Balgus Fleutiaux, 1920
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4083.4.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:D35A42FE-D0A6-4D9A-9A16-71BE5EC00F57 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6084404 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/407D87AE-C833-4438-DFB3-FED3668B2CA9 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Balgus Fleutiaux, 1920 |
| status |
|
Key to the species of genus Balgus Fleutiaux, 1920 , adapted from Bonvouloir (1875) and Chassain & Touroult (2013)
The identification key to the species of Balgus was adapted from Bonvouloir (1875) and Chassain & Touroult (2013), with the inclusion of new characters: presence or absence of a pair of yellow pronotal tubercles capable of emitting green light ( Costa, 1984); thoracic sclerites in lateral view partially visible or hidden under the elytra; shape of eye in lateral view; body format; presence or absence of the anterior pronotal tubercles; presence or absence of the longitudinal median carina on ventrite 5 and the number of longitudinal teeth; format of ventrite 5; shape of the elytral apex; and format of the median longitudinal depression in the anterior region of the head.
1. Pronotum with a pair of yellow tubercles capable of emitting green light (bioluminescence) ( Costa, 1984); thoracic sclerites in lateral view partially visible; eye in lateral view with corrugated surface, dorsal margin sinuous; large size (20–26 mm). (Figure 8)................................................................................. Balgus schnusei
- Pronotum without bioluminescent tubercles; thoracic sclerites, hidden under the elytra, not visible in lateral view; eye in lateral view with spherical surface, dorsal margin not sinuous; small to medium size (7.5–18.7 mm) ( Chassain & Touroult, 2013).. 2
2. Elytra covered with diverse tubercles distributed across the elytral surface......................................... 6
- Elytra covered only with an anterior suboval tubercle or without tubercles........................................ 3
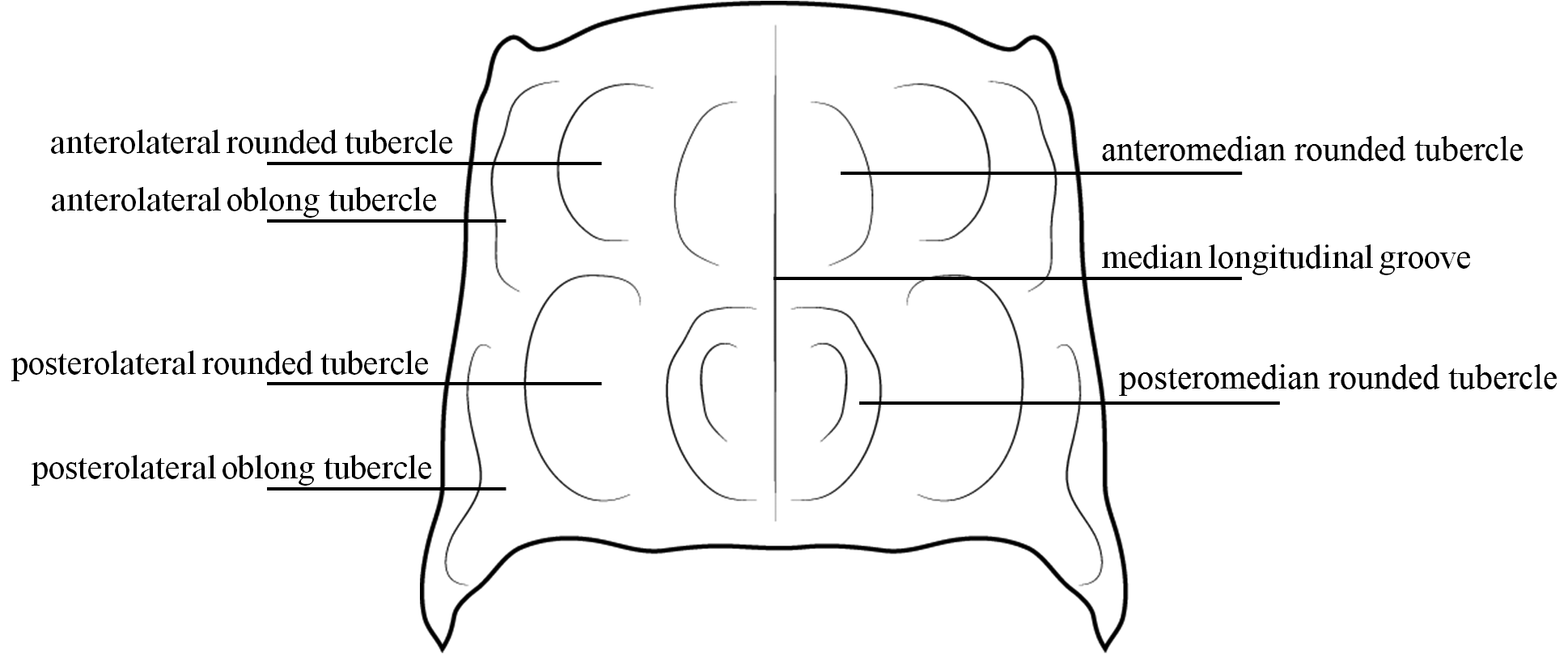
3. Posterior angle of the pronotum with short oblique carina ( Figure 2E View FIGURE 2 )........................................... 4
- Posterior angle of the pronotum without short oblique carina.................................................. 5
4. Scutellum carinate; elytra with an anterior suboval tubercle, covered with strong rugosities........... Balgus subfasciatus
- Scutellum not carinate; elytra without tubercles. ( Figure 2 View FIGURE 2 )..................................... Balgus albofasciatus
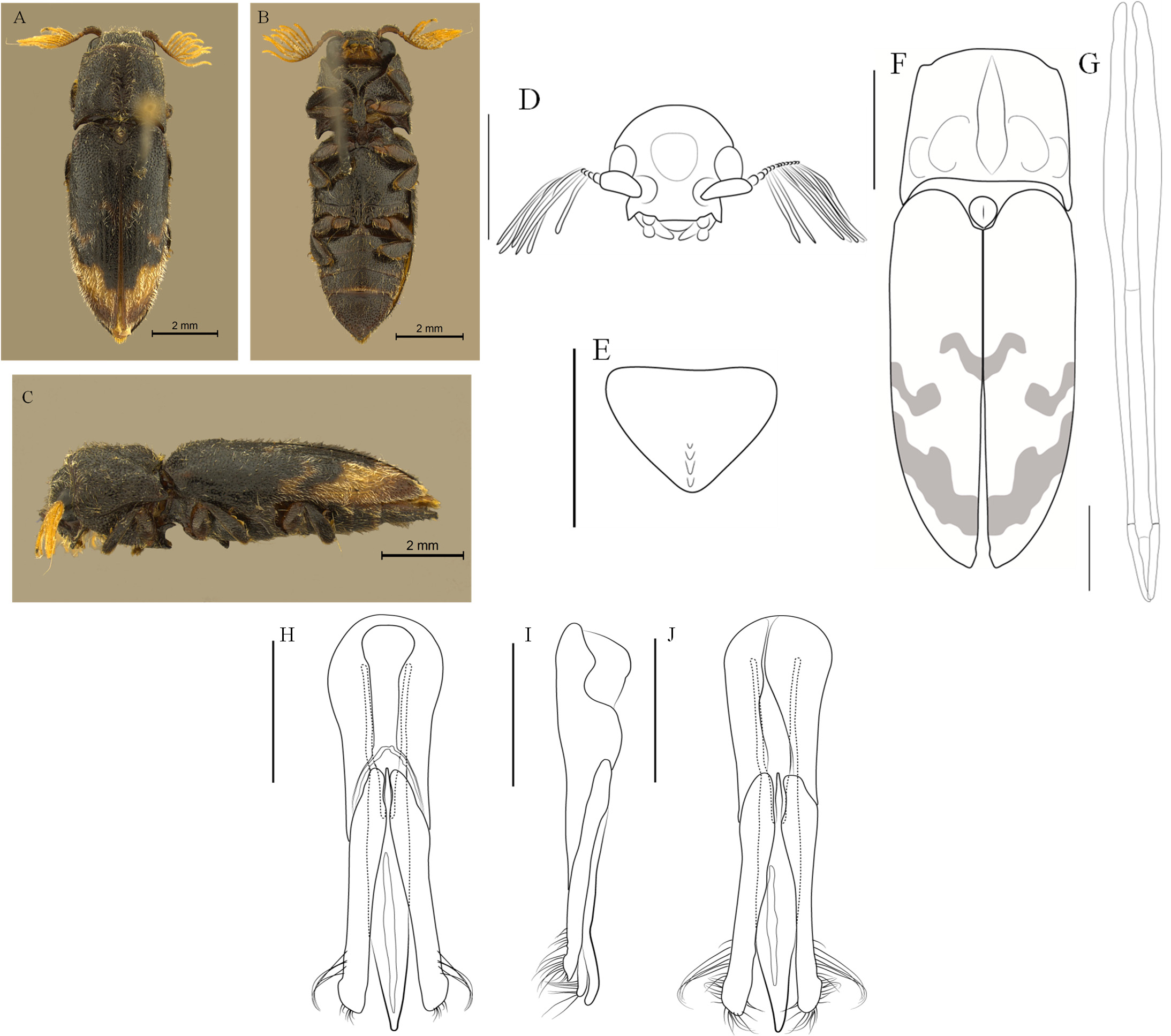
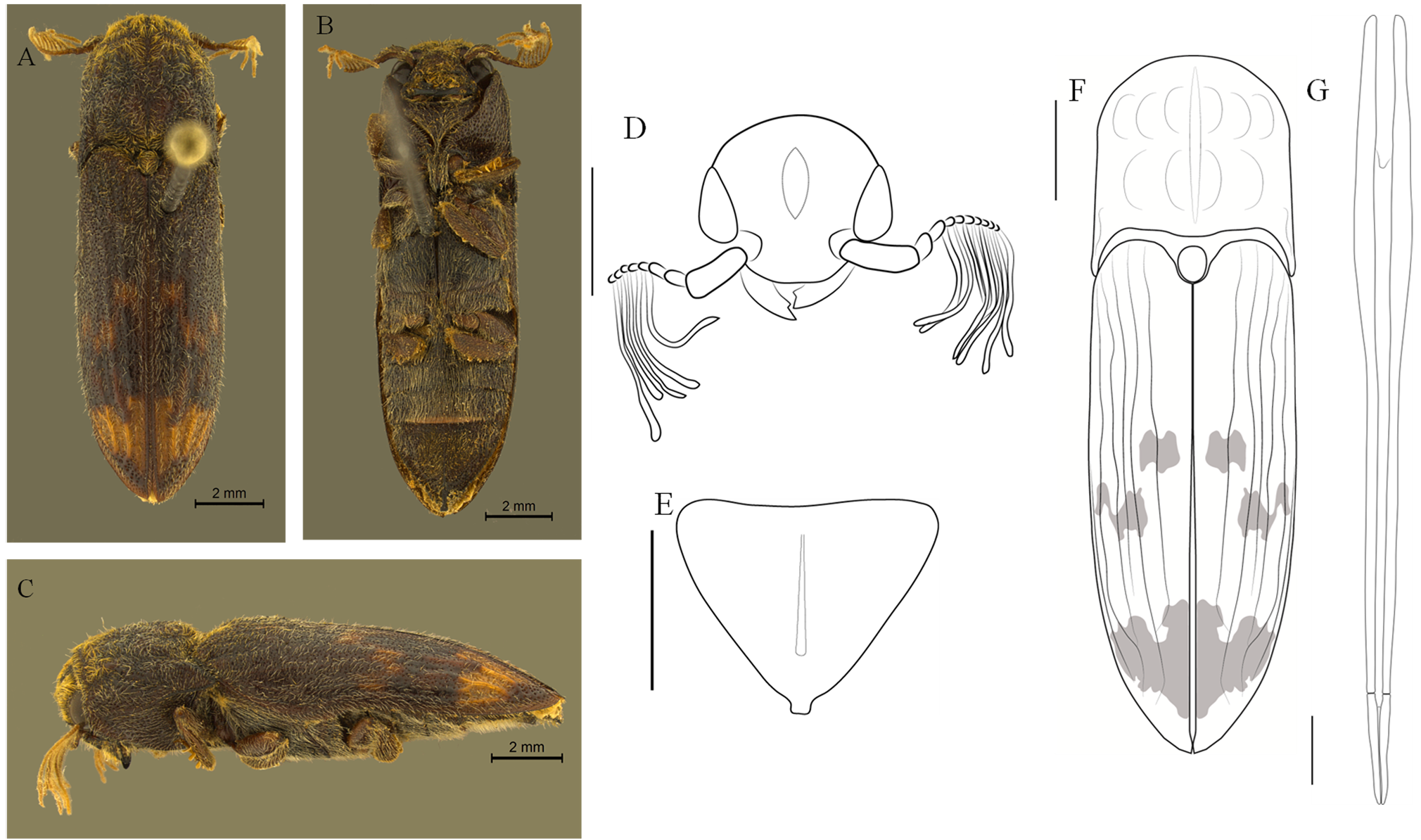
5. Subcylindrical body; dorsal and ventral regions covered with moderately dense pubescence on head and pronotum, much denser on bands on elytra; basal region of elytra slightly rugose, with no elevated longitudinal stria; anterior pronotal tubercles absent; longitudinal median carina of ventrite 5 with three or four longitudinal teeth. ( Figure 4 View FIGURE 4 )........ Balgus eschscholtzi
- Body cylindrical; body covered with dense pubescense; basal region of the elytra with five elevated longitudinal stria and without tranversal rugosities; anterior pronotal tubercles present; longitudinal median carina of ventrite 5 with one longitudinal tooth. ( Figure 7 View FIGURE 7 )......................................................................... Balgus rugosus
6. Apical third of the elytra light brown or yellow, with a large black band on the basal two thirds of the elytra............. 7
- Apical third of the elytra dark brown to black, and may have various yellow or light brown bands, apex always black...... 8
7. Obconical body; elytral apex subrounded; ventrite 5 pentagonal, without longitudinal median carina; longitudinal median anterior depression of head continues posteriorly on a longitudinal groove on the vertex, not V-shaped. ( Figure 6 View FIGURE 6 )................................................................................................... Balgus obconicus
- Subcylindrical body; elytral apex subacuminate; ventrite 5 triangular, with longitudinal median carina; longitudinal median anterior depression of head continues posteriorly on a longitudinal groove on the vertex, V-shaped. ( Figure 5 View FIGURE 5 )..................................................................................................... Balgus humilis
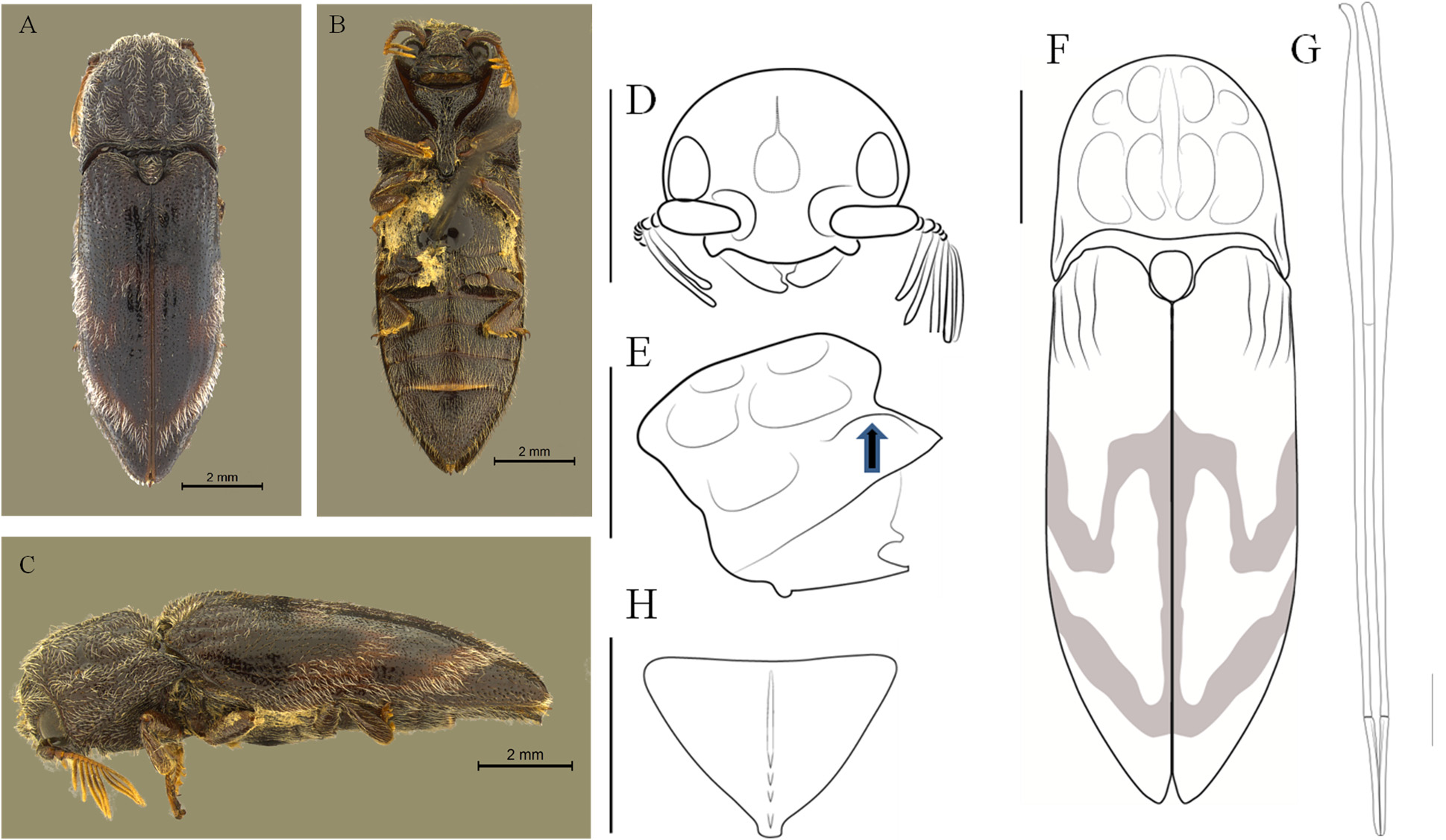
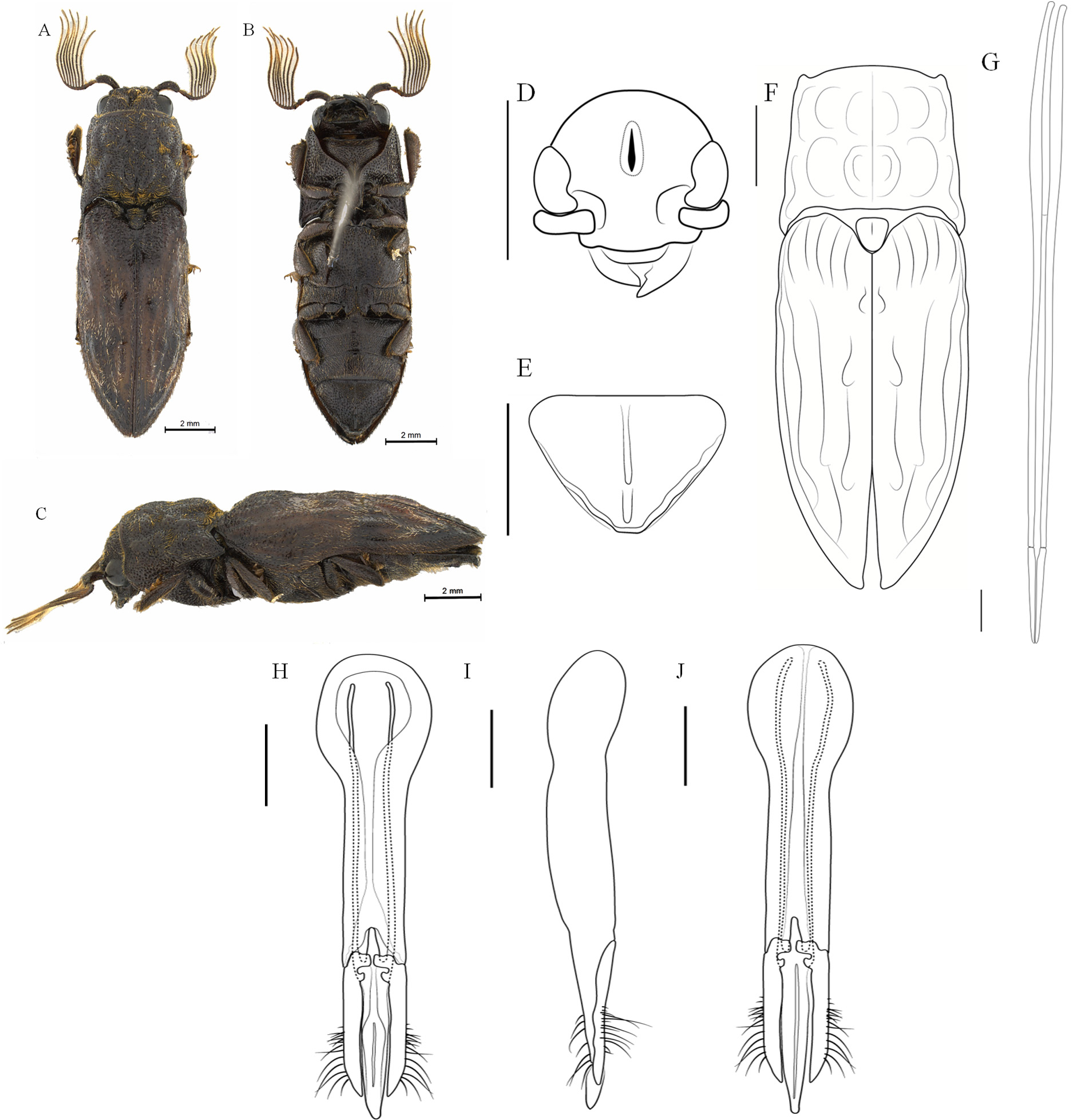
8. Ventrite 5 with sinuous margins; strongly serrate; abruptly narrowed from base to the apex, which is abruptly truncated and curved; longitudinal median carina of the ventrite 5 with two or three longitudinal teeth; pronotum not abruptly attenuate at the anterior third; elytra with subacuminate apex, not narrowed abruptly. ( Figures 1 View FIGURE 1 , 9 View FIGURE 9 )................. Balgus tuberculosus
- Ventrite 5 without sinuous margins; slightly serrate; abruptly narrowed from base to the apex, which is truncated and not curved; longitudinal median carina of the ventrite 5 with two longitudinal teeth; pronotum abruptly attenuate at the anterior third; elytra with subacuminate apex, abruptly narrowed. ( Figure 3 View FIGURE 3 )............................... Balgus eganensis
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |