Raunolina jeddahica, Gnezdilov, 2017
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.1515/aemnp-2017-0054 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:F33D26D4-6819-480A-8F87-2B7E44CF166AX |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4488152 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/403E87C8-FFEF-FFB2-69E5-1A12FBC7B62B |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Raunolina jeddahica |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Raunolina jeddahica View in CoL sp. nov.
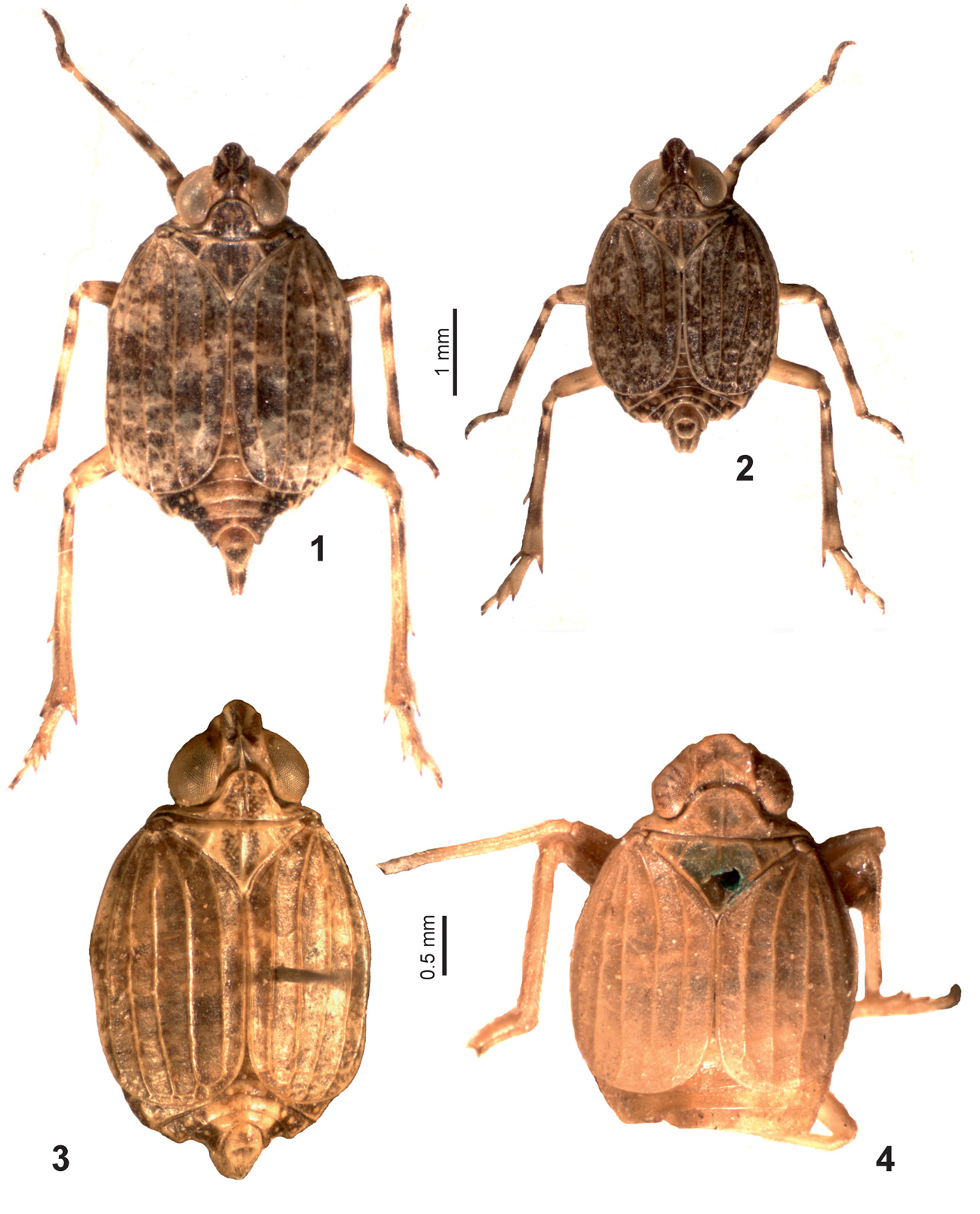
( Figs 3 View Figs 1–4 , 24–31 View Figs 24–31 )
Type locality. Western Saudi Arabia, Makkah region, Briman (= Buraiman, Bryman) near Jeddah (ca. 21°39′N, 39°14′E).
Type material. HOLOTYPE: ♁, “Arabia: / Buraiman / nr. Jedda / 26.I.46 / E.S. Brown. / B.M. 1946 - 289 [printed and hand written] // EB / 189” [hand written] ( BMNH). The specimen dry-mounted on the pin attached to the piece of paralon, abdomen detached, stored in glycerine in a plastic microvial pinned under the specimen.
Description. Coloration. Metope and lateral parts of the head light yellow, with scarce dark brown dots. Postclypeus with dense dark brown dots excluding light yellow median carina. Rostrum light yellow with black apex. Coryphe light yellow, with large dark brown spots ( Fig. 3 View Figs 1–4 ). Pro- and mesonotum light yellow, with dense dark brown dots. Paranotal lobes of pronotum with black lower margins. Fore wings dark brown, with light longitudinal veins. Abdominal tergites dark brown, with light yellow median parts and traces of larval sensory pits. Laterotergites dark brown.Abdominal sternites brown yellowish. Coxae and trochanters light yellow. Fore and middle femora brown yellowish, with two wide black bands. Fore and middle tibiae brown yellowish, except dark brown basal and apical parts and with two wide black bands. Hind femora light yellow, with wide dark brown band apically. Hind tibiae light brown yellowish except black basal part and two wide black bands. Apices of leg spines black.
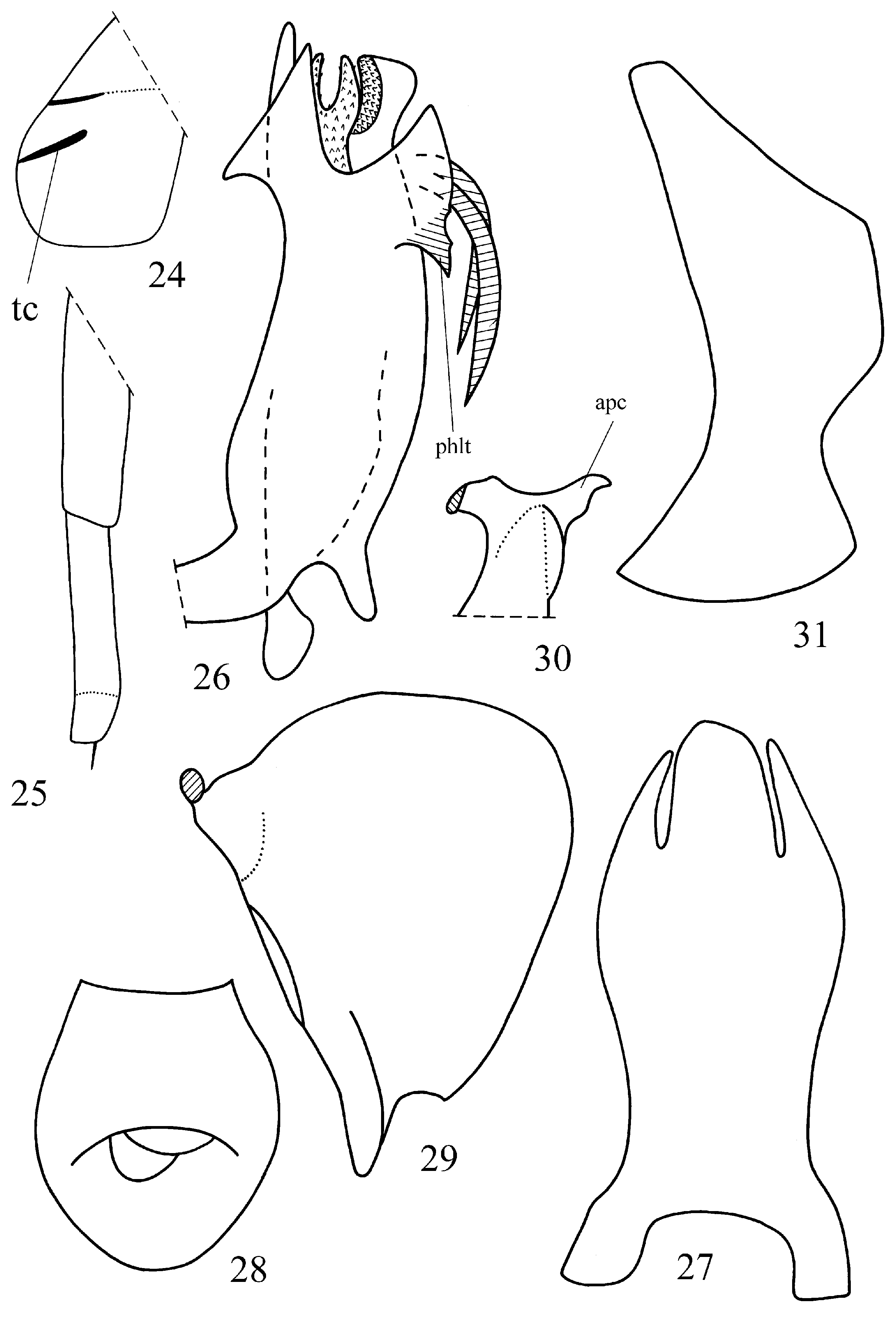
Structure. Resembling R. remanei sp. nov. Metope narrow – narrowest between the eyes and slightly enlarged above postclypeus, with distinct median carina running through postclypeus and with distinct sublateral carina joint with median carina on its upper margin, but not reaching metopoclypeal suture. Lateral (marginal) keels of metope running on lateral parts of postclypeus in its upper half. Postclypeus flattened dorso-ventrally and laterally. Ocelli absent. Pedicel globular, with rhinaria. Rostrum long, surpassing hind coxae on half length of third segment. Third rostral segment shorter than second one, slightly narrowing apically ( Fig. 25 View Figs 24–31 ). Metope and coryphe joint at acute angle (in lateral view). Coryphe concave, its anterior margin strongly convex, its posterior margin acutely angularly concave ( Fig. 3 View Figs 1–4 ). Coryphe longer than wide medially, with an incomplete median carina running from its posterior margin to its middle. Pronotum with strongly protruding anterior margin between the eyes and with a distinct median carina. Paradiscal fields of pronotum narrow. Paranotal lobes of pronotum wide, each with a short transverse carina ( Fig. 24 View Figs 24–31 : tc). Mesonotum slightly longer than pronotum, with distinct median and lateral carinae. Fore wings reaching only hind margin of fifth abdominal tergite, without hypocostal plate and with widely rounded apices. Longitudinal veins of fore wings keel-shaped, simple, excluding short apical furcation of Pcu on left wing; CuP reduced. Transverse veins almost absent excluding single veins r-m, m-cua, and cua-pcu on right wing. Hind femora and tibiae longer than fore and middle ones. Hind tibia with single lateral spine in its distal half and with six apical spines. First metatarsomere as long as second and third metatarsomeres combined, with two latero-apical and six intermediate spines arranged at an arc. Second metatarsomere with only two latero-apical spines. Aroliun of pretarsus distinctly shorter than claws.
Male genitalia ( Figs 26–31 View Figs 24–31 ). Hind margin of pygofer deeply concave in its lower half (in lateral view, Fig. 31 View Figs 24–31 ). Anal tube wide, narrowing apically (in dorsal view, Fig. 28 View Figs 24–31 ). Paraproct short and wide. Phallobase wide and long, almost straight (in lateral view). Dorso-lateral lobes of phallobase fused dorsally ( Fig. 27 View Figs 24–31 ). Each dorso-lateral lobe with a large tooth-shaped process subapically on its dorsal surface and with large rounded lobe covering the ventral aedeagal hooks and bearing a large tooth-shaped process ( Fig. 26 View Figs 24–31 : phlt). Ventral phallobase lobe thick and wide, with rows of denticles on its inner side. Apical aedeagal processes long and wide, bilobed, visible above the phallobase. Ventral aedeagal hooks short (nearly 1/3 of aedeagus length), pointed apically and directed to aedeagal base. Style with massive plate, hind margin convex ( Fig. 29 View Figs 24–31 ). Capitulum of style small, without neck, lateral tooth finger-shaped, apical part of capitulum with one tooth (second teeth rudimentary) ( Fig. 30 View Figs 24–31 : apc).
Measurements. Body length (from apex of coryphe to apex of of anal tube) – 4.5 mm.
Etymology. The species name is the adjective jeddahicus (- a, - um) given after its type locality.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
SuperFamily |
Fulgoroidea |
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |