Pseudomys bolami (Troughton, 1932)
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.6887260 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6868542 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/1E30E275-34A7-FF16-E19E-24FB70AC8127 |
|
treatment provided by |
Carolina |
|
scientific name |
Pseudomys bolami |
| status |
|
Bolam’s Mouse
French: Pseudomys de Bolam / German: Bolam-Australienmaus / Spanish: Ratén de Bolam
Other common names: Bolam's Pseudomys
Taxonomy. Leggadina hermannsburgensis bolami Troughton, 1932 View in CoL ,
Ooldea, South Australia, Australia.
Some specimens from north-west Victoria were described as a subspecies of P. her mannsburgenis, but were later elevated to species rank byD. J. Kitchener and coworkers in 1984, an opinion followed by other authors since that time. In a molecular study, F. Ford in 2006 and B. Breed and Ford in 2007 found P. bolami to belong to
same clade as P. delicatulus , P. hermannsburgensis , and P. novaehollandiae , this view was followed by S. Jackson and C. P. Groves in 2015. Monotypic.
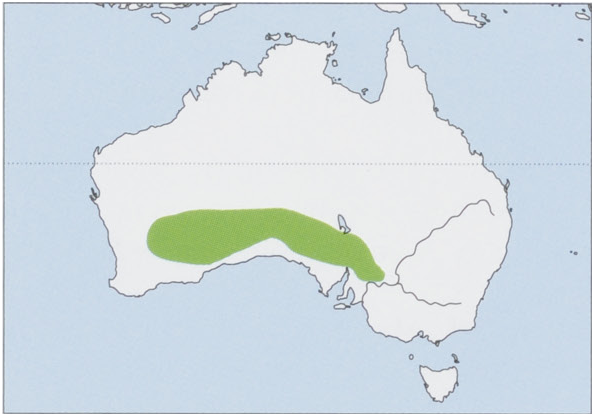
Distribution. S Western Australia, South Australia, and extreme CW New South Wales. View Figure
Descriptive notes. Head-body 50-80 mm,tail 71-103 mm, ear 15-186 mm, hindfoot 18-4-20-1 mm; weight 9-16 g. Bolam’s Mouse exhibits a dull gray-brown dorsal pelage with dark tips on hairs;tail is longer than head-body length. Externally it isvery similar to the Sandy Inland Mouse ( P. hermannsburgensis ), but with longer hindfeet and ears.
Habitat. Chenopod shrubland plains, low Acacia / Eucalyptus ( Fabaceae / Myrtaceae ), and Casuarina (Casuarinaceae) woodland.
Food and Feeding. Bolam’s Mouse is an omnivorous rodent that feeds on a mixture of seed, other plant material (leaves, flowers, stems, roots for ¢.30%), invertebrates (10%), and fungi (1%); owing to the high variability of food resources available, its diet varies with season. It often forages in adjacent swales.
Breeding. Bolam’s Mouse breeds mainly between late winter and early summer and can occasionally breed at other times of year. Litter size is usually four.
Activity patterns. Bolam’s Mouse is nocturnal, and makes burrows in sandy soils.
Movements, Home range and Social organization. Males move more than females. Bolam’s Mouse may use oldrabbit warrens.
Status and Conservation. Classified as Least Concern on The IUCN Red List. Bolam’s Mouse is found in some protected areas, and there appear to be no major threats to it.
Bibliography. Breed & Ford (2007), Ford (2006), Jackson & Groves (2015), Kitchener et al. (1984), Menkhorst (1995), Moseby & Read (2008), Watts & Aslin (1981).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.