Macrostomum chongqingensis Lin and Wang, 2017
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4329.3.5 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:07F0Ad45-3F19-4068-9F58-0416360E5528 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6030229 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/2355465F-036D-CA7D-FF31-52D099DDFF10 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Macrostomum chongqingensis Lin and Wang |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Macrostomum chongqingensis Lin and Wang View in CoL , n. sp.
( Figs 1–3 View FIGURE 1 View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 )
Material examined. Ten specimens (one holotype and nine paratypes), all collected by Mr. H . Zhang in February 2015 under stones in shallow water of Jialing River ( 29°33′41″N, 106°29′54″E) in Chongqing, Peoples Republic of China. Holotype, PLA-Ma0060, serial horizontal sections, 33 slides, 6 µm, H.E. Paratypes: PLA-Ma0061–63, three specimens, serial longitudinal sections, 56–65 slides, 6 µm, H.E.; PLA-Ma0064–65, two specimens, whole mount, H.E.; PLA-Ma0066–69, four unsectioned whole specimens preserved in 10% formaldehyde. Additional three specimens (YL-2016 CQ1–3) were used for DNA extraction and sequencing for 18S rDNA, 28S rDNA, and COI genes ( Table 2). GoogleMaps
Etymology. The new specific name is an adjective, after the location of the discovery, Chongqing municipality.
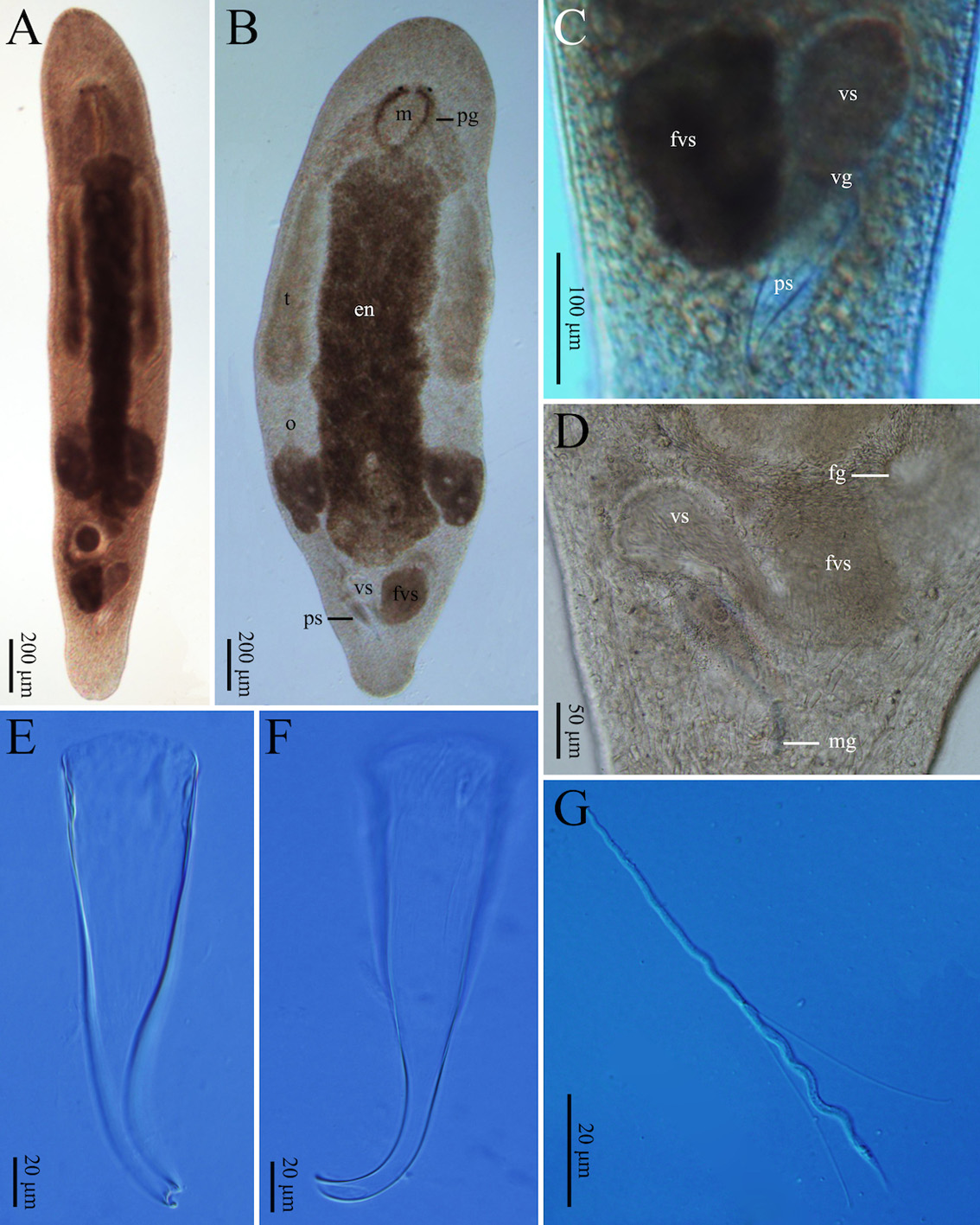
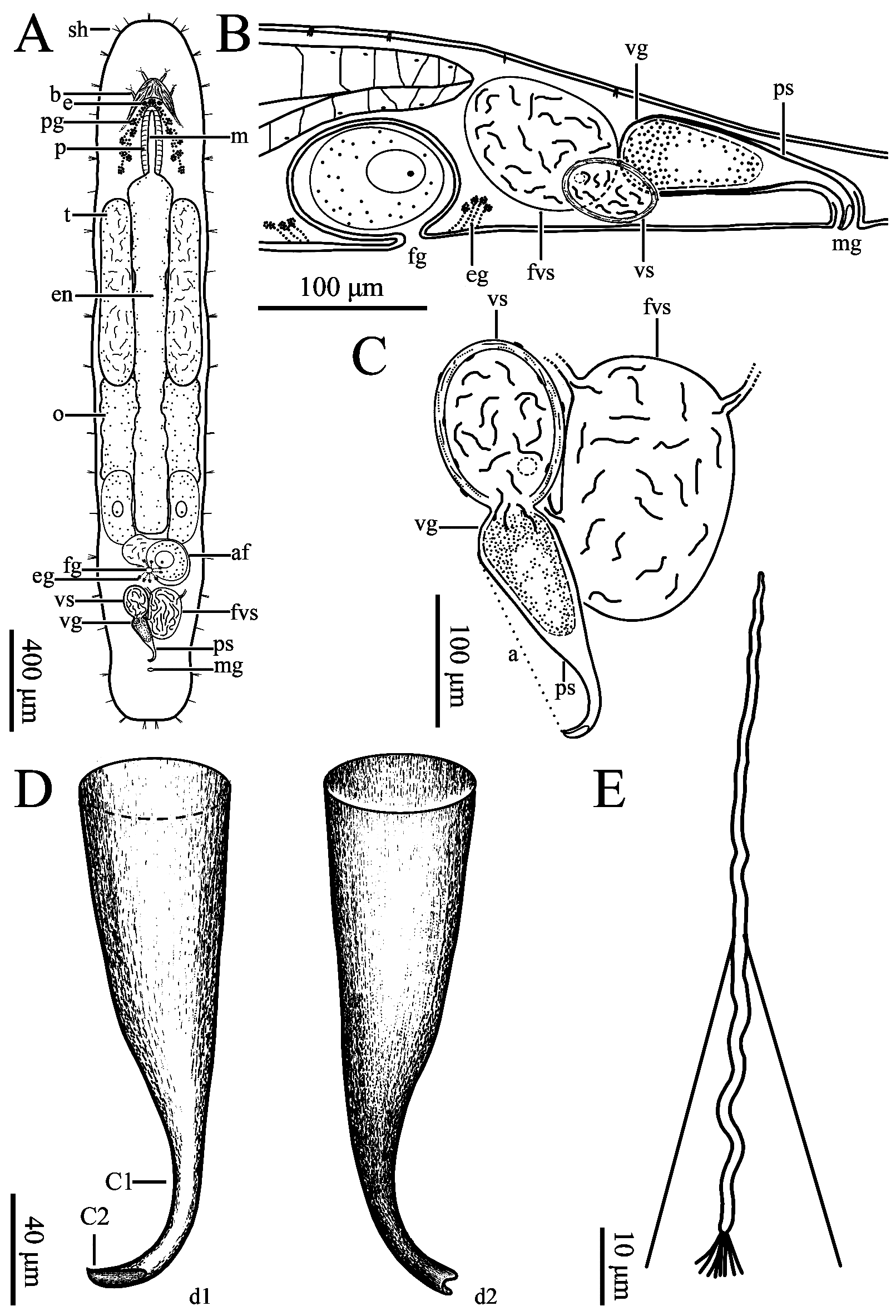
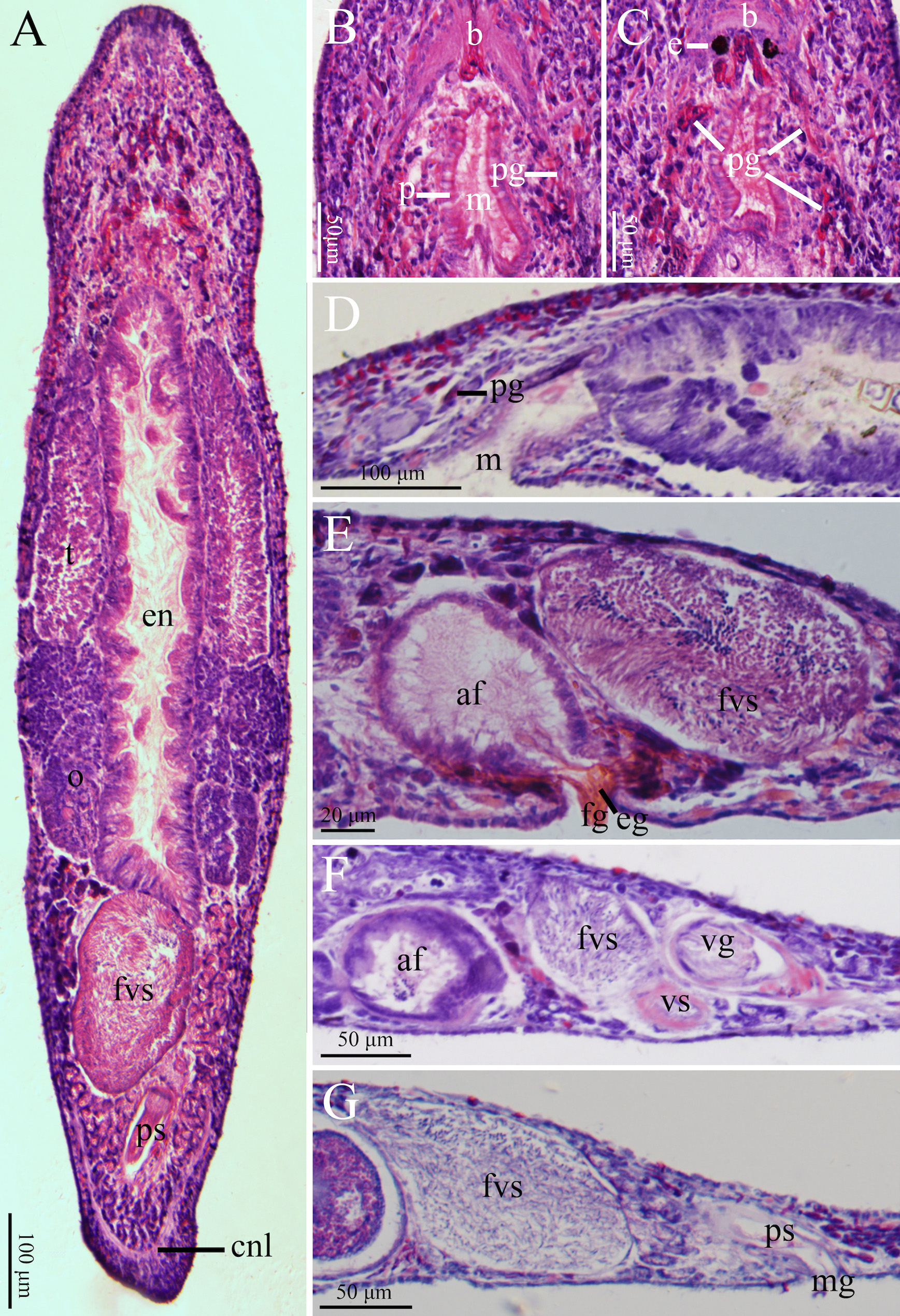
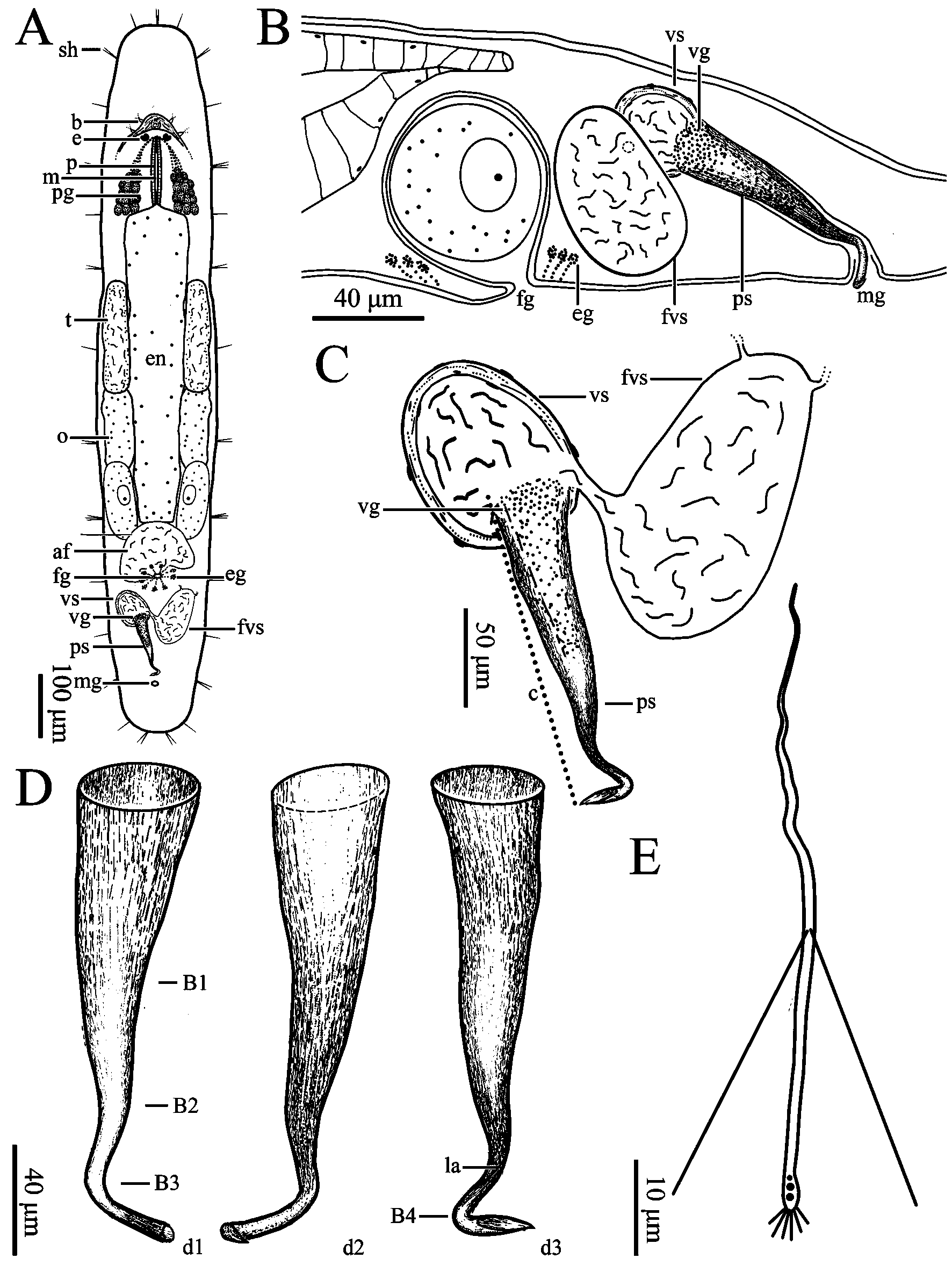
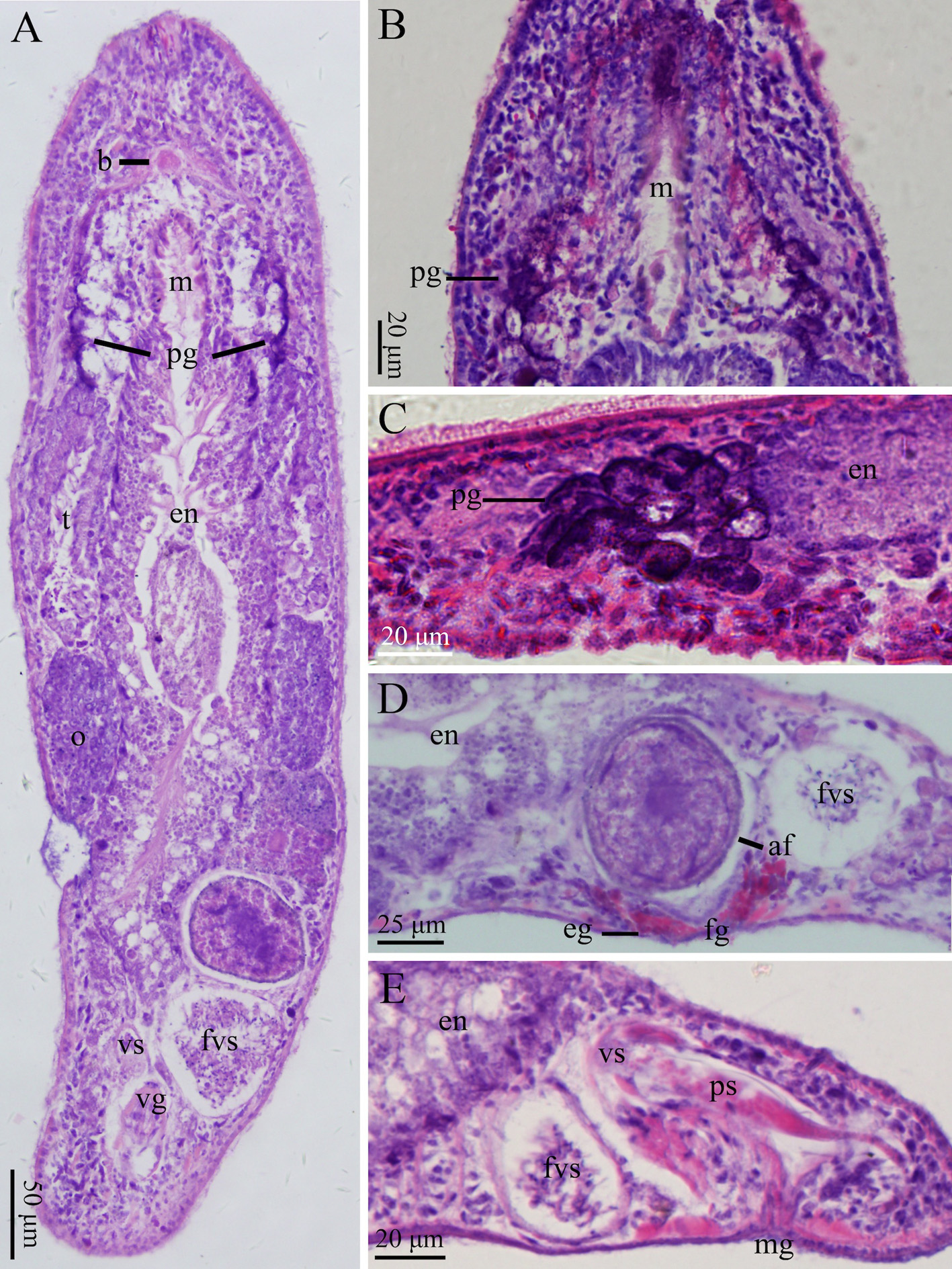
Description. Body flat in shape and milky white in colour. Mature worms slender while moving. Adult body size reaching about 2,300 µm in length and 500 µm in width (n=3, Figs. 1A View FIGURE 1 , 2A View FIGURE 2 ). Rostrum and cauda of body arcshaped. Body surface covered with cilia (3–7 µm long, n=9). Sensory hairs (14–18 µm long, n=5) 1–3 per cluster, primarily distributed on rostrum and cauda ( Fig. 2A View FIGURE 2 ). Body wall 17.0 ± 0.8 µm in thickness (n=3, Fig. 3A View FIGURE 3 ); epidermis covered with rhabdites (1–6 rods per cluster, each 6–16 µm in length, n=5). Pair of pigmented reniform eyes (15–17 µm in diameter, n=6) present at front end of body, with distance being about 48–59 µm, located at about 350 µm from tip of rostrum (n=3, Figs. 1B View FIGURE 1 , 2A View FIGURE 2 , 3C View FIGURE 3 ). Cerebral ganglion (brain) arrow-shaped, located in front of eyes and ventral of head, 72–77 µm in maximum width and 48–52 µm in length (n=3, Figs. 2A View FIGURE 2 , 3B View FIGURE 3 ). Two nerve cords extending from cerebral ganglion running along both sides of ventral body before merged at tail end ( Fig. 3A View FIGURE 3 ). Pharynx oblong, located posterior to eyes, with mouth aperture (also oblong) being 330 µm in length (n=3, Figs. 1B View FIGURE 1 , 2A View FIGURE 2 , 3B, C View FIGURE 3 ). Pharyngeal glands located on both sides of pharynx, arranged in reverse “V” shape from dorsal view, interconnected with pharynx at front end of mouth ( Figs. 2A View FIGURE 2 , 3C View FIGURE 3 ). Gut 1,300–1,367 µm long and 150– 217 µm wide (n=3, Figs. 1B View FIGURE 1 , 2A View FIGURE 2 ). Some well-developed adhesion glands present on surface of tail plate.
Female reproductive system consisting of ovaries, ovarian ducts, female antrum, and female gonopore. Pair of elongated ovaries (each with dimension of about 650 × 130 µm, n=6) located alongside rear half of gut; anterior half of ovary containing oocytes ( Figs. 1B View FIGURE 1 , 3A View FIGURE 3 ). Female antrum situated posterior to gut on ventral side, containing eggs and high density of received sperms. Egg diameter reaching 100 µm before excreted from body via female gonopore. Radiate glands located outside female antrum ( Figs. 2A View FIGURE 2 , 3E View FIGURE 3 ).
Gene Primer Direction Reference Sequence (5'-3') PCR protocal
18S rRNA CY 18sF F / GCGAATGGCTCATT 5m 94°C; 10x (30s 94°C, 30s 61°C
AAATCAG (decreased 0.5°C per cycle), CY 18sR R CTTGTTACGACTTT 2m 72°C); 7m 72°C; 25x (30s 94°C, 30s TACTTCC 56°C, 2m 72°C);
28S rRNA ZX-1 F Schärer et al. 2011 ACCCGCTGAATTTA 5m 95°C; 40x (30s 95°C, 30s 55°C, 2m
AGCATAT 72°C); 7m 72°C
1200R R GCATAGTTCACCAT
CTTTCGG
COI Mac_COIF F Modified from GTTCTACAAATCAT 1m 94°C; 5x (30s 94°C, 90s 45°C, 60s
Folmer et al. 1994 AAGGATATTGG 72°C);
Mac_COIR R TAAACYTCWGGGT 35x (30s 94°C, 90s 51°C, 60s 72°C); 5m GACCAAAAAACCA 72°C
Male reproductive system consisting of testis, vas deferens, false vesicula seminalis, vesicula seminalis, vesicula granulorum, penis stylet, and male gonopore. Pair of short, rod-shaped testes (about 750 × 130 µm, n=6) located alongside anterior half of digestive tract in front of ovaries ( Figs. 1B View FIGURE 1 , 2A View FIGURE 2 , 3B View FIGURE 3 ). Vas deferens running from rear of testis, between digestive tract and ovaries, before entering false vesicula seminalis (200 × 110 µm, n=3); latter being oval in shape, located behind female antrum, and connected to vesicula seminalis to left in “V” shape from ventral view. Vesicula seminalis oval-shaped (about 130 × 80 µm, n=3), having obvious muscular wall, posteriorly connected to vesicula granulorum. Part of vesicula granulorum entering base of penis stylet ( Figs. 1C View FIGURE 1 , 2B, C View FIGURE 2 , 3F View FIGURE 3 ). Penis stylet J-shaped, 180–190 µm (n=3) in length, with two bends (C1 and C2, see Fig. 2D View FIGURE 2 ); C1 located at 3/4 of penis stylet with ~100° bend; C2 right next to C1 with ~120° bend. Diameter of stylet’s base opening 54–57 µm (n=3). Anterior 2/3 of penis stylet funnel-shaped. Diameter of tube becoming rapidly slender at half of penis stylet, being 14–15 µm (n=3) at posterior 1/3 of stylet and distal part. End opening vertical to C2, bending towards male gonopore ( Figs. 1E, F View FIGURE 1 , 2C, D View FIGURE 2 ).
Mature sperm cells 90–93 µm in total length. Length of feeler, body, and shaft being 23–25 µm, 24–25 µm, and 33–34 µm, respectively. Pair of bristles present between body and shaft, 42.53–53.55 µm in length; brushes present at tail of sperm cells, 4.9–5.9 µm in length (n=2, Figs. 1G View FIGURE 1 , 2E View FIGURE 2 ).
Remarks. Macrostomum chongqingensis has i) the eyes lying near the brain, ii) the adhesive plate situated at the hind end of the body, iii) the ovaries that are paired, iv) and the female gonopores that is situated in front of the male gonopores. These features clearly show that this new species belongs to Macrostomum .
The morphology of the penis stylet is an important marker to distinguish between different species in Macrostomum . Comparing with M. chongqingensis , the following six congeners are similar to each other by having the J-shaped penis stylets; these are: M. amurense ( Beklemischev, 1950) , M. contortum ( Beklemischev, 1951) , M. japonicum ( Okugawa, 1930) , M. saifunicum ( Nasonov, 1929) , M. inductum ( Kolasa, 1971) , and M. sinensis ( Wang, 2005) . The comparison in details of those species with M. chongqingensis is listed in Table 1. The penis stylets in M. amurense , M. japonicum , M. saifunicum , and M. sinensis are curved on a single plane while it is not in M. chongqingensis .
From morphological comparison of the penis stylet ( Table 1), it can be seen that there are differences in length and diameter between M. chongqingensis and the other six similar species. Furthermore, in M. contortum , curving in a different plane, the penis stylet with the length of 43.5 µm narrows down from base to distal and becomes the narrowest at distal. In contrast, the length of penis stylet of M. chongqingensis is 180–190 µm. The tube narrows down rapidly at the middle part and remain the same size from that to the distal. In addition, the stylet of M. inductum has three bends, and some parts are covered with a visible lamella. The stylet of M. chongqingensis has only two bends ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 ) without any lamella.
Taking together the above comparisons, M. chongqingensis can be established as a new species.
Material examined. Ten specimens (one holotype and nine paratypes), all collected by Yitao Lin in February 2015 at Xing Lake ( 23°04′32″N, 112°28′44″E), Zhaoqing, Guangdong, Peoples Republic of China. Holotype, PLA- Ma0050, serial horizontal sections, 24 slides, 6 µm, H.E.; Paratypes: PLA-Ma0051, one specimen, serial horizontal sections, 24 slides, 6 µm, H.E.; PLA-Ma0052–55, serial longitudinal sections, 25–30 slides, 6µm, H.E.; PLA- Ma0056, whole mount, H.E.; PLA-Ma0057–59, three unsectioned whole specimens fixed and preserved in 10% formaldehyde. Additional three specimens (YL-2016 ZQ1–3) were used for DNA extraction and sequencing for 18S rDNA, 28S rDNA, and COI genes ( Table 2).
Etymology. The new specific name is an adjective, after the location of the discovery, Zhaoqing City.
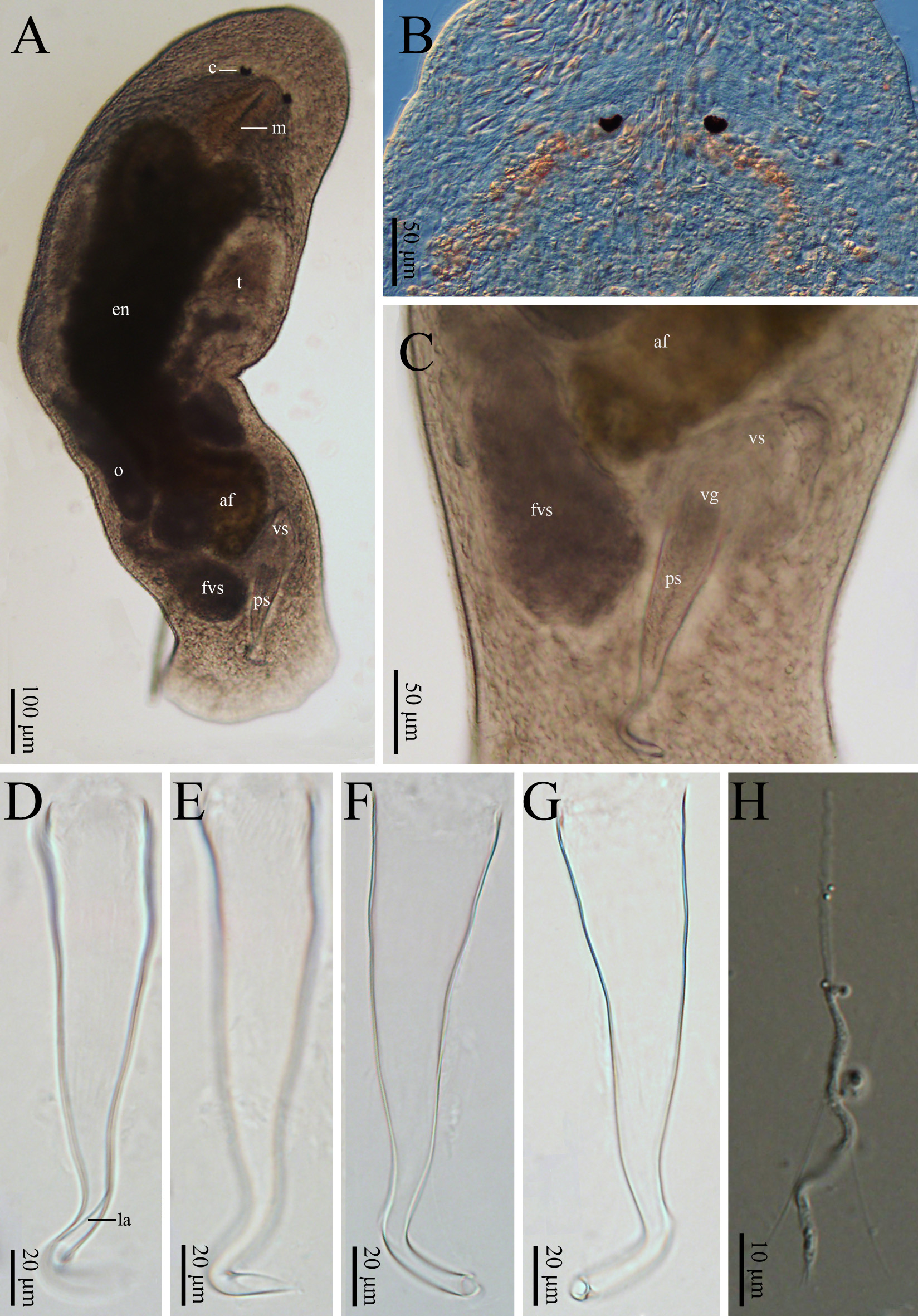
Description. Body about 1,600 µm long and 280 µm wide ( Figs. 4A View FIGURE 4 , 5A View FIGURE 5 ). Body surface covered with cilia (3– 5 µm, n=9). Sensory hairs (1–3 per cluster, each 10–12 µm in length, n=3), primarily distributed on rostrum and cauda. Epidermis covered with rhabdites (1–7 rods per cluster, 6–16 µm in length, n=6). Pair of reniform eyes, with diameter of 13–15 µm (n=6), about 218–226 µm away from tip of head, 40–45 µm away from each other (n=3, Figs. 4A, B View FIGURE 4 , 5A View FIGURE 5 ). Brain crescent-shaped, with widest part being 64–66 µm and length of 20–22 µm; node 14–15 µm in diameter (n=2). Pair of nerve cords extending from cerebral ganglion, running along both sides of ventral body before merging at tail end ( Figs. 4B View FIGURE 4 , 5A View FIGURE 5 , 6A View FIGURE 6 ). Pharynx located posterior to eyes, surrounded by sacciform pharyngeal glands ( Fig. 6B, C View FIGURE 6 ). Mouth opening 208–215 µm in diameter. Gut about 700 µm long and 110 µm wide (n=3). Some well-developed adhesive glands located at tail end.
Female reproductive system consisting of ovaries, ovarian ducts, female antrum, and female gonopore. Pair of elongated ovaries (each with dimension of about 450 × 70 µm, n=6) located alongside rear half of gut; anterior half of ovary containing oocytes ( Figs. 4A View FIGURE 4 , 5A View FIGURE 5 ). Female antrum situated posterior to gut on ventral side, containing eggs and high density of received sperms. Radiate glands located outside female antrum ( Figs. 5A View FIGURE 5 , 6D View FIGURE 6 ).
Male reproductive system consisting of testis, vas deferens, false vesicula seminalis, vesicula seminalis, vesicula granulorum, penis stylet, and male gonopore ( Figs. 4 View FIGURE 4 , 5 View FIGURE 5 , 6 View FIGURE 6 ). In size, testis about 290 × 60 µm (n=6), false vesicula seminalis about 150 × 90 µm (n=3), vesicula granulorum about 120 × 70 µm (n=3); penis stylet 166–175 µm in length, 37–38 µm in basal diameter; gonopore 6–7µm in diameter (n=3). Penis stylet having four bends (B1– B4, Fig. 5D View FIGURE 5 ). B1 bending with ~150° at half way of penis stylet. At rear 1/3 with ~120° bend, B2 covered with visible lamella. B3 located towards end of penis stylet, with ~60° bend. B4 at end of penis stylet with ~60° bend.
Mature sperm cells 75–80 µm in length, with feeler being 27–28 µm long, body 17–18 µm long, and shaft 34–36 µm long. Pair of bristles growing from area near body–shaft connecting area, with length of 32–34 µm. Tail hairs 3–5 µm in length (n=2, Figs. 4H View FIGURE 4 , 6E View FIGURE 6 ).
Remarks. The species is undoubtedly a member of Macrostomum , because it has i) the eyes that lie in the brain, ii) the adhesive plate in the hind end, iii) the ovaries that are paired, and iv) female gonopore that is situated in front of the male gonopore.
There are four congeners that have a similar penis stylet when compared with M. zhaoqingensis : M. saifunicum (Nassonov, 1929) , M. xiamensis ( Wang, 2004b) , M. intermedium ( Tu, 1934) and M. inductum ( Kolasa, 1971) . The detailed comparison of those species with M. zhaoqingensis is listed in Table 4.
Stylet length Diameter of Diameter of Distribution Reference
(µm) basal stylet (µm) distal opening (µm)
M. chongqingense n. sp. 180–190 54–57 14–15 China /
M. amurense View in CoL 150 44 * 5 * Russia Beklemischev, 1950 M. contortum View in CoL 43.5 26 * NA Russia Beklemischev, 1951 M. inductum View in CoL 90–120 28 3.5 * Poland Kolasa, 1971 M. japonicum View in CoL 170 38 * 9.5 * Japan Okugawa, 1930 M. saifunicum View in CoL 130 36 * 6 * Russia and Japan Nasonov, 1929 M. sinenesis 220–280 40– 52 6–7 China Wang?2005
* The authors’ measurement/estimation according to literature or pictures from the literature.
Stylet length Diameter of Diameter of Distribution Reference
(µm) basal stylet (µm) distal opening (µm)
M. zhaoqingensis n. sp. 166–175 37– 38 6–7 China /
M. inductum View in CoL 90–120 28 3.5 * Poland Kolasa, 1971 M. intermedium View in CoL NA NA NA China Beklemischev, 1951 M. saifunicum View in CoL 130 36 * 6 * Russia and Japan Nasonov, 1929 M. xiamensis View in CoL 120–126 30–32 2–3 * China Wang, 2004
* The authors’ measurement/estimation according to literature or pictures from the literature.
For M. zhaoqingensis , its stylet has four bends, different from those in M. saifunicum , M. inductum , and M. intermedium , which have three bends, as well as that of M. xiamensis having one bend. Bending in one plane, the length of the stylet is 130 µm in M. saifunicum , and there is a visible lamella at the stylet. The stylet in M. xiamensis has a complicated curve on different planes, with the length of 120–160 µm. The stylet in M. intermedium bends on a single plane, and its diameter narrows down from the first bend. The stylet in M. inductum has a lamella with the length of 90–120 µm. The stylet in M. zhaoqingensis bends on four planes and B2 is covered with a lamella. Its length is 166–175 µm. For the obvious distinction, M. zhaoqingensis can be established as a new species.
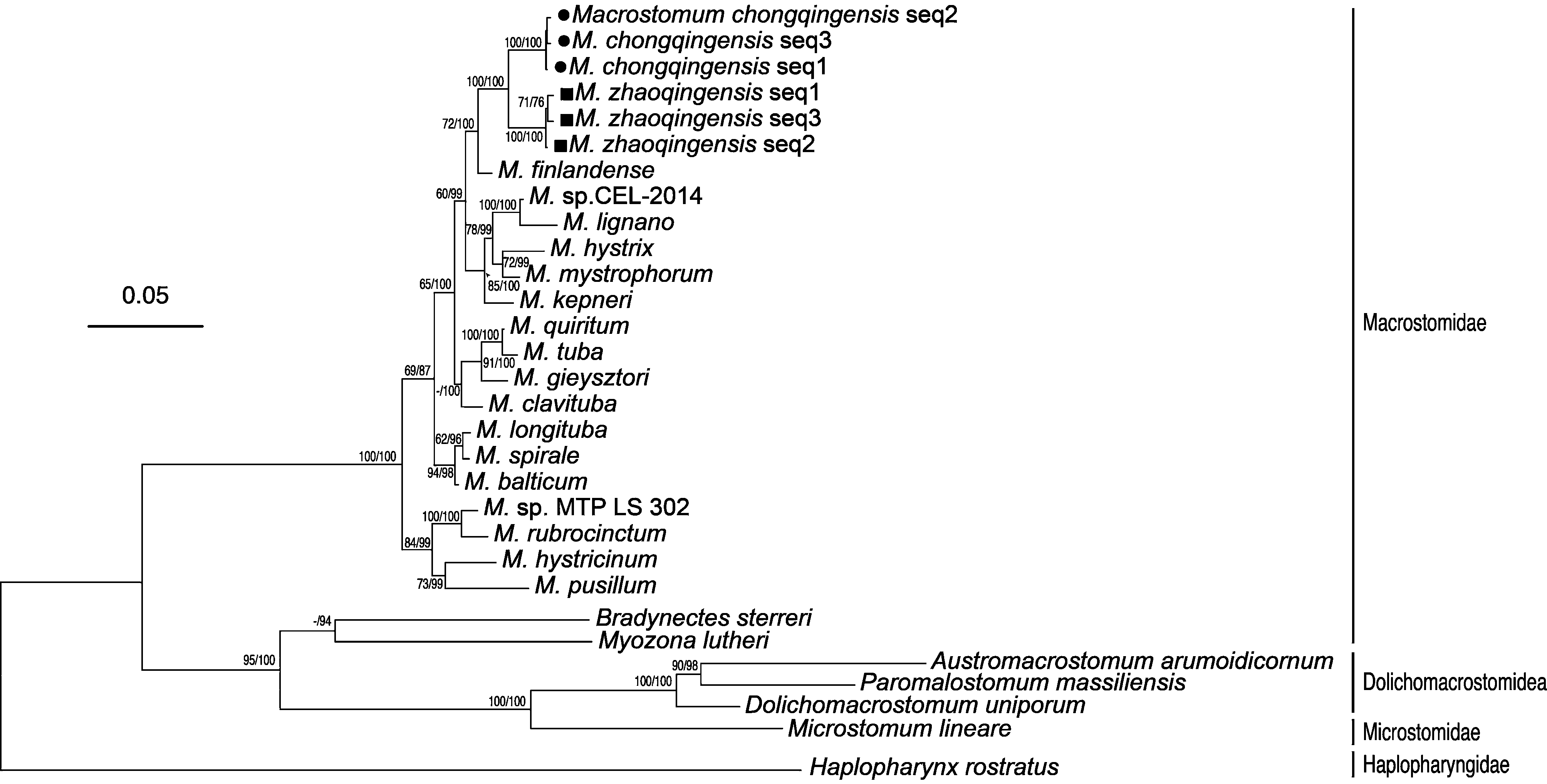
Phylogenetic analysis. The 18S and 28S rDNA together with COI gene phylogenetic tree obviously put the two new species apart from the other used species ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 ). It can be seen that Haplopharynx rostratus is a distant relative. Macrostomorpha is further divided into Macrostomidae , Microstomidae and Dolichomacrostomidae . Macrostomidae is further divided into Macrostomum , Bradynectes , and Myozona . Our species are located in Macrostomum and have a close relative M. finlandense . Even though only five COI sequences of Macrostomum are in Genbank, the phylogenetic tree from the present three gene dataset supports that the two new species in this study belong to Macrostomum . Bootstrap value of 100% suggest M. chongqingensis and M. zhaoqingensis are close relatives and separated into two branches.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
SubPhylum |
Rhabditophora |
|
Class |
|
|
SuperOrder |
Macrostomorpha |
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |