Ranitomeya variabilis (Summers, 1999)
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3083.1.1 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5244627 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/1D338788-950D-1516-C8FC-9EDB3892FA78 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe (2021-08-23 20:40:41, last updated by Plazi 2023-11-04 13:58:37) |
|
scientific name |
Ranitomeya variabilis |
| status |
|
Ranitomeya variabilis View in CoL species group
Figs. 3 View FIGURE 3 , 4 View FIGURE 4 , 9 View FIGURE 9 , 14 View FIGURE 14 , 32 – 37 View FIGURE 32 View FIGURE 33 View FIGURE 34 View FIGURE 35 View FIGURE 36 View FIGURE 37
Tables 1, 4 – 6
A monophyletic assemblage of two species: Ranitomeya variabilis Zimmermann & Zimmermann 1988 and R. amazonica Schulte 1999 .
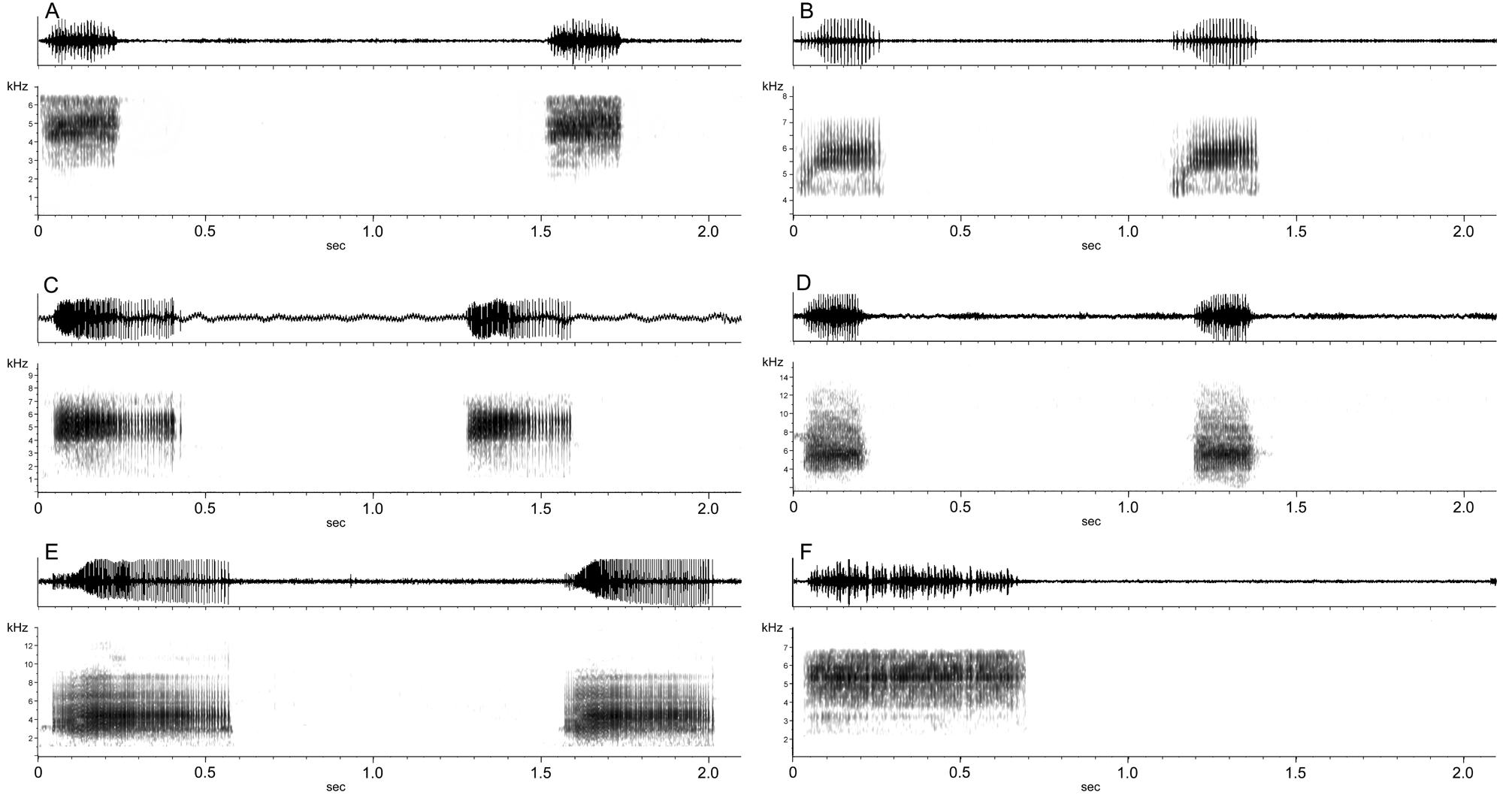
Definition and diagnosis. Medium to large adult size ( SVL 14 – 21 mm); two prevalent dorsal patterns: large ovoid black spots on greenish dorsum or complete yellow to red dorsolateral stripes, middorsal stripe and oblique lateral stripes (note that occasionally these species possess ventrolateral stripes, or an intermediate between oblique lateral and ventrolateral stripes, suggesting this trait is a continuous character); large intestine of larvae entirely pigmented; LTRF 2 (2)/3(1), oral disc emarginated; larvae gray, tadpoles cannibalistic on embryos and other tadpoles; eggs gray; neither males nor females territorial; promiscuous mating system with male parental care; females produce between 2 – 6 eggs per mating. Advertisement calls consist of short, regularly spaced buzz calls, notes 0.16 – 0.44 sec in length, repeated at 24 – 70 notes per minute ( Fig. 14 View FIGURE 14 ) .
Schulte, R. (1999) Pfeilgiftfrosche Artenteil - Peru . INBICO, Wailblingen, Germany, 294 pp.
Zimmermann, H., & Zimmermann, E. (1988) Etho-Taxonomie und zoogeographische Artengruppenbildung bei Pfeilgiftfroschen (Anura: Dendrobatidae). Salamandra, 24, 125 - 160.
FIGURE 3. A consensus Bayesian phylogeny based on 1011 base pairs of aligned mitochondrial DNA sequences of the 12S (12s rRNA), 16S (16s rRNA) and cytb (cytochrome-b gene) regions. Thickened branches represent nodes with posterior probabilities 90 and greater, other values are shown on nodes. Taxon labels depict current specific epithet, number in tree, the epithet being used prior to this revision (contained in parentheses), and the collection locality. A. Top segment. B. Middle segment. C. Bottom segment of phylogeny.
FIGURE 4. Putative species tree for Andinobates, Excidobates, and Ranitomeya. Placement of species where molecular data were lacking (A. altobueyensis, A. viridis, A. abditus, A. daleswansoni and R. opisthomelas) was based on morphology. Andinobates altobueyensis and A. viridis were placed as sister taxa due to the absence of dark pigmentation on dorsal body and limbs and overall similar dorsal coloration and patterning. These species were placed as sister to A. fulguritus (sequenced) on the basis of similar dorsal coloration (bright green to greenish-yellow). Andinobates opisthomelas was placed in the bombetes group in a polytomy with A. bombetes and A. virolinensis (both sequenced) due to their similar advertisement calls and morphology, particularly their red dorsal pattern and marbled venter. Andinobates daleswansoni was placed as sister to A. dorisswansonae due to the absence of a well-defined first toe in both species. Andinobates abditus was placed in the bombetes group based on a larval synapomorphy which appears to be diagnostic of that group (wide medial gap in the papillae on the posterior labium). However, A. abditus was placed as the sister species to all other members of the bombetes group due to the absence of bright dorsal coloration and isolated geographic distribution. Andinobates abditus is currently the only species of its genus known to occur in the east-Andean versant, thus its placement remains speculative until molecular data become available. Photo credits: Thomas Ostrowski, Karl-Heinz Jungfer, Victor Luna-Mora, Giovanni Chaves-Portilla.
FIGURE 9. Known elevation distributions of Ranitomeya. Dotted line is mean for all samples. Dark boxes display the total elevation range of each species, within each contains a corresponding box plot.
FIGURE 14. Advertisement calls of Ranitomeya species in the variabilis group and defleri group. A. Ranitomeya amazonica from 23 km S Iquitos, Loreto, Peru (type locality), recorded at 26° C; B. Ranitomeya amazonica from French Guiana, unknown temperature (call courtesy Erik Poelman); C. Ranitomeya variabilis from Cainarachi valley, San Martín, Peru, recorded at 22° C. D. Ranitomeya variabilis from Cerro Yupatí, Amazonas, Colombia, recorded at 27° C; E. Ranitomeya variabilis from Saposoa, San Martín, Peru, recorded at 24.5 C; F. Ranitomeya defleri from Rio Apaporis, Vaupés, Colombia, recorded at 26° C.
FIGURE 32. Ranitomeya Plate 11. variabilis group. A–P: Ranitomeya variabilis (Highland morph): A: Chazuta, San Martin, Peru; B–G: Upper Cainarachi Valley, San Martin, Peru (Ω); H & I: Borja, Loreto, Peru (24, 46Φ); J: Parque Nacional Ichigkat Muja, Amazonas (D. Rodriquez-Mercado); K: Saposoa, San Martin, Peru (Ω); L: Comparision between Saposoa and upper Cainarachi Valley populations (respectively); M: Xanthosoma sp. that was being used by R. variabilis for tadpole and egg deposition near Saposoa, San Martin, Peru; N: Saposoa, San Martin, Peru (Ω); O: Tocache, San Martin, Peru (C. Torres); P: Macas, Morona Santiago, Ecuador (J. Verkade, Ω). (nΦ = number of individual in phylogeny, Ω = population sampled in phylogeny).
FIGURE 33. Ranitomeya Plate 12. variabilis group: A–P: Ranitomeya variabilis (Lowland morph): A: Contamana, Loreto, Peru (42Φ); B: Shamboyacu, San Martin, Peru (41Φ); C: Lower Huallaga Canyon, San Martin, Peru (‡); D: Callanayacu, San Martin, Peru(‡); E: Barranquita, San Martin, Peru (‡); F: Pongo de Cainarachi, San Martin, Peru (7,8,11Φ); G & H: Bonilla, San Martin, Peru (1,3, 9 Φ); I & J: Varadero, Loreto, Peru (27Φ); K: Quebrada Blanco, Loreto, Peru (Ω); L: Rio Boncuya, Loreto, Peru (G. Gagliardi); M: Upper Rio Nanay, Loreto, Peru; N: Middle Rio Nanay, Loreto, Peru; O & P: Archidona, Napo, Ecuador (EHP and J. Verkade). (nΦ = number of individual in phylogeny, Ω = population sampled in phylogeny).
FIGURE 34. Ranitomeya Plate 13. variabilis group: A–K: Ranitomeya variabilis: A: Archidona, Napo, Ecuador (J. Verkade); B– D: Macuma, Morona-Santiago, Ecuador (J. Verkade and EHP); E &F: Puyo, Pastaza, Ecuador (j. Verkade) G: Yupati, Vaupés, Colombia (14 Φ); H: Embryos, Archidona, Napo, Ecuador (J. Verkade); I: Breeding pair of R. variabilis, Archidona, Napo, Ecuador (J. Verkade); J & K: Yupati, Vaupés, Colombia (14-16 Φ). L–Q: Ranitomeya amazonica: L: Km 41 Iquitos, Loreto, Peru (ET, 26Φ); M: Km 31 Iquitos, Loreto, Peru (PPP); N & O; Km 26 Iquitos, Loreto, Peru (ET, 25, 27Φ); P: Upper Rio Mazan-Pintuyacu, Loreto, Peru (J. J. Lopez-Rojas); Q: Lower Rio Mazan, Loreto, Peru (J. J. Lopez-Rojas). (nΦ = number of individual in phylogeny).
FIGURE 35. Ranitomeya Plate 14. variabilis group: A–Q: Ranitomeya amazonica: A–C: Iquitos, Loreto, Peru; D–K: ‘Arena Blanca’, Loreto, Peru (16–18, 20–24Φ); L: 30 km west of Pevas, Loreto Peru; M: Rio Sucusari, Loreto, Peru (B. Pieper); N & O: Nouragues French Guiana (EHP); P: French Guiana (B.P. Noonan, Ω); Q: Estação Científica Ferreira Penna-Caxiuanã, Para, Brazil.(nΦ = number of individual in phylogeny, Ω=population sampled in phylogeny).
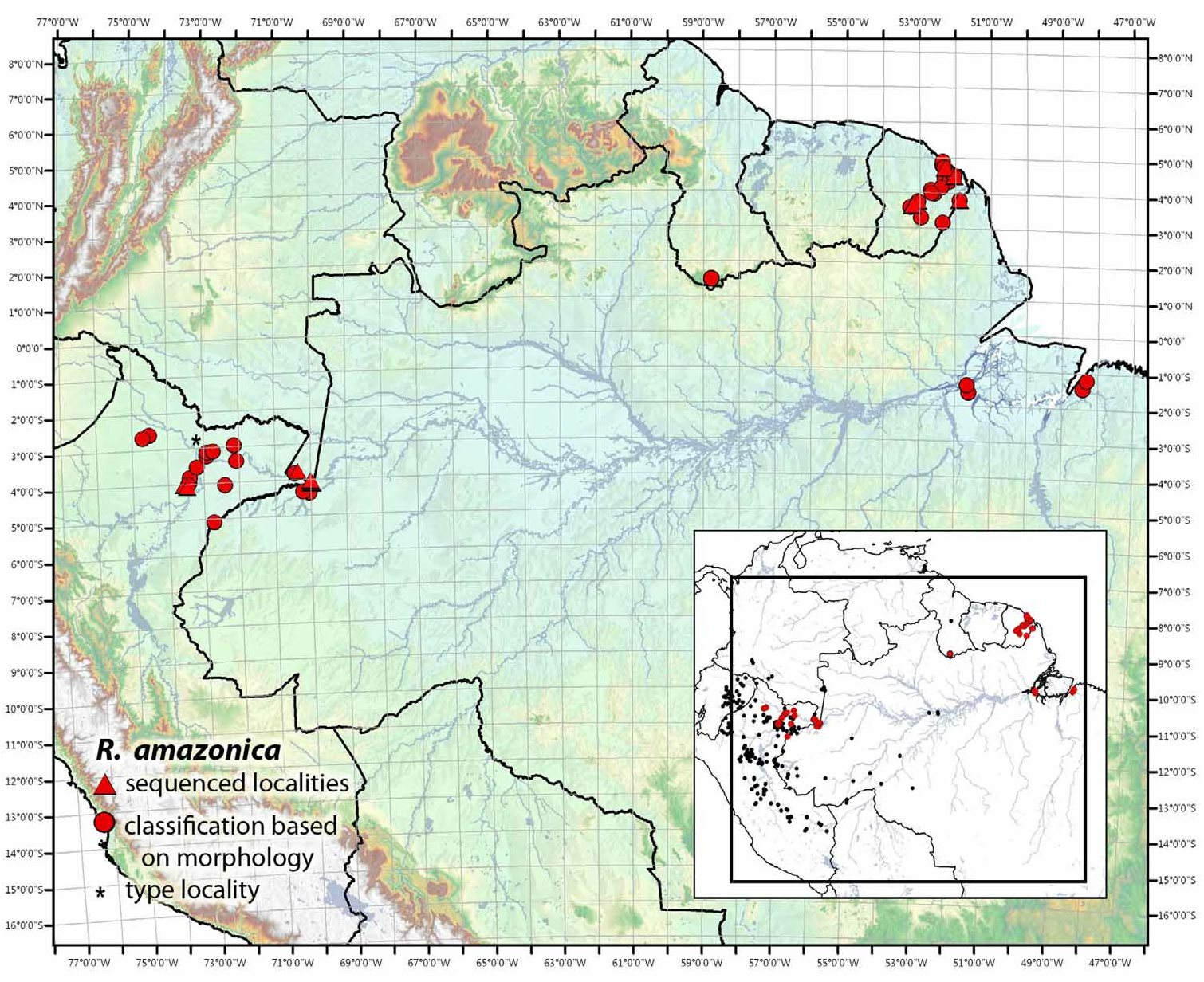
FIGURE 36. Known distribution of Ranitomeya amazonica. The inset map displays the geographic extent of distributions (black circles = all other Ranitomeya).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |