Homalopteroides Fowler 1905
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.3926.1.2 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:20666BE9-1457-41A6-9727-AC0077203595 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5622838 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/2573D038-A900-971D-FF4E-F9BBA4910F08 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Homalopteroides Fowler 1905 |
| status |
|
Homalopteroides Fowler 1905 View in CoL View at ENA
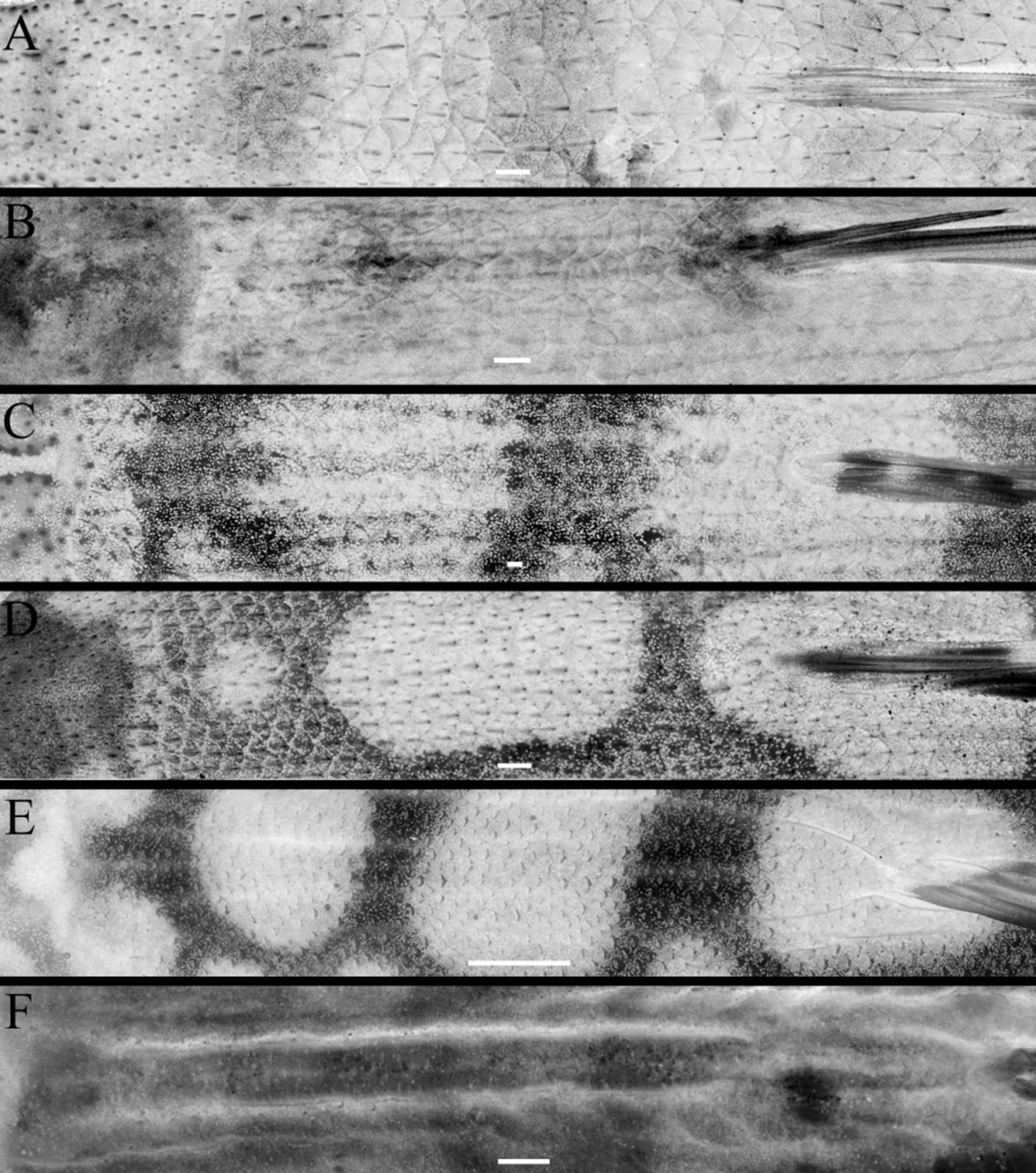
( Figures 3 View FIGURE 3 B, 4C, 5B, 7)
Homalopteroides Fowler, 1905:476 View in CoL . (Type species: Homaloptera wassinkii Bleeker 1853 View in CoL , by original designation; see Randall & Page, 2012:335 fixed type species as H. wassinkii View in CoL , under Code art. 70.3.1). Gender masculine. Chopraia Prashad & Mukerji, 1929:188 (Type species: Chopraia rupicola Prashad & Mukerji, 1929 , by original designation). Gender feminine.
Remarks. Homalopteroides rupicola was originally designated as the type species of Chopraia ( Prashad & Mukerji 1929) . Chopraia was distinguished from other balitorines by “shape of the head, the situation and better development of the eyes, the branchial openings and the fins ( Prashad & Mukerji 1929).” Since these characters are shared with species of Homalopteroides , we treat Chopraia as a junior synonym of Homalopteroides ( Randall & Page 2012) .
Diagnosis. Distinguishing characters are given in Table 4 View TABLE 4 and shown in Figures 3 View FIGURE 3 B, 4C, 5B and 7. Homalopteroides is distinguished by the following combination of characters: without reddish tints on fins ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 B) in life, dorsal-fin origin posterior to pelvic-fin origin; forked caudal fin; 6–8½, 7½ (M) branched dorsal-fin rays; wart-like/keeled scales ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 C), 14–25 predorsal scales; 33–52 total lateral-line scales; anus closer to analfin origin than to pelvic-fin insertion; no adipose keel on caudal peduncle; small rostral cap; 2 thin rostral barbels, widely separated from one another; thin crescentic upper lip; no fleshy pad or lobes between lateral portions of lower lip ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 B); and presence of a central furrow at isthmus.
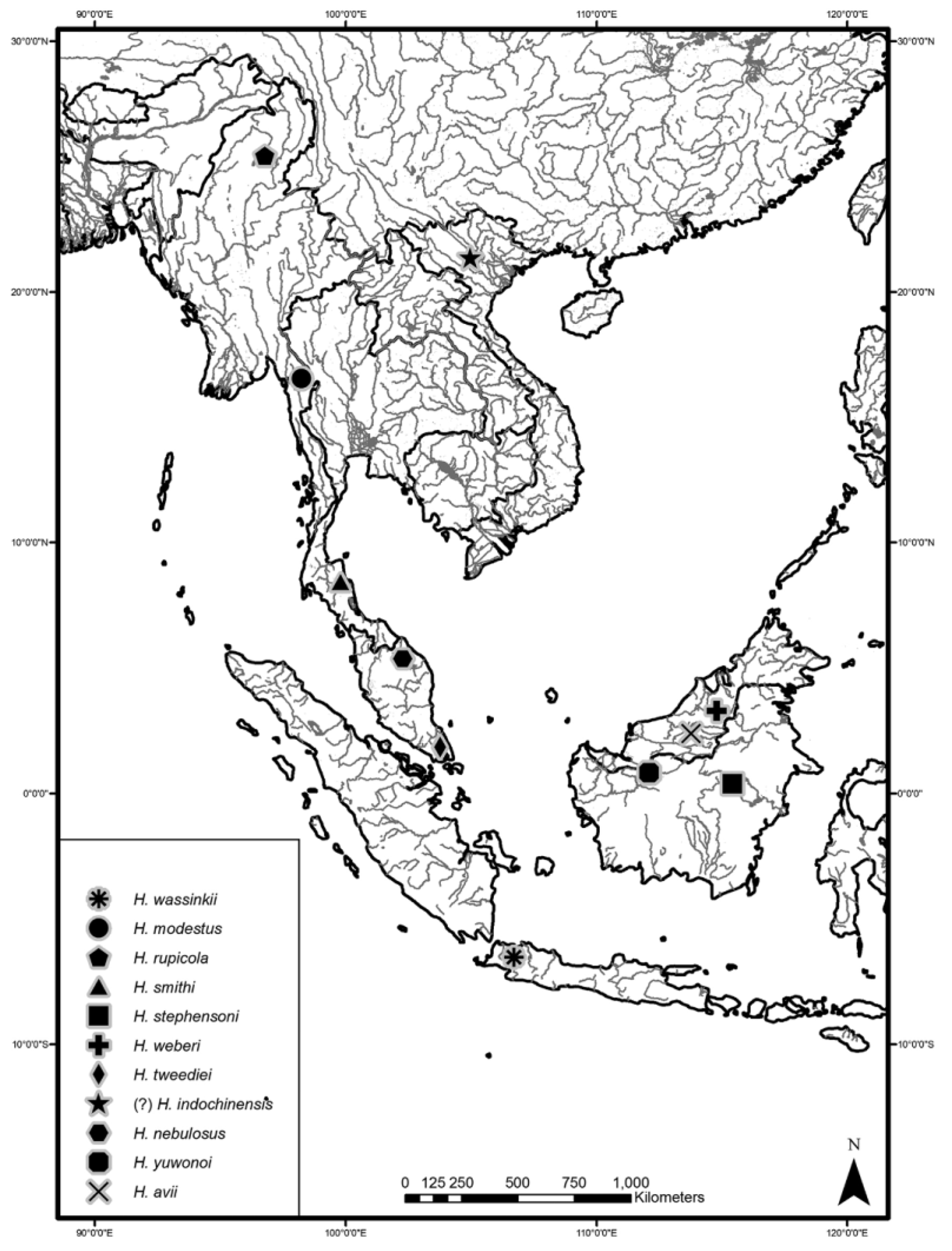
Species included. Homalopteroides wassinkii (Bleeker 1853) , H. modestus (Vinciguerra 1890) , H. rupicola ( Prashad & Mukerji 1929) , H. smithi ( Hora 1932) , H. stephensoni ( Hora 1932) , H. weberi ( Hora 1932) , H. tweediei (Herre 1940) , H. indochinensis ( Silas 1953) , H. nebulosus ( Alfred 1969) , H. yuwonoi ( Kottelat 1998) , and H. avii Randall & Page 2014 . The type localities for species of Homalopteroides are shown in Figure 8 View FIGURE 8 .
Comparison. Homalopteroides is distinguished from Homaloptera by absence vs. presence of reddish tints on fins in life; dorsal-fin origin posterior vs. anterior to pelvic-fin origin; 6–8½, 7½ (M) vs. 7–8½, 8½ (M) branched dorsal-fin rays; 33–52 vs. 59–73 total lateral-line scales; small vs. large rostral cap; medial- and lateral-rostral barbels widely separated from one another at base vs. barbels in close proximity to one another; crescentic rather than triangular upper lip; thin vs. thick upper lip; presence vs. absence of a central furrow at the isthmus; absence vs. presence of fleshy pad between lateral portions of lower lip.
Homalopteroides is distinguished from Homalopterula by having forked vs. truncated or emarginated caudal fin; wart-like/keeled vs. smooth scales; 14–25 vs. 28–56 predorsal scales; 33–52 vs. 57–75 total lateral-line scales; absence vs. presence of adipose keel on caudal peduncle; thin vs. thick upper lip; absence vs. presence of fleshy lobes between lateral portions of lower lip.
Homalopteroides is distinguished from Balitoropsis and Pseudohomaloptera by having dorsal-fin origin posterior vs. anterior to or above the pelvic-fin origin; 6–8½, 7½ (M) vs. 7–9½, 8½ (M) branched dorsal-fin rays; small vs. large rostral cap; medial- and lateral-rostral barbels widely separated from one another at base vs. barbels in close proximity to one another; thin vs. thick upper lip; absence vs. presence of pad between lateral portions of lower lip. It is further distinguished from Balitoropsis by having the anus closer to anal-fin origin than to pelvic-fin insertion.
Material examined. Homalopteroides wassinkii : Java: RMNH 4987 (lectotype of Homaloptera wassinkii ), 1934 (paralectotypes of Homaloptera wassinkii ) (2), 4627 (2); BMNH 1866.5.2.52 (1); ZMA 103.206 (2); UMMZ 155660 (1); MNHN 3122 (syntype of Balitora ocellata ). Sumatra: UF 161619 (7). H. modestus : Thailand: ANSP 179826 (5); NIFI 4517 (1), 3786 (1), 4514 (1); ROM 51147 (2); UF 172926 (1), 173067 (1), 176377 (10), 176408 (2), 176438 (8), 176454 (4), 176544 (1), 176557 (8), 181080 (5), 181160 (9), 181141 (1); ZRC 53385 (1), 53386 (1), 41272 (4). Myanmar: ZRC 22889 (1); BMNH 1893.2.16.50 (paralectotype of Helgia modesta ); ZMA 100.982 (paralectotype of Helgia modesta ). H. rupicola : Myanmar: CAS-SU 28726 (paratype of Chopraia rupicola ); CAS 231681 (2), 231726 (3), 231835 (1), 61338 (1); USNM 378433 (3); ZRC 43569 (2). H. smithi : Thailand USNM 109821 (syntypes of Homaloptera smithi ) (5); ANSP 76852 (1), 76851 (3); BMNH 1934.12.18.34 (1); UF 183330 (3), 183411 (2), 183915 (1). H. stephensoni: Borneo : RMNH 7633 (holotype of Homaloptera stephensoni ); USNM 393671 (3). H. weberi : East Malaysia: BMNH 1895.7.2.81 (syntypes of Homaloptera weberi ) (7); ZMA 100990 (syntype of Homaloptera weberi ). H. tweediei : Malaysia: BMNH 1938.12.1.132 (paratype of Homaloptera tweediei ); CAS-SU 33012 (holotype of Homaloptera tweediei ), 33013 (paratype of Homaloptera tweediei ) (2). H. indochinensis : Vietnam?: BMNH 1933.8.19.50 (holotype). H. nebulosus : Malaysia: BMNH 1967.11.15.15 (paratype of Homaloptera nebulosa ); CAS-SU 66428 (paratype of Homaloptera nebulosa ); ZRC 1759 (paratype of Homaloptera nebulosa ); ZRC 2020 (holotype of Homaloptera nebulosa ); UF 235748 (6). H. yuwonoi : East Malaysia: MZB 5938 (holotype of Homaloptera yuwonoi ). H. avii : East Malaysia: USNM 323875 (holotype of Homalopteroides avii ), 323878 (paratype of Homalopteroides avii ), USNM 323879 (paratypes of Homalopteroides avii ) (2); UF 185293 (paratype of Homalopteroides avii ).
| RMNH |
National Museum of Natural History, Naturalis |
| ZMA |
Universiteit van Amsterdam, Zoologisch Museum |
| UMMZ |
University of Michigan, Museum of Zoology |
| MNHN |
Museum National d'Histoire Naturelle |
| ANSP |
Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia |
| NIFI |
National Inland Fisheries Institute |
| ROM |
Royal Ontario Museum |
| ZRC |
Zoological Reference Collection, National University of Singapore |
| CAS-SU |
California Academy of Sciences, Stanford University Collection |
| CAS |
California Academy of Sciences |
| USNM |
Smithsonian Institution, National Museum of Natural History |
| MZB |
Museum Zoologicum Bogoriense |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
Homalopteroides Fowler 1905
| Randall, Zachary S. & Page, Lawrence M. 2015 |
Chopraia
| Prashad & Mukerji 1929: 188 |
Chopraia rupicola
| Prashad & Mukerji 1929 |
Homalopteroides
| Fowler 1905: 476 |
Homaloptera wassinkii
| Bleeker 1853 |