Sthenelais boa ( Johnston, 1833 )
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5852/ejt.2021.740.1287 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:A1E7F84F-49D0-4DA8-94E6-77E8CA68098F |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4650581 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03FC87CE-1A2A-1644-FDDB-F121FC26FBAE |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Sthenelais boa ( Johnston, 1833 ) |
| status |
|
Sthenelais boa ( Johnston, 1833) View in CoL (emended)
Figs 3–4 View Fig View Fig , 5A–D View Fig
Sigalion boa Johnston, 1833: 322 View in CoL , fig. 42.
Sigalion Idunae Rathke, 1843: 150–155 View in CoL , pl. 9 figs 1–8 (fide Malmgren 1866).
Sthenelais ctenolepis Claparède, 1868: 398 View in CoL , pl. 4 fig. 1a–k, pl. 6 fig. 2 (see Barnich & Fiege 2003).
Sthenelais fuliginosa Claparède, 1868: 404 View in CoL , pl. 4 fig. 2a–h (see Barnich & Fiege 2003).
Sthenelais minor Pruvot & Racovitza, 1895: 465 View in CoL , pl. 20 figs 111–121. Syn. nov.
? Sigalion Estellae Guérin-Méneville, 1843: 2 View in CoL , pl. 1 fig. 1 (see Fauvel 1923; however, description insufficient).
? Sthenelais Audouinii Quatrefages, 1866: 275 View in CoL (see Fauvel 1923; indeterminable according to Chambers & Muir 1997, description by Quatrefages referring to Leanira View in CoL or Sthenelais View in CoL ).
? Sthenelais Edwardsii Quatrefages, 1866: 273 View in CoL (see Fauvel 1923; however, description insufficient).
? Sthenelais Leidyi Quatrefages, 1866: 278 View in CoL (see Pettibone 1963; however, status questionable, see remark below).
Sthenelais boa View in CoL – McIntosh 1900: 408, pl. 26 figs 7–8, pl. 26a fig. 21, pl. 29 fig. 1, pl. 31 fig. 5, pl. 33 fig. 16, pl. 34 fig. 6, pl. 41 figs 19–23. — Fauvel 1923: 110, fig. 41a–l. — Chambers 1985: 27, figs 2c, 12, 15a, 16a–c, 21a. — Hartmann-Schröder 1996: 81, fig. 27. — Chambers & Muir 1997: 155, fig. 50. — Barnich & Fiege 2003: 130, fig. 64. — Wehe 2007: 102, fig. 20. — Gil 2011: 946. — Núñez et al. 2015: 241, fig. 97.
Sthenelais minor View in CoL ? – Saint-Joseph 1899: 171 (specimen checked by Chambers & Muir 1997 = juvenile of Sthenelais boa View in CoL ).
Fimbriosthenelais minor View in CoL – Pettibone 1971: 35–37, fig. 23. — Barnich & Fiege 2003: 117–119, fig. 59. — Gil 2011: 940. — Núñez et al. 2015: 221, fig. 89.
Diagnosis
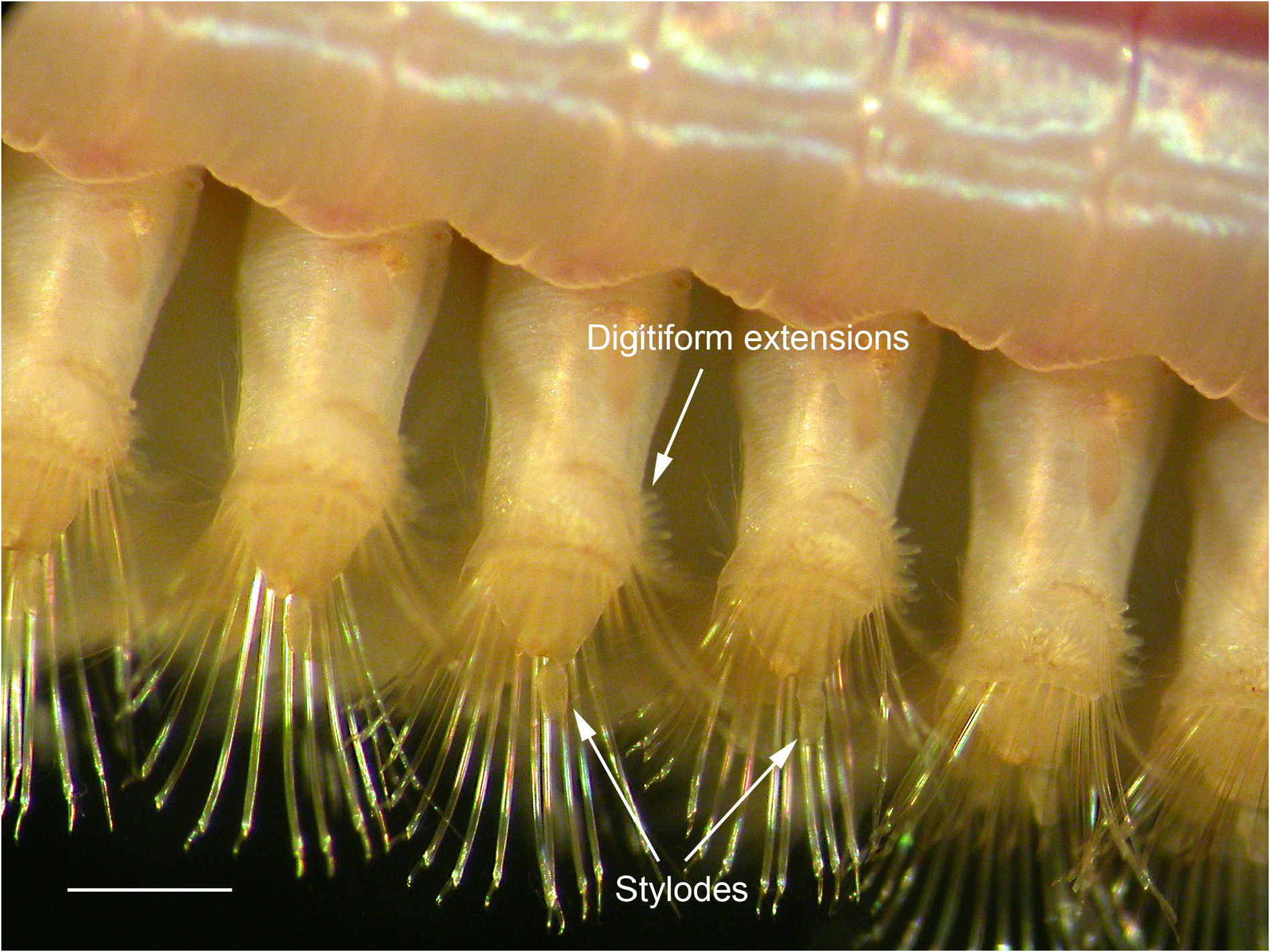
Dorsal cirri absent on segment 3. Ventral body surface smooth. Outer elytral margin straight, with filiform papillae; elytral surface covered by conical microtubercles. Parapodial stylodes smooth (except for minute papillae in parapodia of juveniles or in anteriormost parapodia of adults), more or less clubshaped; notopodia without long dorsal papillae; margins of anterior neuropodial bracts with digitiform extensions. Notochaetae tapering to simple or minutely bidentate capillary tip.
Type material (examined)
UNITED KINGDOM • 2 syntypes; North Sea , Berwick Bay , Northeast England ; EtOH preserved; BMNH 1921.12.16.1 .
The type material of the following species is probably lost or has never been deposited (type localities in brackets): Sigalion Idunae ( Norway, Molde, Northeast Atlantic), Sthenelais ctenolepis and Sthenelais fuliginosa ( Italy, Gulf of Naples, W Mediterranean Sea), Sthenelais minor ( France, near Banyuls, W Mediterranean Sea), Sigalion Estellae and Sthenelais Audouinii ( France, Northeast Atlantic), Sthenelais Edwardsii ( France, Boulogne and St-Vaast, Northeast Atlantic), Sthenelais Leidyi ( United States, New Jersey, NW Atlantic).
Other material (examined)
CROATIA • 1 spec.; central Mediterranean Sea , Adriatic Sea , Rovinj , near Banjole; stn ROV99-02; 45°5.47′ N, 13°36.32′ E; depth 26 m; 20 Aug 1999; EtOH preserved; SMF 10598. (in Barnich & Fiege 2003 as Fimbriosthenelais minor ) GoogleMaps
FRANCE • 1 spec.; W Mediterranean Sea , Banyuls-sur-Mer ; Posidonia beds; depth 5 m; 19 Mar 1997; EtOH preserved; SMF 10629. ( Fig. 4C, F–I View Fig )
IRELAND • 3 specs; Irish Sea , Arklow Bank ; stn ASUARK06 D06a; 5 Oct. 2006; EtOH preserved; TUM 39683. ( Fig. 4A–B, D–E View Fig , 5A–D View Fig )
THE NETHERLANDS • 1 spec.; E Schelde estuary , Zandkreekdam ; stn ZLOSZK4; 51.55° N, 3.88° E; 1 m depth; 30 Jan. 2006; EtOH preserved; Eurofins TvH collection 335780 GoogleMaps • 1 spec.; E Schelde estuary , Vondelingenplaat ; stn ZLOSV5; 51.57° N, 3.94° E; 1 m depth; 11 Feb. 2008; EtOH preserved; Eurofins TvH collection 351374 GoogleMaps • 1 spec.; North Sea , artificial reef ; stn 10-80 ZUID/NZKR1; 52.25° N, 4.29° E; 18 m depth; 19 Oct. 1994; EtOH preserved; Eurofins TvH collection 10855 GoogleMaps • 1 spec.; Voordelta , W of Westenschouwen ; stn RefZRand_95; 51.68° N, 3.65° E; 17 m depth; 8 Oct. 2018; EtOH preserved; Eurofins TvH collection 429007 GoogleMaps • 3 specs; Voordelta , N of Domburg ; stn RefZuid_372; 51.64° N, 3.39° E; 20 m depth; 14 Sep. 2018; EtOH preserved; Eurofins TvH collection 429132 GoogleMaps • 4 specs; Voordelta , near Brouwersdam; stn BB_zra_168 rv01; 51.78° N, 3.85° E; 4 m depth; 5 Sep. 2018; EtOH preserved; Eurofins TvH collection 429068 GoogleMaps • 1 spec.; Voordelta , W of Visschershoek ; stn BVO_614; 51.79° N, 8.80° E; 3 m depth; 28 Sep. 2018; EtOH preserved; Eurofins TvH collection 429209 GoogleMaps .
UNITED KINGDOM • 1 spec.; S England , Portland Harbour ; stn MBIPH0905 FDD1a; 2005; EtOH preserved; TUM 37130 • 1 spec.; Isle of Wight ; stn CEFEIOW06 G12c; 2006; EtOH preserved; TUM 39122 .
Further Mediterranean material see Barnich & Fiege (2003).
Description
PROSTOMIUM. Median antenna with long, smooth, tapering style; ceratophore with large auricles. Lateral antennae fused to inner dorsal side of tentaculophores, very short, not reaching half the length of dorsal tentacular cirri. Two pairs of eyes present ( Fig. 4A View Fig ).
TENTACULOPHORES. Dorsal tentacular cirri long, size and shape similar to median antenna. Ventral tentacular cirri slightly shorter than dorsal ones ( Fig. 4A View Fig ).
ELYTRA. With filiform and shorter, clavate papillae on outer lateral margin and surface covered by conical microtubercles ( Fig. 4B–C View Fig ).
CIRRI. Dorsal cirri absent from segment 3. Ventral cirri with basal knob but without long basal papillae.
PARAPODIA. Stylodes without papillae, more or less club-shaped (occasionally minute papillae present in parapodia of juveniles or in anteriormost parapodia of adults) ( Fig. 5A–D View Fig ). Parapodia of anterior and middle body with stylodes variably present on anterior side of notopodial bract, on neuropodial acicular lobe and on lower part of bilobed posterior neuropodial bract. Margins of neuropodial anterodorsal and anteroventral bracts with digitiform extensions. Without long dorsal papillae on notopodia ( Figs 3 View Fig , 4D–E View Fig ).
CHAETAE. Notochaetae slender, spinous, tapering to simple or minutely bidentate capillary tip. Upper neurochaetae mainly slender compound falcigers with multi-articled blade and minutely bidentate tip and few simple, spinous chaetae. Middle neurochaetae stout compound falcigers with short singlearticled blade and bidentate tip. Lower neurochaetae slender compound falcigers with multi-articled blade and minutely bidentate tip ( Fig. 4F–I View Fig ).
SIZE. Length up to 200 mm, width up to 10 mm for about 200 segments (see Chambers & Muir 1997). Syntypes of Sigalion boa (BMNH 1921.12.16.1): 1 complete specimen, length about 170 mm, width 7 mm for about 205 segments; 1 complete specimen, length about 140 mm, width 7 mm for about 195 segments. Specimens figured: TUM 39683: anterior fragments: large specimen width 6 mm ( Figs 4A–B, D–E View Fig , 5A–B View Fig ); medium specimen width 4 mm ( Fig. 5C View Fig ), small specimen width 3 mm ( Fig. 5D View Fig ); SMF 10629: anterior fragment, width 3.5 mm ( Fig. 4C, F–I View Fig ).
Remarks
The description above is emended for the potential presence of minute papillae on the stylodes of anteriormost parapodia in adults (and in general in parapodia of juveniles) and for terminology used in description of the neuropodial bracts.
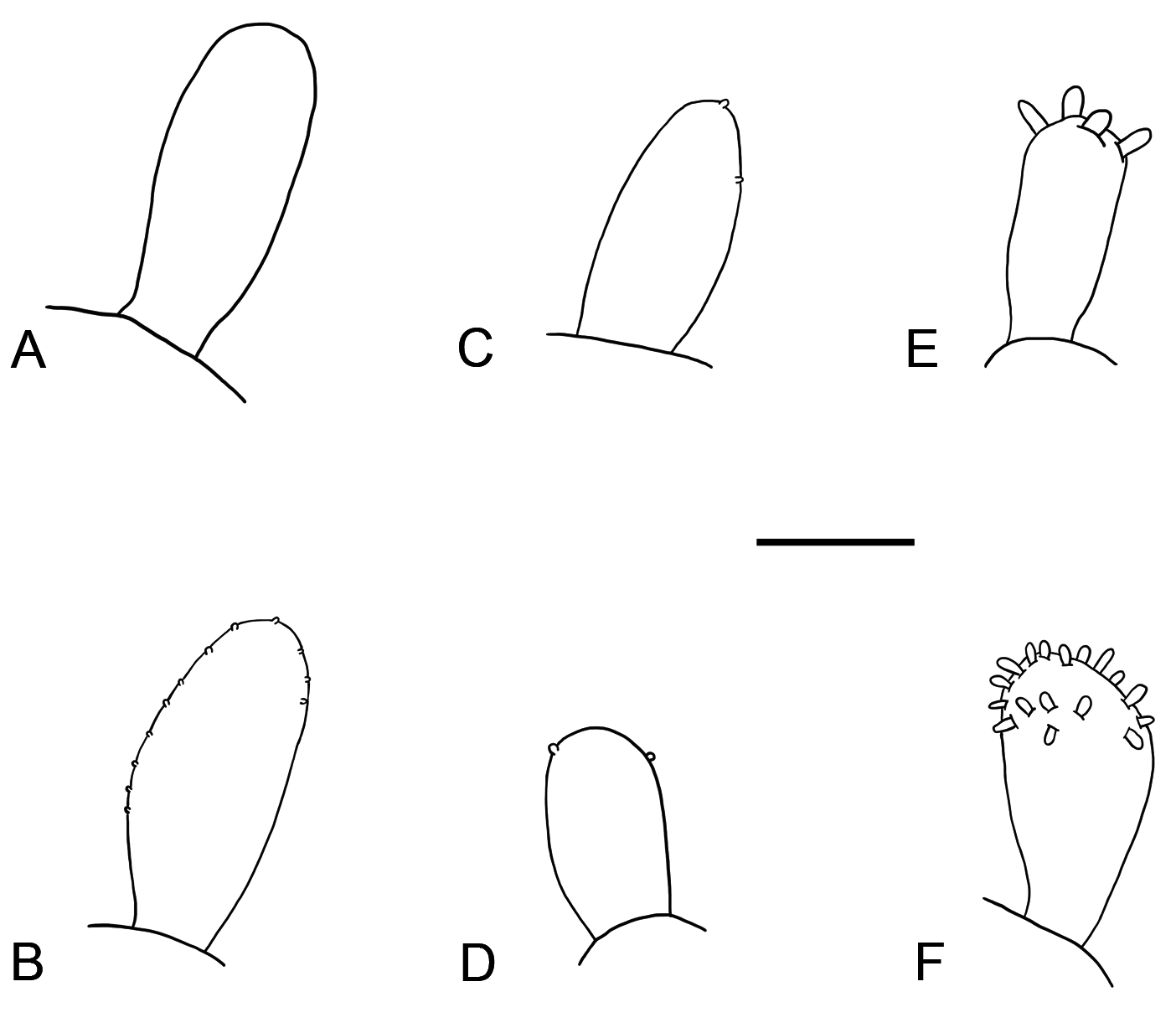
After examination of numerous specimens (see above), we agree with Chambers & Muir (1997) that adult Sthenelais boa have smooth stylodes on the majority of parapodia, but can have minute papillae on the stylodes of some anterior parapodia. Also juveniles may have minutely papillated stylodes.
Chambers & Muir (1997) checked Saint-Joseph’s specimen of Sthenelais minor ?, which was used by Pettibone (1971) for the description of Fimbriosthenelais minor , and concluded that this specimen is a juvenile of Sthenelais boa . Consequently, they listed Fimbriosthenelais minor sensu Pettibone as a synonym, but they did not include Sthenelais minor Pruvot & Racovitza, 1895 in the synonymy.
Although the type material of Sthenelais minor is probably lost, the original description and figures clearly show the diagnostic characters of Sthenelais boa . We, therefore, confirm the synonymy of both species.
The presence of minute papillae on the stylodes of Sthenelais boa leaves us with a taxonomic dilemma regarding the validity of the genus Fimbriosthenelais . This has been discussed in the past by Barnich & Fiege (2003) and Gil (2011).According to Pettibone (1971), the genus Fimbriosthenelais was established for species with papillated stylodes, while the stylodes of Sthenelais are smooth. Thus, we could agree with Chambers & Muir (1997) and move all species of Fimbriosthenelais back into Sthenelais .
During this study, however, we noted that under moderate magnification (compound microscope 400 ×) the papillae on the stylodes of Fimbriosthenelais longipinnis and F. zetlandica are much larger and more easily observed than on the stylodes of Sthenelais boa , where, if present at all, they are minute and difficult to see. To allow for a comparison of the sizes of these papillae, Fig. 5 View Fig presents stylodes of the different species drawn to the same scale.
For the time being, we suggest to emend the respective generic diagnoses and preserve the genus Fimbriosthenelais . Further studies, including also new species described after Pettibone’s revision from
other parts of the world and combining morphological and molecular data, would be helpful to support the validity of Fimbriosthenelais .
Sthenelais leidyi was a new name established by Quatrefages (1866) for Sigalion mathildae in Leidy (1855) [not Sigalion mathildae Audouin & Milne-Edwards, 1832 ]. Pettibone (1963) listed S. leidyi as a synonym of S. boa in her study of polychaetes from New England (NW Atlantic). The head figured by Leidy (1855) possibly shows a Sthenelais , but the description is insufficient to attribute it to any known species. We therefore consider this synonymy questionable for the time being, as a revision of species and type material outside the Northeast Atlantic is beyond the scope of this paper.
In Chambers & Muir (1997) Sigalion carringtonii Carrington, 1865 is listed as a synonym of Sthenelais boa without reference to examination of type material. Mackie & Chambers (1990), however, investigated the syntypes of S. carringtonii and placed it in synonymy with Sigalion mathildae Audouin & Milne Edwards, 1832 ; this view was already adopted earlier by McIntosh (1900) and Hartman (1959) and is followed herein.
Distribution and habitat
Widely reported throughout the area. In the Northeast Atlantic present around the British Isles (RB data, based on TUM reference collection, and Chambers 1985), in the Skagerrak ( Hartmann-Schröder 1996), the southern North Sea (south of the Frisian Front) (TvH data), along the French Atlantic coast ( Fauvel 1923) and around the Iberian Peninsula ( Núñez et al. 2015). In the Mediterranean Sea present in the Western and Eastern Mediterranean, the Adriatic and the Aegean Sea ( Barnich & Fiege 2003). Also recorded from other areas in the Atlantic and Indo-Pacific; however, these records require confirmation. Occurring on various substrates from shallow waters to 200 m depth.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Sthenelais boa ( Johnston, 1833 )
| Barnich, Ruth & Haaren, Ton Van 2021 |
Fimbriosthenelais minor
| Nunez J. & Barnich R. & Brito M. & Fiege D. 2015: 221 |
| Gil J. C. 2011: 940 |
| Barnich R. & Fiege D. 2003: 117 |
| Pettibone M. H. 1971: 35 |
Sthenelais boa
| Nunez J. & Barnich R. & Brito M. & Fiege D. 2015: 241 |
| Gil J. C. 2011: 946 |
| Wehe T. 2007: 102 |
| Barnich R. & Fiege D. 2003: 130 |
| Chambers S. J. & Muir A. I. 1997: 155 |
| Hartmann-Schroder G. 1996: 81 |
| Chambers S. J. 1985: 27 |
| Fauvel P. 1923: 110 |
| McIntosh W. C. 1900: 408 |
Sthenelais minor
| Saint-Joseph A. de 1899: 171 |
Sthenelais minor
| Pruvot G. & Racovitza E. G. 1895: 465 |
Sthenelais ctenolepis Claparède, 1868: 398
| Claparede E. 1868: 398 |
Sthenelais fuliginosa Claparède, 1868: 404
| Claparede E. 1868: 404 |
Sthenelais Audouinii Quatrefages, 1866: 275
| Quatrefages M. A. de 1866: 275 |
Sthenelais Edwardsii Quatrefages, 1866: 273
| Quatrefages M. A. de 1866: 273 |
Sthenelais Leidyi Quatrefages, 1866: 278
| Quatrefages M. A. de 1866: 278 |
Sigalion Idunae Rathke, 1843: 150–155
| Rathke H. 1843: 155 |
Sigalion Estellae Guérin-Méneville, 1843: 2
| Guerin-Meneville F. E. 1843: 2 |
Sigalion boa
| Johnston G. 1833: 322 |