Hemiphyllodactylus serpispecus, Eliades & Phimmachak & Sivongxay & Siler & Stuart, 2019
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4577.1.8 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:B1E733BD-8C82-451C-BFD3-469B2D815F9D |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5943311 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/2E34878A-FFF5-FFAF-FF12-5545FCE1FA13 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Hemiphyllodactylus serpispecus |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Hemiphyllodactylus serpispecus sp. nov.
( Figs. 4 View FIGURE 4 D–F, 5, 6)
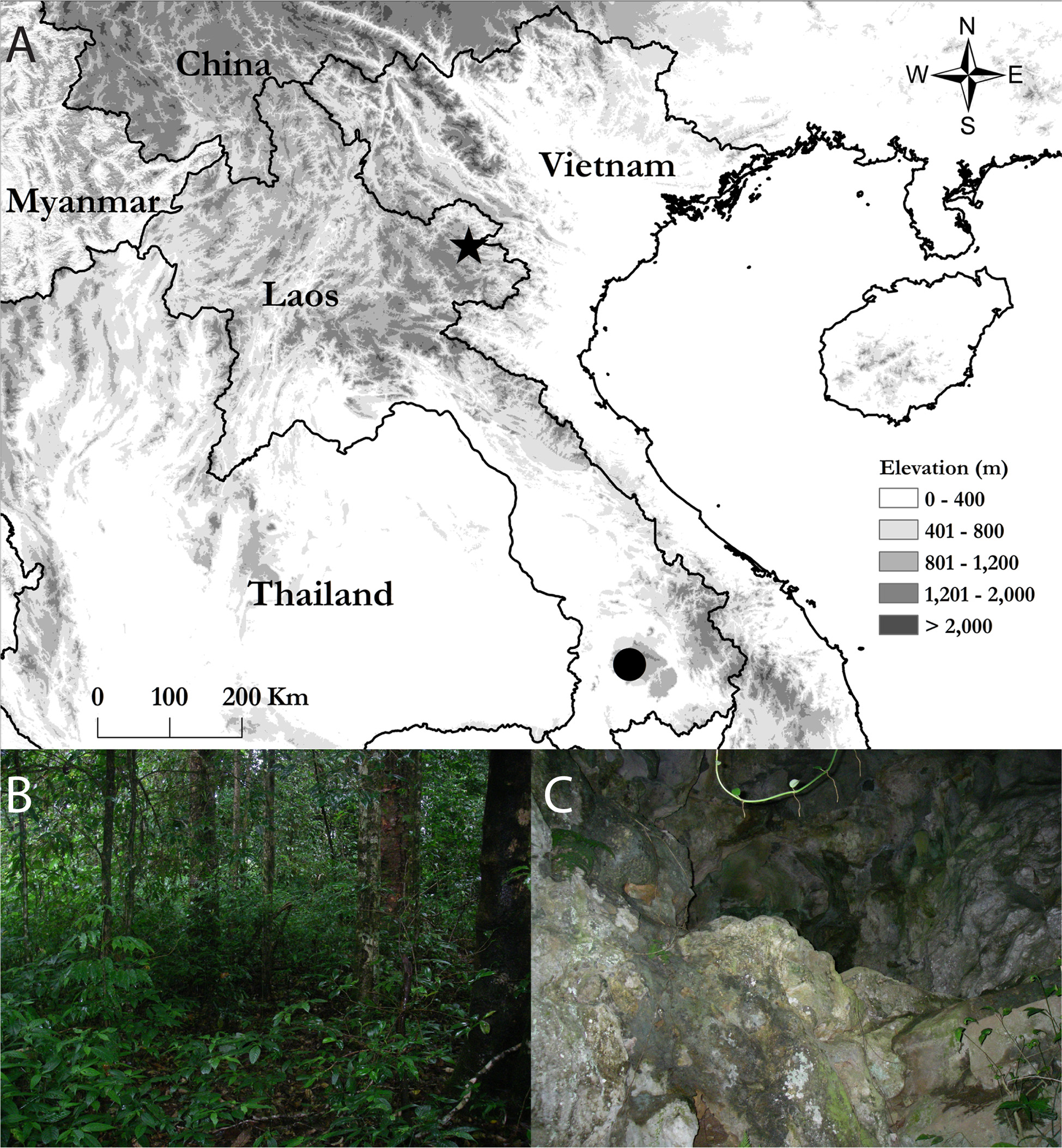
Holotype. NUOL 0 0 476 (field number BLS 17278), adult male, Tham Ngou Leium Cave , Viengxay District, Houaphanh Province, Laos, 20.40725°N, 104.23068°E, WGS84 ( Fig. 1A View FIGURE 1 ), 889 m elev., collected 19 September 2015 by BLS, SP, Fongfany Lybounyasao, and Phousavanh Inthapanya. GoogleMaps
Diagnosis. Hemiphyllodactylus serpispecus sp. nov. can be distinguished from all congeners by having the following combination of characters: supralabials 11; infralabials nine; precloacofemoral pores 11 in males (females unknown); subdigital lamellae on Fingers II–V 3-4-4-4; total lamellae on hand 15; subdigital lamellae on Toes II–V 3-4-4-5; total lamellae on foot 16; dorsal scales across midbody within one orbital diameter 26; ventral scales across midbody within one orbital diameter 10; cloacal spurs two; chin scales seven; and internasals two.
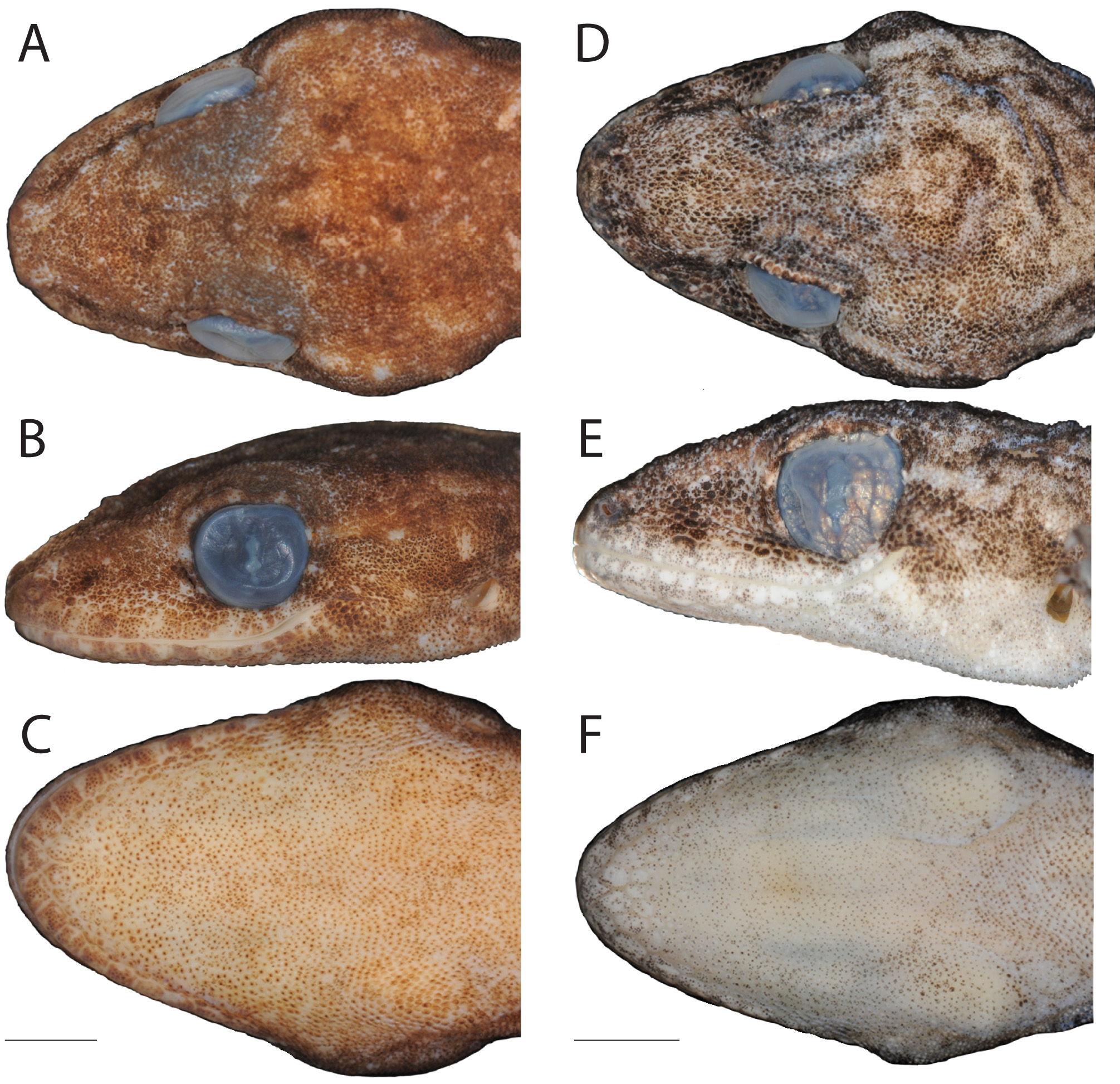
Description of holotype. Adult male; head triangular in dorsal profile, distinct from neck (HeadL 10.4 mm; HeadW 7.7 mm; HeadD; 4.6 mm); loreal and interorbital regions smooth; rostrum long (NarEye 3.3 mm; NarEye/ HeadL 32%); prefrontal region slightly concave; canthus rostralis smooth, rounded; snout long (SnEye 4.0 mm; SnEye/HeadL 38%), narrow (SnW 1.5 mm), rounded in dorsal profile; eye large (OrbD 2.4 mm); ear small, ovoid (EarL 0.5 mm); EyeEar greater than orbit diameter (EyeEar 4.0 mm; EyeEar/OrbD 167%); rostral scale wider than high, bordered posteriorly by two large supranasals and two internasals (Internas); nares bordered anteriorly by rostral scale, ventrally by first supralabial, dorsally by supranasal, posteriorly by two postnasals (CircNa); supralabials square, 11/11 (left/right), tapering from rostral to a point in line with posterior margin of orbit (Suplab); infrablabials square, 9/9, tapering from mental to a point in line with posterior margin of orbit (Inflab); scales on head small, rounded, largest on rostrum; superciliaries unequally sized, imbricate; mental triangular, bordered laterally by first infralabials and posteriorly by two large postmentals; each postmental bordered anterolaterally by first infralabial; seven chin scales touching infralabials and mental ( Chin); scales in gular region rounded, non-overlapping, becoming larger and more ovoid on venter.
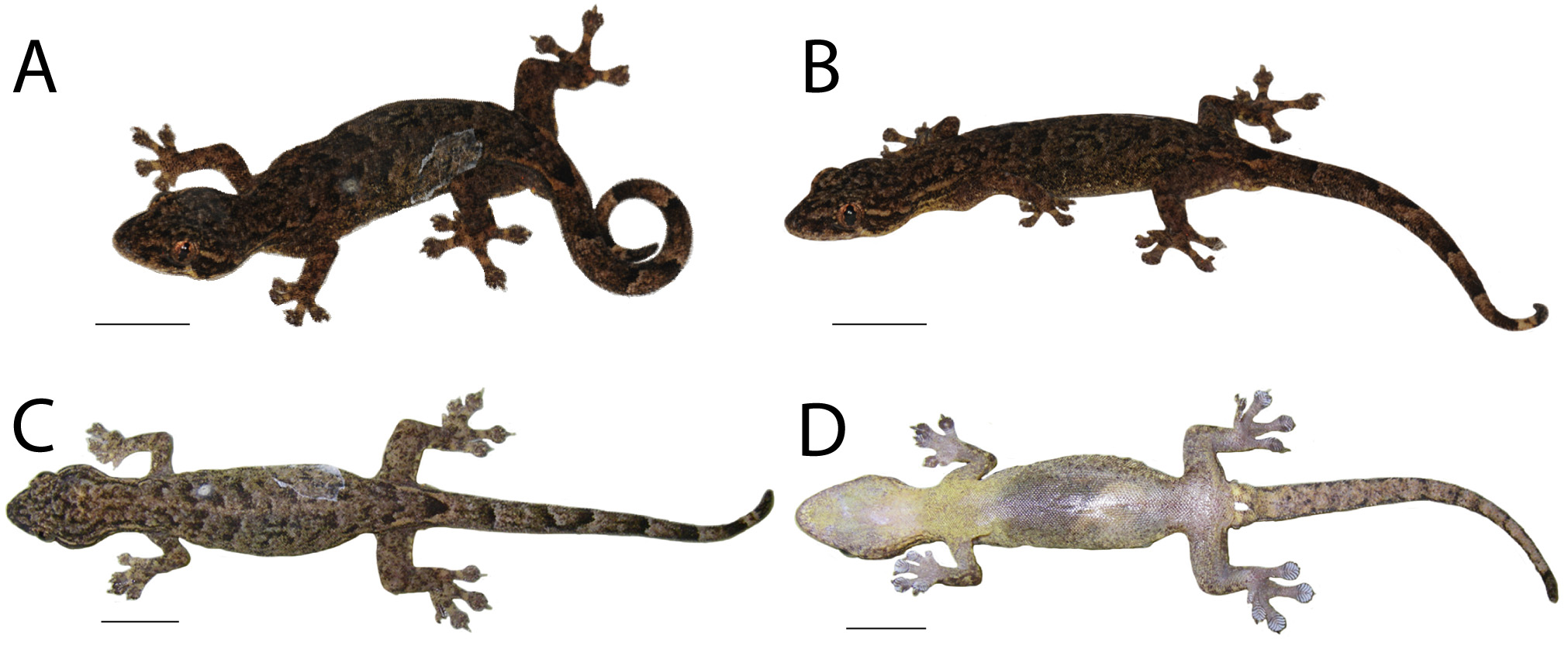
Body small, elongate (SVL 41.9 mm; TrunkL 21.4 mm); widest at midbody; ventrolateral fold absent; dorsal body scales small, granular, scales within one orbital diameter 26 (Dorsal); tubercles absent (Tub); ventral body scales smooth, somewhat rounded, subimbricate, scales within one orbital diameter 10 (Ventral); enlarged precloacal and femoral scales 17; continuous precloacal and femoral scales with pores 11 (Pore); precloacal groove absent; fore-limbs relatively short (ForeL 4.6 mm), dorsally covered with granular, subimbricate scales, smaller smooth scales ventrally; palmar scales flat, unevenly shaped, non-overlapping; Finger I vestigial, clawless, subdigital lamellae rectangular, four (IFingLm); Fingers II–V well-developed; proximal subdigital lamellae undivided, rectangular; distal lamellae divided, angular, U-shaped, except terminal lamellae rounded, undivided; lamellar formula on Fingers II–V 3-4-4-4 on both hands (II–VFingLm), total lamellae on hand 15 (TotFingLm); claws on Fingers II–V well-developed, unsheathed, strongly curved; hind limbs short (CrusL 6.0 mm), dorsally covered with granular, subimbricate, unevenly sized scales, ventrally covered with smooth scales, larger than dorsal scales; plantar scales small, smooth; Toe I vestigial, clawless; subdigital lamellae rectangular, four (IToeLm); Toes II–V well-developed; proximal subdigital lamellae undivided rectangular; distal lamellae divided, angular, and U-shaped except terminal lamellae rounded, undivided; lamellar formula on Toes II–V 3-4-4-5 on left foot and 3-5-5-5 on right foot (II–VToeLm), total lamellae on foot 16 (TotToeLm); cloacal spurs two (CloacS); tail long (TailL 35.2 mm), round in cross-section, narrow (TailW 3.1 mm), intact, tapers towards tip; dorsal scales on tail larger than on body and head, smaller than subcaudals; subcaudals large, flat, imbricate.
Coloration in life. Dorsal surfaces of head and body Olive-Brown (Color 278), mottled with light and dark brown patches ranging from Smoke Gray (Color 267) to Dusky Brown (Color 285). Weak chevron pattern of Dusky Brown (Color 285) on paravertebral surfaces from neck to base of tail. Faint postorbital stripe of Drab Gray (Color 256) from posterior edge of eye to level of fore-limb. Labial scales Smoke Gray (Color 266) with darker speckles ranging from Smoke Gray (Color 267) to Dusky Brown (Color 285). Medium Sulphur Yellow (Color 94) speckles on dorsolateral and ventrolateral surfaces posterior to the jaw. Sharp contrast of Dusky Brown (Color 285) to Smoke Gray (Color 267) in supraciliary region. Dorsal surface of tail Brownish Olive (Color 276), mottled with patches ranging from Smoke Gray (Color 267) to Dusky Brown (Color 285). Triangular marking at base of dorsal surface of tail Dusky Brown (Color 285), outlined posteriorly in Ground Cinnamon (Color 270). Weak lateral stripe along length of tail Dusky Brown (Color 285). Ventral surfaces mostly Smoky White (Color 261) with speckles of Raw Umber (Color 280) and Medium Sulphur Yellow (Color 94) ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 A–B).
Coloration in alcohol. As in life, except dorsal surfaces of the head, body, limbs, and tail faded to Grayish- Horn Color (Color 268); (2) lateral stripe on tail not visible; (3) chevron pattern on paravertebral surfaces not visible; (4) postorbital stipe faded to Smoky White (Color 261); (5) labial coloration faded to Smoky White (Color 261) with speckling of Raw Umber (Color 280); (6) all yellow coloration on dorsolateral, ventrolateral, and ventral surfaces faded to Smoky White (Color 261) ( Figs. 4 View FIGURE 4 D–F, 6).
Distribution and natural history. Hemiphyllodactylus serpispecus sp. nov. is known only from the holotype that was collected at night (2045 h) approximately 1 m above the ground on a limestone karst formation near the entrance to Tham Ngou Leium Cave ( Fig. 1C View FIGURE 1 ). The cave had been developed for tourism at the time of our visit and only scrub and secondary vegetation surrounded the limestone karst block containing the cave.
Etymology. The specific epithet is derived from the Latin serpens for snake and specus for cave, in reference to the type locality of Tham Ngou Leium, which means “Python Cave” in the Lao language.
Comparisons. Hemiphyllodactylus serpispecus sp. nov. can be differentiated from all other congeners in mainland Southeast Asia and southern China by a combination of the following characters: chin scales seven ( versus ± 9 in H. aurantiacus and H. zugi ); postmentals distinctly enlarged ( versus not enlarged in H. aurantiacus ); circumnasal scales three ( versus ± 4 in H. flaviventris H. khlonglanensis , H. kiziriani , and H. linnwayensis ); internasal scales two ( versus 4–11 in H. banaensis ); supralabial scales 11 ( versus eight or nine in H. tonywhitteni ); dorsal scales within one orbital diameter 26 ( versus Ĺ 22 in H. aurantiacus , H. banaensis , H. changningensis , H. chiangmaiensis , H. flaviventris , H. huishuiensis , H. khlonglanensis , H. linnwayensis , H. montawaensis , H. tonywhitteni , H. yunnanensis , and H. zugi ); ventral scales within one orbital diameter 10 ( versus Ĺ 8 in H. changningensis , H. linnwayensis , H. montawaensis , and 14–16 in H. zugi ); total lamellae on hand 15 ( versus Ĺ 13 in H. aurantiacus , H. chiangmaiensis , H. longlingensis , and H. yunnanensis ); total lamellae on foot 16 ( versus Ĺ 13 in H. aurantiacus , H. chiangmaiensis and 19 in H. banaensis , H. dushanensis , H. flaviventris , and H. zugi ); subdigital lamellae on Finger I four ( versus three in H. huishuiensis , H. tonywhitteni and ± 5 in H. banaensis , H. dushanensis , H. flaviventris , H. jinpingensis , H. khlonglanensis , H. kiziriani , and H. longlingensis ); subdigital lamellae on Toe I four ( versus three in H. huishuiensis and ± 5 in H. dushanensis , H. flaviventris , H. jinpingensis , H. khlonglanensis , H. kiziriani , and H. longlingensis ); and continuous precloacofemoral pores 11 ( versus ± 13 in H. aurantiacus , H. banaensis , H. changningensis , H. chiangmaiensis , H. dushanensis , H. jinpingensis , H. khlonglanensis , H. longlingensis , H. montawaensis , H. tonywhitteni , and H. zugi ).
| NUOL |
National University of Laos |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |