Felisacus indicus, Namyatova & Cassis, 2016
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.1206/0003-0090-403.1.1 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/296A879F-5646-750D-5EAC-FF3DFE470BDE |
|
treatment provided by |
Carolina |
|
scientific name |
Felisacus indicus |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Felisacus indicus , sp. nov.
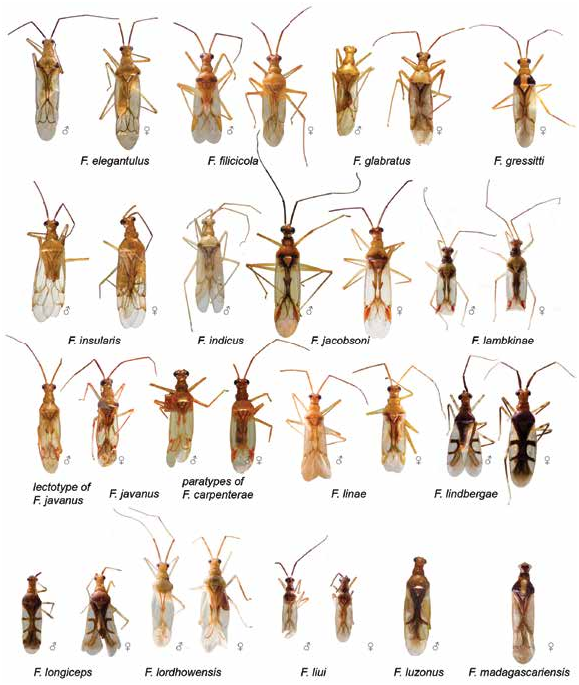
Figures 5 View FIGURE 5 , 8K View FIGURE 8 , 12A, B View FIGURE 12 , 14O View FIGURE 14 , 18 View FIGURE 18
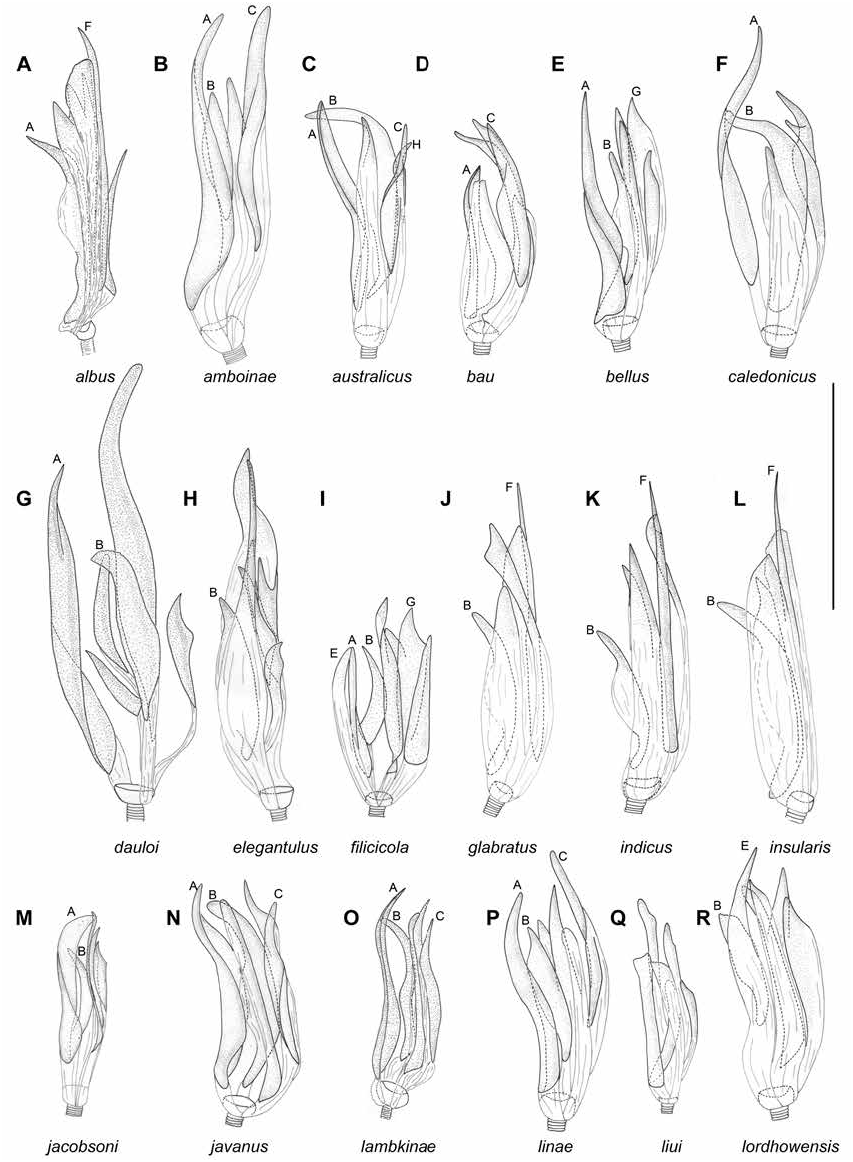
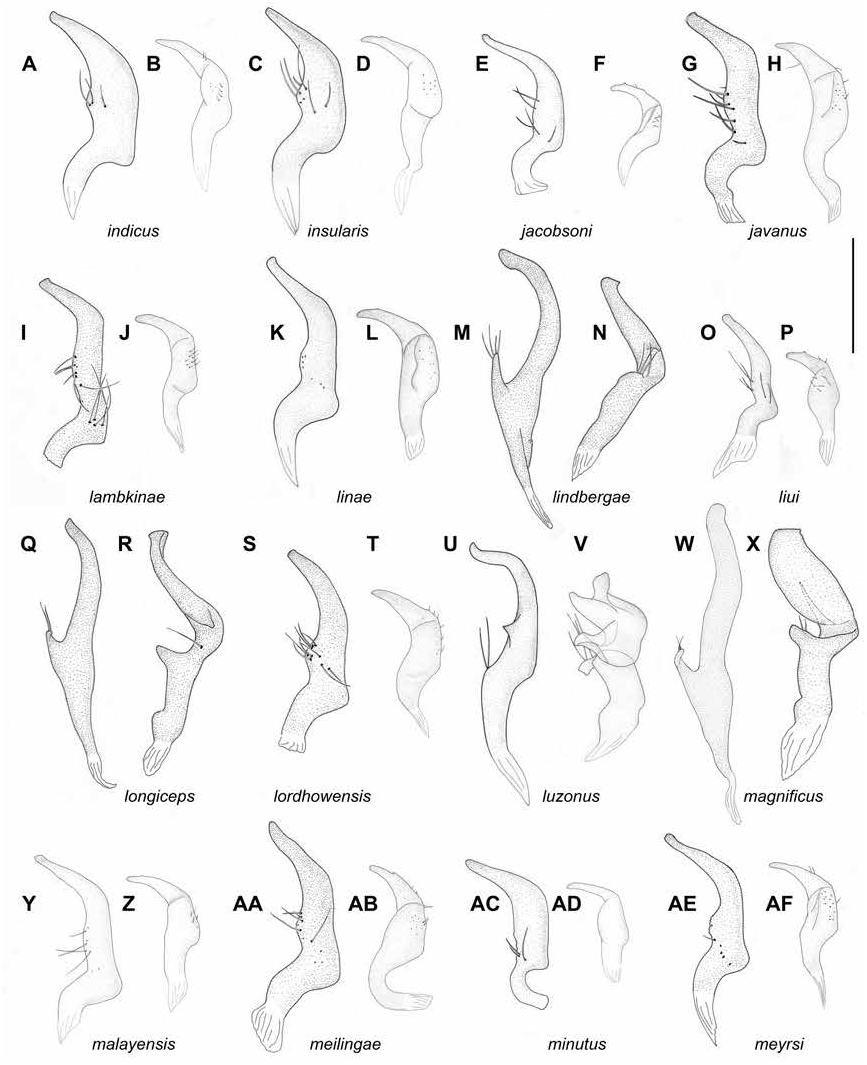
DIAGNOSIS: Recognized by the following set of characters: coloration of dorsum mostly whitish yellow, pronotum with brown humeral angles; cuneus opaque, whitish yellow with yellow apex and margins (fig. 5), cylindrical antennal segment I (as in Namyatova et al., 2016: fig. 8A), transverse depression on head delimiting occipital region extending laterally, vertex in males ca. 1.2× as wide as eye, upraised (as in Namyatova et al., 2016: fig. 6D); labium reaching middle of metasternum; cuneus ca. 2–2.5× as long as its width at base; genital capsule almost as long as wide (fig. 14O); medial part of right paramere twice as wide as basal part, and shorter than apical and basal parts combined; its outer margin straight and inner margin widened (fig. 12A); vesica with five spicules, including spicules B and F, without serrate spicules (fig. 8K).
DESCRIPTION: Male. Total length 4.0. COL- ORATION (fig. 5): Head: Mostly whitish yellow with reddish markings. Eye whitish yellow. Labium: Segments I–III whitish yellow, segment IV yellow. Antenna: Segments I–II whitish yellow with reddish tinge, segments III–IV pale brown. Thorax: Pronotum whitish yellow with brown anterior margin and posterior angles; punctures between anterior and posterior parts pale brown; mesoscutum and scutellum whitish yellow with pale brown punctures between them; thoracic pleura whitish yellow; scent gland evaporative area whitish basally and pale brown apically. Hemelytron: Inner part of clavus opaque, whitish yellow, with brown margins; outer part of clavus whitish and translucent; corium translucent, area along inner margin of corium pale brown anteriorly and whitish yellow posteriorly; embolium opaque, whitish yellow, with apex and margins pale brown; cuneus opaque, whitish yellow, with yellow apex and margins; membrane translucent, colorless; membrane cell mostly whitish yellow, pale brown anteriorly. Legs: Coxae whitish; femora and tibiae mostly whitish yellow, hind femur red apically; hind tibia whitish with reddish tinge; tarsi whitish, pale brown dorsally. Abdomen: Uniformly whitish yellow. SURFACE AND VESTITURE: Corium smooth, often with scarce shallow punctures. Dorsum with suberect setae most often slightly longer than diameter of antennal segment II; antennal segment I and femora with suberect setae shorter than diameter of antennal segment II; abdomen clothed with suberect short simple setae. STRUCTURE AND MEASUREMENTS: Body ca. 4.3× as long as pronotum width. Head: Depression delimiting occipital region present dorsally and laterally (as in Namyatova et al., 2016: fig. 4E); distance between depression and pronotum distinctly shorter than eye diameter; longitudinal sulcus on dorsal surface longer than eye diameter; distance from eye to pronotum slightly longer than eye diameter, not swollen laterally (as in Namyatova et al., 2016: fig. 4E); vertex ca. 1.2× as wide as eye; vertex upraised; buccula ca. 0.2–0.25× as long as clypeus. Labium: Reaching middle of metasternum; segments I and II strongly reduced, combined length shorter than segment III; segment I slightly shorter than wide (as in Namyatova et al., 2016: figs. 6D, 9C), segment II slightly longer than wide, elongate dorsally, segment IV ca. 1.5× as long as segment III. Antenna: Segment I cylindrical (as in Namyatova et al., 2016: fig. 8A), ca. 1.3× as long as head width, ca. 0.9× as long as pronotum width; segment II ca. 1.7× as long as head width, ca. 1.1× as long as pronotum width. Thorax: Anterior part of pronotum only slightly shorter than posterior part; collar delimited; posterior part upraised; posterior margin concave; pronotum ca. 1.2× as wide as long and ca. 1.5× as wide as head; mesoscutum exposed. Hemelytron: Area along inner margin on corium almost flat; inner margin of cuneus convex, costal margin ca. 2–2.5× as long as base. Abdomen: Genital capsule weakly rotated to left-hand side. Genitalia: Genital capsule (fig. 14O) almost as long as wide; ventral wall twice as long as dorsal wall, its posterior margin smooth, semioval, without outgrowth, not curved; left side of genital cap- sule not widened; right paramere socket slightly acute and left paramere socket rounded; distance between paramere sockets subequal to half of genital capsule with at base. Right paramere (fig. 12A) distinctly curved in apical half; apex almost straight posteriorly; medial part twice as wide as basal part, bearing setae, with outer margin straight and inner margin convex; outer angle distinct; inner angle rounded, without setae; basal part of right paramere ca. 0.15– 0.2× as long as rest of paramere; apical part of right paramere lost. Left paramere (fig. 12B) L-shaped; apical part not flattened, with toothlike outgrowth on posterior side medially (as in fig. 11G) and without outgrowth on dorsal surface; middle part widened, without swelling or outgrowth; setae only on middle part near outer margin. Aedeagus conjunctiva weakly sclerotized; secondary gonopore placed at base of vesica in repose; sclerotization of ductus seminis around secondary gonopore of shorter than wide; vesica with five spicules including spicules B and F (fig. 8K).
Female. Unknown.
DISTRIBUTION: India (fig. 18).
HOST PLANTS: Unknown.
DISCUSSION: Felisacus indicus is similar to F. albus in external morphology (figs. 4, 5), and the structure of the genital capsule (fig. 14A, O) and parameres (cf. fig. 11A, B with fig. 12A, B). Felisacus albus differs from F. indicus by the humeral angles of the pronotum whitish yellow, the cuneus is whitish yellow to yellow with a reddish tinge and the presence of seven vesical spicules (fig. 8A). Felisacus indicus is also similar to F. insularis in color patterning (fig. 5), the shape of the right paramere (cf. fig. 21A with 12C) and the presence of spicules B and F (cf. fig. 8K with 8L). The latter species differs by the head and the humeral angles yellow, the ventral wall of the genital capsule ca. 1.7× as long as the dorsal wall (fig. 14P), and the vesica has a serrate spicule (fig. 8L).
MATERIAL EXAMINED: Holotype: INDIA: Kerala: Kerala Prov , 10 ° N 76.5 ° E, 1991, P.K. Sumodan, 13 (00017872) ( NML). GoogleMaps
| NML |
National Microbiology Laboratory, Public Health Agency of Canada |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.