Stigmaeus pulchellus Kuznetzov, 1978
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.1051/acarologia/20152165 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/3607B64E-9626-FFBB-ECFE-4D0CFE70FA03 |
|
treatment provided by |
Marcus |
|
scientific name |
Stigmaeus pulchellus Kuznetzov, 1978 |
| status |
|
Stigmaeus pulchellus Kuznetzov, 1978
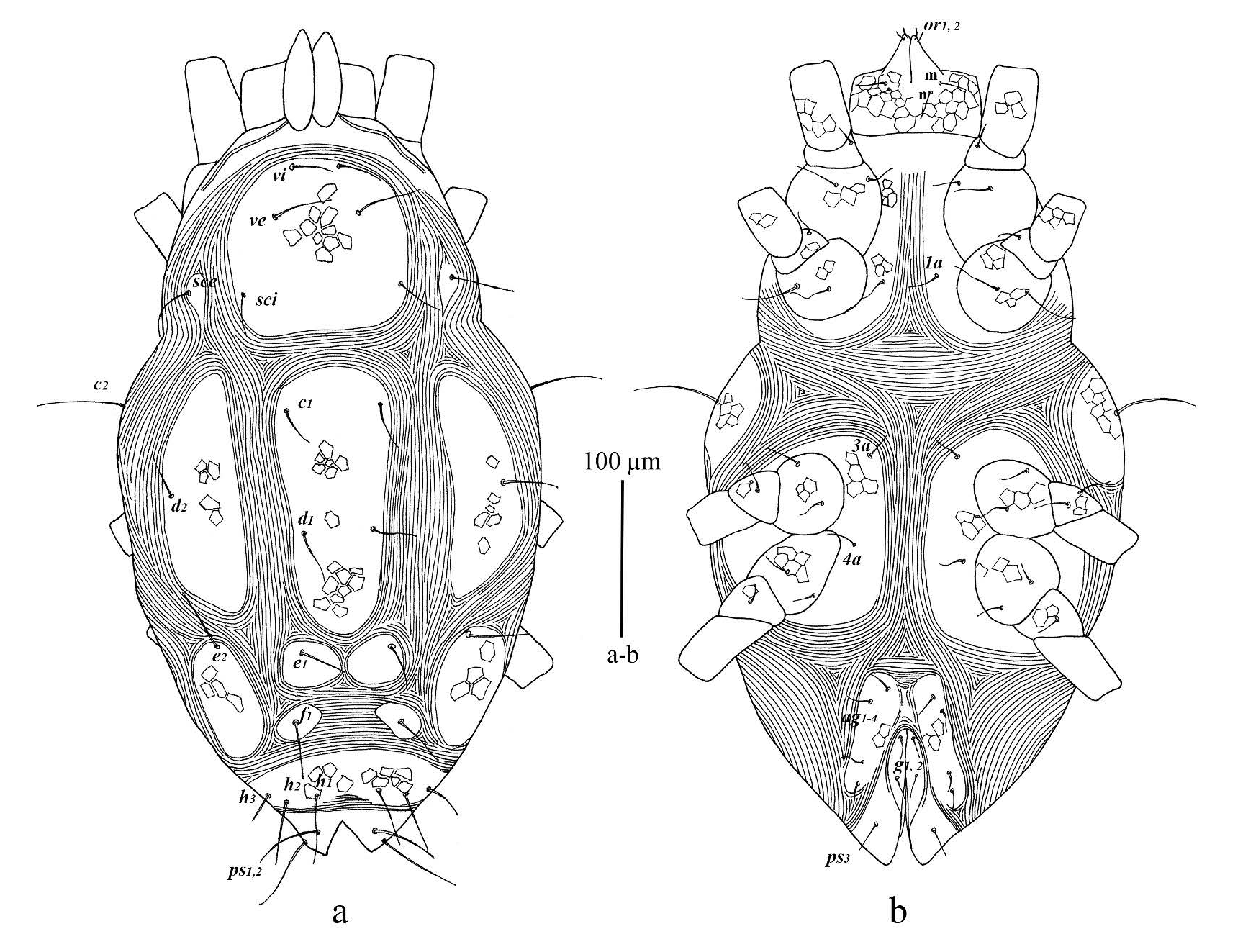
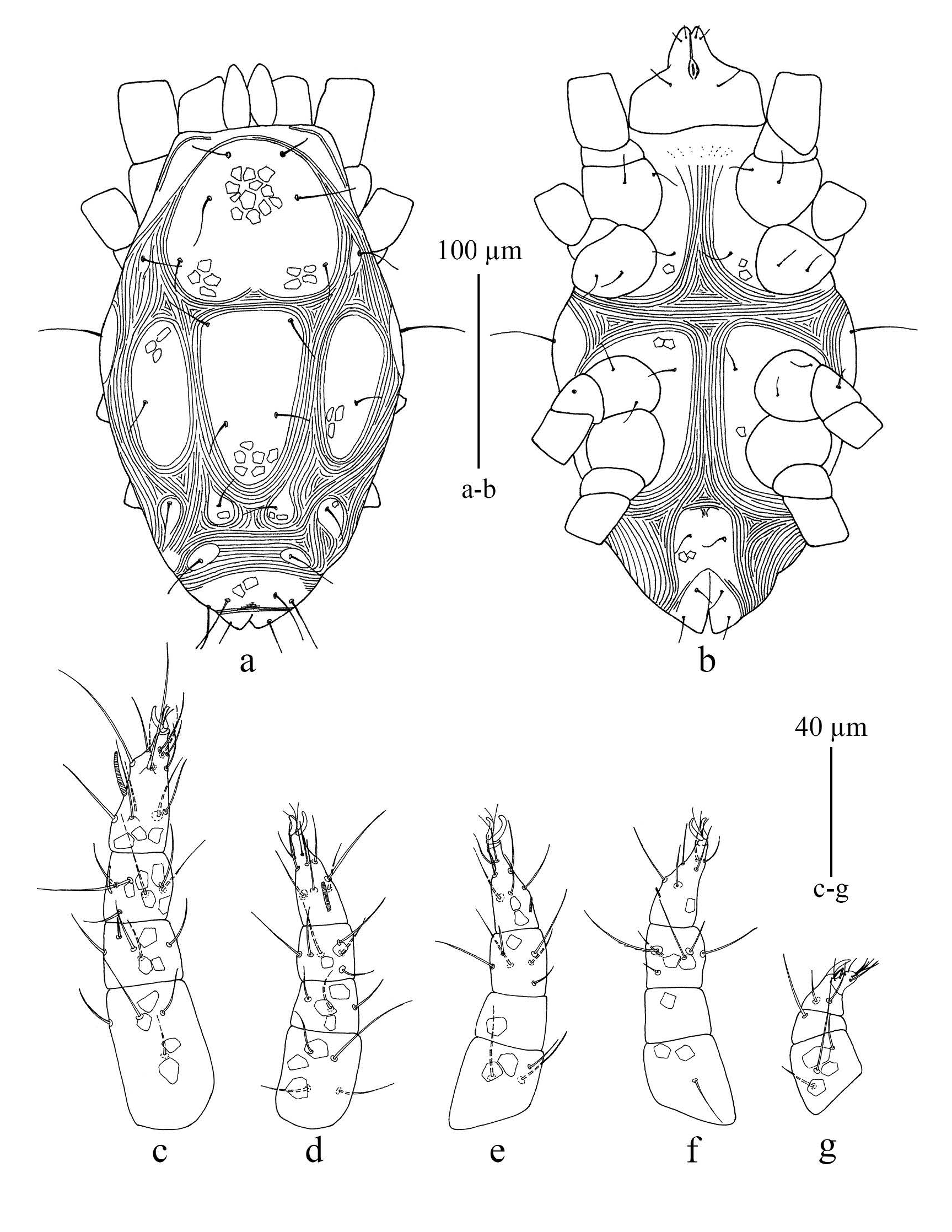
Female (n = 13) ( Figures 1-2 View FIGURE View FIGURE ): Idiosoma oval, length of body (including gnathosoma) 505 – 552; width of body 269 – 311. Gnathosoma ( Figure 2e View FIGURE ). Length of gnathosoma 60 – 67; subcapitulum with two pairs of subcapitular setae (m and n), m 23 – 30, n 21 – 29 and two pairs of adoral setae, or 1 and or 2; distances m -m 29 – 38, n -n 23 – 26; palpi five segmented, palp tarsus with five simple setae + one tridentale eupathidium + one solenidion; palp tibia with two setae + one seta-like accessory claw + one well-developed claw; palp genu with one seta; palp femora with three setae; palp trochanter without seta.
Dorsum ( Figure 1a View FIGURE ) — Body elongated. Dorsum with 14 pairs of setae (setae h 3 present); all dorsal shields reticulated; propodosomal shield with tree pairs of setae (vi, ve and sci); setae sce located on small auxiliary shields; eyes and postocular bodies absent; central shield elongate and with 2 pairs of setae (c 1 and d 1); humeral shields with seta c 2; marginal shields elongate and with setae d 2; median zonal shield divided and with seta e 1; lateral zonal shields wide and with setae e 2; intercalary shields with f 1; suranal shield entire, recessed posteriorly and with 3 pairs of setae (h 1, h 2 and h 3); dorsal body setae faintly spinulate; c 2 is the longest dorsal seta. Length of setae as follows: vi 26 – 29, ve 37 – 48, sci 29 – 33, sce 36 – 44, c 1 29 – 34, c 2 42 – 57, d 1 26 – 35, d 2 29 – 35, e 1 29 – 36, e 2 26 – 37, f 1 32 – 38, h 1 36 – 44, h 2 35 – 45, h 3 24 – 26; distances between dorsal setae: vi -vi 28 – 36, ve -ve 45 – 60, vi -ve 29 – 34; ve -sci 49 – 53, sci -sce 29 – 36, c 1 -c 1 51 – 66, c 1 -d 1 61 – 76, d 1 -d 1 40 – 46, d 1 -d 2 68 – 87, d 1 -e 1 73 – 80, e 1 - e 1 49 – 62, e 1 - e 2 50 – 61, e 1 -f 1 38 – 47, f 1 -f 1 52 – 76, h 1 -h 1 31 – 40, h 1 -h 2 15 – 17, h 2 -h 3 10 – 13, h 2 -h 2 68 – 94, h 3 -h 3 93 – 101; ratios vi / vi -vi 0.8 – 1, c 1 / c 1 -c 1 0.5 – 0.6, d 1 / d 1 -d 1 0.6 – 0.8, e 1 / e 1 - e 1 0.5 – 0.7, f 1 / f 1 -f 1 0.5 – 0.6.
Venter ( Figure 1b View FIGURE ) — Endopodal shields separated, with subcutaneous reticulation and with ventral setae 1a 20 – 23, 3a 20 – 24, 4a 21 – 25; aggenital shields with subcutaneous reticulation and bearing four pairs of aggenital setae (ag 1 -ag 4), length of ag 1 17 – 20, ag 2 18 – 20, ag 3 19 – 21, ag 4 21 – 29; anogenital area with two pairs of genital setae and three pairs of pseudanal setae (ps 1 -ps 3); length of anogenital setae; g 1 18 – 22, g 2 25 – 31, ps 1 40 – 53, ps 2 50 – 54, ps 3 21 – 25.
Legs ( Figures 2 View FIGURE a-d) — Length of legs I-IV: Leg I 157 – 186; leg II 125 – 151; leg III 129 – 151; leg IV 149 – 173; counts of setae (solenidia and setae κ included) of legs I - IV: coxae 2, 2, 2, 2; trochanters 1, 1, 2, 1; femora 4, 4, 3, 2; genua 6(κ), 5, 2, 2; tibiae 7(’, ’ p), 6(’ p), 6(’ p), 6(’ p); tarsi 14(ω), 10(ω), 8(ω), 8(ω).
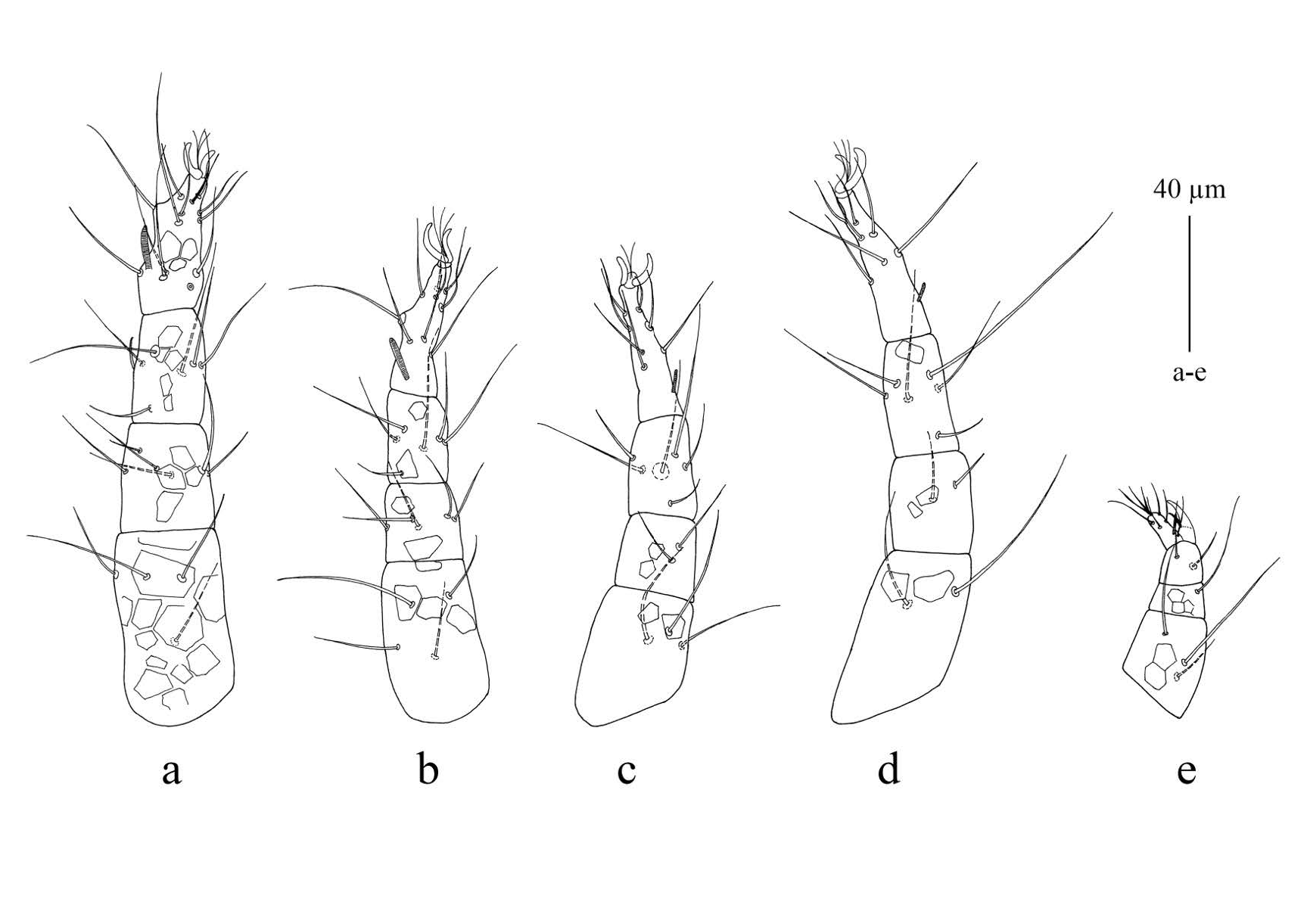
Male (n = 9) ( Figure 3 View FIGURE ): Length of body (including gnathosoma) 343 – 391; width of body 159 – 192. Gnathosoma ( Figure 3g View FIGURE ). Length of gnathosoma 52 – 57; subcapitulum with two pairs of subcapitular setae (m and n), m 19 – 24, n 17 – 22 and two pairs of adoral setae, or 1 and or 2; distances m -m 25 – 31, n -n 17 – 20; n: m 0.9 – 1; palpal chaetotaxy as in female.
Dorsum ( Figure 3a View FIGURE ) — All dorsal shields reticulated; propodosomal shield with tree pairs of setae (vi, ve and sci); setae sce located on small auxiliary shields; eyes and postocular bodies absent; central shield elongate and with 2 pairs of setae (c 1 and d 1); humeral shields with setae c 2; marginal shields elongate and with setae d 2; median zonal shield divided and with setae e 1; lateral zonal shields wide and with setae e 2; intercalary shields with f 1; suranal shield entire and with two pairs of setae (h 1, and h 2); dorsal body setae faintly spinulate; c 2 is the longest dorsal setae. Dimensions of setae as follows: vi 20 – 22, ve 29 – 32, sci 21 – 23, sce 26 – 29, c 1 20 – 24, c 2 36 – 42, d 1 20 – 24, d 2 21 – 27, e 1 21 – 23, e 2 21 – 24, f 1 22 – 26, h 1 23 – 28, h 2 30 – 32; distances between dorsal setae: vi -vi 20 – 26, ve -ve 41 – 48, vi -ve 23 – 26, ve -sci 39 – 43, sci -sce 18 – 22, c 1 -c 1 40 – 49, c 1 -d 1 52 – 58, d 1 -d 1 32 – 37, d 1 -d 2 40 – 47, d 1 - e 1 49 – 52, e 1 - e 1 27 – 39, e 1 - e 2 22 – 30, e 1 -f 1 26-31, f 1 -f 1 46 – 59, h 1 -h 1 24 – 29, h 1 -h 2 10 – 13, h 2 -h 2 50 – 54; ratios vi / vi -vi 0.8 – 1.0, c 1 / c 1 -c 1 0.5, d 1 / d 1 -d 1 0.6 – 0.7, e 1 / e 1 - e 1 0.6 – 0.8, f 1 / f 1 -f 1 0.4 – 0.5.
Venter ( Figure 3b View FIGURE ) — Ventral view similar to that of the female. Lengths of setae: 1a 18 – 20, 3a 16 – 19, and 4a 16 – 18 and ratio 1a: 3a: 4a 1-1.2:1-1.2:1. Aggenital area with three pairs of setae, ag 1 16 – 19, ag 2 19 – 21 and ag 3 18 – 22; anogenital area with three pairs of pseudanal setae ps 1 6, ps 2 9 – 10 and ps 3 17 – 19.
Legs ( Figures 3 View FIGURE c-f) — Length of legs: leg I 135 – 150, leg II 110 – 120, leg III 106 – 120, leg IV 125 – 139. Setal formulae of leg segments as follows: coxae 2, 2, 2, 2; trochanters 1, 1, 2, 0; femora 4, 4, 3, 2; genua 5(κ), 3, 0, 0; tibiae 7(’, ’ p), 6(’ p), 6(’ p), 6(’ p); tarsi 15(2 ω), 11(2 ω), 9(2 ω), 9(2 ω).
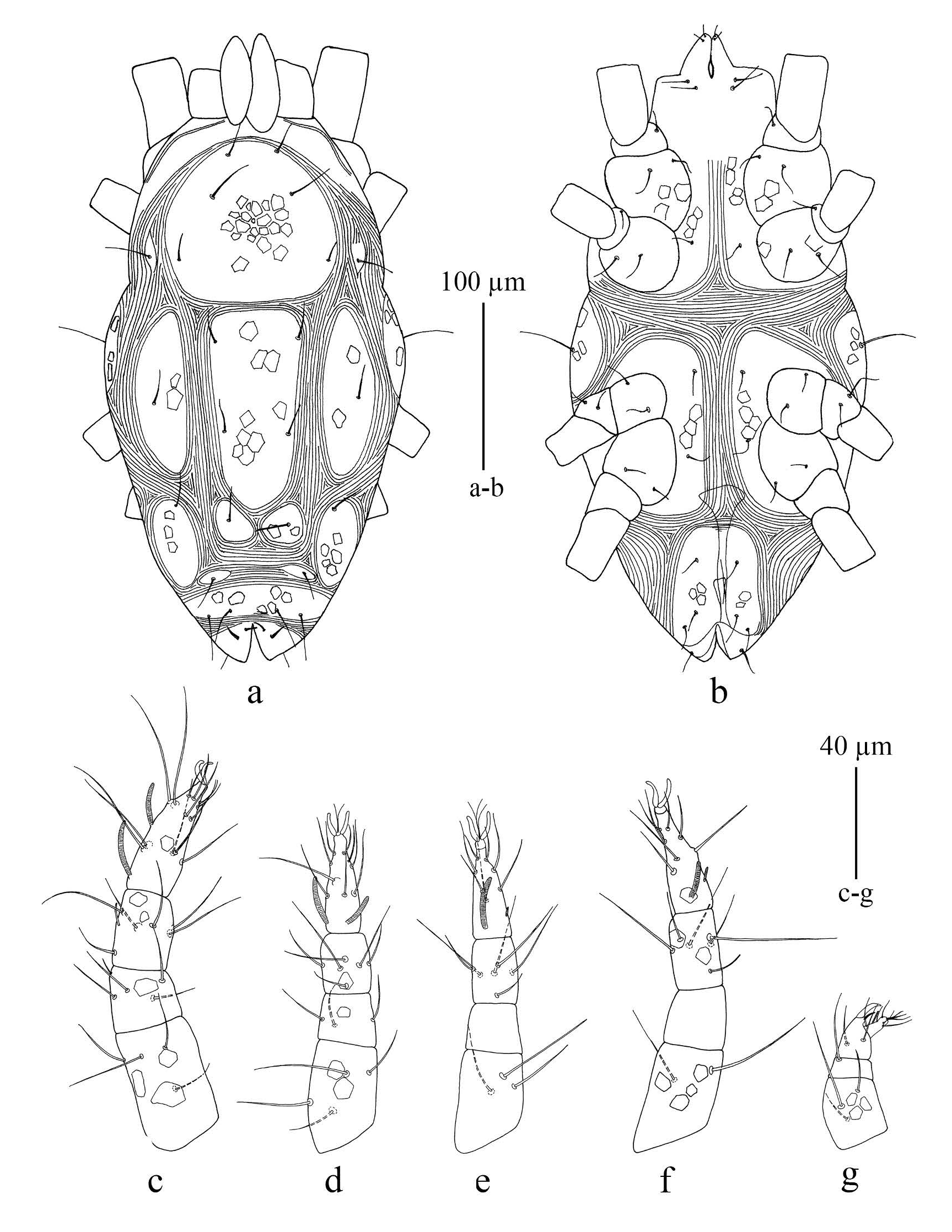
Deutonymph (n = 6) ( Figure 4 View FIGURE ): Length of body (including gnathosoma) 396 – 469, width 189 – 278. Gnathosoma ( Figure 4g View FIGURE ). Length of gnathosoma 55 – 59; subcapitulum with two pairs of subcapitular setae (m and n), m 18 – 23, n 16 – 20 and two pairs of adoral setae, or 1 and or 2; distances m -m 26 – 34, n -n 19 – 22; palpal chaetotaxy as in female.
Dorsum ( Figure 4a View FIGURE ) — Dorsal view similar to that of the female except suranal shield without setae h 3; length of dorsal setae: vi 21 – 24, ve 34 – 39, sci 26 – 27, sce 32 – 35, c 1 25 – 28, c 2 42 – 44, d 1 22 – 29, d 2 27 – 30, e 1 27 – 30, e 2 29 – 33, f 1 32, h 1 34 – 39, h 2 32 – 36, h 3 24 – 26; distances between dorsal setae: vi -vi 26 – 33, ve -ve 47 – 57, vi -ve 23 – 30, ve -sci 41 – 49, sci -sce 23 – 36, c 1 -c 1 51 – 60, c 1 -d 1 62 – 66, d 1 -d 1 33 – 38, d 1 -d 2 53 – 78, d 1 - e 1 50 – 67, e 1 - e 1 40 – 46, e 1 - e 2 45 – 54, e 1 -f 1 34 – 39, f 1 -f 1 52 – 57, h 1 -h 1 26 – 30, h 1 -h 2 12 – 16, h 2 -h 2 55 – 65; ratios vi / vi -vi 0.6 – 0.8, c 1 / c 1 -c 1 0.5, d 1 / d 1 -d 1 0.6 – 0.8, e 1 / e 1 - e 1 0.6 – 0.7, f 1 / f 1 -f 1 0.6.
Venter ( Figure 4b View FIGURE ) — Ventral view similar to that of the female. Lengths of setae: 1a 17 – 20, 3a 17 – 18, 4a 15 – 18; aggenital shields with subcutaneous reticulation and bearing three pairs of aggenital setae (ag 1 -ag 3), length of ag 1 13 – 15, ag 2 15 – 16 and ag 3 12 – 17; anogenital area with three pairs of pseudanal setae (ps 1 -ps 3); length of anogenital setae; ps 1 32 – 34, ps 2 31 – 42, ps 3 18 – 22.
Legs ( Figures 4 View FIGURE c-f) — Length of legs I-IV: Leg I 145 – 155; leg II 114 – 124; leg III 114 – 127; leg IV 123 – 137; counts of setae (solenidia and setae κ included) of legs I - IV: coxae 2, 2, 2, 2; trochanters 1, 1, 2, 0; femora 4, 4, 3, 2; genua 5(’), 3, 0, 0; tibiae 7(’, ’ p), 6(’ p), 6(’ p), 6(’ p); tarsi 14(ω), 10(ω), 8(ω), 8(ω).
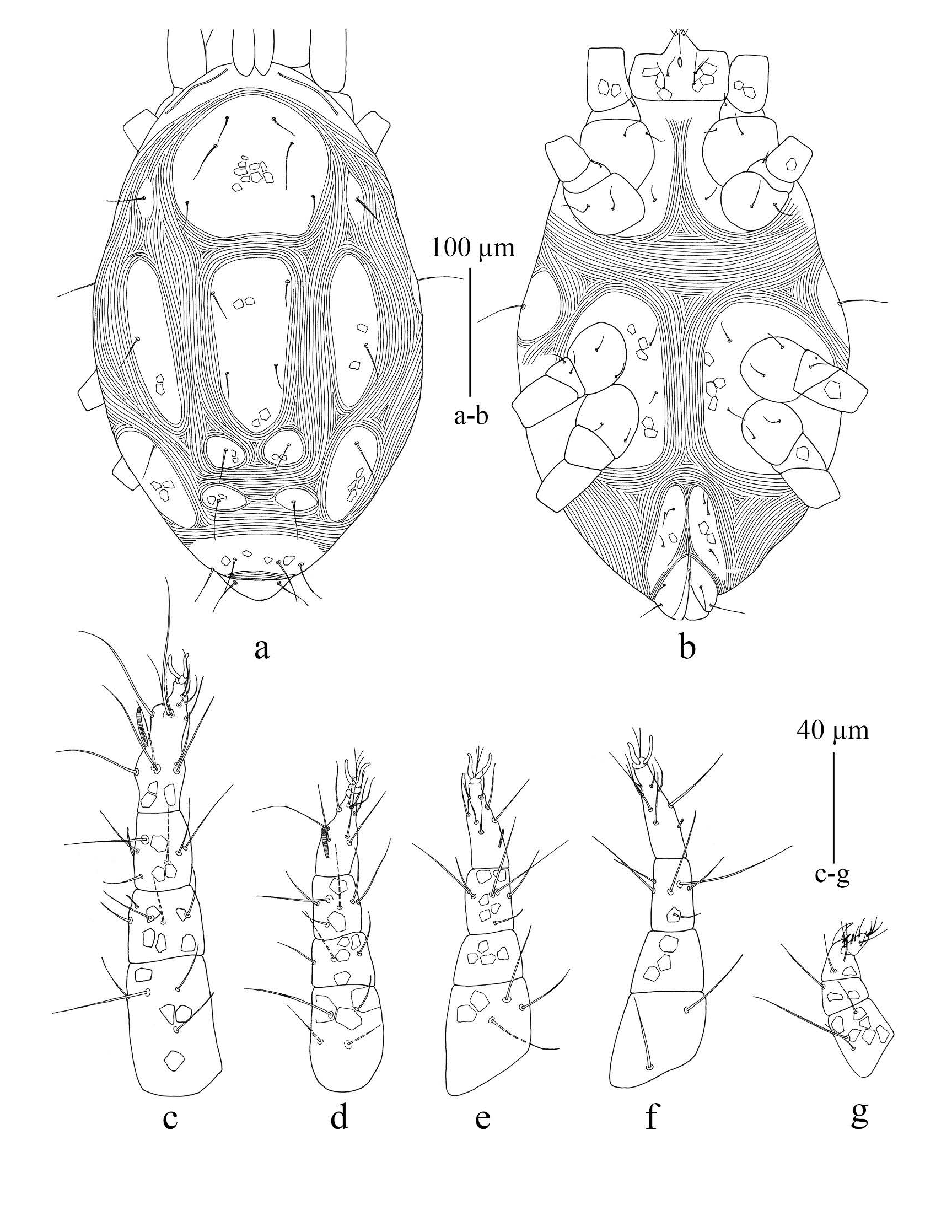
Protonymph (n = 7) ( Figure 5 View FIGURE ): Length of body (including gnathosoma) 311 – 399, width 161 – 238. Gnathosoma ( Figure 5g View FIGURE ). Length of gnathosoma 50 – 53; subcapitulum with one pair of subcapitular setae n 16 – 17 and two pairs of adoral setae, or 1 and or 2; distances n -n 20 – 25; palpal chaetotaxy as in female.
Dorsum ( Figure 5a View FIGURE ) — Dorsal view similar to that of the female except suranal shield without setae h 3; length of dorsal setae: vi 17 – 19, ve 31 – 35, sci 20 – 23, sce 28 – 31, c 1 22 – 25, c 2 39 – 45, d 1 23 – 25, d 2 23 – 26, e 1 24 – 27, e 2 26 – 29, f 1 28 – 32, h 1 24 – 32, h 2 25 – 34; distances between dorsal setae: vi -vi 25 – 31, ve -ve 44 – 54, vi -ve 22 – 24, ve -sci 34 – 45, sci -sci 74 – 85, sci -sce 17 – 26, c 1 -c 1 44 – 48, c 1 -d 1 48 – 54, d 1 -d 1 25 – 32, d 1 -d 2 41 – 64, d 1 - e 1 41 – 51, e 1 - e 1 28 – 40, e 1 - e 2 23 – 36, e 1 -f 1 24 – 35, f 1 -f 1 42 – 51, h 1 -h 1 21 – 29, h 1 -h 2 9 – 15, h 2 -h 2 40 – 52; ratios vi / vi -vi 0.6 – 0.7, c 1 / c 1 -c 1 0.5 – 0.6, d 1 / d 1 -d 1 0.7 – 1.0, e 1 / e 1 - e 1 0.7 – 1.0, f 1 / f 1 -f 1 0.6 – 0.7.
Venter ( Figure 5b View FIGURE ) — Ventral view similar to that of the female. Lengths of setae: 1a 15 – 17, 3a 15 – 16; without setae 4a; aggenital shields with subcutaneous reticulation and bearing one pair of aggenital setae ag 1 11 – 14; anogenital area with three pairs of pseudanal setae (ps 1 -ps 3); length of anogenital setae; ps 1 17 – 22, ps 2 13 – 19, ps 3 14 – 17.
Legs ( Figures 5 View FIGURE c-f) — Length of legs I-IV: Leg I 121 – 130; leg II 97 – 104; leg III 95 – 101; leg IV 98 – 105; counts of setae (solenidia and setae κ included) of legs I-IV: coxae 2, 2, 2, 0; trochanters 0, 0, 1, 0; femora 4, 4, 3, 1; genua 5(κ), 3, 0, 0; tibiae 7(’, ’ p), 6(’ p), 6(’ p), 6(’ p); tarsi 14(ω), 10(ω), 8(ω), 7(ω).
Material examined: 13 females, 9 males, 6 deutonymph and 7 protonymph from litter and soil un- der Astragalus sp. , Turkey, Hakkari, Berçelan Mountain (37°43’075"N, 43°44’264"E, 3075 m), 25 June 2014 .
The Turkish specimens resembles the type specimens and Iran specimens in most respects but differ in the length of body (including gnathosoma) 505 – 552. It is seen that the Turkish specimens are bigger: the length of body is 350 – 388 in the type specimen. The length of dorsal setae is similar to that of type specimen and longer than those of Iranian specimen. Apart from these, the other measurements and the features of our specimens resemble those of the type specimen in all respects ( Kuznetsov 1978; Zarei and Bagheri 2012). Males of this species exhibit the same features of the female descriptions, except that the male tarsi I-IV are with two solenidia instead of one solenidion in female; the length of body and dorsal setae are shorter than those of the female; no setae h 3 on the suranal shield; trochanteral chaetotaxy of the male 1, 1, 2, 0 and that of the female 1, 1, 2, 1; genual chaetotaxy of the male 5(κ), 3, 0, 0 and that of the female 6(κ), 5, 2, 2; the female bears 4 aggenial setae and the male bears 3 aggenital setae.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.