Zenodosus sanguineus (Say, 1835)
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.175098 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6252879 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/392B1921-FFA5-BF21-FEF0-6B8CD899DB31 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Zenodosus sanguineus (Say, 1835) |
| status |
|
Zenodosus sanguineus (Say, 1835)
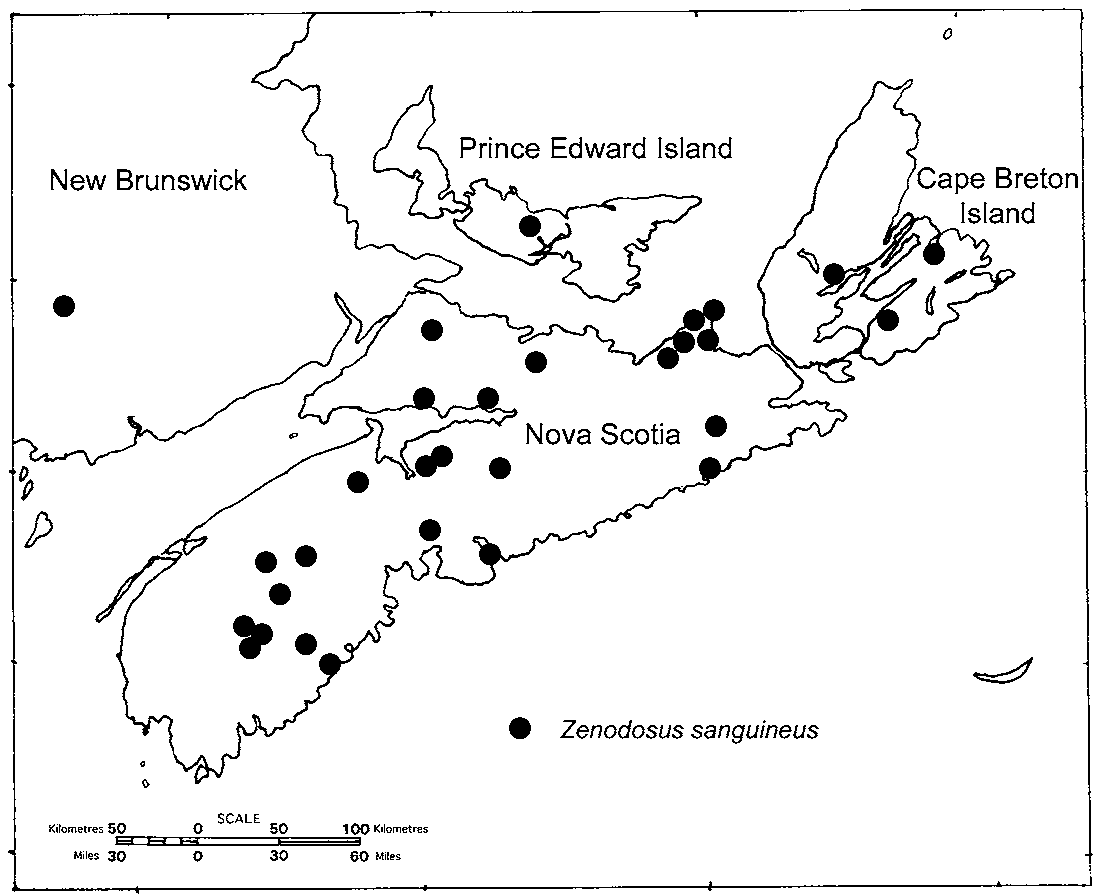
NEW BRUNSWICK: Yor k C o.: Fredericton, 14.ix.1987, N. Albert, UMNB; New Brunswick (no further data), NBM. NOVA SCOTIA: 75 specimens examined from Annapolis, Antigonish, Cape Breton, Colchester, Cumberland, Guysborough, Halifax, Hants, Inverness, Kings, Pictou, Queens, and Richmond counties. The earliest record is from 1967 ( Inverness Co.: Bras d'Or Lake, 17.v.1967, J. Gilhen, NSMC). PRINCE EDWARD ISLAND: Queens Co.: St. Patricks, 17.viii.2002, C.G. Majka, CGMC; St. Patricks, 25.vi.2003, C.G. Majka, CGMC.
Newly recorded in New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and Prince Edward Island. Widely distributed in the region ( Figure 1 View FIGURE 1 ). In Nova Scotia observed in association with the galleries of scolytines ( Curculionidae ) “feeding” on red spruce ( Picea rubens Sarg ,) ( Pinaceae ); also in white pine ( Pinus strobus L.) ( Pinaceae ) and eastern hemlock ( Tsuga canadensis (L.) Carr.) ( Pinaceae ) forests. Knull (1951) reported it as diurnal and found under the bark of trees infested with lignicolous boring insects.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Thaneroclerinae |
|
Genus |