Gomphostemma thomsonii 3enth. ex Hook.f
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.1007/s12225-021-09991-y |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7618332 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/2733879D-FFB3-1C34-0C7E-90D61C75FC2C |
|
treatment provided by |
Valdenar |
|
scientific name |
Gomphostemma thomsonii 3enth. ex Hook.f |
| status |
|
7. Gomphostemma thomsonii 3enth. ex Hook.f View in CoL .
( Hooker 1883: 698); Prain (1891: 231); Mukercee (1920: 209). Type: India, Khasia Mts, Churra, 900 – 1300 m [3000 – 3000 ft], 11 Aug. 1830, Hooker & Thomson 2063 (lectotype K [K000826322], selected here; isolectotype K [K000826323]).
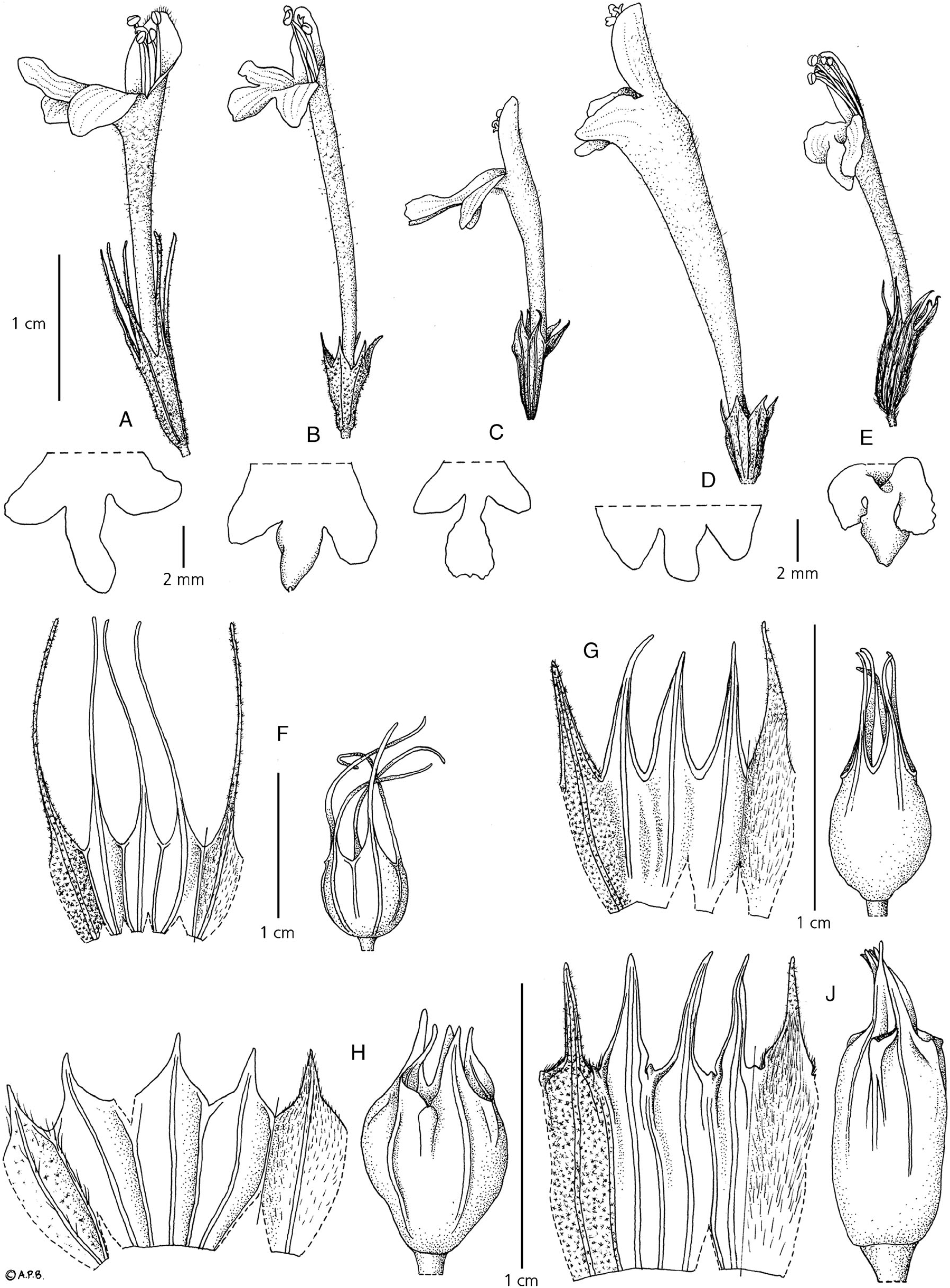
Herb up to 1 m tall. Stems erect, woody at base, obtusely quadrangular with longitudinal grooves, tomentose with dense stellate hairs; internodes straight. Leaoes petiolate, chartaceous; blades elliptic-ovate, 15 – 26 × 9 – 13 cm, apex acute, margin serrate, base cuneate, upper side dull green with 2 – 3-celled simple hairs, bifurcate hairs or stellate hairs, lower side pale green tomentose with dense stellate hairs confined on midrib and veins; petioles 30 – 120 mm long, with dense stellate hairs. Inflorescence axillary with opposite cymes sessile, unbranched, congested with axis not visible between flowers, exceeding 20 mm wide when pressed, excluding corolla, inserted at the upper nodes at which leaves are usually present; verticils few – manyflowered; bracts deciduous, ovate or ovate-lanceolate, 3 – 12 × 2 – 8 mm, broader than the calyx; bracteoles linear, 6 – 10 mm long. Flowering calyx tubular-infundibular, 8 – 10 mm long, 10-ridged, outside with dense branched hairs, inside tomentose with simple hairs; tube 2 – 6 mm long; lobes narrow triangular, c. 2 mm long, apex acuminate. Fruiting calyx infundibular, 10 – 12 mm long; tube 5 – 8 mm long; lobes 3 – 2 mm long, apex subulate. Corolla pale yellow, 13 – 20 mm long, throat narrow, not enlarged, sometimes gradually dilated towards the throat, outside tomentose with simple hairs, inside glabrous; tube straight, 12 – 13 mm, exserted from the calyx; posterior lip ovate, 2 – 6 mm long, apex and margin entire; anterior lip 3-lipped, subequal, slightly longer than posterior lip. Staminal filaments slightly fleshy. Style slender. Nutlets solitary, oblong, 3 – 6 mm long, slightly wrinkled. Fig. 6E, J View Fig .
DISTRIBUTION. India (Meghalaya). Map 2 View Map 2 .
SPECIMENS EXAMINED. INDIA. Meghalaya: Khasia, Churra, 900 – 1300 m [3000 – 3000 ft], 11 Aug. 1830, Hooker & Thomson 2063 (lectotype K; isolectotype K); ibid., 1200 m [2000 ft], 13 June 1833, Hooker & Thomson s.n. (K); Khasia, 900 – 1300 m [3000 – 3000 ft], Hooker & Thomson s.n. (BM, C, G, L, P, TC?).
HABITAT. In evergreen forest; alt. 900 – 1300 m.
CONSERVATION STATUS. Gomphostemma thomsonii is known from four collections, three localities with AOO of 16 km 2 with 2 km width grid size. The habitat in Sumatra is threatened by oil palm plantations ( Fitzherbert et al. 2008). Hence, the taxon is given the status of Endangered (EN B2ab(ii)).
NOTES. Gomphostemma thomsonii is distinguished by having broad leaves, 90 – 130 mm wide and long petioles, 30 – 120 mm long. It is morphologically similar to G. paroiflorum by having congested cymes and calyx lobes not longer than the tube at maturity but G. paroiflorum has narrower leaves, 20 – 90 mm wide.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |