Lepidodactylus zweifeli, Kraus, 2019
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4651.2.7 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:8EDF08F7-72E7-4EA4-B2AB-810A7EA74941 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/7722DE9A-EA83-44EF-96D4-C010B041DBA8 |
|
taxon LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:act:7722DE9A-EA83-44EF-96D4-C010B041DBA8 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Lepidodactylus zweifeli |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Lepidodactylus zweifeli sp. nov.
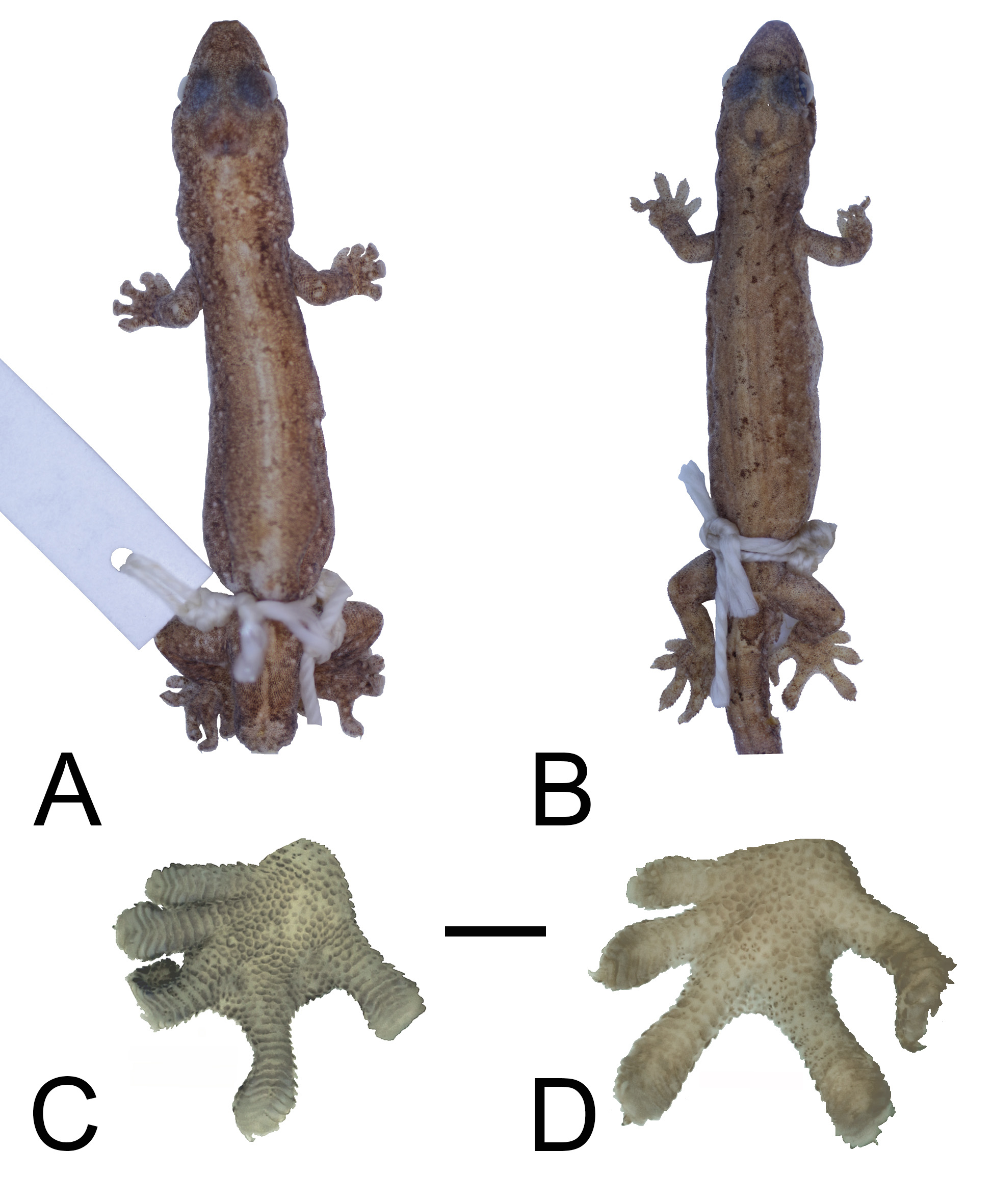
Fig. 1B, D View FIGURE 1
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:7722DE9A-EA83-44EF-96D4-C010B041DBA8
Holotype. AMNH 105088 About AMNH (field tag RZ 08430), mature male, collected by R. Zweifel at Wanuma, 4.90°S, 145.33°E, 2200 feet [= 670 m], Adelbert Mts. , Madang Province, Papua New Guinea, 5 August 1969. GoogleMaps
Paratype. Same data as holotype ( AMNH 105087 About AMNH ) .
Diagnosis. A medium-sized (adult SVL 41–44.5 mm) species of Lepidodactylus having a subcylindrical tail without a lateral fringe of enlarged scales; all subterminal scansors entire; 40 enlarged precloacal/femoral scales in three series extending along entire femoral region, 38 precloacal/femoral pores in three series in the sole male, with the lateral series on each thigh separated by 2–3 scales from the precloacal series; 9–12 T4 lamellae, 7–8 T1 lamellae; fairly narrow toes (T4W/T4L = 0.24–27) with basal webbing (T3T4webL/T4L = 0.10–0.13, T4T5webL/T4L = 0.08–0.12); narrow snout (EN/IN = 1.72–1.79); and dorsum with dark-brown markings but no pale spots.
Comparisons with other species. The subcylindrical tail without a lateral fringe of enlarged scales and the series of undivided scansors under all toes place Lepidodactylus zweifeli sp. nov. in Brown and Parker’s (1977) Group I. Lepidodactylus zweifeli sp. nov. differs from other Melanesian members of this group as follows: from L. browni , L. flaviocularis , L. mutahi , and L. orientalis in having the precloacal/femoral pore series arrayed into three series (versus a continuous row in the other species); from L. magnus in its much smaller size (SVL = 41–44.5 mm versus 50–70 mm in L. magnus ), fewer lamellae on T1 (7–8 versus 9–12 in L. magnus ), and in having the precloacal/femoral pores arrayed in three series (versus usually in a single series in L. magnus , which may, however, have one or a few scales disrupting the series); and from L. pumilus in having the femoral and precloacal pore series separated by only 3–5 scales (versus 7–12 scales in L. pumilus ), and less toe webbing (T3T4webL/T4L = 0.10–0.13 versus 0.18–0.19 in L. pumilus , Fig. 1D View FIGURE 1 ), especially between T4 and T5 (T4T5webL/T4L = 0.08–0.12 versus 0.23 in L. pumilus ). Lepidodactylus zweifeli sp. nov. differs from L. aignanus sp. nov. in its larger size (SVL 41–44.5 mm versus 37.5 mm in L. aignanus sp. nov.), in having enlarged femoral scales (absent in L. aignanus sp. nov.) such that the total number of enlarged precloacal/femoral scales is 40 (versus 17 in L. aignanus sp. nov.), narrower toes (T4W/T4L = 0.24–27 versus 0.33 in L. aignanus sp. nov., Fig. 1C View FIGURE 1 versus 1D), less toe webbing (T3T4webL/T4L = 0.10–0.13 versus 0.26 in L. aignanus sp. nov., Fig. 1C View FIGURE 1 versus 1D), narrower snout (EN/IN = 1.72–1.79 versus 1.61 in L. aignanus sp. nov.), and dorsum without pale spots (versus with lateral and dorsolateral rows of pale spots in L. aignanus sp. nov., Fig. 1A View FIGURE 1 versus 1B).
Description of holotype. A mature male of medium size (SVL = 41.0 mm, TrL = 21.0 mm). Head relatively long (HL/SVL = 0.23) and wide (HW/HL = 0.76), distinct from neck. Loreal region slightly inflated; no distinct canthus rostralis. Top of snout, area between nares, and area posterior to nares concave. Snout tapered and rounded at tip, relatively long (SN/HL = 0.43), longer than eye diameter (SN/EY = 1.5). Eye relatively large (EY/HL = 0.28, EY/ EN = 0.84); pupil vertical, constricted into series of four lobes; supraciliaries slightly larger than adjacent granules. Ear opening small (Ear/HL = 0.065), compressed, oriented diagonally from posterodorsal to anteroventral; distance between ear and eye slightly larger than eye diameter (EE/EY = 1.1). Rostral wider (1.7 mm) than high (0.9 mm), highest just medial to nares, lower between these points; length 0.5 mm; dorsal portion with short groove on posterior 0.2 mm. Supranasals separated by three internasals. Rostral in contact with first supralabials, two supranasals, and three internasals. External nares circular; each bordered by rostral, two supranasals, first supralabial, and one postnasal. Mental shallowly triangular, shorter (0.60 mm) than wide (0.75 mm). Mental bordered posteriorly by two enlarged postmentals, these bordered posteriorly by slightly enlarged scales that progressively decrease in size posteriorly prior to granular chin scales. First two infralabials bordered below by somewhat enlarged scales; remaining scales below infralabials of approximately same size as throat scales. Supralabials to mid-orbital position eight on each side, to angle of jaw 14 on each side. Infralabials 11 on right, 10 on left.
Body of modest habitus (TrL/SVL = 0.51), slightly depressed. Dorsal scales on head, body, limbs, and throat tiny, juxtaposed granules, larger on sides and snout; tubercles absent. Ventral scales larger, flat and smooth, subimbricate, gradually decreasing in size laterally to become granular.
Enlarged precloacal/femoral scales in three series of 12-16-12 scales separated by four slightly smaller scales on right, and three on left; those on thighs only slightly larger than adjacent scales. Precloacal/femoral pores in three series of 12-14-12. Enlarged scales form a pubic patch between the precloacal series and vent; no row of tiny scales between the precloacal series and either side of the pubic patch; nine scales in a row between apex of enlarged precloacal series and vent. Scales on palms and soles rounded, smooth.
Fore- and hindlimbs relatively small but well-developed (FA/SVL = 0.095, CS/SVL = 0.12). Digits well-developed, narrowly dilated throughout their length (T4W/T4L = 0.27), all but first fingers and toes with recurved claws; clawed phalanges laterally compressed, free above and extending slightly beyond terminal scansors. Subdigital lamellae narrow and smooth, all undivided except for second scansor divided on right first toe; lamellae extend for only slightly more than half length of each toe (T4 scansor L/T4L = 0.54, Fig. 1D View FIGURE 1 ). Lamellae of manus 6–8–10 –9–7 on right, 7–8–9–9–7 on left; of pes 8–9–9–10 –8 on right, 7–9–9–9–8 on left. Relative lengths of digits on manus and pes I <II <V <III <IV. Webbing present between all digits except fingers 1–3 on manus and toes 1–2 on pes; toes only basally webbed (T3T4webL/T4L = 0.13, Fig. 1D View FIGURE 1 ).
Tail complete, subcylindrical, relatively narrow (TW/SVL = 0.076); lateral margins without skin flanges or spines. Scales of tail small, flat, smooth, subimbricate, larger ventrally than dorsally. Cloacal sacs swollen, with small external orifices situated near lateral margins of vent, cut on right side; two enlarged, blunt postcloacal spurs on each side of tailbase; midventral scales of sac not distinctly larger than those ventrolaterally.
Color in preservative: Dorsal ground color yellowish brown with small, dark-brown markings dorsally, laterally, and on limbs; dark markings connecting to form weak dorsolateral stripe in scapular region and extending posterior to forearm insertion ( Fig. 1B View FIGURE 1 ). Dark-brown markings on tail forming vague, narrow bands. Snout spotted with small dark-brown markings. Venter pale straw with many brown scales scattered throughout; palms and soles brown. Iris black; pupil pale gray.
Measurements (in mm). SVL = 41.0, TrL = 21.0, TL = 37.0, TW = 3.1, FA = 3.9, CS = 5.1, HL = 9.3, HW = 7.1, Ear = 0.6, EE = 2.9, EY = 2.6, SN = 4.0, EN = 3.1, IN = 1.8, T4L = 4.8, T4W = 1.3, T4lamellaeL = 2.6, T3T4webL = 0.6.
Variation. The enlarged precloacal and femoral scales are in three series in the female paratype (12-16-12 scales right to left), with five small scales intervening between these. The paratype has a greater number of entire lamellae (12 on each fourth toe), ten scales in a row between the apex of the enlarged precloacal series and the vent, narrower toes (T4W/T4L = 0.24), less webbing (T3T4webL/T4L = 0.10), and a relatively smaller eye (EY/SVL = 0.056, EY/ EN = 0.84) than the holotype. It is more heavily dusted with dark brown laterally and dorsolaterally, with the darkbrown markings forming series of short dashes dorsally and four short lines behind head and in scapular region. The head is more densely spotted with brown markings, and the brown markings are denser on the tail.
Measurements of paratype (in mm). SVL = 44.5, TrL = 22.0, TL = 45.0, TW = 3.1, FA = 3.9, CS = 5.2, HL = 9.9, HW = 7.2, Ear = 0.6, EE = 3.1, EY = 2.5, SN = 4.5, EN = 3.4, IN = 1.9, T4L = 5.0, T4W = 1.2, T4lamellae L = 3.1, T3T4webL = 0.5.
Etymology. The name is a genitive honorific for the collector, Richard Zweifel, whose contributions to knowledge of the herpetofauna of New Guinea and nearby islands were foundational to current understanding.
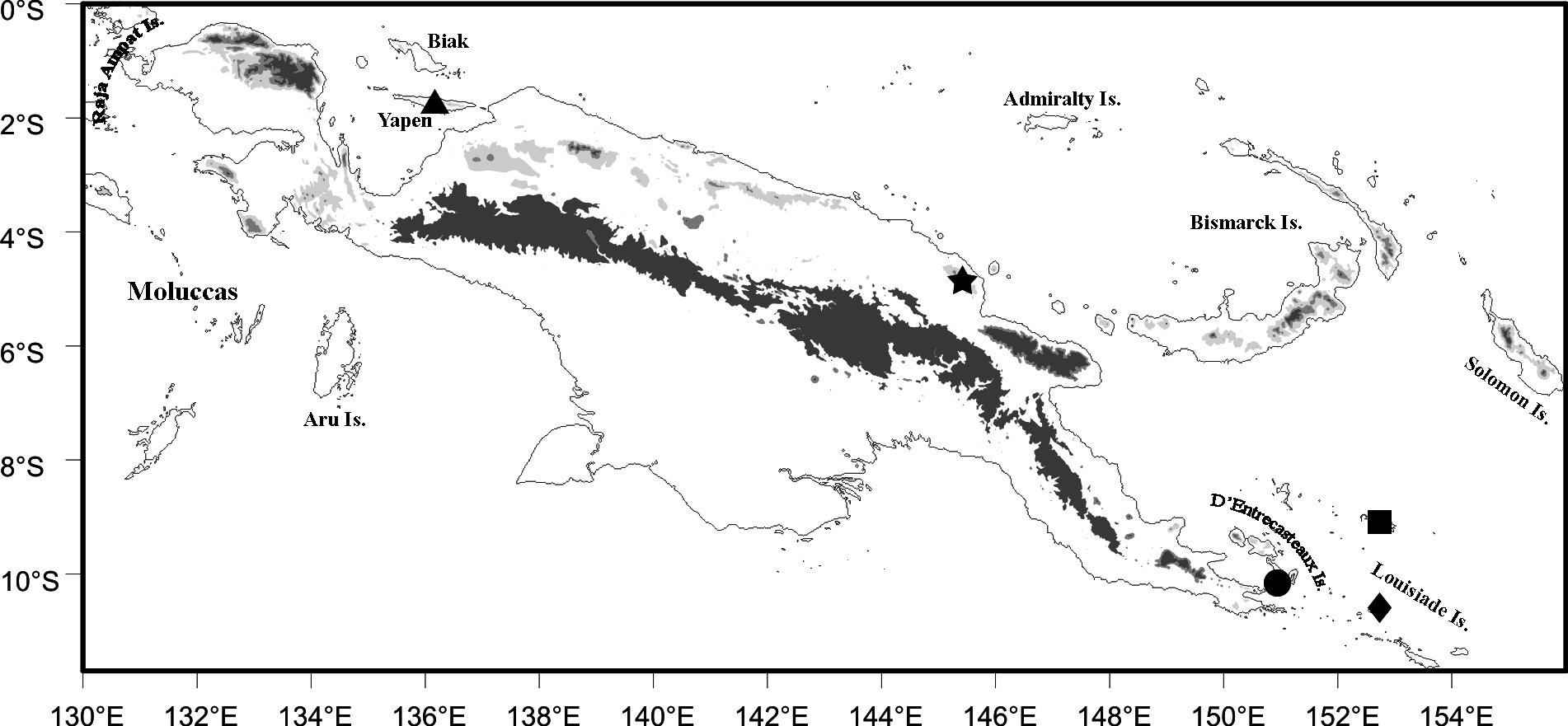
Range. Known only from the type locality, but likely to occur throughout the hill forests of the Adelbert Mts. ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 ).
Remarks. These specimens were briefly discussed by Brown & Parker (1977), who noted that they were similar in webbing but smaller than L. magnus and were more like L. pumilus in size and possibly pore pattern. As noted above, in addition to size, L. zweifeli sp. nov. differs from L. magnus in its tripartite distribution of the precloacal/ femoral pores and in having fewer T4 lamellae. The easiest way to distinguish L. zweifeli sp. nov. from L. pumilus is by the extensive webbing of the latter (especially between T4 and T5).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |