Apatania crymophila McLachlan 1880
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.5306.3.2 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:264C8FCC-CB13-463A-BBAD-A75422C77EEC |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8065979 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/090D87B3-FFC1-FF9F-FF0A-D6F4FEE7F806 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Apatania crymophila McLachlan 1880 |
| status |
|
Apatania crymophila McLachlan 1880 View in CoL View at ENA .
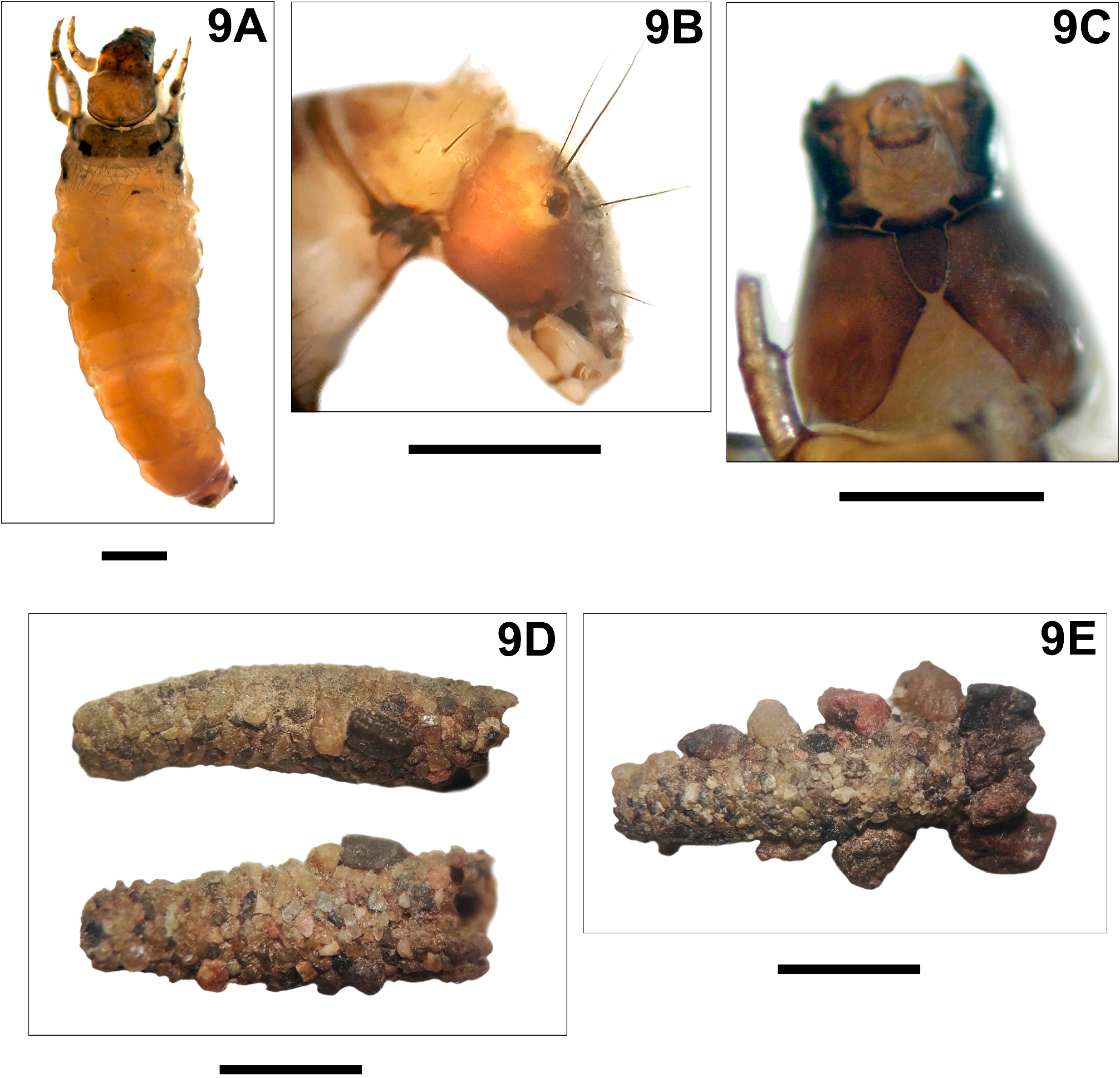
The mesonotum shows distinct, large, diamond-shaped posterolateral spots ( Fig. 9A View FIGURE 9 ). The surface of the protonum is covered by short thick secondary setae ( Fig. 9B View FIGURE 9 ). The pairs of postocular primary setae on the head are shorter than the frontal setae; the posterior part of the head is light-colored ( Fig. 9B View FIGURE 9 ). The length of the gula is greater than its width by a factor of more than 1.5 ( Fig. 9C View FIGURE 9 ). The cases have a shape of slightly curly conic tubes ( Fig. 9D View FIGURE 9 ) made of small mineral particles; ballast particles of larger size are often mounted laterally ( Fig. 9E View FIGURE 9 ). The length of the cases does not exceed 1.5 cm ( Figs 9D, 9E View FIGURE 9 ). The longest cases are typical of the latest larval instars, when cases are attached to rocks on the bottom; the size of the cases of younger, mobile larval instars does not exceed 1 cm. This species was the most numerous in the assemblages of Trichoptera on water moss.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |