Diplectrona aurovittata ( Ulmer 1906 )
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.5047.3.6 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:21097A70-0DDE-4CC0-A594-7F508D7DDE2D |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5540931 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/2057162A-FFF6-FFCF-FF10-FA51FB16A6AF |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Diplectrona aurovittata ( Ulmer 1906 ) |
| status |
|
Diplectrona aurovittata ( Ulmer 1906) View in CoL , NEW RECORD FOR INDIA
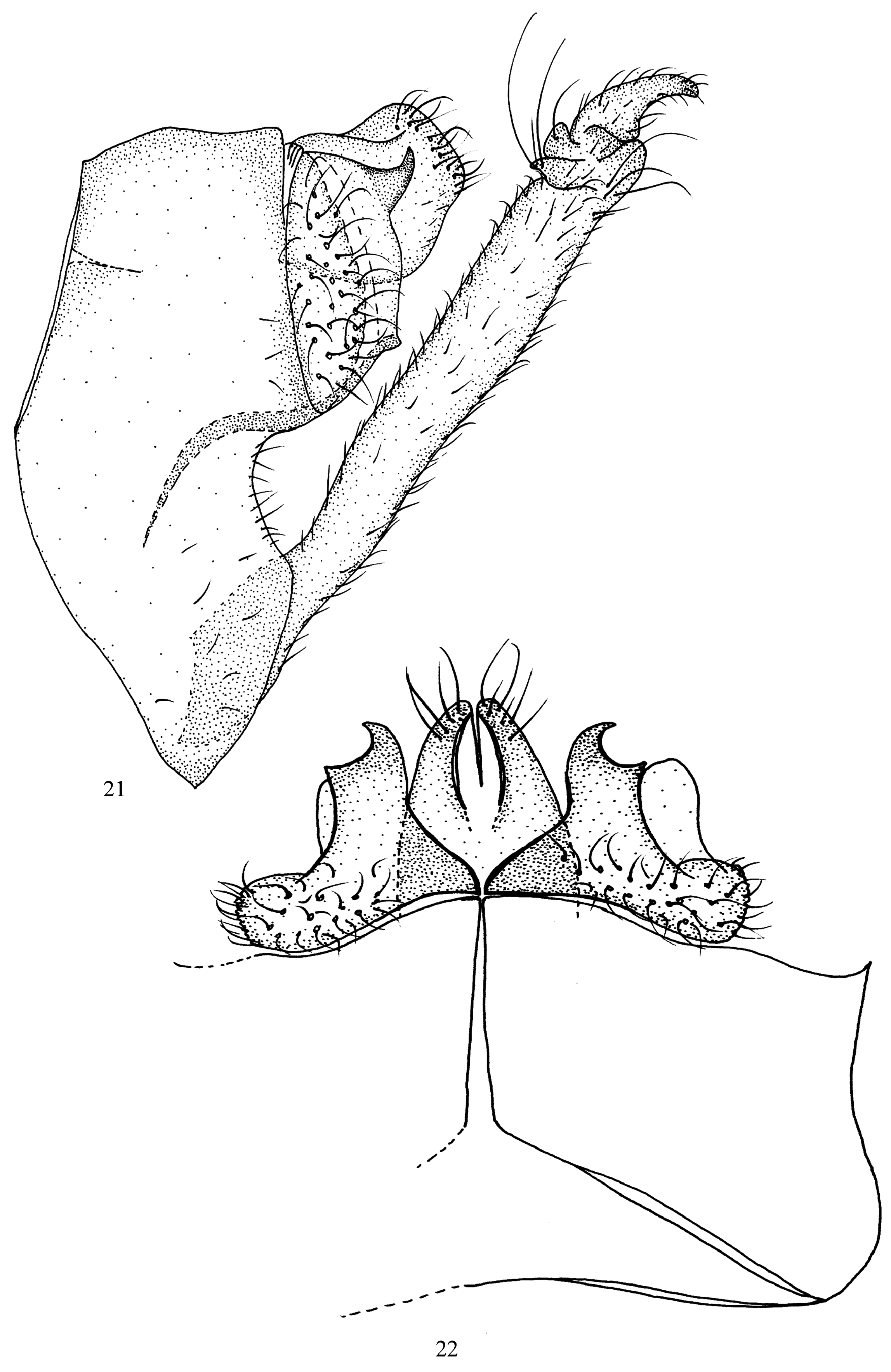
( Figs 21, 22 View FIGURES 21–22 )
Hydromanicus aurovittatus Ulmer 1906: 80–82 , 109, figs 79, 80; holotype male: Java, Preanger, 5000 ft., v. d. Weele, deposited originally in Ulmer’s collection, now in the Natural History Museum in Hamburg ( Weidner 1964; Malicky 2002).
Diplectrona aurovittata (Ulmer) View in CoL ; Ulmer 1951: 310–312, plate 15 fig. 455, plate 16 figs 470–473, new combination, male redescribed; Malicky (2002), male redescribed; Armitage et al. (2005), reported from Vietnam; Malicky (2007), reported from Indonesia (Sumatra); Nuntakwang et al. (2007), reported from Thailand, Laos, Vietnam, Malaysia, Indonesia (Sumatra, Java, Kalimantan); Malicky et al. (2011), reported from Indonesia (Sulawesi); Malicky et al. (2014), reported from Indonesia (Bali, Java, Lombok, Sumatra); Malicky et al. (2014), reported from Indonesia (Lombok); Yang et al. (2016), reported from China (Guangdong, Guangxi, Sichuan) and Indonesia.
Diagnosis. According to Malicky (2013), D. obscura ( Ulmer 1930) is a synonym of D. aurovittata . These two species are very similar. No wing patterns are visible (perhaps because our specimens are preserved in alcohol). However, differences exist that distinguish these species ( Malicky 2002). Variants for this species also exist ( Malicky 2002), but we infer that illustrated variations depend on the orientation of a specimen as drawings or photographs are prepared. For example, in dorsal view ( Fig. 22 View FIGURES 21–22 ), the left lateral lobe of tergum X is very similar to that of the type of D. aurovittata , but the right lateral lobe appears smaller because it was drawn by rolling the genitalia slightly. Differences are clear and obvious. The differences include the following: In D. aurovittata the mesocaudal lobes of tergum X are directed dorsad in lateral view and the lateral (outer) edges of the lateral lobes of tergum X are pointed in dorsal view; whereas in D. obscura the mesocaudal lobes of tergum X are directed posterad in lateral view, and the lateral (outer) edges of the lateral lobes of tergum X are rounded in dorsal view.
Material examined. India, Mizoram, Champai , 1670 m, 27-iv-2012, Pandher, ( NZC), 2 males .
Distribution. Oriental Biogeographic Region: India (Mizoram), Indonesia (Bali, Java, Kalimantan, Lombok, Sulawesi, Sumatra), Thailand, Laos, Vietnam, Malaysia, China (Guangdong, Guangxi, Sichuan).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Diplectrona aurovittata ( Ulmer 1906 )
| Pandher, Manpreet Singh, Kaur, Simarjit, Garima, Deepti & Parey, Sajad H. 2021 |
Hydromanicus aurovittatus
| Ulmer, G. 1906: 82 |