Diaphoromyrma sofiae, Fernández, Fernando, Delabie, Jacques Hubert Charles & Nascimento, Ivan Cardoso Do, 2009
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.275130 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6213210 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/1B1E074B-FFA5-1235-5CAA-FCF1E78CACE5 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Diaphoromyrma sofiae |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Diaphoromyrma sofiae View in CoL , sp. n.
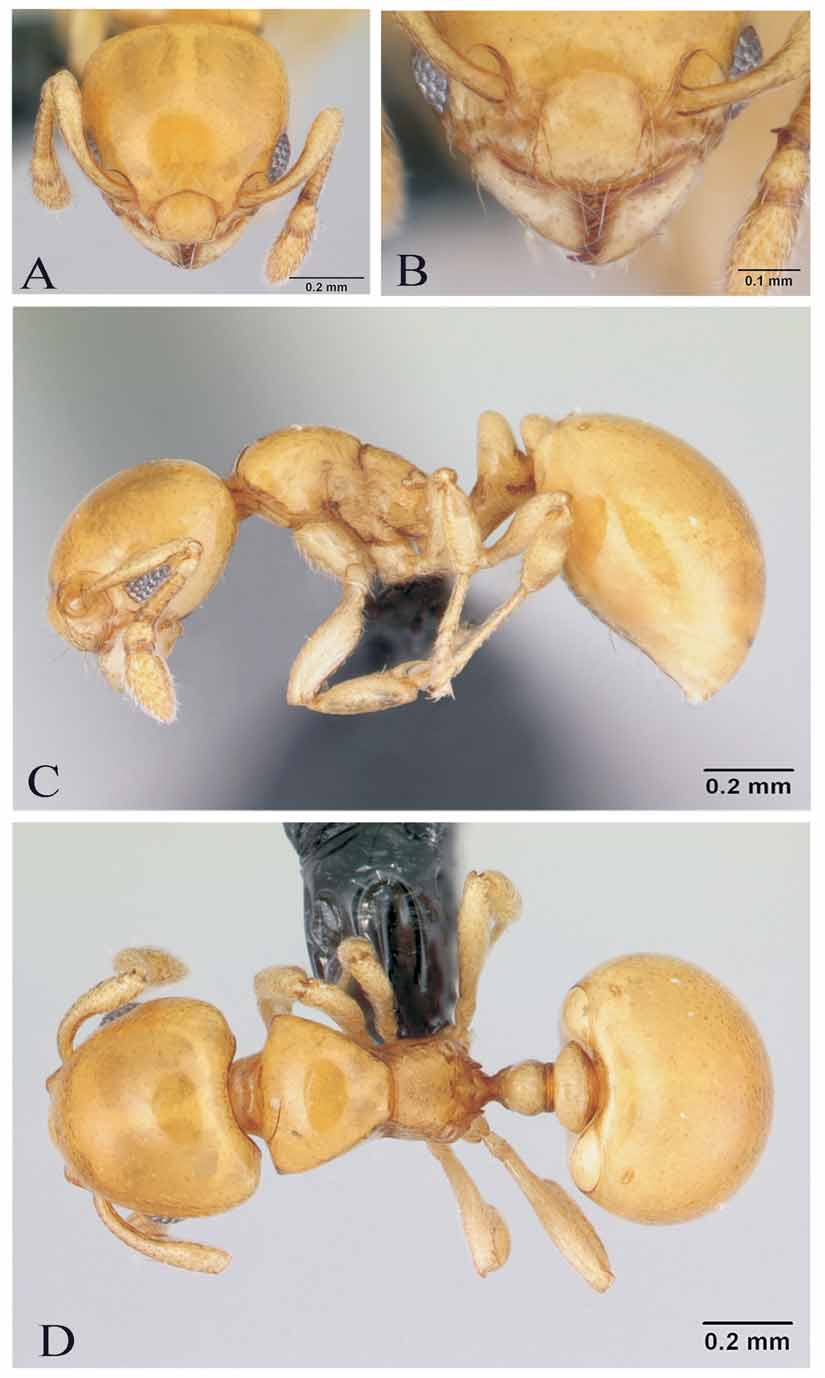
( Figs. 1 View FIGURE 1 & 2 View FIGURE 2 )
Type material: Holotype worker, Brazil: Bahia, Santa Cruz Cabrália, Sucupira-b, Veracel Celulose reserve áreas, Winkler trap, 16º16’32”S 39º16’13”W, 5 November 2006, I. C. do Nascimento col., deposited in CPDC.
Paratypes: 18 workers, same data as holotype; 19 workers, Brazil: Bahia, Santa Cruz Cabrália, Sucupirac, Winkler traps, 16º15’08”S 39º16’55”W, 1 December 2006, I. C. do Nascimento col.; 13 Workers, Brazil, Bahia, Santa Cruz Cabrália, Sucupira-c, Winkler traps, 16º15’08”S 39º16’55”W, 19 January 2007, I. C do Nascimento col., deposited in BMNH, CASC, CPDC, IAvH, IBUS, ICN, IMLA, INPA, LACM, MCZC, MIZA, MNHN, MZSP, PSWC, USNM.
Non type material: 2 workers, Brazil: Bahia, Santa Cruz Cabrália, Pequizeiro, Winkler traps, 16º17’28”S 39º25’05”W, 8 August 2006, J. R. M. Santos & J. C. S. Carmo cols.; 9 workers, Brazil, Bahia, Santa Cruz Cabrália, EVC-E – Etapa 2, Winkler traps, 16º18’54”S 39º09’34”W, 12 April 2007, I. C do Nascimento col.; 4 workers, Brazil, Bahia, Santa Cruz Cabrália, Sucupira-b, Winkler traps, 16º16’32”S 39º16’13”W, 19 January 2007, I. C do Nascimento col.; 5 workers, Brazil: Bahia, Santa Cruz Cabrália, Sucupira-c – Etapa 2, Winkler traps, 16º15’08”S 39º16’55”W, 10 January 2007, I. C. do Nascimento col., deposited in CPDC; 2 workers, Brazil, Bahia, Porto Seguro, Estação Pau-Brasil (ESPAB-CEPLAC), Projeto BIOTA /FAPESP, Winkler traps [8, 26], 16o23’33”S 39o10’99”W, 16 June 2000, J. R. M. Santos & J. C. S. Carmo cols., deposited in MZSP.
Worker measurements. Holotype (Paratypes n = 10): HW 0.54 (0.51 – 0.54); HL 0.58 (0.57 – 0.60); SL 0.40 (0.39 – 0.40); EL 0.14 (0.14); PW 0.42 (0.39 – 0.42); WL 0.51 (0.47 – 0.56); PL 0.18 (0.15 – 0.22); PPL 0.13 (0.08 – 0.13); GL 0.90 (0.76 – 0.90); TL 2.39 (2.09 – 2.48); CI 93 (85 – 93); SI 74 (71 – 76).
Description. Head broadly triangular, with rounded sides, narrowed anteriorly, vertex and sides slightly convex ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 A). Mandibles triangular, with 5 teeth on the masticatory border, the apical and subapical larger than the others. Antenna with 9 segments. Scape clearly fails to reach the vertexal margin. Eyes well developed, situated near anterior margin of the head, with about 8 ommatidia in their maximum diameter.. In dorsal view, promesonotum trapezoidal, sides and dorsum well defined ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 D). Promesonotum strongly convex in lateral view ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 C). Promesonotal suture well defined dorsally and laterally. Propodeum unarmed. Propodeal spiracles conspicuous, situated on the edge of declivitous face of propodeum, their aperture obliquely directed backward and upward ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 C). Metapleural gland bullae conspicuous, bigger than propodeal spiracle. Propodeal lobes small, rounded. Petiole in profile with short anterior peduncle, followed by a high and narrow node, its apex narrowly pointed. Petiolar peduncle attains petiolar mid length.
Petiolar spiracle at base of node. Subpetiolar process present, as a keel-like lamella that ends in rounded apex anteriorly. Postpetiole low, rounded in frontal view ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 E), noticeably wider than long in dorsal view. Gaster without humeral angles basally. Head, promesonotum, petiole, postpetiole, gaster, scapes and legs smooth and shining. Lower side of mesopleuron and petiolar peduncle finely reticulated; propodeum with fine reticulation on the declivous face, between the propodeal spiracles and on the metasternal lobes. Body devoid of standing pilosity, except for very short, sparse minute hairs on head, legs and scape. Reclined minute hairs on thorax and gaster. Pilosity denser and longer on antennae. Row of hairs on the anterior clypeal margin, including median hair (not visible in the Automontage Picture). Central clypeal hair accompanied by two lateral hairs, although both lateral hairs not in the same plane (in full face view the 3 hairs appearing as the same length). Body yellow, eyes and mandibular teeth dark. Pilosity golden.
Gyne, male, and larva: Unknown.
Etymology. The specific name honors our colleague myrmecologist Sofia Campiolo, from Universidade Estadual de Santa Cruz (Bahia, Brazil) and Driades Institution, who obtained the research funds from Veracel Celulose, allowing an extensive regional ant survey.
Comments. The combination of traits in the diagnosis differentiates this thus far monotypic genus from any other myrmicine. The unique shape of the promesonotum, trapezoidal in dorsal view and with well defined angles at the sides; the comparatively high and narrow petiolar node, contrasting with the broader, low and round postpetiolar node, the low position of the insertion of the postpetiole on the anterior face of first gastral segment, and the dorsal extensions of abdominal sternite 4 are unique and represent potential apomorphies of Diaphoromyrma .
Usually in myrmicine ants the dorsal margin of the postpetiole is higher than the top of first gastral tergite, in lateral view. In Diaphoromyrma the joining of the postpetiole with the gaster is so ventral that the postpetiole in lateral view is very low relative to the upper margin of the gaster. The rounded and recurved anterolateral extensions of the fourth abdominal sternite, which curve up onto the dorsal surface of the segment and are visible in dorsal view, delimiting two round semicircular areas ( Figs. 1 View FIGURE 1 D, E), are unique in Myrmicinae. Some cephalotines have differentiated anterolateral extensions on abdominal segment 4, but from the tergite, and not from the sternite (Ward, comm. per.).
There are rows of setae on the anterior clypeal margin, including a central seta. Although not shown on the Automontage view ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 B), the central seta is visible on the SEM picture ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 A).
As with some other myrmicine ant genera recently described ( Tyrannomyrmex , Dolopomyrmex, Tropidomyrmex ), Diaphoromyrma is difficult to relate to any of the tribal taxa defined by Bolton (2003). The central clypeal seta is characteristic of the Solenopsidini (sensu Bolton 1987), although they may not be homologous, but the clypeal configuration differentiates Diaphoromyrma from this group as defined in Bolton (2003:57). As pointed out by Bolton (1987 and 2003:57), Allomerus and Diplomorium are problematical genera in the Solenopsidini , as the posterior portion of the clypeus is relatively broad. However, Diaphoromyrma lacks any of the diagnostic attributes of both genera (antennal club segments constricted basally in Allomerus and postpetiole broadly attached to the gaster in Diplomorium ; and also antennal club 3- segmented in both genera). The 2-segmented antennal club and the specialized first segment of the gaster suggest that Diaphoromyrma is not closely related to either of these genera.
The membership of Diaphoromyrma in Stenammini or Adelomyrmecini (the other tribes of the solenopsidine tribe group [ Bolton 2003]) is unlikely. Diaphoromyrma lacks the specialized lamellate hairs on the ventral side of masticatory margin of adelomyrmecine mandibles ( Fernández 2004) or the various traits listed in Bolton (2003:58) for stenammines, namely the clypeal configuration. Although Diaphoromyrma possess the clypeus broadly inserted between the frontal lobes, it lacks any of the traits defining the tribes Myrmicini , Lenomyrmecini , Pheidolini , Tetramoriini or Paratopulini . Diaphoromyrma should also be compared with the formicoxenine tribe group ( Bolton 2003:65). The membership of the genus in the tribe Formicoxenini is complicated by several differences: the toruli are slightly exposed in Diaphoromyrma (partially visible in only a few taxa of Formicoxenini , Bolton 2003), the propodeal lobes are relatively reduced (present and usually rounded in Formicoxenini ), the antenna is 9-segmented with 2-segmented club (antenna with 8 to 12 segments and with 3 or 4–segmented club in Formicoxenini , but never with this combination, Bolton 2003). This genus is also clearly not a member of the other myrmicine tribes as presented or proposed in Bolton (2003).
According to an ongoing ant phylogenetic study by Phil Ward´s research group in Davis, University of California, Diaphoromyrma is not closely related to Solenopsis group. These studies offer strong support for a Solenopsidini sensu stricto clade, which is quite distinct from Diaphoromyrma and other myrmicines (Ward, com. per.).
Further collections and studies on gynes and males may throw some light on the phylogenetic affiliations of this new, enigmatic genus.
Ecological comments. This undescribed taxon was collected in litter samples taken in three rain forest remnants in the extreme southern portion of the State of Bahia, Brazil, using the Winkler technique, according to Agosti et al. (2000) methodology. The landscape is dominated by forested valleys inserted in the coastal plateau (Barreiras Formation, Tertiary origin). Most of the vegetation of the remnants was in an initial or medium stage of regeneration, in a region where eucalypt plantations currently predominate. Forty 1m 2 litter samples were taken in each remnant, and D. sofiae was found in 5%, 10%, and 25% of samples in the remnants Pequizeiro, Sucupira B, and Sucupira C at Santa-Cruz Cabrália, respectively, while it was collected in 4% of samples in the ESPAB Mata Atlântica coastal wet forest reserve at Porto Seguro using the same methodology. This finding reinforces the biotic importance of this region and the Atlantic coastal forest of Brazil in general, an abundant source of recent information on ant biodiversity and other important biological features ( Lacau & Delabie 2002, Lacau et al. 2004, Mariano et al. 2004, Delabie et al., 2007, Fernández 2007).
| CPDC |
Centro de Pesquisas do Cacau |
| IBUS |
Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro |
| ICN |
Instituto de Ciencias Naturales, Museo de Historia Natural |
| IMLA |
Fundacion e Instituto Miguel Lillo |
| INPA |
Instituto Nacional de Pesquisas da Amazonia |
| LACM |
Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County |
| MIZA |
Museo del Instituto de Zoologia Agricola Francisco Fernandez Yepez |
| MNHN |
Museum National d'Histoire Naturelle |
| MZSP |
Sao Paulo, Museu de Zoologia da Universidade de Sao Paulo |
| USNM |
Smithsonian Institution, National Museum of Natural History |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |