Felisacus longiceps Poppius, 1915
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.1206/0003-0090-403.1.1 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/296A879F-5674-7539-5E93-FD3BFD3C0920 |
|
treatment provided by |
Carolina |
|
scientific name |
Felisacus longiceps Poppius, 1915 |
| status |
|
Felisacus longiceps Poppius, 1915 View in CoL
Figures 5 View FIGURE 5 , 10H View FIGURE 10 , 12Q, R View FIGURE 12 , 14V View FIGURE 14 , 19 View FIGURE 19
Felisacus longiceps Poppius, 1915b: 55 View in CoL (original description).
Felisacus okinawanus Miyamoto, 1965: 166 View in CoL ; new synonymy.
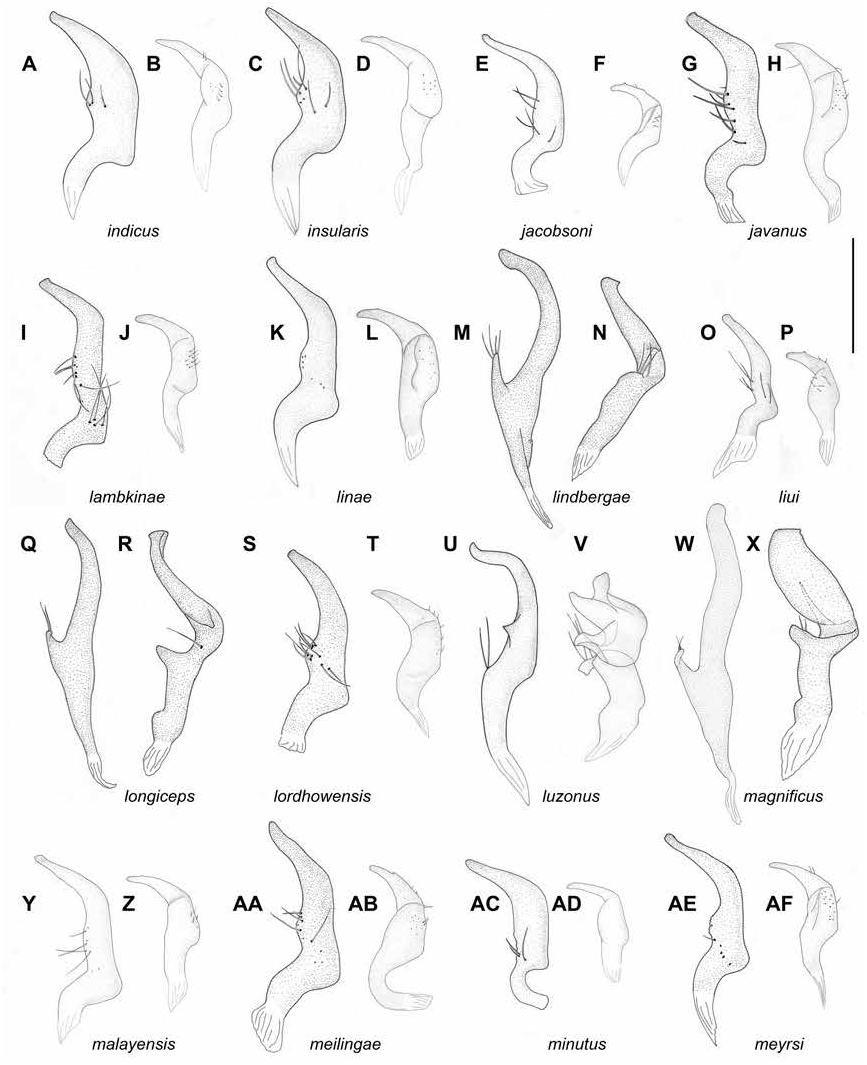
DIAGNOSIS: Recognized among congeners by the following combination of characters: presence of dark brown C-shaped marking on corium, with anterior part reaching R+M and not inclined posteriorly (fig. 5); antennal segment I widened (as in Namyatova and Cassis, in press: fig. 8B), red, reddish brown, or brown; antennal segment II often mostly yellow; vertex flat and not widened laterally; labium reaching posterior margin of mesosternum; dark band in apical part of fore- and middle femora usually absent; right paramere sickle shaped with outgrowth on inner angle slightly curved (fig. 12Q); apical part of left paramere narrow, with toothlike outgrowth apically and outgrowth on dorsal surface; medial part of left paramere with narrow outgrowth (fig. 12R); apical half of ductus seminis sclerotized, hooked; vesica without sclerite (fig. 10H).
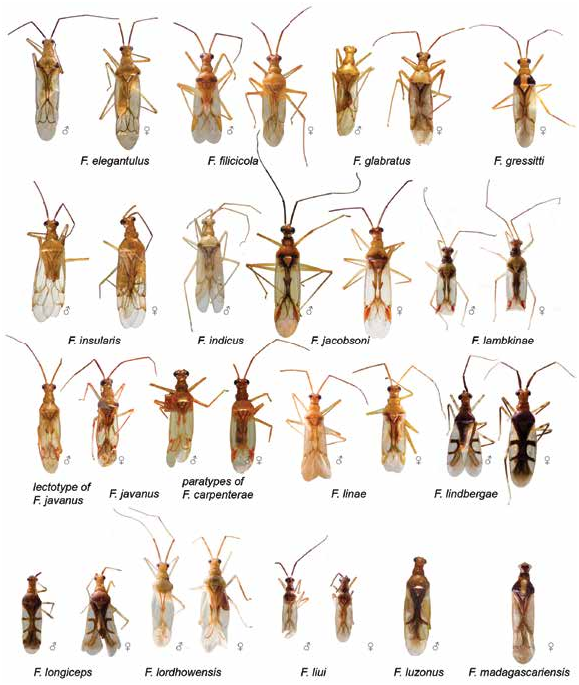
REDESCRIPTION: Male. Total length 3.0–3.4. COLORATION (fig. 5): Head: Mainly pale brown, sometimes with reddish markings; anterior side, clypeus, mandibular and maxillary plates, and tubercle around antennal fossa yellow, often buccula and apex of clypeus and rarely lateral side behind eye brown. Eye brown with reddish tinge. Labium: Segment I yellow to pale brown; segment II pale brown; segment III yellow to pale brown; segment IV yellow, rarely labium uniformly yellow to pale brown. Antenna: Segment I brown or reddish brown; segment II yellow to dark brown, segments III–IV pale brown. Thorax: Anterior part of pronotum yellow to pale brown, sometimes with brown anterior margin; posterior part of pronotum brown, rarely yellow or pale brown; scutellum and mesoscutum pale brown to brown; thoracic pleura pale brown to brown, rarely yellow, scent gland evaporative area whitish yellow. Hemelytron: Clavus opaque, uniformly brown to dark brown, rarely pale brown; corium, embolium, cuneus, and membrane mostly translucent, colorless; corium with pale brown anterior angles and C-shaped dark brown marking, reaching R+M anteriorly and posteriorly, its anterior part not inclined posteriorly; embolium pale brown basally and brown apically, with pale brown or yellow margins; cuneus yellow, red, or brown apically, with reddish brown or yellow outer margin and colorless inner margin; membrane gradually changing color from pale brown to brownish basally and grayish apically; membrane cell pale brown to brown. Legs: Coxae whitish yellow; femora whitish yellow basally and brown apically, often with reddish tinge apically, sometimes with brown marking at apical part, rarely fore- and middle femora whitish yellow to yellow, with reddish markings apically, sometimes with brown band on apical half of hind femur; basal part of tibiae yellow to brown, often with reddish tinge, apical part whitish yellow, rarely tibiae uniformly whitish yellow; tarsi uniformly whitish yellow. Abdomen: Whitish yellow to pale brown ventrally and laterally, reddish apically and brown dorsally. SURFACE AND VESTITURE: Corium smooth, with shallow and scarce punctation. Dorsum and femora clothed with setae subequal to or longer than antennal segment II diameter; antennal segment I clothed with suberect setae shorter than antennal segment II diameter; abdomen clothed with short erect setae. STRUCTURE AND MEA- SUREMENTS: Body ca. 3.9–4.2× as long as pronotum width. Head: Transverse depression delimiting occipital region present only dorsally; distance between depression and pronotum slightly longer than eye diameter; longitudinal sulcus on dorsal surface of head shorter than eye diameter; distance from eye to pronotum longer than eye diameter, not swollen; vertex ca. 1.9–2.5× as wide as eye, flat (Namyatova et al., 2016: fig. 6E). Labium: Reaching posterior margin of mesosternum or slightly surpassing it; segments I and II shorter than wide, combined subequal to half of segment III; dorsal surface of segment II not elongate (as in Namyatova et al., 2016: fig. 6E); segment III shorter than ventral side of head; segment IV ca. 1.5× as long as segment III. Antenna: Segment I slightly longer than head width, swollen basally (as in Namyatova et al., 2016: fig. 8B), ca. 1.0–1.3× as long as head width, ca. 0.6–0.7× as long as pronotum width; segment II ca. 1.6–1.7× as long as head width, ca. 0.8–1.0× as long as pronotum width; segment III slightly longer than segment II and twice as long as segment IV. Thorax: Anterior part of pronotum shorter than posterior part; collar delimited, posterior part slightly upraised; posterior angles not delimited with depression; posterior margin of pronotum concave; pronotum ca. 1.3× as wide as long and ca. 1.7–2.0× as wide as head; mesoscutum usually exposed, sometimes not exposed. Hemelytron: Area along inner margin of corium swollen; inner margin of cuneus straight (as in Namyatova et al., 2016: fig. 13F), outer margin of cuneus twice as long as base. Abdomen: Angle between genital capsule and rest of abdomen varying from very small to almost right. Genitalia: Genital capsule (fig. 14V) twice as long as wide; ventral wall ca. 1.5× as long as dorsal wall, with posterior margin of ventral wall not curved, with small toothlike outgrowth; right side of genital capsule folded, left side of genital capsule not widened; paramere sockets distinctly acute; distance between paramere sockets ca. 0.3× as long as genital capsule width at base. Right paramere (fig. 12Q) sickle shaped; apex slightly concave; medial part nar- rower than basal part, without setae, outer margin of medial part convex, inner margin concave, without swelling; outer angle absent; inner angle present with curved outgrowth bearing setae; basal part of paramere slightly shorter than rest of paramere. Left paramere (fig. 12R) apical part not flattened, with toothlike outgrowth apically and with outgrowth on dorsal surface; inner margin with narrow outgrowth, with setae near outgrowth. Aedeagus (general view as in Namyatova et al., 2016: fig. 22M) vesica without spicules; apical half of ductus seminis sclerotized, hooked apically, secondary gonopore placed near phallotheca mouth in repose (fig. 10H).
Female. Total length 3.5. COLORATION (fig. 5): Head: Similar to male, often with reddish markings on dorsal surface, frons, mandibular and maxillary plates, and clypeus; antennal segment II often yellow, rarely pale brown apically or uniformly pale brown. Thorax: Similar to male, but posterior part of pronotum sometimes pale brown with brown posterior margin. Abdomen: As in male. SURFACE AND VESTITURE: As in male. STRUCTURE AND MEASUREMENTS: Structure as in male; body ca. 3.8–4.0× as long as pronotum width; vertex ca. 1.8–2.2× as wide as eye; antennal segment I ca. 1.1–1.2× as long as head width, ca. 0.6× as long as pronotum width; segment II ca. 1.2–1.6× as long as head width, ca. 0.7–0.8× as long as pronotum width; pronotum ca. 1.2–1.4× as wide as long and ca. 1.8–2.0× as wide as head. Genitalia (as in figs. 16A, B): Dorsal labiate plate very small and transparent, as wide as distance with apodemes of second valvulae, without striations or membranous ridge medially; semicircular sclerite and sclerotized rings absent; lateral oviducts placed in anterior part; spermathecal gland attached near anterior margin; dorsal labiate plate without distinct tubercles, without membranous lobe posteriorly.
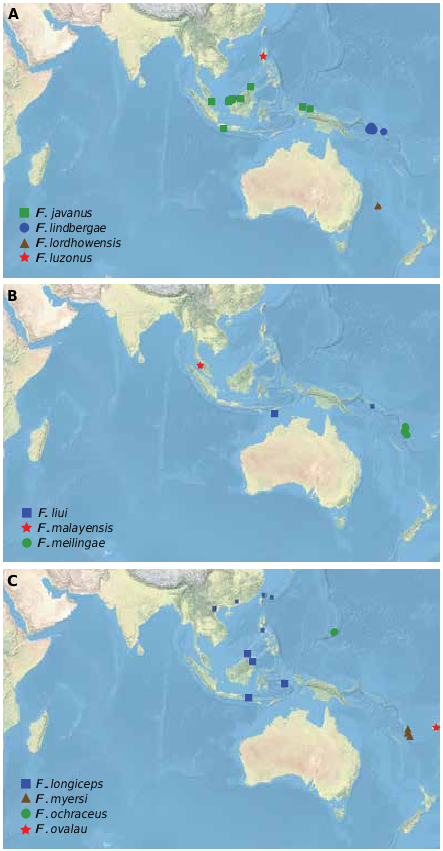
DISTRIBUTION: Borneo, Japan (Ryukyu Is.), Vietnam (fig. 19).
HOST PLANTS: Many specimens were collected from Nephrolepis biserrata (Davalliaceae) and Plesioneuron sp. (Thelypteridaceae) on Ambon and Sulawesi islands.
DISCUSSION: Felisacus capitatus , F. longiceps , F. magnificus , F. okinawanus , and F. pulchellus are very similar externally (see discussion for F. magnificus for details). The identification of the material belonging to this group of species was not straightforward, as the types of F. longiceps , F. magnificus , and F. pulchellus are either females or had lost genitalia, and we could not examine the types of F. capitatus and F. okinawanus from Kyushu University, where they are preserved according to the initial description ( Miyamoto, 1965).
We divided all the material examined for the above five taxa into three species, based on the structure of the male genitalia, particularly for that of the parameres. We identified one of them as Felisacus magnificus (see its discussion for details). The second species is paler, often having a pale brown pronotum; in this species if the posterior part of the pronotum is dark brown, then antennal segment I and the legs are almost uniformly yellow. This pattern of coloration is similar to F. longiceps . The parameres and coloration of this species are also similar to F. okinawanus (figs 12Q, R; Miyamoto, 1965: figs. 43–46). On the basis of these observations, we synonymized F. okinawanus with F. longiceps . The third species was unlike any other among the described taxa, and we describe it as a new species, F. zuparkoi .
Felisacus magnificus and F. zuparkoi differ from F. longiceps externally by the antennal segment II, and the posterior part of pronotum dark brown, whereas both species have dark bands on the fore- and middle femora. Felisacus magnificus also differs from F. longiceps by the straight right paramere (fig. 12W) and the broad left paramere (fig. 12X). F. zuparkoi differs in the broad outgrowth on the inner margin of the left paramere (fig. 13AE) and the presence of a vesical spicule (fig. 10P).
Felisacus longiceps is also similar to F. ceylonicus and F. lindbergae . Felisacus ceylonicus differs from F. longiceps by its vertex broad laterally behind the eye and the outgrowth on the medial part of the left paramere distinctly curved (fig. 11R). Felisacus lindbergae can be separated from F. longiceps by the labium almost reaching the posterior margin of the prosternum, the brown antennal segment II, the presence of dark bands on the fore- and middle femora and the straight outgrowth on the inner angle of the right paramere (fig. 12M).
MATERIAL EXAMINED: Holotype ( Felisacus longiceps ). TAIWAN: Chip-Chip, no date provided, unknown collector, 1♀ (00018972) ( HNHM). Additional material: CHINA: Guandong: Mt Dinghu [Dinghu Shan, Dinhushan], 23.1751 ° N 112.5533 ° E, 28 Nov 1959, Rodendorf, 13 (00271521) ( ZISP). INDONESIA: Maluku: Ambon Island nr Ambon City, 3.60706 ° S 128.28328 ° E, 23 Aug 2012, F. Konstantinov, Nephrolepis biserrata (Sw.) Schott (Davalliaceae) , det. Michael Lovave ( LAE herbarium, PNG), 53 (00271434–00271438), 2♀ (00271439, 00271440) ( ZISP). West Nusa Tenggara: Lombok Island, Senaru, Panorama track to Sendang Gila Waterfall, 8.30111 ° S 116.40833 ° E, 28 Aug 2012, F. Konstantinov, 133 (00271441–00271453), 1 sex unknown (00271351), 8♀ (00271454–00271461) ( ZISP); 30 Aug 2012, F. Konstantinov, Nephrolepis biserrata (Sw.) Schott (Davalliaceae) , det. Michael Lovave ( LAE herbarium, PNG), 93 (00271462–00271470), 2 sex unknown (00271471, 00271472), 9♀ (00271473–00271481) ( ZISP). Lombok Island, Senaru, track to Tiu Kelep Waterfall, 8.30111 ° S 116.40833 ° E, 31 Aug 2012, F. Konstantinov, Nephrolepis biserrata (Sw.) Schott (Davalliaceae) , 43 (00271482–00271484, 00271424) Plesioneuron sp. (Thelypteridaceae) , 13 (00386467) ( ZISP). Lombok Island, nr Senaru, 8.31689 ° S 116.40381 ° E, 29 Aug 2012, F. Konstantinov, 113 (00271485–00271495), 8♀ (00271496–00271499, 00271501–00271504), 1 sex unknown (00271350) ( ZISP). Lombok Island, nr Senaru, 8.31956 ° S 116.405 ° E, 31 Aug 2012, F. Konstantinov, Nephrolepis biserrata (Sw.) Schott (Davalliaceae) , 1♀ 00271500) Plesioneuron sp. (Thelypteridaceae) , det. Michael Lovave ( LAE herbarium, PNG), 53 (00386617–00386621), 3♀ (00271515–00271517) ( ZISP). JAPAN: Okinawa: Ishigaki Is., Ryukyu Islands, 24.4 ° N 124.2 ° E, 01 Nov 1952, G.E. Bohart, 23 (00043262, 00043263) ( BPBM); 10 Nov 1952 – 15 Nov 1952, G.E. Bohart, 13 (00043261) ( BPBM); 14 Oct 1999, Belokobylskij, 13 (00271505) ( ZISP). MALAYSIA: Sabah: Kalabakan, 4.4167 ° N 117.4833 ° E, 08 Nov 1958 – 15 Nov 1958, T.C. Maa, 13 00043186) ( BPBM). West Coast Residency [Coast Residency], Ranau, 6.08333 ° N 116.5 ° E, 500 m, 08 Oct 1958 – 11 Oct 1958, T.C. Maa, 23 (00043344, 00043345) ( BPBM). PHIL- IPPINES: Laguna: Los Banos, 14.17086 ° N 121.24334 ° E, no date provided, Baker [no date], 1♀ (00018446) ( MZH). TAIWAN: N Taiwan, Nei-Hu, Taipei, 25.09074 ° N 121.55972 ° E, 28 Aug 1963, Hsien, 1♀ (00005965) ( BPBM). VIET- NAM: Ha Noi: 70 km NWW Ha Noi BaVi, 21.087 ° N 105.302 ° E, 22 Nov 1990, Belokobylskij, 1♀ (00018444) ( ZISP). Hòa Bình: Hoa Binh: Near Mai Chau [Mai Chon, Mai Chou], 20.667 ° N 105.084 ° E, 31 Oct 1990, Belokobylskij, 3♀ (00018436, 00018442), 53 (00018437, 00018439, 00018440, 00271520) ( ZISP); 01 Nov 1990, Belokobylskij, 13 (00018438) ( ZISP); 02 Nov 1990, Belokobylskij, 1♀ (00018443) ( ZISP); 03 Nov 1990, Belokobylskij, 23 (00386603) ( ZISP); 04 Nov 1990, Belokobylskij, 23 (00018441) ( ZISP).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.