Anomala katherine Jin, Weir, Ślipiński
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.3872.5.9 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:41BDCF15-0657-4CC8-82DC-37D04C5DDE38 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6141594 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/214087F6-FF8F-0838-FF26-2E77CA4E028E |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Anomala katherine Jin, Weir, Ślipiński |
| status |
|
Anomala katherine Jin, Weir, Ślipiński , & Pang,new species
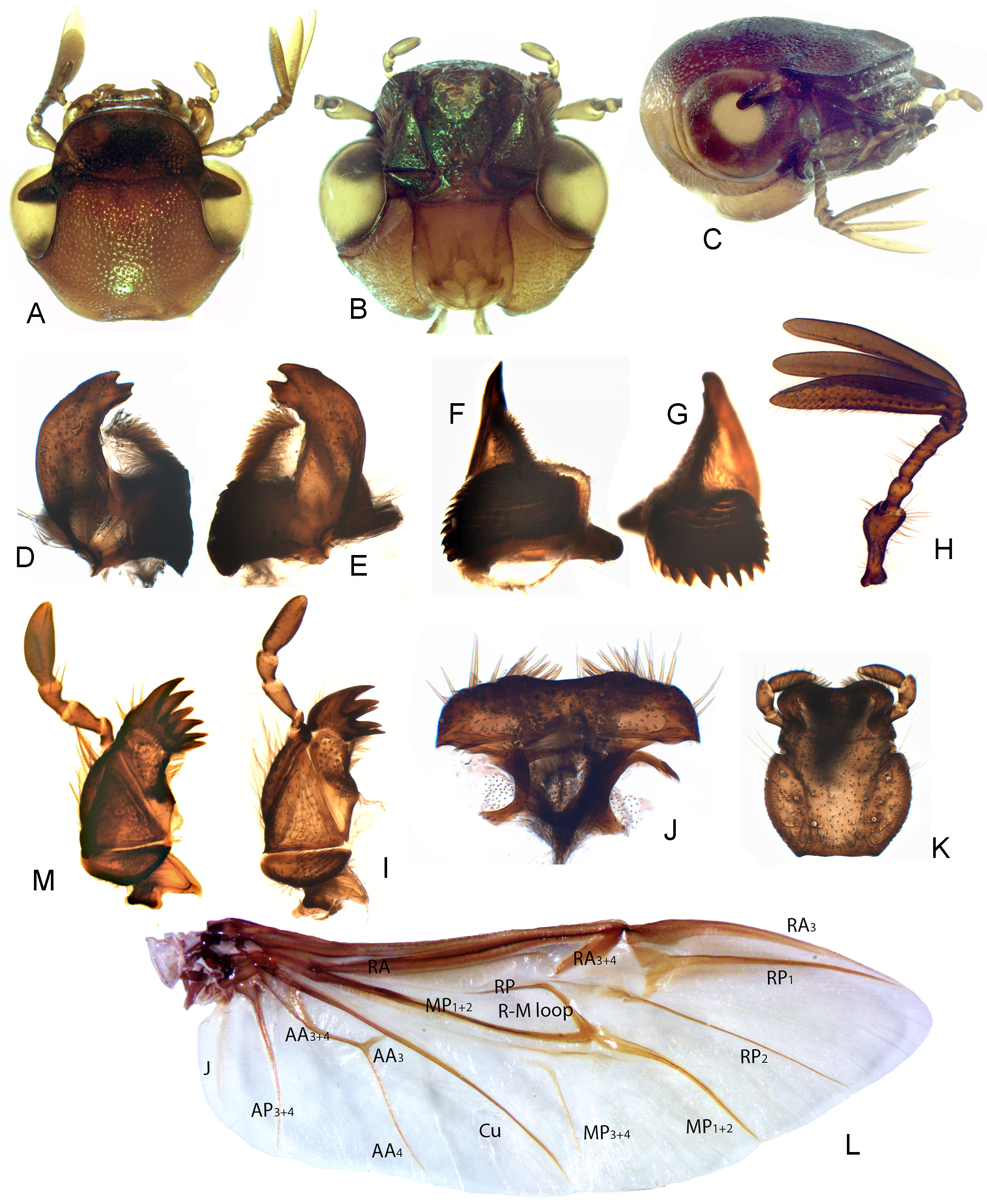
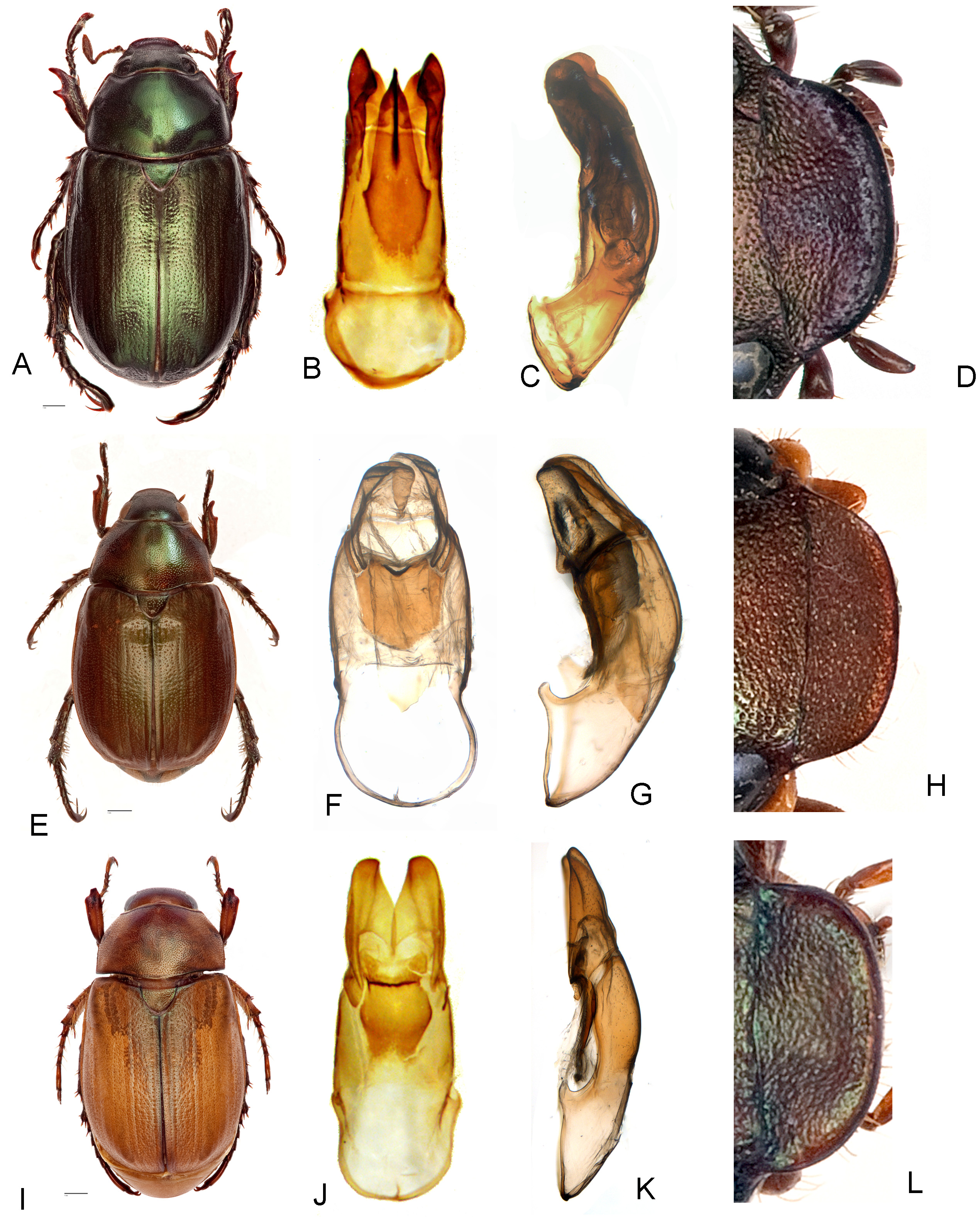
( Figs. 1A–L View FIGURES 1 A – M , 2A–J View FIGURES 2 A – J , 3I –L View FIGURES 3 A – L , 4C–E, H–K View FIGURES 4 A – K , 5 View FIGURE 5 )
Diagnosis. Anomala katherine is distinguished from the similar species by the combination of the following characters: clypeus weakly reflexed along anterior margin ( Fig. 3L View FIGURES 3 A – L ); maxilla with five sclerotised teeth on apex of galea ( Fig. 1I View FIGURES 1 A – M ); protibia with single tooth along external margin ( Fig. 2F View FIGURES 2 A – J ); pronotum with marginal bead at base incomplete medially ( Fig. 4C View FIGURES 4 A – K ); abdominal ventrites with long and sparse setae forming transverse rows in the middle with most of the setae directed posteriorly and surpassing posterior margins of their ventrites; pygidium uniformly yellow or brown ( Fig. 3I View FIGURES 3 A – L ); phallobase longer than parameres with well sclerotised ventral plate ( Fig 3J View FIGURES 3 A – L ), the plate does not extend to parameres; parameres fused at bases but broadly separated apically; endophallus with single setal patch. The new species appears to be very similar to A. crypsinoa Ohaus (Ohaus 1916) described from “Moa und Dama Inseln bei Timor” but differs in having parameres broadly separated apically.
Etymology. Named after its type locality Katherine Gorge in the Northern Territory of Australia; name is noun in apposition.
Description. Length 11.0–13.0 mm; width 6.0– 7.5 mm.
Male. Colour. Dorsum light brown ( Fig. 3I View FIGURES 3 A – L ), venter mostly yellowish brown. Elytra yellowish or reddish brown with metallic green or violet shine; head, anteromedian area and pronotal base, margins of scutellum and elytra usually darker to blackened; legs, particularly metalegs darker often with strong green shine.
Head. Clypeus subrectangular with anterior and lateral margins weakly upturned ( Fig. 3L View FIGURES 3 A – L ); frontal clypeus about as thick as labrum ( Fig. 1C View FIGURES 1 A – M ). Clypeus densely and coarsely punctate; punctures variable and often confluent; interspaces irregularly wrinkled and feebly shiny. Frontoclypeal suture distinct, straight. Frontal punctures similar in size and density to those on clypeus but punctures on vertex much sparser and smaller than frontal ones with smooth and more distinctly shiny interspaces. Ratio of frontal interocular distance to head width: 0.58–0.61. Antenna as in Fig. 1H View FIGURES 1 A – M , club equal in length to shaft.
Pronotum subtrapezoidial ( Fig. 2A View FIGURES 2 A – J ), widest at base, 0.6–0.7 times as long as broad, broadly curved anteriorly from a point shortly before middle. Anterior angles weakly acute; posterior angles obtuse. Pronotal base with marginal bead incomplete medially in front of scutellum. Pronotal punctures about as large as those on vertex, about 0.2–0.5 diameter apart; interspaces smooth and shiny.
Scutellum ( Fig. 4C View FIGURES 4 A – K ) densely punctate, glabrous and rounded apically.
Elytra. 1.1–1.2 times as long and wide and 2.1–2.5 times as long as pronotum. Each elytron with 7 weakly defined punctate striae ( Fig. 4D View FIGURES 4 A – K ), punctures as large as those on pronotum; all intervals irregularly punctate, 2nd widest, 1st (sutural), 3rd and sometimes 5th weakly raised throughout, 4th broadly raised near elytral apex.
Pygidium with marginal bead complete but very fine with long, erect setae along margin. Surface fine and densely transversely rugose, feebly shiny, usually glabrous ( Fig. 4E View FIGURES 4 A – K ).
Venter. Abdominal ventrites 2–5 with long, sparse setae forming transverse rows in the middle, directed posteriorly and surpassing the posterior margins of their ventrites. Ventrite 6 with apical fine line curved forward and enclosing a smooth apical area.
Legs. Protibia with blunt apical tooth and single sharp tooth on outer margin ( Fig. 2F View FIGURES 2 A – J ); larger claws of protarsi and mesotarsi apically, unequally bifurcate, those of protarsi enlarged ( Fig. 4H View FIGURES 4 A – K ); mesotibia sinuate before the terminal tooth ( Fig. 2G View FIGURES 2 A – J ); apex of metatibia with short dense spines ( Fig. 2H View FIGURES 2 A – J ).
Aedeagus as in Figs. 3J, K View FIGURES 3 A – L .
Female. Externally similar to male but the split protarsal claws not enlarged ( Fig. 4I View FIGURES 4 A – K ), antenna with club shorter than shaft and ventrite 6 with apex evenly curved, without smooth apical area.
Types. Holotype male: Northern Territory: “ 14°19'S, 132°25'E, Katherine Gorge, N.T., 24 km NE of Katherine , 16.x.72, M.S. Upton” (ANIC). Paratypes: same data as the holotype (5♂, 3♀; ANIC); “ 12°06'S 133°04'E, Cooper Creek, N.T., 19 km, E. by S. of Mt. Borradaile, 2.xi.72, at light, E. Britton” (19♂, 9♀; ANIC); same data but 9.xi.72, M.S. Upton” (7♂, 1♀ANIC); same data but T.A. Weir & T. Angeles (5♂, 5♀; NTM); “ 12°17'S 133°20'E, Cooper Creek, NT., 11 km S. by W. of Nimbuwah Rock, 1.xi.72, at light, E.B. Britton” (18♂, 8♀; ANIC); same data but T.A. Weir & T. Angeles (4♂, 11♀; NTM); “ 13°15'S 131°06'E, Adelaide River, N.T., 17.x.72, M.S. Upton” (9♂, 3♀; ANIC); “Tindal, N.T., 14°31'S 132°22'E, 1–20 Dec.1967, light trap, W.J.M. Vestjens” (1♀; ANIC); “ 12°23'S 132°56'E, 7 km NW by N of Cahills Crossing, N.T. (East Alligator River), 4.xi.72, E. Britton” (1♀ ANIC); “ 12°26'S 132°58'E, 1 km S of Cahill’s Crossing (East Alligator River), N.T., 3.xi.1972, at light, E. Britton” (1♀; ANIC); “ 12°06'S 132°46'S, Nourlangie Creek, 6 km E of Mt. Cahill, N.T., 12.x.1972, T. Weir” (1♂, NTDA).
Anomala antiqua (Gyllenhal) ( Figs. 1M View FIGURES 1 A – M , 3A–3D View FIGURES 3 A – L , 4A View FIGURES 4 A – K , 5 View FIGURE 5 )
Melolontha antiqua Gyllenhal, 1817: 196 .
Anomala antiqua: Carne, 1958: 170 ; Cassis & Weir, 1992: 363; Zorn, 2006a: 257. For full synonmy see Zorn 2006a: 257.
Diagnosis. Anomala antiqua is distinguished from the other Australian species by the combination of the following characters: clypeus strongly reflexed along anterior margin ( Fig. 3D View FIGURES 3 A – L ); maxilla with 7 heavily sclerotised teeth on apex of galea ( Fig. 1M View FIGURES 1 A – M ); protibia with 2 teeth along external margin ( Fig. 3A View FIGURES 3 A – L ); pronotum with marginal bead at base complete medially ( Fig. 4A View FIGURES 4 A – K ); pygidium uniformly brown or green; phallobase distinctly shorter than parameres with well sclerotised and apically pointed ventral plate ( Fig 3B View FIGURES 3 A – L ), the plate extends to parameres; parameres fused at bases but broadly separated apically. This species is also on average larger and has distinctive green colouration of the dorsal side.
Types. “ 2793 T N.T. [on mounting card]/ Anomala Australasia, Blackb. ” (1, BMNH; syntype).
Material examined. Specimens from ANIC (455), QM (37), AM (6), ASCU (2). Queensland: 11 km NW Mareeba, Southedge Tobacco Research Station; 12 km SSE Heathlands; 12 km E by N Heathlands; 12 km SE of Daintree; 14 km ENE Heathlands; 15 km NE by E Heathlands; 1 km S Heathlands; 20 km N of Mt. Carbine; 2 km NNW Jowalbinna; 6 km NNE Coen; 6 km SE of Chillagoe; Airville; Archer River; Atherton; Ayr; Bald Hills Station, 30 km N of Cooktown; Batavia Downs; Bucasia; Burdekin Rural Education Centre 30 km SW Ayr; Cairns; Cairns area, near Lake Placid; Cardwell; Conway Beach, 27 km SE Proserpine; Cooktown, Walker Bay; Crystal Creek, 23 mi. SSE of Ingham; Cunnamulla; Davies Creek (10.6 road km from Kennedy Hwy), 17 km EbyS of Mareeba; Deeral; Fletcher Creek rest area; Four Mile Beach, Port Douglas; Funnel Creek; Gap Creek; Gordonvale; Green Hills; Gulf Development Road between Mount Surprise and Newcastle Range; Gympie; Hann River; Heathlands; Helenslee Stn., Homestead, 48 km SW Charters Towers; Helenvale; Ipswich; Iron Range; Jourama Falls National Park; Kamerunga, Cairns; Kuranda; Lansdowne Station, 7 km S of Woodstock; Laura; Mareeba; Mary Creek; Meringa; Mount Elliot National Park; Moreton; Mount Surprise; Mount Carbine; Mount Garnet; Mount Spec; Mount White; Palm Cove; Prince of Wales Island, Gulf of Carpentaria; Rochford Scrub; Sarina; Shiptons Flat; Sliver Plains Homestead, Cape York; Station Creek, 11 m. N Mount Molloy; The Boulders, 5 km W of Babinda; Thursday Island; Toomba; Townsville; W Claudie River, Iron Range; Weipa; Woodstock; Yeppoon. Northern Territory: 14 km NW of Cape Crawford; 3 km SSW of Katherine ; Adelaide River; Casuarina Beach , 10 km NNE of Darwin; Daly River Mission; Holmes Jungle, Berrimah, 10 km S Darwin; Katherine Gorge, 24 km NE of Katherine ; McArthur River, 14 km S by W of Cape Crawford; Tindal. Western Australia: Kimberley Research Station via Wyndham; Kununurra; Wyndham. New South Wales: Cabramatta.
Distribution. Widely distributed in Oriental and southeastern part of the Palaearctic Regions from China to India. Introduced to Australia: Northern Territory, Western Australia, Queensland, ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 ). The Cabramatta specimen probably represents an interception.
Notes. The earliest Australian records that we have been able to find are: QLD: Cairns 1890, Cape York 1909; NT: Adelaide River 1892, Darwin 1916; WA: Wyndham 1929.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Anomala katherine Jin, Weir, Ślipiński
| Jin, Mengjie, Weir, Tom, Ślipiński, Adam & Pang, Hong 2014 |
Anomala antiqua:
| Zorn 2006: 257 |
| Zorn 2006: 257 |
| Cassis 1992: 363 |
| Carne 1958: 170 |
Melolontha antiqua
| Gyllenhal 1817: 196 |