Begonia gemella Warb. ex L.B.Sm & Wassh. [§ Petermannia
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.24823/EJB.2022.405 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10524585 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03FFFE04-FFB2-FFC3-FF94-17A69F20FCC9 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Begonia gemella Warb. ex L.B.Sm & Wassh. [§ Petermannia |
| status |
|
7. Begonia gemella Warb. ex L.B.Sm & Wassh. [§ Petermannia View in CoL ], Phytologia 52: 443 (1983).
– Type: Indonesia, Sulawesi, Minahasa , Koorders, S.H. 16243B (lectotype K [K000761119], designated by Smith & Wasshausen [1983: 443]; isolectotype B [B100217767]). Begonia gemella Warb. ex Koord., Natuurw. Tijdschr. Ned. - Indië 63: 91 (1904), nom. nud. Figure 5 View Figure 5 .
Perennial, monoecious herb, creeping up to c. 1 m long. Stem creeping, internodes 1.5–4 cm long, brownish-greenish, glabrous except for microscopical glandular hairs. Leaves basifixed, alternate; stipules persistent, 5–8 × 4–5 mm, isophyllus, ovate, with an abaxially slightly prominent midrib, apex narrowed into a bristle projecting up to 1 mm, margin entire, white-pinkish, translucent, abaxially glabrous; petioles 7.5–11 cm long, terete, concolorous with the stem, glabrous except for microscopic glandular hairs and very sparse pilose hairs on the joint of the petiole and lamina; lamina 5–9.5 × 4.5–8 cm, asymmetrical, broadly ovate to suborbicular, base cordate and lobes sometimes slightly overlapping, apex acuminate, margin denticulate to shallowly lobed, adaxial surface green, with red line along the margin, glabrous, abaxial surface pale green, glabrous; venation palmate-pinnate, primary veins 6–8, actinodromous, secondary veins craspedodromous. Inflorescences protogynous; female inflorescences basal to male, single-flowered, peduncles 7–11 mm long, green-reddish, glabrous, bracts stipule-like, 5–6 × 3 mm, ovate, reddish, glabrous, translucent, bracteoles persistent, anisophyllus, ovate to broadly ovate, c.3 × 4 mm, reddish, glabrous, translucent; male inflorescence a thyrse composed of up to 3 monochasial partial inflorescences with shortly developed internodes, each with up to 4 flowers, primary peduncle 1.5–2 cm long, partial inflorescence peduncle 1.5–4 cm long, shorter towards the apex, bracts persistent, stipule-like, 3–5 × 2–3 mm, ovate, reddish, translucent, midrib slightly prominent projecting up to 0.5 mm at the apex, bracteoles persistent, minute, hair-like. Male flowers: pedicels 15–18 mm long, white-pinkish, glabrous; tepals 2, white to white tinged with pink or greenish, 8.5–16.5 × 11–13 mm, broadly ovate, base slightly cordate, apex rounded, outer surface glabrous; androecium of 75–77 stamens, yellow, filaments up to c. 1.5 mm long, slightly fused at the very base, anthers up to c. 1 mm long, oblong to narrowly obovate, dehiscing through unilaterally positioned slits that are c.1/2 as long as the anthers. Female flowers: pedicels 7–10 mm long, reddish-greenish, glabrous; bracteoles persistent, tepals 5, white tinged with pink, 10–16 × 5–8 mm, obovate, outer surface glabrous; ovary (excluding wings) c.10 × 5–6 mm, narrowly obovate, red, glabrous, locules 3, placentation axile, placentae bilamellate, wings 3, equal, greenish-reddish, base rounded apex truncate to rounded, up to 8 mm at the widest point (apically or subapically); style c. 4 mm long, basally fused, 3-branched, each stylodium bifurcate in the stigmatic region, stigmatic surface a spirally twisted papillose band, orange. Fruits: peduncles 7–13 mm long; pedicels 8–11 mm long, bracteoles persistent; seed-bearing part (excluding the wings) 11–12 × 6–7 mm, obovate, glabrous, dehiscent, splitting along the wing attachment, wing shape as for ovary, up to 9 mm at the widest point (apically or subapically). Seeds barrel-shaped, c. 0.2 mm long.
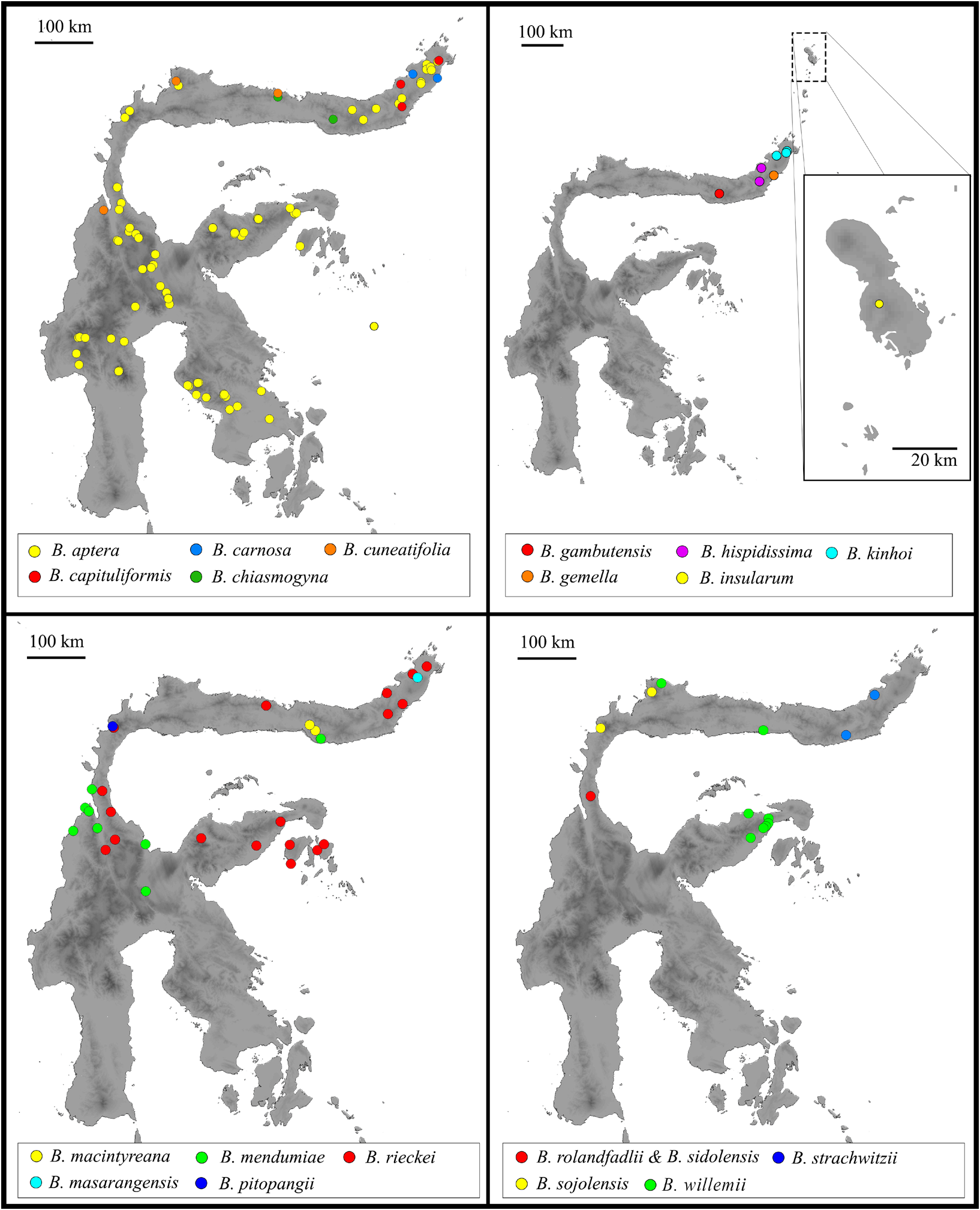
Distribution. Indonesia: endemic to Sulawesi, North Sulawesi Province (eastern North biogeographical region), Southeast Minahasa, Ratatotok (see Figure 2 View Figure 2 ).
Habitat. This species grows on lowland limestone karst walls, in disturbed habitats, in half shade to full shade, at 20–250 m elevation.
Etymology. The name is derived from Latin gemellus (‘a twin’, ‘twin-born’), probably in reference to the few-flowered male inflorescences.
Proposed IUCN conservation category. Critically Endangered (CR), B1ab(iii)+B2ab(iii). Begonia gemella is known from only two collections from small patches of limestone karst in Ratatotok, Southeast Minahasa. The area is not legally protected, and the type locality is in a very accessible area at a roadside. Potential threats, such as mineral mining activities and agriculture (coconut and cocoa plantations), were observed in the vicinity. Given the very small AOO (4 km 2), this indicates that the species should be considered Critically Endangered ( IUCN Standards and Petitions Subcommittee, 2019).
Additional specimens examined. INDONESIA. Sulawesi. Northern arm of Sulawesi. Eastern North Sulawesi: Cultivated, Ratatotok, Minahasa, W.H. Ardi, WI s.n. ( KRB) ; Sulawesi, Basaan, Ratatotok, Southeast Minahasa : 3 ii 2019, W.H. Ardi WI402 ( BO, CEB, FIPIA; SING) ; 3 ii 2019, W.H. Ardi WI403 ( BO, CEB, FIPIA, SING) .
Creeping stems are relatively rare in the large Begonia section Petermannia but can be found in several species endemic to Sulawesi ( B. carnosa , B. flacca Irmsch. , B. gemella , B. mattampensis Ardi & D.C.Thomas ). Begonia gemella is similar to B. carnosa in that it has a creeping stem and grows in limestone karst habitats, but it differs by its glabrous stem and petiole (vs sparsely to moderately hairy stem and petioles), 1-flowered female inflorescences and a shorter peduncle 0.7–1.1 cm long (vs [1- or] 2-flowered, peduncle 2–5 cm long), and the male inflorescence is a thyrse composed of up to 3 monochasial partial inflorescences with shortly developed internodes, each with up to 4 flowers, and partial inflorescence peduncle 1–4 cm long (vs a thyrse composed of up to 3 cymose partial inflorescences, each branching dichasially with up to 5–8 flowers, and peduncles of the partial inflorescences 2.5–7 cm long).
| KRB |
KRB |
| FIPIA |
FIPIA |
| SING |
SING |
| KRB |
Kebun Raya Bogor |
| BO |
Herbarium Bogoriense |
| CEB |
Tadulako University |
| FIPIA |
Institut Teknologi Bandung |
| SING |
Singapore Botanic Gardens |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |