Mesocletodes robustus Por, 1965
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.2096.1.14 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/38758798-FFCB-FF92-FF67-749BFEA2F1CC |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Mesocletodes robustus Por, 1965 |
| status |
|
Redescription of Mesocletodes robustus Por, 1965
( Figs 25–30 View FIGURE 25 View FIGURE 26 View FIGURE 27 View FIGURE 28 View FIGURE 29 )
Type material (used for comparison):
Paratype: 1 female dissected, mounted on 2 slides, coll. no. Cop 52 1–2, Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Israel
Redescription is based on collected material: Angola Basin, 27.07.2000. 1 female, dissected, mounted on 6 slides, coll. no. SMF 31422/1–6 at station 346/1 ( 16°17.0’S / 05°27.0’E, 5389m) GoogleMaps , 1 female, dissected, mounted on 7 slides, coll. no. SMF 31423/1–7 at station 346/7 ( 16°17.0’S / 05°27.0’E, 5389m) GoogleMaps , 1 female mounted on 1 slide, coll. no. SMF 31435/1 at station 346/6 ( 16°17.0’S / 05°27.0’E, 5389m) GoogleMaps .
Description of female. Habitus ( Figs 25B View FIGURE 25 ) of cylindrical shape, no clear distinction between prosome and urosome. Body length 1327µm. Rostrum tipped, slightly protruding, with 2 sensilla. Cphth blotched as depicted, with several setules and with dorsal triangular cuticular process, which is curved and points in a posterior direction. Process with 4 distal apertures. Distal margins of cphth and prosomites with denticulated hyaline frill, urosomites with bare hyaline frill. Long sensilla on distal margins of body somites, except the penultimate one. P2–P4 bearing body somites dorsally with rows of spinules, P5-bearing somite and urosomites with additional lateral rows of spinules. Telson square, with dorsal cuticular process peaking in a small spine (like M. abyssicola ), 1 sensillum on each side of the process. Somites covered by spinules. Genital double-somite incompletely fused. P2–P4 bearing body somites with thickened cuticula at the insertions of legs.
A1 ( Fig. 26A View FIGURE 26 ) 8-segmented, acrothek on segments 4 and 8. First segment without setae, proximally and medially with 1 row each of spinules. Second segment with a strong protrusion bearing a strong, bipinnate seta. Spines of A1 with 1 STE each.
Setal formula: I:0, II:8, III:6, IV:3+Aes, V:1, VI:2, VII:3, VIII:7 +Aes.
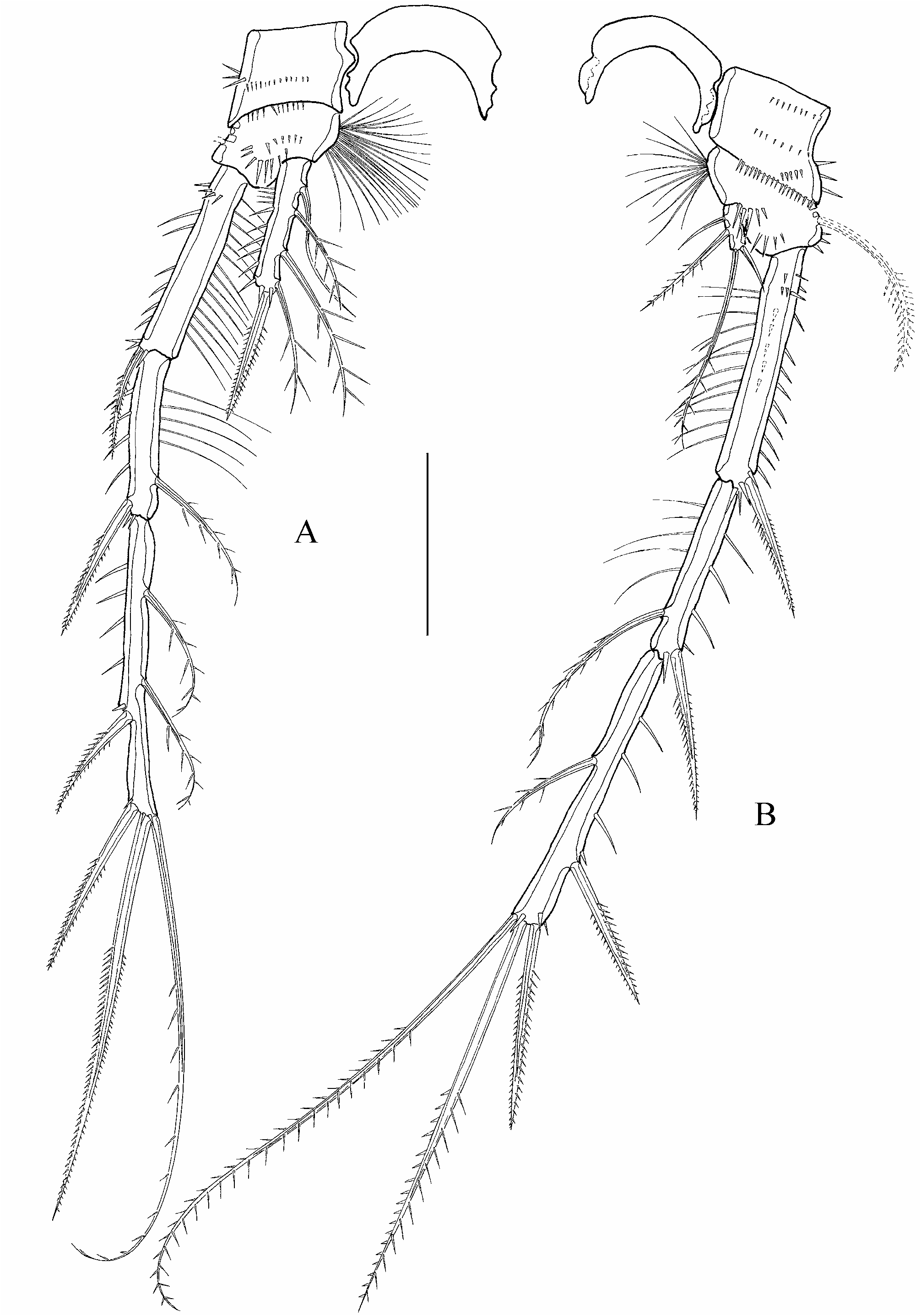
A2 ( Fig. 26B View FIGURE 26 ) basis with spinules. Exp 1-segmented with 2 bipinnate setae of unequal length. Enp1 with corona of spinules. Enp2 with long, outer spinules, 2 bipinnate, medial spines with 1 STE each and 6 terminal elements. 1 outer unequal bipinnate spine, 3 geniculated, coarse bipinnate setae, 1 annulated, bipinnate seta fused to 1 fine, unipinnate inner seta at its base. Enp2 with terminal spinules of different length.
Md lost during preparation.
Mxl ( Fig. 27A View FIGURE 27 ) arthrite of the praecoxa with 10 armature elements: 2 surface setae (depicted beneath). 2 toothlike setae with strong terminal spinules, 1 undulated, tooth like seta with strong spinules terminally, 2 brushlike setae, 1 depressed, swung, unipinnate seta, 1 unipinnate seta on a protrusion, 1 single, unipinnate seta, very long spinules on the surface (depicted beneath). Coxal endite with 5 setae, incompletely fused to pinnate terminal seta. Corona of spinules at the base of coxal endite. Basis with 7 setae, segments of enp and exp not expressed.
Mx ( Fig. 27B View FIGURE 27 ) syncoxa with several rows of spinules and 2 endites. Proximal endite with 1 bare seta, distal endite with 3 setae: 1 strongly bipinnate and 2 bare setae. Basis with 3 setae: 2 pinnate setae, incompletely fused to basis and 1 bare seta. Enp small, 1-segmented, with 2 long, bipinnate setae.
Mxp ( Fig. 27C View FIGURE 27 ) syncoxa with 2 long, bipinnate setae. Enp 1 segmented and fused to strong claw. Basis and enp lost during dissection.
P1 ( Fig. 28A View FIGURE 28 ) coxa with several spinules. Basis with 1 inner and 1 outer spine, net-like structure close to the insertion of outer seta. Exp 3-segmented. Exp1 and exp2 without inner armature. Exp3 with 1 outer and 2 terminal, bipinnate spines with distal tube pores and 1 short bipinnate inner seta. Enp 1-segmented, extremely long and broad. Enp with 1 bare inner seta, 1 bipinnate, terminal seta and 1 bipinnate, terminal spine. Intercoxal sclerite ( Fig. 27B View FIGURE 27 ) with 2 triangular holes, covered with many long strong spinules. Setal formula as in Table 5.
P 2–P 4 ( Figs 28C, D View FIGURE 28 ; 29A, B View FIGURE 29 ) coxae with several spinules. Bases with outer seta and inner setular tufts. Net-like structure close to the outer seta of P2, P3 and P4 with a lateral porus. Exp 3- segmented, increasing in length posteriorly. Exp1 without inner armature, but with inner spinules. Exp2 with inner seta and 5 long, inner spinules. Exp3 with 2 bipinnate outer spines, 1 bipinnate, terminal spine, 1 bipinnate seta terminally and 2 (P2 and P3) or 1 (P4) inner, bipinnate setae. P2–P4 Enp 1-segmented, decreasing in length and broadness posteriorly. Enp with 1 bare seta, 3 bipinnate setae and 1 bipinnate spine (P2 and P3) or 2 bare and 2 bipinnate setae (P4). All spines with spinules close to their insertions. Intercoxal sclerites as depicted for P2. Setal formula as in Table 5.
P5 ( Fig. 30) outer lobe of basenp with spinules and setophore. Inner lobe of basenp barely protruding, with inner setular tuft, spinules and 1 long inner seta, 1 long, median seta and one short, outer seta. The outer and median seta are close to each other, the long, inner seta separated from the former two elements. Net-like structure close to exp insertion. Exp approximately 9 times longer than broad, with 5 setae and 1 terminal tube pore. Exp covered by spinules, especially in the proximal part. Setal formula as in Table 5.
Furcal rami ( Fig. 25A View FIGURE 25 ) approximately 13 times longer than broad (the widest part measured at its base), the insertion surrounded by spinules of anal somite. Furcal ramus with spinules and 7 setae: I and II close to the beginning (ventral and lateral) III subdistally, IV and V terminally, VI ventrally terminal, VII in the middle of furcal ramus. Setae I, II, III, VI are bare, IV lost during sample treatment, V bipinnate (lost during preparation) VII triarticulate and bare.
Male unknown.
| SMF |
Forschungsinstitut und Natur-Museum Senckenberg |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |