Cytospora piceae Fan, 2018
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/phytotaxa.383.2.4 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10530819 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03FD87D4-FF80-8360-FF05-02B64F3A8E7D |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe (2021-05-24 22:38:05, last updated 2024-01-19 00:41:19) |
|
scientific name |
Cytospora piceae Fan |
| status |
|
Cytospora piceae Fan View in CoL Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3
MycoBank 828432
Holotype:— China, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, Bole Mongol Autonomous Prefecture , 44°46’13.44”N, 81°13’58.72”E, from branches of Picea crassifolia , July 2017, C.M. Tian & X.L. Fan, holotype CF 20176561, ex-type living culture CFCC 52841. GoogleMaps
Etymology:—Named after the host genus on which it was collected, Picea .
Descriptions:—Asexual state: Conidiomata pycnidial, ostiolated, immersed in bark, scattered, erumpent through the surface of bark when mature. Locules multiple, discoid, circular to ovoid, arranged vesicularly with common walls, (680–)720–1190(–1200) μm (= 945 ± 130 µm, n = 30) in diam. Conceptacle absent. Ectostromatic disc white to light brown, circular, disc dark, (160–)230–290(–310) µm (= 255 ± 36 µm, n = 30) in diam., with one ostiole in the centre of disc. Ostiole conspicuous, circular to ovoid, dark brown to black at the same level as the disc, (65–)70–115(– 130) µm (= 93 ± 17 µm, n = 30) in diam. Conidiophores hyaline, branched at base or not branched, thin walled, filamentous, (12–)13.5–19.5(–20) μm (= 16.5 ± 3 µm, n = 30). Conidiogenous cells enteroblastic, polyphialidic. Conidia hyaline, allantoid, eguttulate, smooth, aseptate, thin-wall, (4.5–)5–5.5(–6) × 1–1.5 µm (= 5.2 ± 0.3 × 1.3 ± 0.1 µm, n = 50). Sexual morph: not observed.
Culture characteristics: Cultures on PDA are initially white, becoming saffron after one week. The colonies are tight, thin with a uniform texture, lacking aerial mycelium, up to 1.8 cm after four weeks. Sterile.
Materials examined: — China, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, Bole Mongol Autonomous Prefecture , 44°46’15.32”N, 81°13’57.54”E, from branches of Picea crassifolia , July 2017, C.M. Tian & X.L. Fan, deposited by X.L. Fan, CF 20176562, living culture CFCC 52842 GoogleMaps .
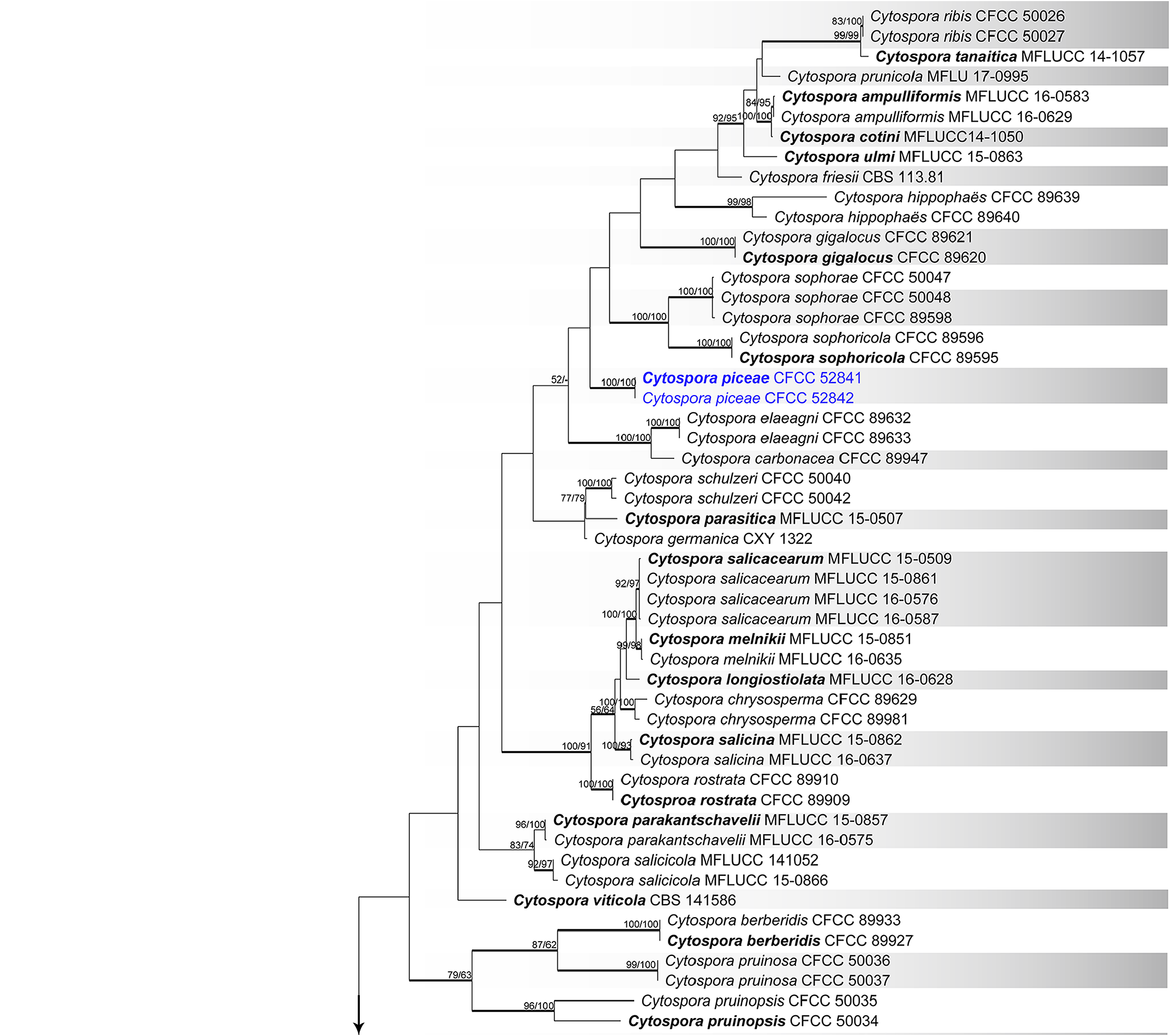
Notes:— Cytospora piceae is associated with canker disease of Picea crassifolia . The phylogenetic inferences resolved this species as a confused clade in ITS phylogram ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 ), which was closed to Cytospora friesii and C. mougeotii . To clarify this clade, the second analysis indicated this species represented an individual clade with high support value (MP/ML/BI = 100/100/1) based on combined multilocus gene phylogenetic analysis, which was distinguish from other available species ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 ). Morphologically, Cytospora piceae has larger conidia than those of C. friesii (5–5.5 × 1–1.5 vs. 4–5 × 1 µm), and wider than C. mougeotii (5–5.5 × 1–1.5 vs. 5–7 × 0.7–1 μm) ( Saccardo 1884). Cytospora piceae is thus here considered as a novel species.
Saccardo, P. A. (1884) Sylloge fungorum 3. Typis Seminarii, Italy.
FIGURE 1. Phylogram of Cytospora based on ITS gene. MP and ML bootstrap support values above 50 % are shown at the first and second position. Thickened branches represent posterior probabilities above 0.95 from BI. Ex-type strains are in bold. Strains in current study are in blue.
FIGURE 2. Phylogram of Cytospora based on combined ITS, LSU, ACT, RPB2 and TEF1-α genes. MP and ML bootstrap support values above 50 % are shown at the first and second position. Thickened branches represent posterior probabilities above 0.95 from BI. Ex-type strains are in bold. Strains in current study are in blue.
FIGURE 3. Morphology of Cytospora piceae from Picea crassifolia (CF 20176561).A, B: Habit of conidiomata on twig. C: Transverse section of conidioma. D: Longitudinal section through conidioma. E: Conidiophores and conidiogenous cells. F: Conidia. G: Colonies on PDA after two weeks. Scale bars: B–D = 500 μm; E–F = 5 μm.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |