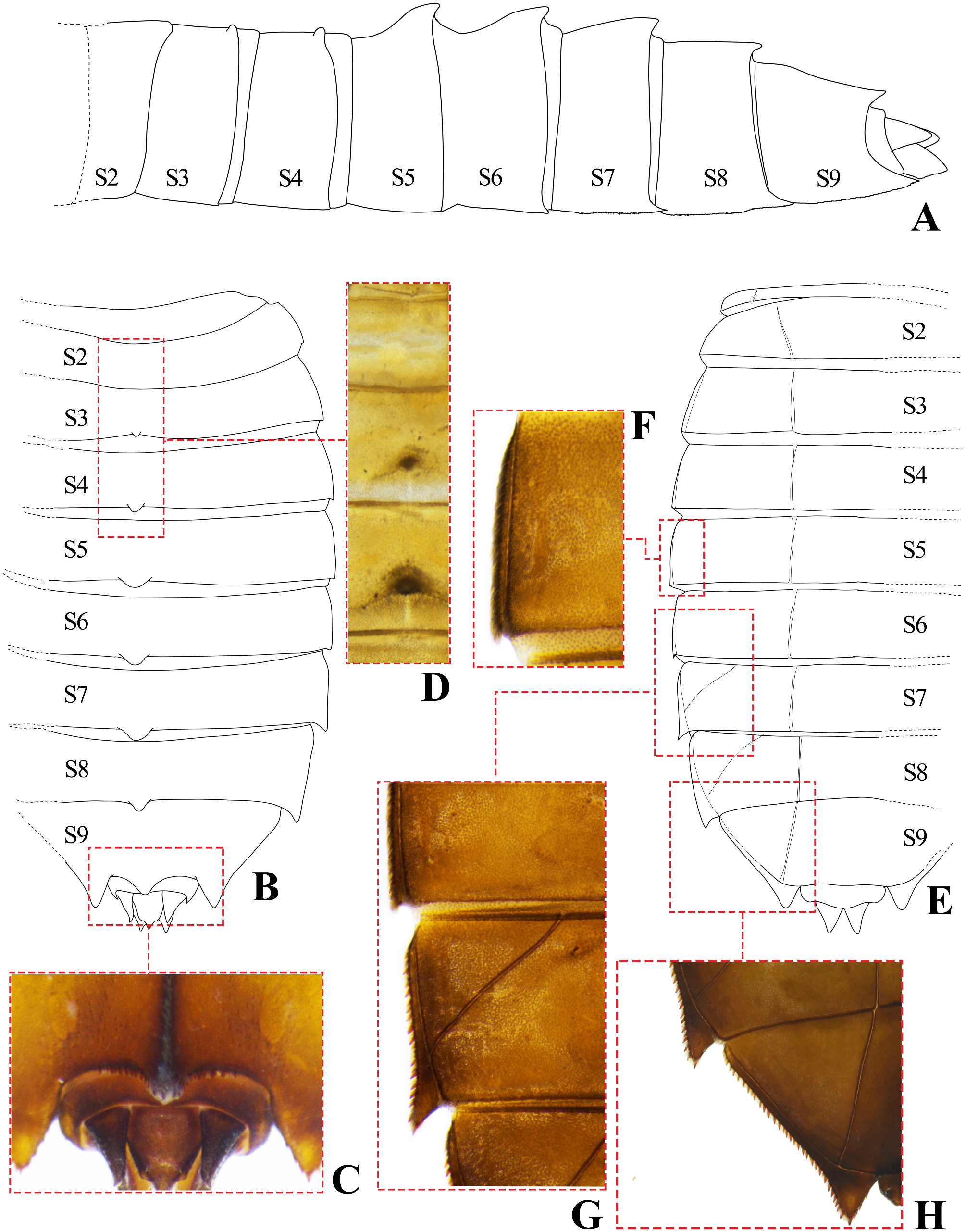
Abdomen. flat and slightly ovate, with a complex pattern of pale and dark spots on S3–8 ( Fig. 4A View FIGURE 4 ), S1 strongly reduced, S2–8 nearly equal in length, S9 largest almost covering S10, S10 small; dorsal spines on S3–9 ( Fig. 4B, D View FIGURE 4 ), those on S2–3 unsharpened, shorter, those on S5–9 roundly pointed and posteriorly directed, each spine with a cluster of spines. Terga S2–9 covered with SLS, with a row of small spines at the middle of posterior margin ( Fig. 4C View FIGURE 4 ), with scattered minute and long SS; tergite S10 with scattered, small SPS on posterior margin; lateral spines on S5–9 ( Fig. 4E–H View FIGURE 4 ) pointed posterolaterally (S9>S8=S7>S6>S5); lateral margins of S2–6 with dense, small SS, S6–9 with small serrations ( Fig.4 F–H View FIGURE 4 ). Sterna S1–S6 and S9 divided into three sternites, sterna S7–8 divided into five sternites ( Fig. 4E View FIGURE 4 ). Female gonapophyses vestigial, bilobed, lobes conical with apices rounded, the space in between equal to the basal width of each lobe. Anal appendages ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 ) longer than S10 dorsal length, almost blunt, densely covered with minute SS setae; cerci slightly shorter than epiproct, apices blunt and directed outwards; epiproct shorter than paraprocts, almost triangular-shaped, stout, feebly decurved and rounded at tip, with a pair of dorsolateral tubercles; paraproct rounded, stout, dorsal carina with long SPS and ventromedial carina with small serrations, apices blunt and directed outwards.
Differential diagnosis. This study brings the number of species known from larval stage of the genus Heliogomphus to seven. Larva of H. chaoi can be separated from other known larvae in the genus Heliogomphus by a combination of characters as follows (in paretheses other species): Dorsal spines present on S3–9 (S 4–9 in H. kelantanensis and H. selysi ; S 9 in H. retroflexus ). Lateral spines present on S7–9 (S 6–9 in H. kelantanensis ). Protuberances on postocular lobe (absent in H. bekeri , H. drescheri , H. scorpio , H. retroflexus , and H. selysi ).
Measurements (mm). (n=4); Total length 20.4−22.4; abdomen length 12.1−13.4; maximum width of head 3.6−4.0; head length 3.5−4.0; maximum width of prementum 7.0−7.5; prementum length 6.95−7.30; labial palp length 3.1−3.4; movable hook length 2.1−2.2; femur length (fore: mid: hind) 2.3−2.5: 3.0: 4.4−5.0; tibia length (fore: mid: hind) 2.7−3.3: 2.7−3.0: 3.8−4.2; tarsus length (fore: mid: hind) 0.6−1.0: 1.0−1.2: 2.0; cerci length 1.4−1.5; epiproct length 1.7−1.9; paraprocts length 1.5−1.7.
Habitat and Ecology. In Hoa Trung, the larvae of Heliogomphus chaoi were found in a pool among leaf litter ( Fig. 6A View FIGURE 6 ). They occur with other gomphid species such as H. aluoiensis , Leptogomphus uenoi Asahina, 1996 , L. inouei Karube, 2014 , Gomphidia abbotti Williamson, 1907 , Melligomphus minimus ( Karube, 2014) , and Paragomphus capricornis ( Förster, 1914) .
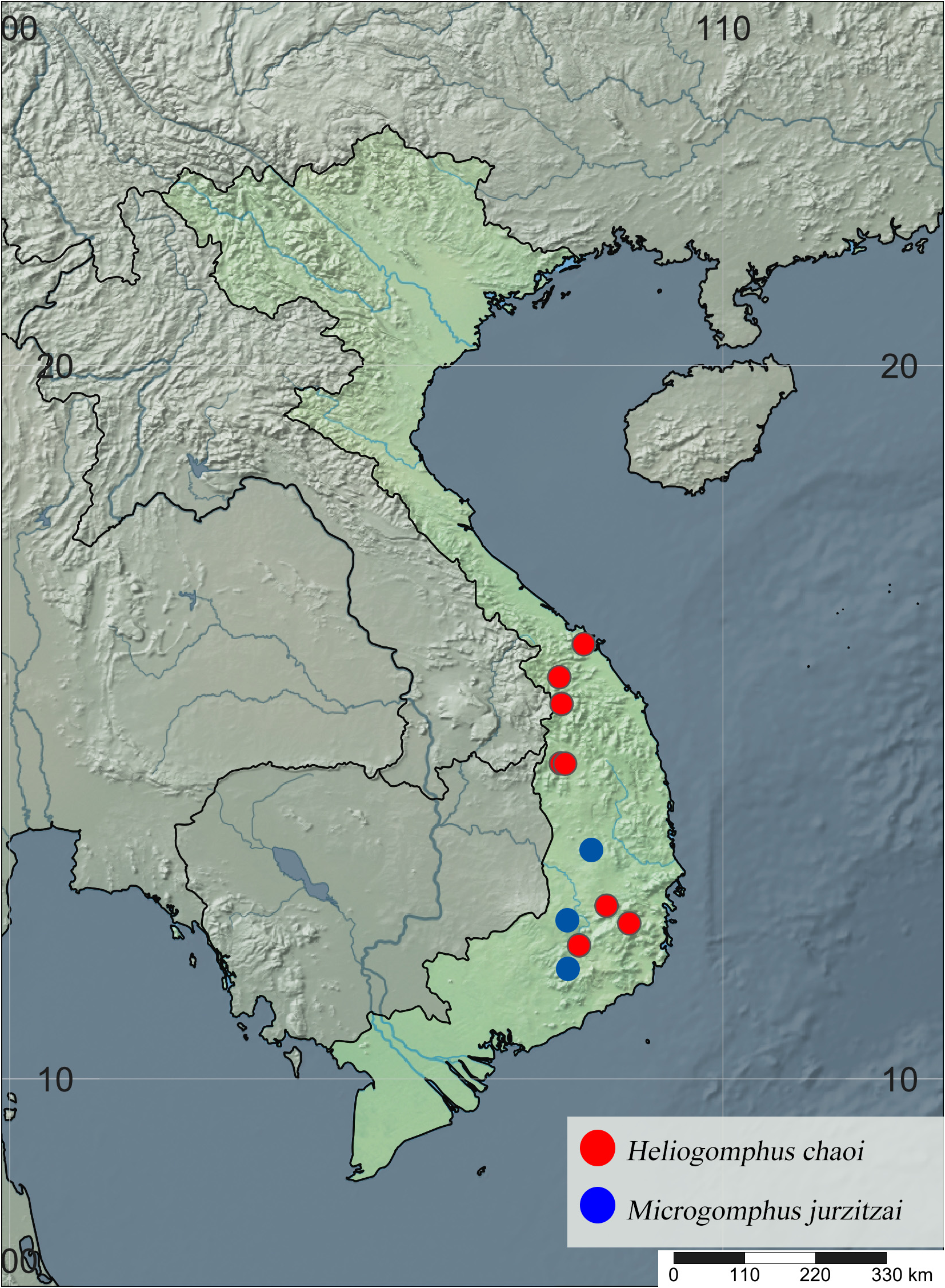
Distribution. ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 ). Vietnam: Quang Nam (Song Thanh National Park; Aso, Dong Giang), Da Nang (Hoa Trung, Hoa Lien; Son Tra Nature Reserve), Kon Tum (Chu Mom Ray National Park), Dak Nong (Ta Dung National Park) and Lam Dong (Bidoup Nui Ba National Park; Bao Loc) Provinces ( Karube 2004; Karube et al. 2020; this study).
| T |
Tavera, Department of Geology and Geophysics |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |