Diplodasys sanctimariae, Hummon, William D. & Todaro, Antonio, 2009
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.191139 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6213374 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/2C3387EA-864B-9141-FF73-B7DF0330F858 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Diplodasys sanctimariae |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Diplodasys sanctimariae View in CoL new species [Dpd smar]
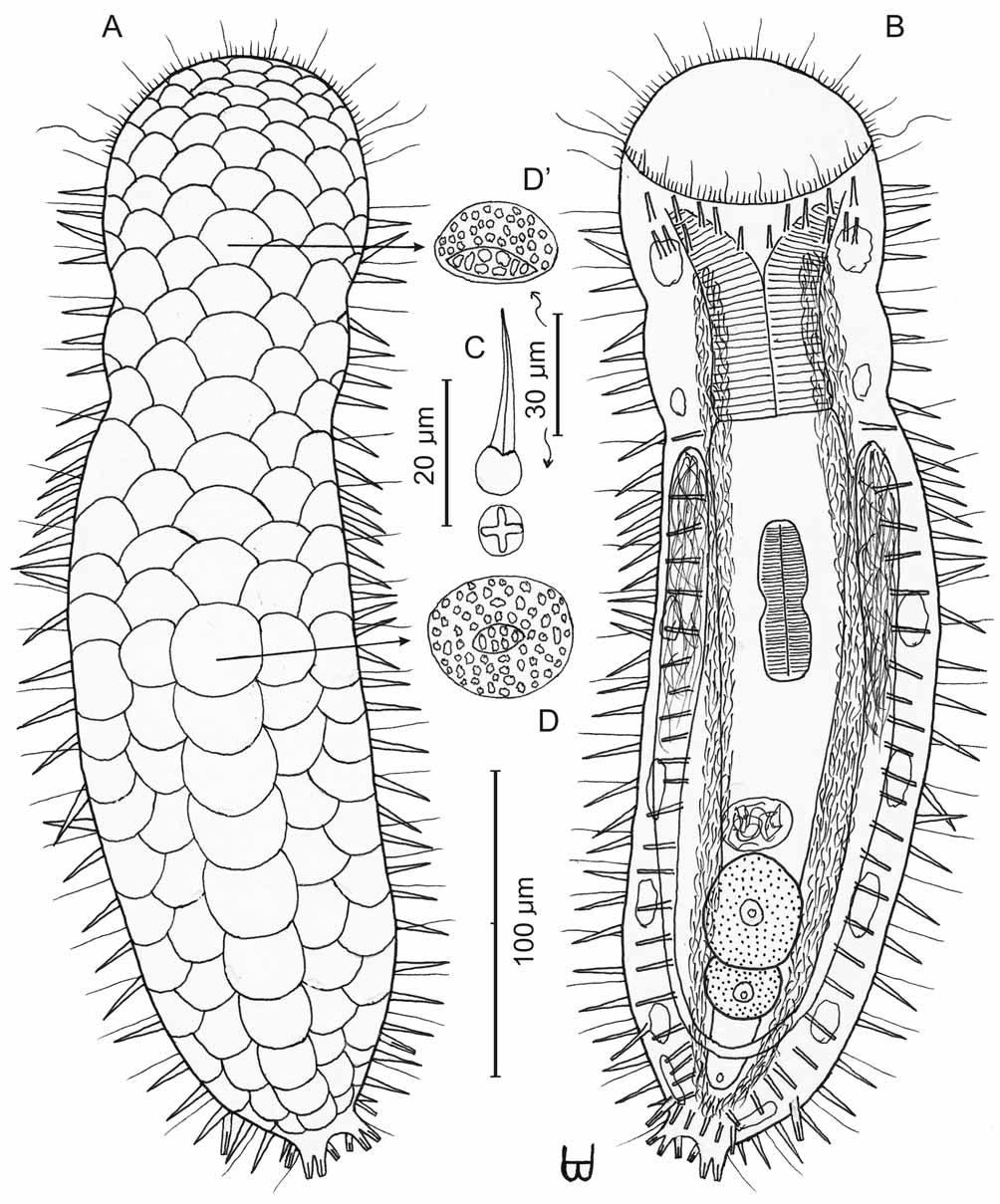
Figure 4 View FIGURE 4 A–D’
Diplodasys View in CoL sp. A ( Todaro, Hummon, Balsamo, Fregni & Tongiorgi 2001: p. 122); ( Hummon 2001 – 2009: W Med Database)
Diagnosis: Adult Lt 375 Μm; PhJIn at U32. Head with broadly ovoid mouth, oral hood rounded, without pestle organs; neck narrows twice to the PhJIn, then swells in the trunk region, before narrowing slowly, then quickly to a narrow caudum, bearing short pedicles. Glands 7 per side, of various shapes and sizes. Laterally are 32–33 spines per side in profile, 3–4 each on the pharyngeal swellings and the rest on the trunk. Squamous scales cover the dorsum in 5 columns, imbricated mid-trunk to oral hood from the upper-most 14th scale at U53 and in the opposite direction back to the caudum; each scale appears fenestrated throughout, with 6–8 apertures in an oblong section that is distinct from the remainder of the scale, which is filled with apertures; the oblong section is central in the middle scale, but is rearward in the other scales; ventral scales occur in 5 columns, being diamond to rhomboidal in shape, but without fenestrations. TbA 8 per side bordering the ventral rim (L 8 Μm), with an arc of 5 tubes inserting medial to lateral, and a set of 3 lying behind the outermost tubes of the arc, all projecting forward and inserting directly on the postoral body surface at U14-U17; TbVL 2 per side, both duo-gland, at U90 and U97; TbV 24 per side, at U33-U94, all being of similar size and regularly spaced along to just behind the intestinal region, with 2 of these in the post-anal region; TbD are absent; TbP 10 (L 6–8 Μm), 3 per side on the caudal pedicles, all duo-gland, forming the fused ‘two fingers and a thumb’ typical of the family, but lacking a cirratum-like element inserting between the ‘fingers,’ and 4 total forming a transverse row just behind the anus. Locomotor ciliature: forms two lateral bands that run the length of the body, merging behind the anus. Mouth subterminal, as broad as the fore end of the body, rim bears tactile hairs of two lengths; non-cuticularized buccal cavity narrows quickly; broad pharynx has inconspicuous basal pharyngeal pores at U30; intestine narrows front to rear; anus at U91. Hermaphroditic; testes bilateral, beginning just behind the PhJIn, with vasa deferentia running rearward and joining just before the anus; 2 developing eggs were seen in the hindgut region; caudal organ not seen; small hyaline sac-like frontal organ, oblong in shape and bearing motile sperm, occurred before the foremost egg.
Description: Adult Lt 375 Μm; LPh 97 Μm to PhJIn at U32 ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 A, B). Body medium-short in length as an adult, ventrally flattened, dorsally vaulted; head end with broad ovoid mouth, oral hood rounded, without pestle organs; neck narrows twice to the PhJIn, then swells in the trunk region, before narrowing slowly, then quickly to a narrow caudum, bearing short pedicles. Widths at ventral rim to PhJIn/fore trunk to rear trunk/ caudal base and locations along the length of the body are as follows: 83/76,82,75/95,66/30 Μm at U13/ U21,U27,U32/U55,U82/U97, respectively. Glands 7 per side, of various shapes (roundish to oblong) and sizes (4 x 7 to 6 x 16 Μm).
Cuticular Armature: Laterally are 32–33 spines per side as seen in profile, 3–4 each on the two pharyngeal swellings and the remainder on the trunk ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 C); they are longest on the foretrunk (16 Μm), shortest on the hindtrunk (6 Μm), and are + shaped in cross-section. Squamous scales cover the dorsum in 5 columns, imbricated mid-trunk to oral hood from the upper-most scale (the 14th scale in Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 D, and the 7th in Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 D’) centering at U53 and in the opposite direction back to the caudum; each scale appears fenestrated throughout, with 6–8 apertures in an oblong section that is distinct from the remainder of the scale, which is filled with apertures; the oblong section is central in the middle scale, but is rearward in the foreward and rearward scales. Ventral scales occur in 5 columns, being diamond to rhomboidal in shape, but without fenestrations.
Adhesive tubes: TbA 8 per side bordering the ventral rim (L 8 Μm), with an arc of 5 tubes inserting medial to lateral, and a set of 3 lying behind the outermost tubes of the arc, all projecting forward and inserting directly on the postoral body surface at U14-U17; TbVL 2 per side, both duo-gland, at U90 and U97; TbV 24 per side (L 10–13 Μm), from U33 to U94, all being of similar size and regularly spaced in, to just behind, the intestinal region, with 2 of these in the post-anal region; TbD are absent; TbP 10 (L 6–8 Μm), 3 per side on the caudal pedicles, all duo-gland, forming the fused ‘two fingers and a thumb’ typical of the family, but lacking a cirratum-like element inserting between the ‘fingers,’ and 4 total forming a transverse row just behind the anus.
Ciliation: Mouth rim bears a corona of some 65 short (L 3 Μm) tactile and 18 longer (L 14–18 Μm) vibratile cilia; other sensory hairs (L 20–26 Μm) occur in lateral columns on either side of the body, numbering 20–22 per side. Ventral locomotor cilia form two lateral bands that run the length of the body, merging behind the anus.
Digestive tract: Mouth subterminal, as broad as the fore end of the body, width 83 Μm; non-cuticularized buccal cavity narrows quickly; broad pharynx has inconspicuous basal pharyngeal pores at U30; intestine is broadest in front, narrowing slightly to the rear; anus is at U91.
Reproductive tract: Testes occur bilaterally in this subfamily, beginning just behind the PhJIn, with vasa deferentia running rearward and joining just foreward of the anus; 2 developing eggs were seen in the hindgut region; caudal organ not seen, but a hyaline, sac-like frontal organ, oblong in shape (14 x 20 Μm) and bearing motile sperm, was seen before the foremost egg.
Ecology: Occasional in frequency of occurrence (10–30% of samples), rare to prevalent in abundance (less than 1% to greater than 30% of a sample, sometimes occurring as a co-dominant [cdom]); sublittoral in fine to very coarse, medium to poorly sorted, sand at 1–12 m water depth, sometimes between patch reefs of coral, sometimes in depressions in reef platforms.
Geographical distribution: MED: EUROPE: CYPRUS: {Protaras [2-videos]}; ITALY: Puglia: Santa Maria di Leuca^ 39°,47'N/18°,18'E}. MED: AFRICA: EGYPT: {Abu Ramada 2 [video], Tareef el-Reeh S [cdom] [video], Tip RM [video]}.
Remarks: Diplodasys sanctimariae n. sp. does not have an extant specimen, the description and Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 being based on the drawing of a live type specimen (ICZN, Article 73.1.2) from Santa Maria di Leuca, which was lost in the process of transfer. There being no adult on video, we designate as paratypes (ICZN, Article 72.4.3) WDH video #2534, from Protaras, Cyprus in the Mediterranean Sea: Lt 315 Μm, LPh 155 Μm; WDH #827, a subadult also from Protaras: Lt 200 Μm; LPh 102 Μm; and WDH #824, a juvenile from Abu Ramada, Egypt in the Red Sea: Lt 122 Μm; LPh 62 Μm The 12 m water depth collection from Abu Ramada was taken by SCUBA, the 4 m collections by snorkling.
Etymology: The species is named (ICZN Article 32.5.2.4.1) after the location in Puglia, Santa Maria di Leuca, from which it was first found.
Taxonomic affinities: Diplodasys sanctimariae n. sp. is the only medium sized animal (compare Clausen 2004: Tab. 3) that has two incisions in the pharyngeal region, single spines along the sides (with 3 or 4 before the first incision and 3 or 4 between the first and second, 30 on the trunk), 5 columns of both dorsal and ventral scales, a caudum with paired pedicles, the central dorsal plate having an inner oblong with 6 fenistrations and an outer circlet bearing fenestrations throughout, TbA in 2 rows of 5 and 3 per side, TbV 24 per side, and a transverse row of TbP that lies just behind the anus, as well as 3 each on the pedicles.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |