Murina eleryi Furey et al. 2009
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.3161/150811012X654231 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4329635 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/16319E21-FFD4-FF9C-697D-FF70FDD11234 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Murina eleryi Furey et al. 2009 |
| status |
|
Murina eleryi Furey et al. 2009 View in CoL
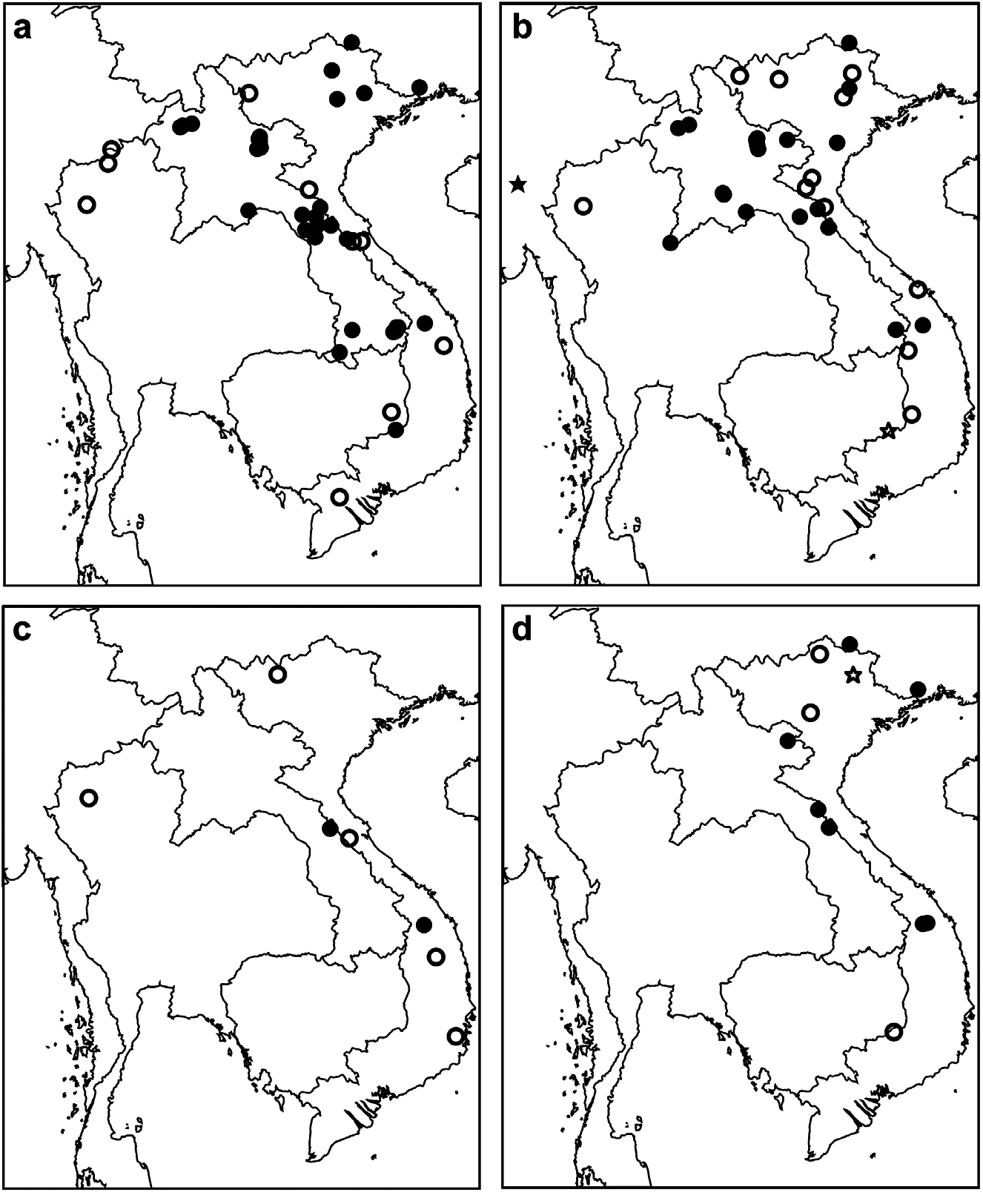
( Figs. 3f View FIG , 4f View FIG , 5f View FIG ; Tables 1 View TABLE , 2; Map Fig. 1d View FIG )
Murina aurata: Francis et al. 1999: 233, 2010: 6 View in CoL ; Francis 2008: 253 (part).
Specimens examined from Laos
ROM: 1 ♂, 2 ♀♀ ; EBD: 1 ♀ (see Appendix for details, including information from adjacent countries and the literature) .
Description
The fur of the dorsum is banded with dark grey to blackish bases for about 25% of the length, then a paler whitish to buffy band that blends into an orange brown band, then a dark brown band. Some of the longer hairs then have golden tips for up to 15% of the length giving a gilded appearance. The ventral fur has dark grey or blackish bases for about 50% of the length, with silvery grey to white distal half. The tail membrane is sparsely covered with long yellow-brown hairs, and the feet and legs are thickly haired. The ears are small and rounded; the tragus straight, pointed and whitish. The wing membrane is inserted on the side of the toe, near the base of the claw.
This is the smallest Murina in Laos ( Tables 1 View TABLE and 2), particularly in skull dimensions ( Fig. 3f View FIG ). The anterior upper premolar (P 2) is substantially shorter than the posterior premolar (P 4), while the canine is slightly longer than P 4 ( Fig. 4f View FIG ). In the mandible, P 2 is substantially smaller in surface area, and about 2/3 the height of P 4, while C 1 is about 50% taller than P 4 ( Fig. 5f View FIG ).
Discussion
These specimens were originally reported by Francis et al. (1999) as M. aurata Milne-Edwards 1872 , based on their small size and the similarity in fur colour to the description in Hill (1983), although with some hesitation given that the canines, although small, were longer than the posterior premolars, contrary to the keys in Hill (1992). However, they agree well in both fur colour and cranial shape with the description of M. eleryi by Furey et al. (2009).
Distribution and ecology
Three of the specimens that we captured in Laos were found in wet evergreen montane forest in the Annamite Mountains, at an altitude of 1000–1140 m. An additional five specimens were captured during surveys in Vietnam, in Quang Nam province. Four of these were captured in premontane evergreen forest at about 830 m, but one was caught in secondary forest at the base of the hills at 200 m. Additional specimens from the ROM in southern China, together with those reported by Furey et al. (2009) suggest it may be widely distributed through Vietnam and adjacent areas of Laos, though possibly largely in montane regions ( Fig. 1d View FIG ).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Murina eleryi Furey et al. 2009
| Francis, Charles M. & Eger, Judith L. 2012 |
Murina aurata:
| Murina aurata: Francis et al. 1999: 233 |