Tarsonemus striatus, Khaustov, 2017
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.24349/acarologia/20174187 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/345487A2-F442-FFF2-FC57-F935FF08FE47 |
|
treatment provided by |
Marcus |
|
scientific name |
Tarsonemus striatus |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Tarsonemus striatus n. sp.
( Figures 1-11 View FIGURE View FIGURE View FIGURE View FIGURE View FIGURE View FIGURE View FIGURE View FIGURE View FIGURE View FIGURE View FIGURE )
Zoobank: AAE737EE-99B0-4A20-B8AE-9293AC340DDE
Description
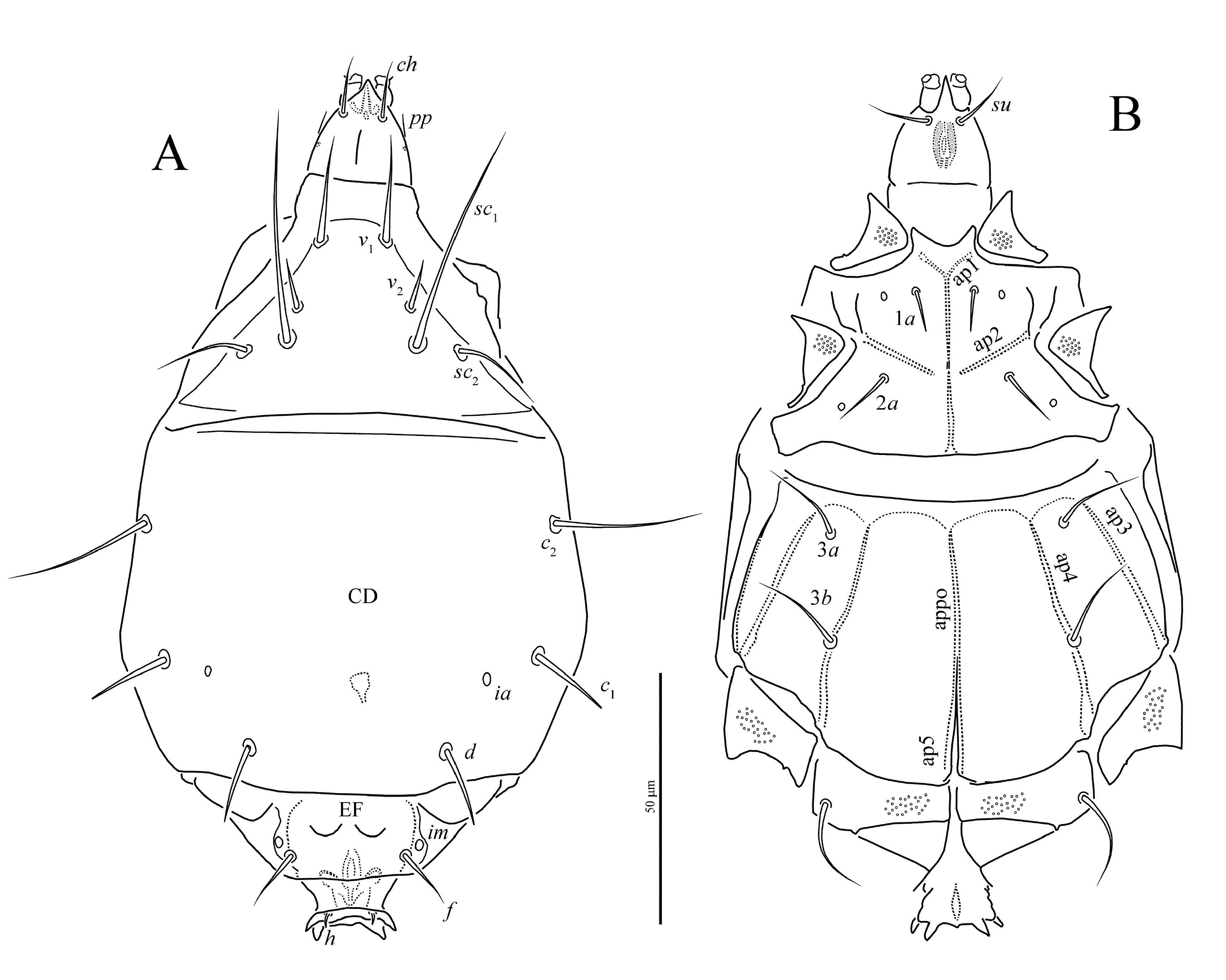
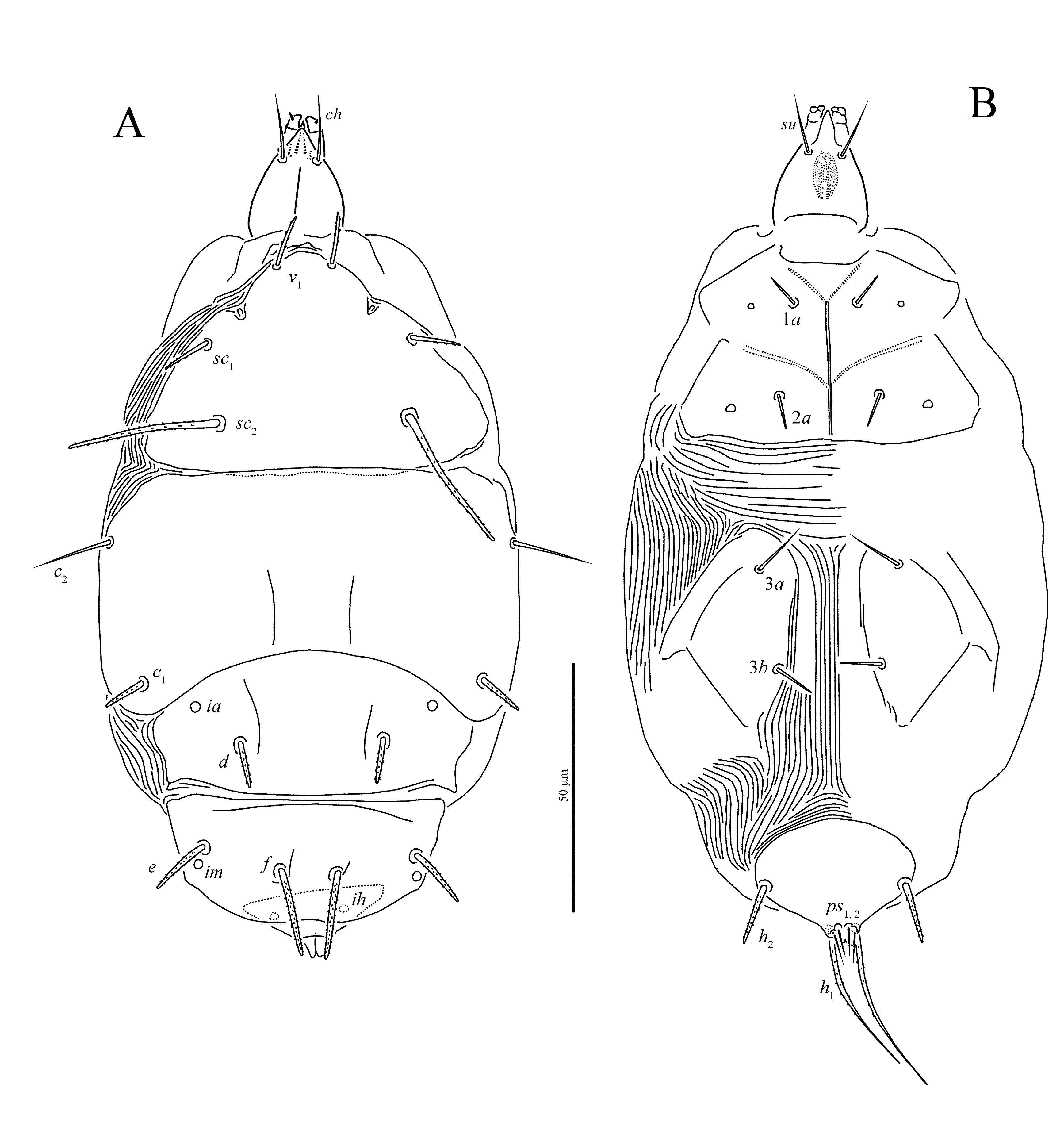
Female ( Figures 1-4 View FIGURE View FIGURE View FIGURE View FIGURE , 11 View FIGURE ) — Length of idiosoma
180 (170-190), width 110 (105-125).
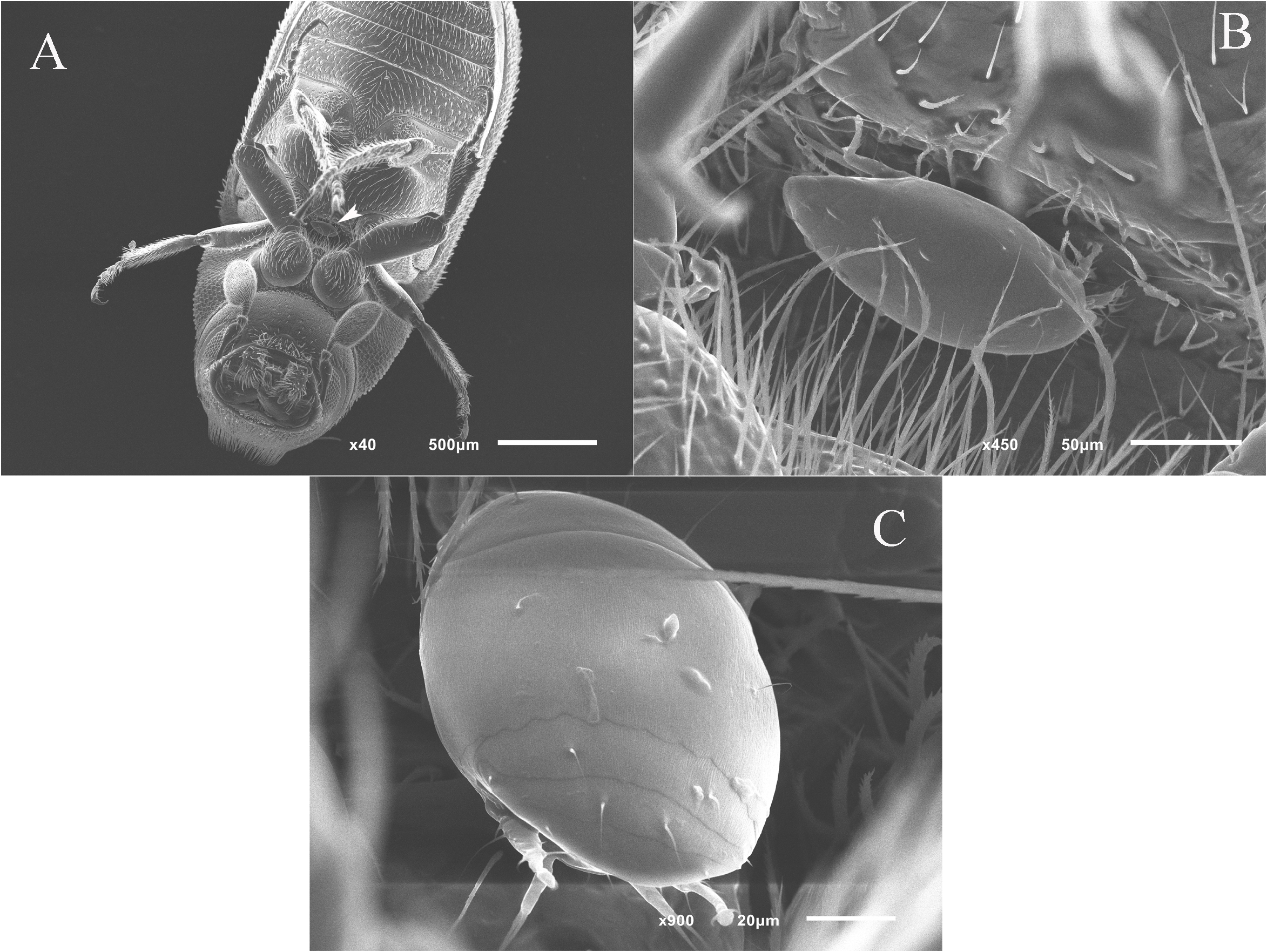
Gnathosoma — Gnathosomal capsule subtriangular, slightly longer than its width. Length of gnathosomal capsule 29 (27-29), width 23 (20-23). Dorsomedian apodeme well developed, extending nearly entire distance from union basally with circumcapitular apodeme to level of insertion of dorsal gnathosomal setae (ch). Gnathosoma with dorsal pair of setae ch 13 (13-14) subequal to subcapitular setae su 13 (12-13); both setae slender and smooth. Palpcoxal setae (pp) subequal to ch, slen- der and pointed. Palps short 8 (7-8) cylindrical, with short dorsolateral setae. Pharynx ( Figure 2D View FIGURE ) with well-developed muscular sheath and with inconspicuous pair of glandular structures at its posterior extremity.
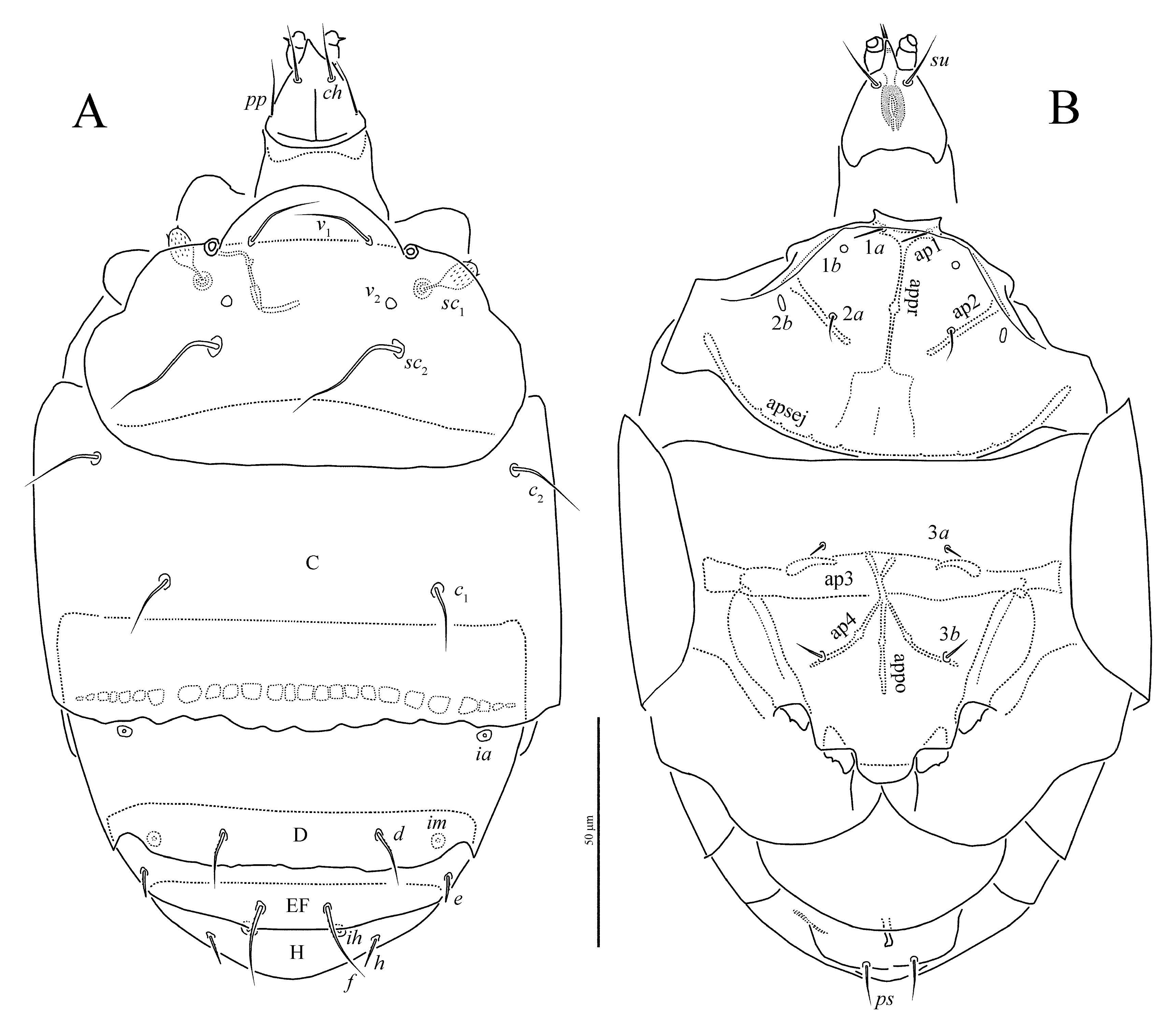
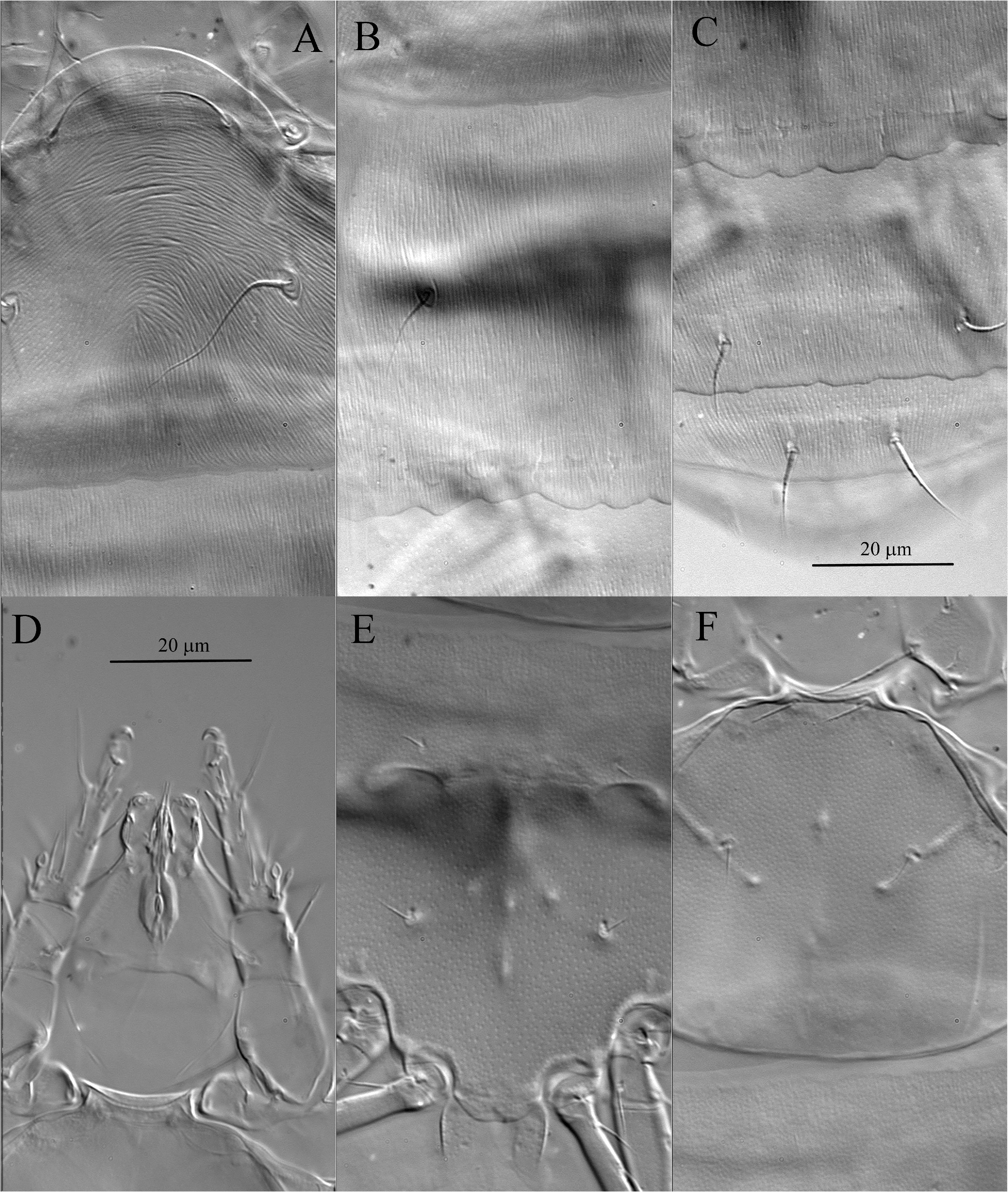
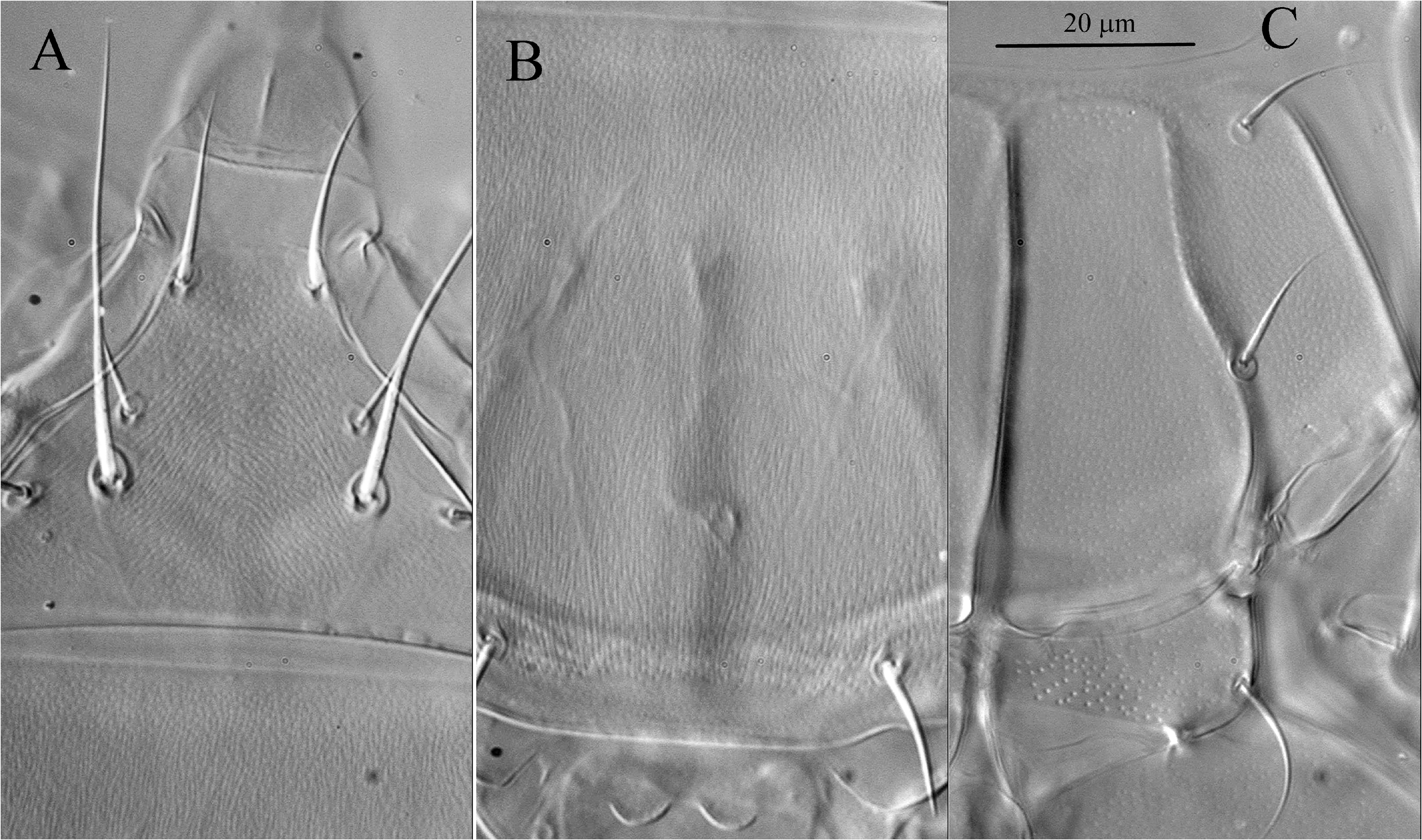
Idiosomal dorsum ( Figures 1A View FIGURE , 2 View FIGURE A-C, 11C) — Prodorsal shield with distinct linear microsculpture ( Figure 2A View FIGURE ); margin of shield distinctively triarcuate anteriorly and laterally, although lateral arches sometimes inconspicuous if folded ventrally. Prodorsum without median apodeme. Tracheal trunks without sclerotized sacs. Pseudostigmatic organs capitate, ellipsoidal, finely spiculate but with two larger spicules apically, and completely covered by prodorsal shield. All hysterosomal tergites with fine longitudinal striation ( Figures 2 View FIGURE B-C, 11C). Setae v 1, sc 2, c 1 and c 2 smooth and pointed; setae d and f weakly barbed and pointed; setae e and h blunt-ended and weakly barbed. Posterior margin of tergite C distinctly undulate ( Figures 2 View FIGURE B-C, 11C), posterior margin of tergite D sometimes also weakly undulate. Lengths of dorsal setae: v 1 18 (17 - 19), sc 2 36 (34 - 36), c 1 21 (17 - 22), c 2 25 (22 - 26), d 14 (13-15), e 7 (6-7), f 20 (19-21), h 7 (6-7). Distances between setae: v 1 - v 1 26 (25-28), v 2 - v 2 36 (35-37), sc 2 - sc 2 39 (38-40), c 1 - c 1 60 (59-63), c 2 - c 2 97 (91-98), c 1 - c 2 34 (31-34), d-d 36 (34-37), e-e 71 (66-72), e-f 28 (26-30), f -f 15 (14-15), h-h 39 (36-39).
Idiosomal venter ( Figures 1B View FIGURE , 2 View FIGURE E-F) — Prosternal apodeme (appr) extending posteriad only slightly beyond apodemes 2 (ap2), and with nodule between apodemes 1 (ap1) and ap2. Ap2 very slightly curved, and ending with small nodule medially. Sejugal apodeme (apsej) well developed, continuous, and with few weak processes directed anteriorly. Anterior sternal plate with uniform, very small dimples ( Figure 2F View FIGURE ). Setae 1 a needle-like; 2 a pointed, smooth. Apodemes 3 (ap3) united medially to form one continuous, subsurface band across metapodosomal venter, and extending laterally beyond anterior extremities of trochanters III. Setae 3 a and 3 b minute, needle-like. Apodemes 4 (ap4) reach- ing slightly posteriad of 3 b bases. Tegula rounded, short, flanked on either side by short, curved, conspicuous line. Posterior sternal plate with distinctly larger dimples in central part and smaller laterally ( Figure 2E View FIGURE ). Pseudanal setae smooth, pointed, about as long as distance between their bases. Lengths of ventral setae: 1 a 7 (7), 2 a 9 (7-9), 3 a 4 (4), 3 b 5 (5-6), ps 10 (7-10). Width of tegula 13 (12-13).
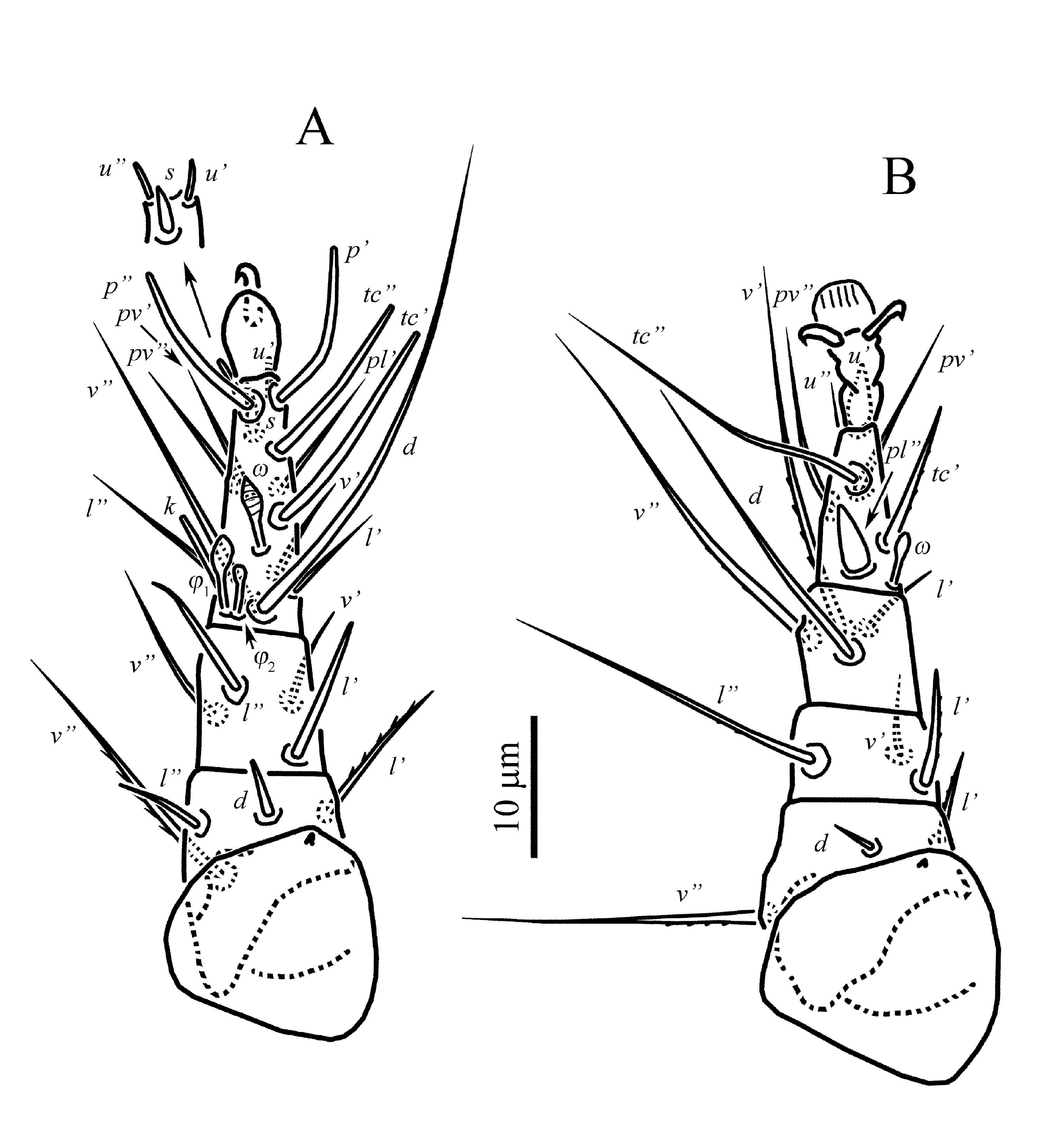
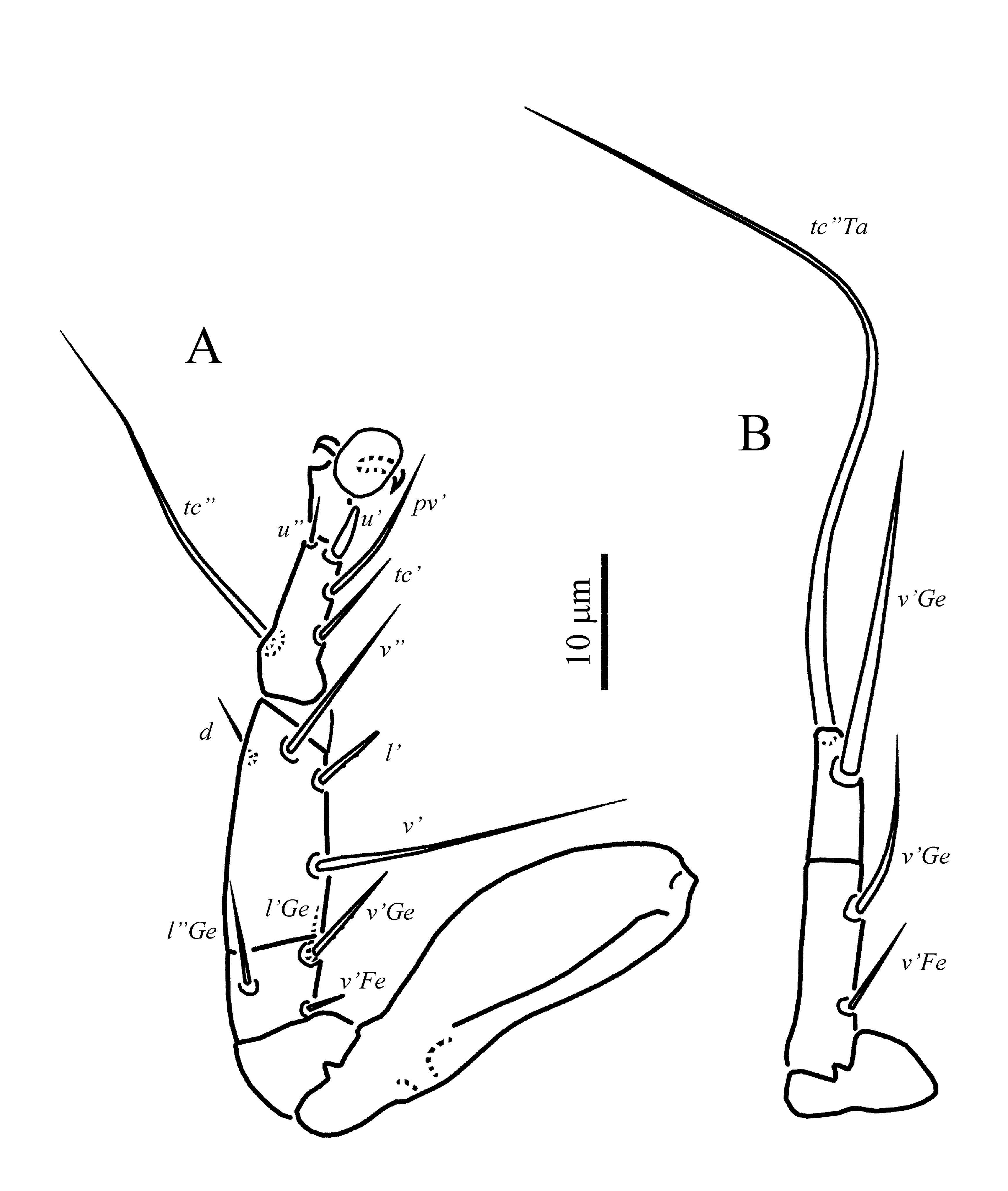
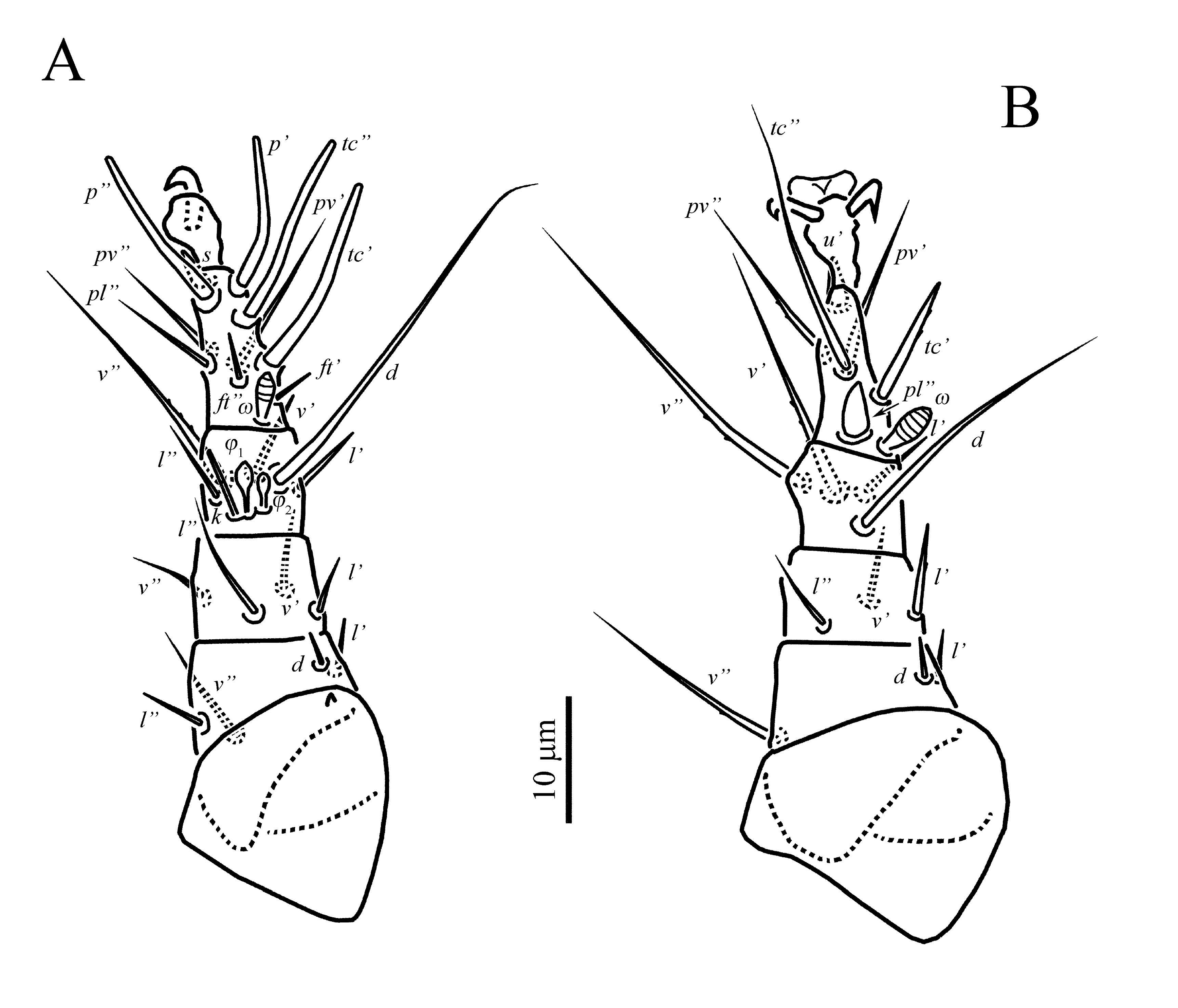
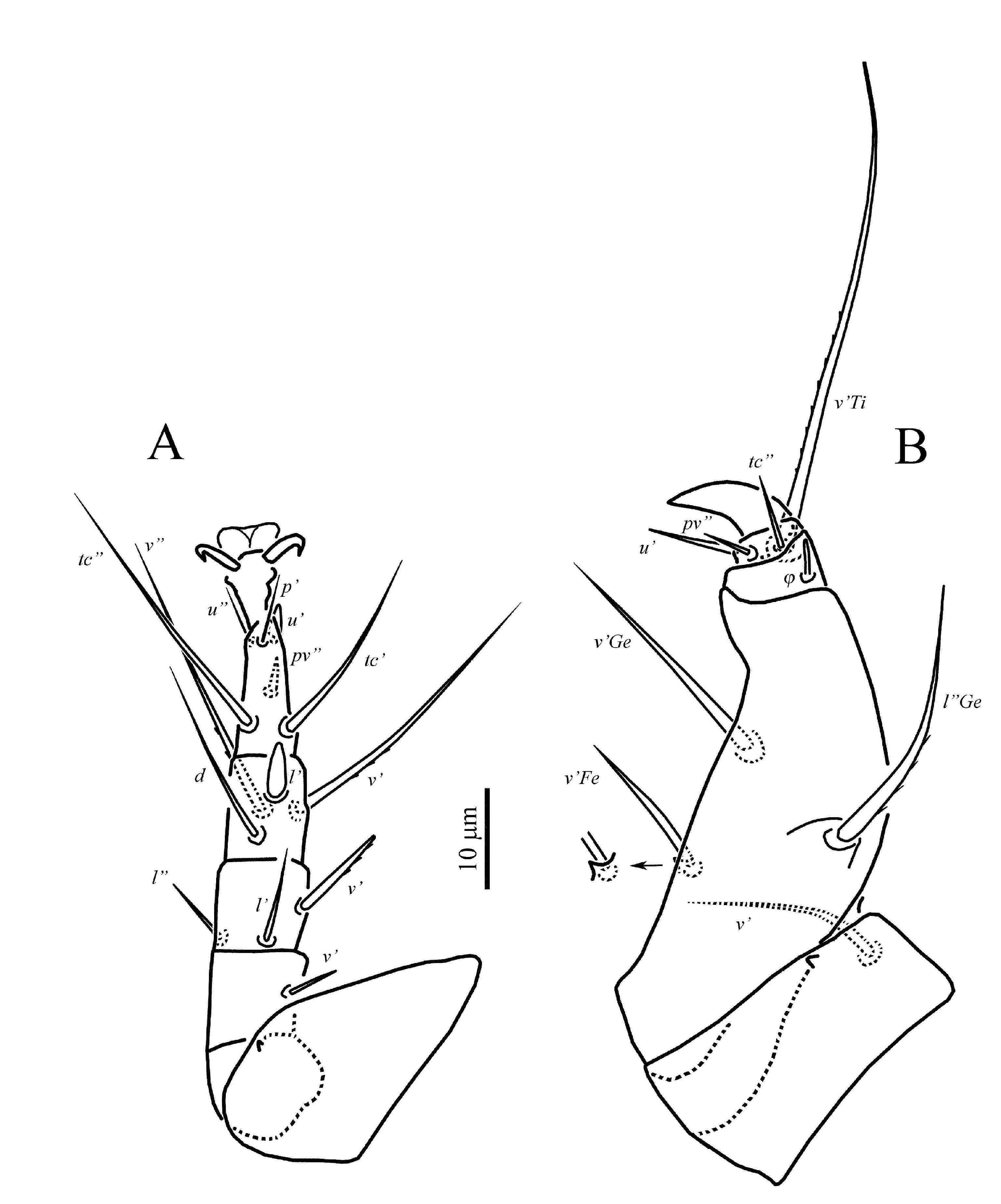
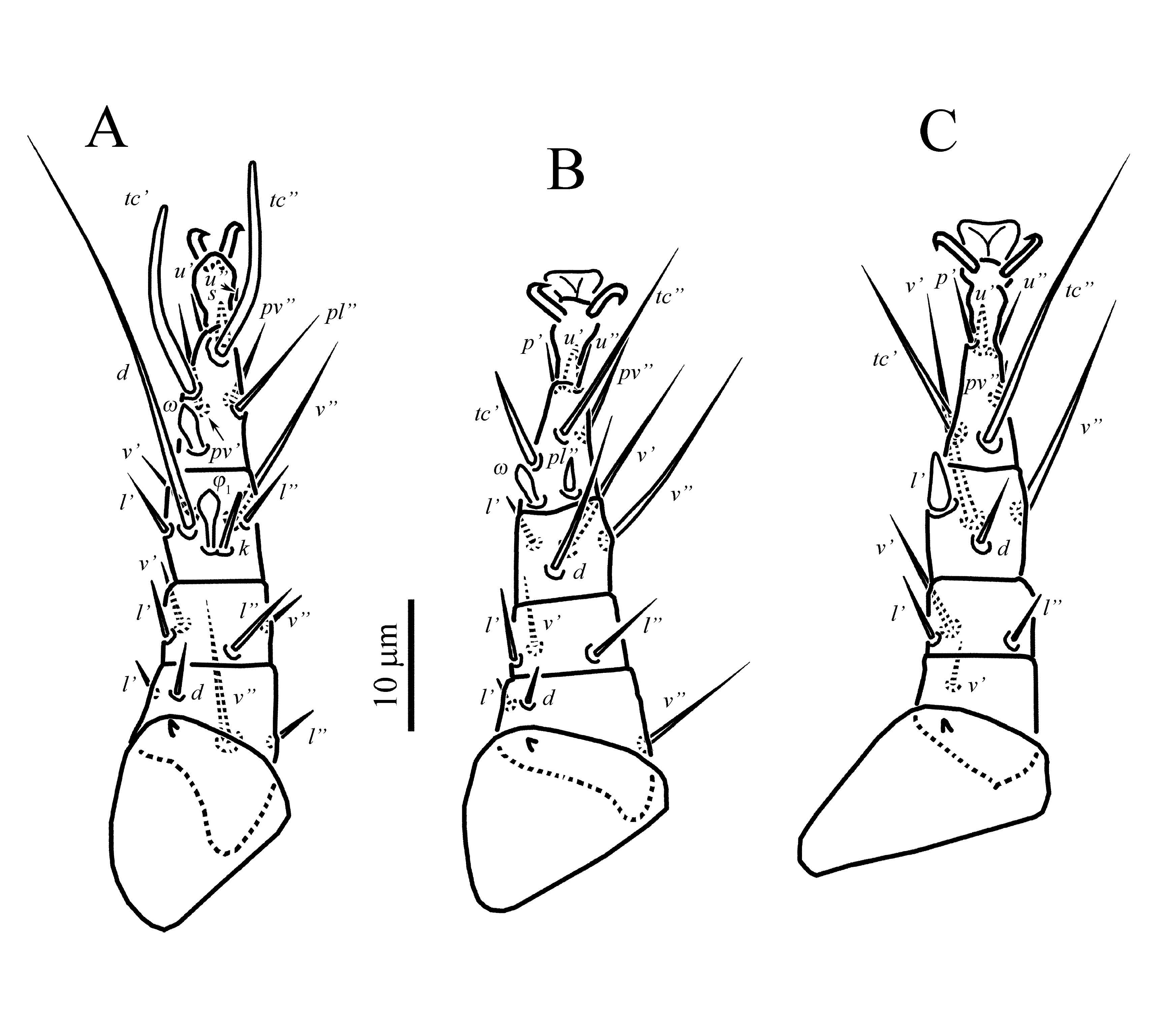
Legs ( Figures 3-4 View FIGURE View FIGURE ) — Legs: chaetotaxy (including unguinal setae u’, u” on tibiotarsus I and u” on tarsi II and III) of leg I: Fe4-Ge4-TiTa6(2F)+10(1ř); leg II: Fe3-Ge3-Ti4-Ta7(1ř); leg III: FeGe1+3-Ti4-Ta5. Lengths of legs: I 60 (56-60), II 58 (55-58), III 53 (49- 54), IV 32 (30-33). Leg I ( Figure 3A View FIGURE ). Solenidion ř capitate, with slightly pointed tip; solenidia F 1 and F 2 capitate; seta k 7 (6-7) rod-shaped, slightly longer than solenidion F 1. Lengths of solenidia: ř 6 (6) = F 1 6 (5-6)> F 2 4 (3-4). Seta d of femur slightly thickened, blunt-ended and smooth; seta s slightly thickened, spiniform; unguinal setae (u) short, blunt-ended; setae l” of femur, (l) and v’ of genu blunt-ended and smooth; seta l’ of femur distinctly barbed and slightly blunt-ended, seta v” of femur distinctly barbed and pointed; other leg setae (except eupathidia) pointed and smooth. Femur with weak flange near base of seta v”. Leg II (Figure 3B). Solenidion ř 4 (4) capitate. Setae pl” and u’ spine-like; setae l’ of femur, l’ of genu, and tc’ of tarsus blunt-ended and weakly barbed; seta d of femur needle-like; setae v’ of genu and l’ of tibia slightly blunt-ended and smooth; setae v” of femur, l” of genu, and (v) of tibia long, pointed and weakly barbed; other leg setae pointed and smooth. Leg III ( Figure 4A View FIGURE ). Setae v’ of femur and l’ of genu needlelike; setae v’ of genu and l’ of tibia blunt-ended and weakly barbed; seta u’ slightly thickened, spiniform; other leg setae pointed and smooth. Leg IV ( Figure 4B View FIGURE ). Seta v’ of femur slightly blunt-ended, smooth; other leg setae pointed and smooth.
Male ( Figures 5-8 View FIGURE View FIGURE View FIGURE View FIGURE ) — Length of idiosoma 125-150, width 85-95.
Gnathosoma — Gnathosomal capsule, including pharyngeal structures, similar to that of female. Length of gnathosomal capsule 21-23, width 16-20. Lengths of gnathosomal setae: ch 11-13, su 10-12.
Idiosomal dorsum ( Figures 5A View FIGURE , 8 View FIGURE A-B) — Prodorsal shield weakly sclerotized, with poorly defined edges, subtriangular, with weak linear microsculpture and small uniform dimples ( Figure 8A View FIGURE ). All dorsal setae smooth; setae c 1 and d blunt-ended; other dorsal setae pointed. Tergite CD with delicate longitudinal striation and very small dimples ( Figure 8B View FIGURE ). Tergite EF smooth, with two arch-like lines. Cupules ia situated posteromedially to bases of c 1; cupules im situated just anterolaterally to bases of setae f. Lengths of dorsal setae: v 1 18 - 22, v 2 10 - 12, sc 1 43 - 48, sc 2 18 - 19, c 1 13 - 16, c 2 27 - 31, d 14-18, f 12- 14. Distances between setae: v 1 - v 1 12-13, v 2 - v 2 22-23, sc 1 - sc 1 26-28, sc 2 - sc 2 42-43, c 1 - c 1 68-77, c 2 - c 2 74-84, c 1 - c 2 28-29, d -d 35-40, f -f 21-23.
Idiosomal venter ( Figures 5B View FIGURE , 8C View FIGURE ) — Appr extending posteriorly to posterior edge of prosternal plate, but weakened along its posterior half between ap1 and ap2. Ap2 straight, not uniting with appr. Apsej indistinct. Setae 1 a and 2 a inserted well behind ap1 and ap2, respectively. All ventral setae smooth; setae 1 a needle-like, other ventral setae pointed. Anterior and posterior sternal plates with uniform, very small dimples ( Figure 8C View FIGURE ). Ap3, ap4, and apodemes 5 (ap5) well developed. Setae 3 a inserted between anterior ends of ap3 and ap4; setae 3 b inserted on ap4 Lengths of ventral setae: 1 a 7-8, 2 a 11-12, 3 a 18-21, 3 b 17-20.
Legs ( Figures 6-7 View FIGURE View FIGURE ) — Legs: chaetotaxy of leg I: Fe4-Ge4-Ti6(2F)-Ta10(1ř); leg II: Fe3-Ge3- Ti4-Ta6(1ř); leg III: Fe1-Ge3-Ti4-Ta6; leg IV: Tr1- FeGe1+2-Ti1(1F)-Ta3. Lengths of legs: I 53-59, II 51-62, III 64-71, IV 50-66. Leg I ( Figure 6A View FIGURE ). Solenidia on tibia and tarsus I as in female. Lengths of solenidia: ř 3-4> F 1 4-5> F 2 3; seta k 5-6. Seta d, (l) of femur, l’, v’ of genu, l’, v’ of tibia, and (ft) of tarsus blunt-ended and smooth; seta s slightly thickened, spiniform; setae v” of tibia weakly barbed and pointed; other leg setae (except eupathidia) pointed and smooth. Leg II ( Figure 6B View FIGURE ). Solenidion ř 5 capitate. Setae pl” and u’ spine-like; setae l’ of genu and tc’ of tarsus blunt-ended and weakly barbed; seta d, l’ of femur, v’ of genu, and l’ of tibia needlelike; setae v” of femur, (v) of tibia and pv” of tarsus long, pointed and weakly barbed; other leg setae pointed and smooth. Leg III ( Figure 7A View FIGURE ). Setae v’ of femur and l” of genu needle-like; setae v’ of genu blunt-ended and weakly barbed; setae l’ of tibia u’, pv” of tarsus thickened, spiniform; other leg setae pointed and smooth. Leg IV ( Figure 7B View FIGURE ) stout. Trochanter conspicuously punctate ( Figure 8C View FIGURE ). Femorogenu robust, with small projection near base of seta v’ of femur. Setae l” of genu and v’ of tibia weakly barbed, blunt-ended; all tarsal setae needle-like; other leg setae pointed and smooth. Seta v’ of tibia almost as long as leg IV. Tarsal claw strongly developed. Solenidion F 4 rod-shaped.
Larva ( Figures 9 View FIGURE , 10 View FIGURE ) — Length of idiosoma 140-
150, width 83-92.
Gnathosoma — Gnathosomal capsule, including pharyngeal structures, similar to that of female, but palpcoxal setae not evident. Length of gnathosomal capsule 25-28, width 19-20. Lengths of gnathosomal setae: ch 13-14, su 11-13.
Idiosomal dorsum ( Figure 9A View FIGURE ) — Dorsal shields of idiosoma weakly sclerotized, smooth. Prodorsal shield subtriangular. Dorsal setae c 2 smooth, pointed; other dorsal setae distinctly blunt-ended and barbed. Posterior margin of tergite C deeply concave. Segment HPs almost completely covered by tergite EF. Setae h 1 long, slightly rounded at the
Khaustov A.A.
tip. Lengths of dorsal setae: v 1 9 - 10, sc 1 10 - 11, sc 2 28 - 29, c 1 9 - 11, c 2 17 - 18, d 10-11, e 14-16, f 17-21, h 1 31- 33, h 2 14. Distances between setae: v 1 - v 1 10, sc 1 - sc 1 40-41, sc 2 - sc 2 37-40, c 1 - c 1 67-69, d-d 29-30, e-f 16-17, f -f 8-11, h 1 - h 1 5, h 2 - h 2 15.
Idiosomal venter ( Figure 9B View FIGURE ) — Ventral plates of idiosoma weakly sclerotized, smooth. Ap1 longer than in adults, ap2 curving posteromedially, not uniting with appr. All ventral setae smooth; setae 1 a, 2 a and 3 b needle-like, other ventral setae pointed. Lengths of ventral setae: 1 a 7, 2 a 7, 3 a 10-13, 3 b 8-9, ps 1,2 5-7.
Legs ( Figure 10 View FIGURE ) — Legs: chaetotaxy of leg I: Fe4- Ge4-Ti6(1F)-Ta8(1ř); leg II: Fe3-Ge3-Ti4-Ta7(1ř); leg III: Fe1-Ge3-Ti4-Ta6. Lengths of legs: I 46-47, II 44- 46, III 46-47. Leg I ( Figure 10A View FIGURE ). Solenidia on tibia and tarsus I capitate. Lengths of solenidia: ř 4 = F 1 4; seta k 5. All setae of leg I smooth. Seta d, (l) of femur, all setae of genu, l”, v’ of tibia, and (u) of tarsus needle-like; seta s slightly thickened, spiniform; other leg setae (except eupathidia) pointed and smooth. Leg II ( Figure 10B View FIGURE ). Solenidion ř 3- 4 capitate. All leg setae smooth. Setae pl” and u’ spine-like; setae d, l’ of femur, l’, v’ of genu, l’ of tibia, and u” of tarsus needle-like; seta tc’ of tar-
Acarologia 57(3): 673–687 (2017)
sus slightly thickened, blunt-ended; other leg setae pointed. Leg III ( Figure 10C View FIGURE ). All leg setae smooth. Setae v’ of femur and (l) of genu needle-like; setae l’ of tibia u’, pv” of tarsus thickened, spiniform; other leg setae pointed and smooth.
Type material — Female holotype, slide AK280816, Primorsky Krai, Lazo reg., 43°30’04.6”N, 133°34’47.1”E, 902 m. a.s.l., 28 August 2016, between coxae I and II of adult bark beetle Polygraphus proximus Blandford, 1894 under the bark of Manchurian fir ( Abies nephrolēpis ), coll. A.A. Khaustov. Paratypes: 18 females, same data; 1 female, 3 males and 5 larvae, same locality and date, but in the galleries of Polygraphus proximus under the bark of Manchurian fir.
Etymology — The specific epithet of the new species is derived from Latin word striatus meaning striate and refers to the presence of distinct linear microsculpture on the idiosomal tergites of the female and male.
Differential diagnosis — The female of the new species is very similar to T. triarcus Lindquist, 1969 , described from North America, in having a triarcuate prodorsal shield, continuous ap3, and similar shape and position of idiosomal setae. The female of the new species differs from T. triarcus by the presence of distinct linear microsculpture on the idiosomal tergites (absent in T. triarcus ), undulate posterior margin of tergite C (not undulate in T. triarcus ), and by the absence of seta pv” on tarsus III (present in T. triarcus ). The male of the new species differs from the male of T. triarcus by the presence of weak linear microsculpture on the idiosomal tergites (absent in T. triarcus ) and presence of a short projection near the base of seta v’ of femur IV (absent in T. triarcus ).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.