Bursaphelenchus gerberae, Giblin-Davis & Kanzaki & Ye & Center & Thomas, 2006
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.1189.1.2 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:D45D11D5-67A4-4D8A-820A-DF96D8555DD3 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/0836BC70-2506-FF81-FE8F-921CD1BEFB68 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Bursaphelenchus gerberae |
| status |
|
Description of Bursaphelenchus gerberae n. sp. ( Figs. 1–4 View FIGURE 1 View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 View FIGURE 4 )
Measurements were made of male and female specimens in temporary water mounts ( Table 1).
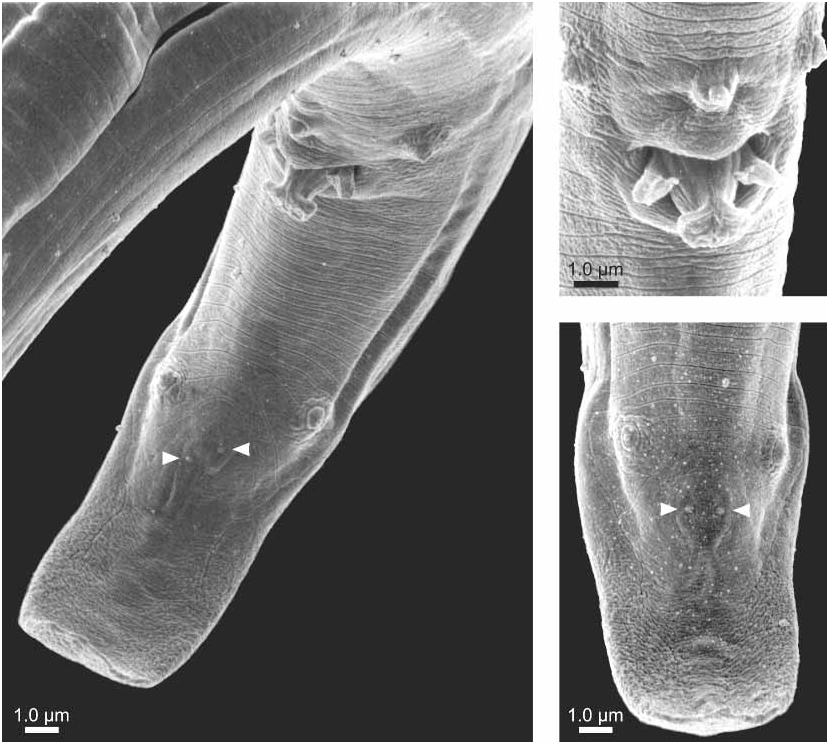
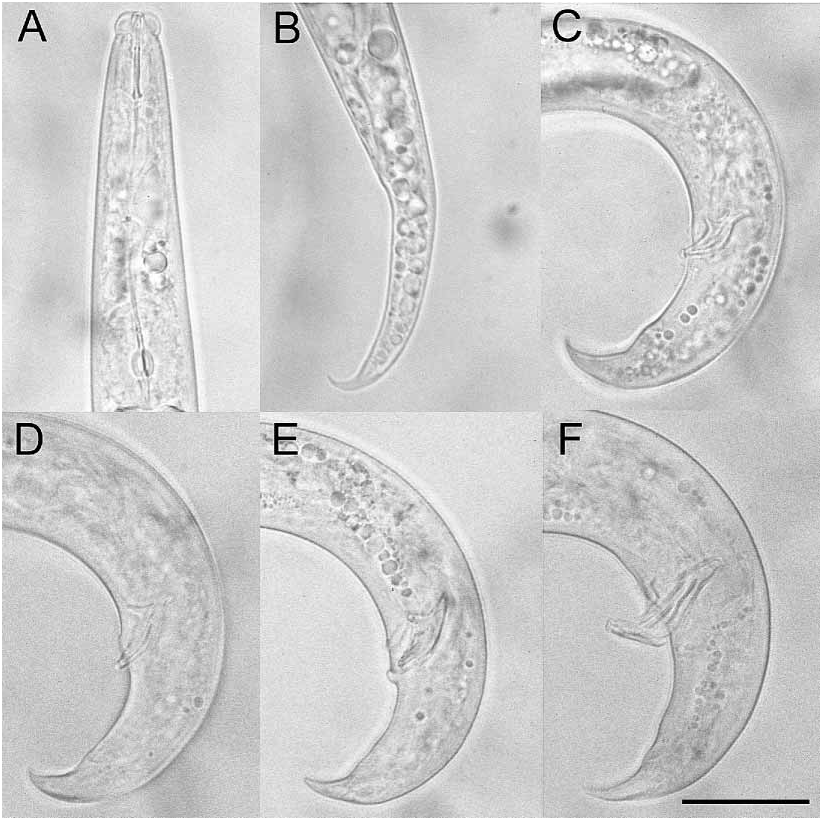
Morphological description Males: Body cylindrical, tapered at both ends, Jshaped when heat killed ( Fig. 1B View FIGURE 1 ). The anterior regions (exterior and interior) of adult males and females were the same and are only described in detail for the male. Cuticle with fine annulation, annules about 0.70.8 m wide at midbody ( Figs. 1C View FIGURE 1 , 3A View FIGURE 3 ). Lateral field with three incisures ( Fig. 1C View FIGURE 1 , 3A View FIGURE 3 ), beginning just above level of metacorpus, extending posteriorly to level of ventral preanal papilla; less distinct from ventral preanal papilla to beginning of bursal flap (= caudal alae) at level of subventral pair of postanal papillae (P3). Head distinctly offset from body, lip region in lateral view less than 2.5 times wider than tall ( Figs. 1C View FIGURE 1 , 2A View FIGURE 2 ). En face pattern (SEM) consisting of a clearly defined circular oral aperture (about 0.03 m) surrounded by a dorsoventrally elongated labial disc, with a long indentation on each lateral side, and a small slit on each subdorsal and subventral side ( Fig. 2B–C View FIGURE 2 ). These slits and indentations may represent the inner labial sensillae. Labial disc surrounded by circular plate comprised of fused lateral, subventral and subdorsal lip sectors, about 1.61.7 m in diameter ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 ). Labial sensillae obscured; a composite of several SEM en face patterns suggests two lateral outer labial sensillae open mediolaterally onto circular lip sector plate ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 ). Circular lip sector plate surrounded by hexaradiate cephalic sectors, two subdorsal, two lateral, and two subventral ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 ). Porelike amphidial apertures, dorsomedially located on lateral cephalic sectors and a slightly elevated cephalic papilla clearly resolved on each subdorsal and subventral cephalic sector ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 ). Six to eight transverse striae visible on head with SEM ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 ). Stylet two part; cone short, about 2/5 total stylet length, shaft with slight basal thickenings ( Fig. 1C View FIGURE 1 ). Procorpus cylindrical, about two and one half stylet lengths long ending in welldeveloped metacorpus ( Fig. 1A–C View FIGURE 1 ). Dorsal esophageal gland orifice opens into lumen of metacorpus less than one metacorpal valve length above metacorpal valve ( Fig. 1C View FIGURE 1 ). Esophagointestinal junction less than one metacorpal valve width behind metacorpus. Postcorpus glandular, overlaps intestine dorsally about 3 metacorpal lengths long ( Fig. 1C View FIGURE 1 ). Excretory pore posterior to nerve ring, hemizonid about one stylet length behind excretory pore ( Fig. 1C View FIGURE 1 ). Gonad reflexed, sperm amoeboid ( Fig. 1B View FIGURE 1 ). Tail arcuate, about 2.6 anal body widths long; terminus clawlike from lateral view ( Figs. 1B,H View FIGURE 1 ). Spicules separate, ventrally arcuate with gradual lamina taper from calomus to tip, rostrum sharplypointed to conical, condylus elongate and truncate with slight posterior recurvature, distal ventral end with small cucullus and in SEM with apparent lateral projection ( Fig. 3A–B View FIGURE 3 ), spicule length measured along its arc/capitulum width (distance between condylus and rostrum) ratio is about 2.1; spicule length measured along its arc/spicule width posterior to rostrum is about 2.4; junction of rostrum and calomus smoothly curved; lamina complex with midpoint widened and rounded; lamina dorsal contour often smoothly and symmetrically curved ( Figs. 1H, J–O View FIGURE 1 ); ratio of depth of capitulum depression divided by the capitulum width about 0.15. Spicules are recurved so that a line drawn through the anteriormost points of the condylus and rostrum (along the capitulum) and extending the posterior dorsal lamina intersects ventrally at less than a 14º angle ( Figs. 1J–O View FIGURE 1 , 4C View FIGURE 4 ). Seven preanal and postanal papillae present; one preanal papilla (P1) in ventral midline about 2 m above cloaca ( Figs. 1G–H View FIGURE 1 , 3A–B View FIGURE 3 ), one pair subventral preanal papillae (P2) in line with P1 papilla ( Figs. 1G–H View FIGURE 1 , 3A–B View FIGURE 3 ), one subventral pair of postanal papillae (P3) at about 55% of a tail length behind cloaca ( Figs. 1G–H View FIGURE 1 , 3A View FIGURE 3 ), one small ventral pair of papillae (P4) about 22–24
m from tail terminus ( Figs. 1G–H View FIGURE 1 , 3A,C View FIGURE 3 ). Occasional asymmetry was observed in P3 and P4 papillae arrangement ( Fig. 3A,C View FIGURE 3 ). Bursa rounded in ventral view and pointed in lateral view ( Figs. 1G–H View FIGURE 1 , 3A,C View FIGURE 3 ).
in temporary water mounts (measurements in m).
Females: Body ventrally arcuate or straight when killed by heat treatment ( Fig. 1A View FIGURE 1 ). Lateral field with three incisures; decreases to two incisures posterior to level of anus; extending almost to tail terminus. Ovary single, anteriorly outstretched, oocytes in single file except at anterior half of ovary ( Fig. 1A View FIGURE 1 ). Vulva domeshaped slit in ventral view which gives the appearance of a small vulval flap in lateral view, but is not a true vulval flap ( Fig. 1D View FIGURE 1 ). Vagina straight with anteriorly projected incline in lateral view, paired and threecelled structures at back of uterus facing vagina ( Fig. 1 D View FIGURE 1 ). Postuterine sac about 3 vulva body diameters long, about 54% of vulvalanus distance, sometimes filled with sperm ( Fig. 1A,D View FIGURE 1 ). Anus domeshaped slit in ventral view. Tail strongly recurved ventrally, about 4.8 times longer than anal body width, and finely rounded to digitate ( Figs. 1A, E–F View FIGURE 1 , 4B View FIGURE 4 ).
Diagnosis
Bursaphelenchus gerberae n. sp. is distinguished from other described species of Bursaphelenchus by significant molecular sequence differences in the nearfull length small subunit (SSU) rDNA (GenBank accession number = AY508024 View Materials ), D2D3 expansion segments of the large subunit (LSU) rDNA ( AY508092 View Materials ) and partial mitochondrial DNA COI ( AY508055 View Materials ) ( GiblinDavis et al. 2005; Ye et al. 2006). In addition, B. gerberae n. sp. can be differentiated from those Bursaphelenchus that are closest to it morphologically and molecularly by a combination of character differences in stylet, rostrum, condylus, and lamina shape of male spicules, and c’ and postuterine sac length in females.
Relationships Bursaphelenchus gerberae n. sp. is closest to Bursaphelenchus hylobianum Korentchenko 1980 , B. paracorneolus Braasch 2000 and B. hofmanni Braasch 1998 based upon a tree inferred from near full length SSU sequences from 37 isolates of 20 species ( GiblinDavis et al. 2005; Ye et al. 2006). These species and B. corneolus Massey 1966 , which has not been sequenced, share the morphological characters of three lateral incisures (except B. hylobianum with two and B. corneolus with an unknown number), male caudal papillae arrangement (single preanal P1 papilla, pair of pre/adanal P2 papillae, pair of postanal P3 papillae, and one pair of small P4 papillae at base of bursa), separate mittenshaped spicules with cucullae, female vulva a domeshaped slit in ventral view which gives the appearance of a small vulval flap in lateral view, but is not a true vulval flap, and female tail strongly ventrally recurved. In addition to significant molecular sequence differences ( GiblinDavis et al. 2005; Ye et al. 2006), Bursaphelenchus gerberae n. sp., which possesses a stylet with small basal swellings, rounded bursa in ventral view, a pointed rostrum and an elongate and truncate condylus with slight posterior recurvature, spicules recurved so that lines drawn through the anteriormost points along the capitulum and extending the posterior dorsal lamina intersects ventrally at about a 14º angle ( Figs. 1J–O View FIGURE 1 , 4C View FIGURE 4 ), postuterine sac about 3 vulva body diameters long (54% of vulvalanus distance), and a female tail c’ of 4.8 (4.4–5.6), can be differentiated from B. paracorneolus because it possesses a bursa with a truncate posterior edge in ventral view, condylus rounded with no posterior recurvature ( Fig. 4E View FIGURE 4 ), and a female tail c’ of less than 3.8. Bursaphelenchus hofmanni can be differentiated from B. gerberae n. sp. because of the following characteristics; a digitate rostrum and rounded condylus with no posterior recurvature, spicules recurved so that lines drawn through the anteriormost points along the capitulum and extending the posterior dorsal lamina intersects dorsally at 10–29º ( Fig. 4D View FIGURE 4 ), and a female tail c’ of less than 3.4. Bursaphelenchus hylobianum can be separated from B. gerberae n. sp. because both sexes have two lateral incisures and males possess spicules with a blunt and rounded rostrum and the cucullus shape gives spicule tips a characteristic broadly truncate appearance in lateral view ( Fig. 4F View FIGURE 4 ). Lastly, B. corneolus differs from B. gerberae n. sp. because it lacks basal stylet swellings in both sexes and the postuterine sac is about 4.4 vulva body diameters long or about 67% of vulvalanus distance in females.
Biological characteristics
The life history of B. gerberae n. sp. is different from all other known species of Bursaphelenchus in that it is the only known mycophagous species that is associated with the palm weevil, Rhynchophorus palmarum (Gerber & GiblinDavis 1990A). Bursaphelenchus cocophilus , the other Bursaphelenchus species known to be associated with R. palmarum , is an obligate plant parasite. Although coconut is the plant host, it was a dying tree, which may or may not be important relative to the natural history of this nematode.
Type host and locality
Holotype male and allotype female and paratypes are from a 28dayold culture on M. fructicola . The original culture was started with dauer juveniles of B. gerberae n. sp. isolated during a dissection of R. palmarum from a red ring diseased coconut palm from Manzanilla, Trinidad (10.49805º N; 61.04824º W) in 1988.
Type designations
Holotype male and allotype female and additional material deposited at the University of CaliforniaRiverside Nematode Collection . Paratypes (males and females same data as holotype) deposited at the University of California , Davis ; USDA Nematode Collection , Beltsville , Maryland ; and the Nematology Department, Rothamsted Experiment Station, Harpenden Herts., England .
Etymology
This species name is derived from the family name of Dr. Karin Gerber, in her honor, for her discovery of this nematode during her postdoctoral research in Trinidad with the first author.
Laboratory culture
Monilinia fructicola was a suitable host for B. gerberae n. sp. The mean yields per plate after 7, 14, 21, and 28 days post inoculation were 63,000 + 26,576, 601,800 + 14,425, 269,200 + 49,215, and 351,900 + 46,188, respectively. This suggests similar population dynamics to what has been reported for other species of Bursaphelenchus on M. fructicola ( Giblin & Kaya 1984) .
| USDA |
United States Department of Agriculture |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |