Pomerantzia subterranea, Fan, Qing-Hai & Chen, Yan, 2005
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.169764 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5628175 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03FBBA7B-1832-FC7F-FC40-66BFFD0819DF |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Pomerantzia subterranea |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Pomerantzia subterranea sp. n. ( Figs. 1–9 View FIGURE 1 View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 View FIGURE 4 View FIGURE 5 View FIGURE 6 View FIGURE 7 View FIGURE 8 View FIGURE 9 )
Material examined
Holotype: adult female, CHINA: Fujian, Fuzhou, Jinshan Campus of Fujian Agricultural and Forestry University, from soil at a depth of 20 cm under Pinus sp. on shaded slopes of Miaofeng Hill, 2 Nov 2002, by Fan, Q.H. & Zhang, L.
Paratypes: 1 adult female, 2 tritonymphs and 1 deutonymph, same data as holotype; 2 adult females and 1 tritonymph, same data as holotype except date (30 Nov 2002); 1 tritonymph, same data as holotype except depth (40 cm).
All types are deposited in the College of Plant Protection, Fujian Agricultural and Forestry University, Fuzhou 350002, China.
Diagnosis
Female. Peritremes small, each side with 4 chambers. Setae c2 situated on platelets posterior to c1; setae h2 obviously posterior to h1. Ventral shields apart from coxae III. Aggenital valves bearing 4 pairs of setae. Genital valves bearing 5 pairs of setae. Ovipositor bearing at least 12 setae. Counts of setae and solenidia on legs I–IV: coxae (including 1a, 2 a, 3a and 4a) 4 + 1 elcp, 4, 4, 4; trochanters 1, 1, 2, 1; basifemora 5, 4, 3, 3; telofemora 5, 5, 4, 5; genua 12 + 1, 5, 5, 5; tibiae 12 + 3, 5 + 1, 5 + 1, 9 + 1; tarsi 18 + 7 + 1, 14 + 2, 11, 11.
Tritonymph. Peritremes, positions of c2 and h2, and ventral shields as in adult female, but aggenital valves bearing 3 pairs of setae; genital valves bearing 3 or 4 pairs of setae; coxa IV with 3 setae; genu I with 11 + 1; tibia IV with 7 + 1; tarsus I with 18 + 6 + 1.
Deutonymph. Peritremes, positions of setae c2 and h2 and ventral shields as in adult female, but aggenital and genital valves each bearing 2 pairs of setae; coxae III–IV with 3, 2; basifemora II–IV with 3, 1; telofemur IV with 4; genu I with 8 + 1; tibia II with 10 + 2 and IV with 6 + 1; tarsus I with 17 + 5 + 1.
Description
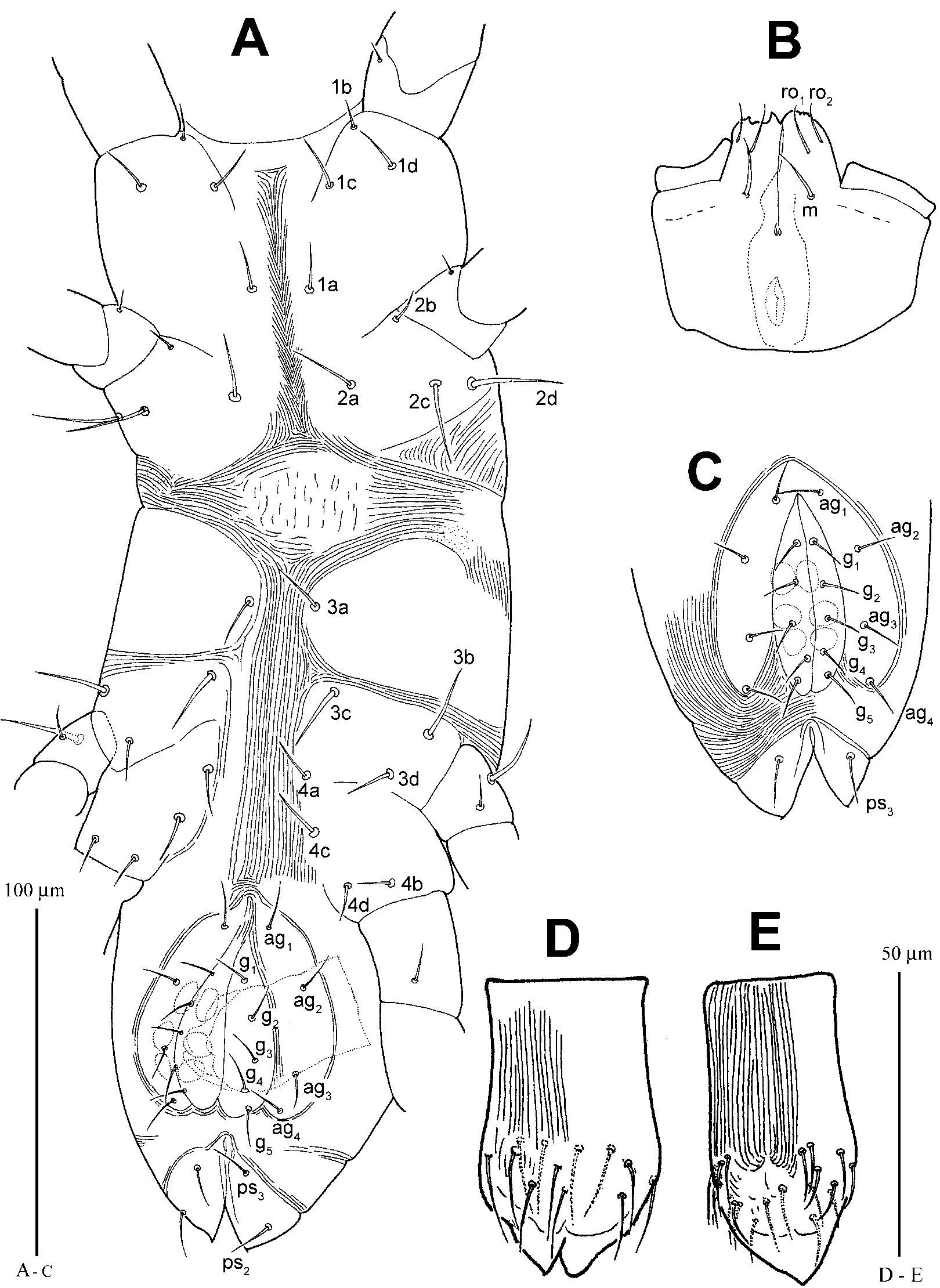
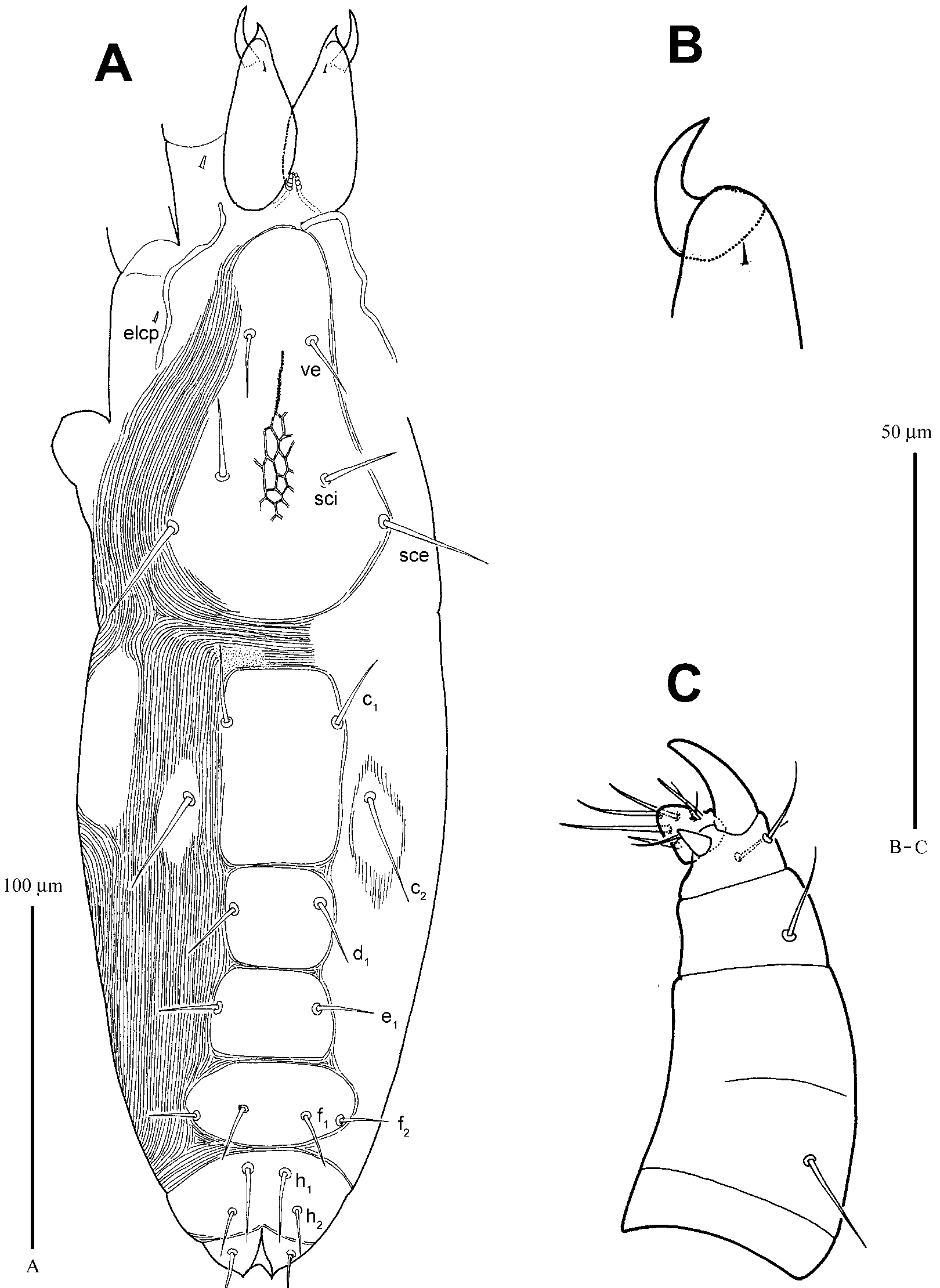
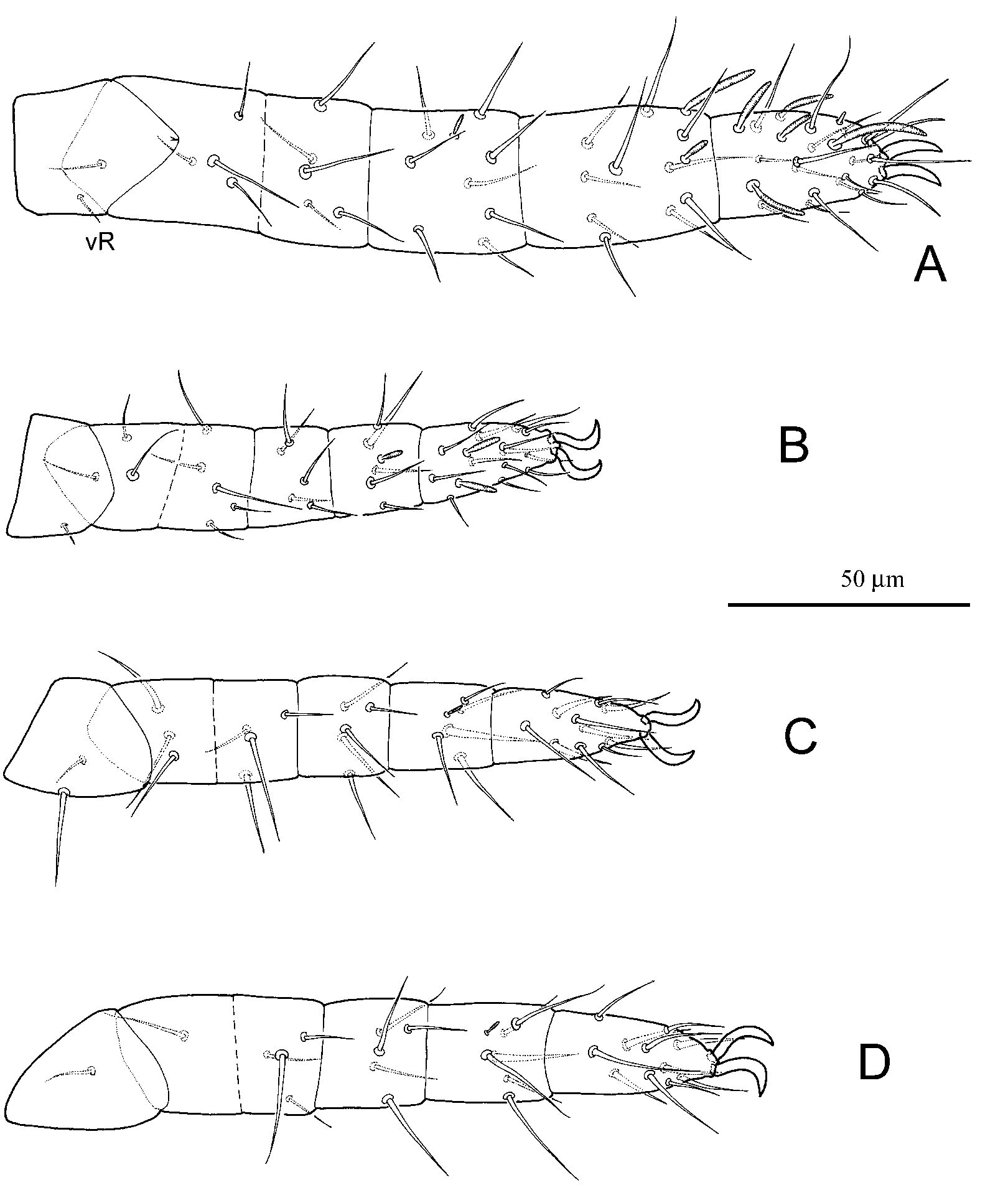
ADULT FEMALE ( Figs. 1–3 View FIGURE 1 View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 ; n=4)
Gnathosoma . Chelicerae (72 (72–75)) about 3.4× length of movable digits (21). Peritremes small, each side with 4 chambers. Palp 81 (79–81) long, palpfemur longer than length of palptibia plus palptarsus, terminal palptibial claw strong (18), accessory claw conical (6 (5–6)); counts of setae and solenidia from palptrochaner to palptarsus: 0, 1, 1, 2 + 1 terminal claw + 1 accessory claw, 4 + 1 + 4 eupathidia. Subcapitular setae m (17 (16– 17)) about as long as width of m–m (17), rostrum with 2 pairs of setae, ro1 (11) and ro2 (11 (10–11)).
Idiosoma. Narrowly oval in shape (341 (341–350) long, 118 (118–123) wide). All dorsal setae smooth. Prodorsal shield ornamented with a longitudinal refringent ridgelike mark conecting a reticulated band behind setae ve, bearing 3 pairs of setae, ve (20 (19– 20)), sci (23 (23–24)) and sce (35 (33–35)); distances: ve–ve 20 (19–20), ve–sci 43 (42– 43), sci–sci 31 (31–32) and sci–sce 21 (20–21). Hysterosomal shield C longitudinally rectangular, with 1 pair of setae, c1 (23 (20–23)), on its anterior half part; setae c2 (35 (31– 35)) obviously longer than other hysterosomal setae, situating on platelets posterior to c1; shields D and E, nearly square, each bearing 1 pair of setae, d1 (21 (19–21)) and e1 (20 (19–20)); shield F nearly trapezoid, bearing 2 pairs of setae, f1 (19 (18–19)) and f2 (15 (13–15)), f2 widely spaced and slightly posterior to f1; shield H trapeziform, bearing 2 pairs of setae, h1 (19 (17–19)) and h2 (17 (16–17)), h2 obviously posterior to h1; distances c1–c1 31 (31–35), c1–c2 28 (26–28), c1–d1 61 (60–61), d1–d1 26, d1–c2 38 (38–40), d1– e 1 29 (29–31), e1– e 1 31 (31–32), e1–f1 37 (37–40), f1–f1 20 (20–24), f1–f2 15, f1–h1 12, h1–h1 12, h1–h2 12 (12–16), h2–h2 16 (15–16).
Ventral setae simple, 1a 15 (14–15), 2a 20 (17–20), 3a 13 and 4a 12 (12–13). A pair of shields present anterior to coxae III. Aggenital valves bearing 4 pairs of setae, ag1 14 (13– 14), ag2 13 (12–13), ag3 12 (11–12) and ag4 12 (11–12). Genital valves bearing 5 pairs of setae, g1 11 (10–11), g2 11 (10–11), g3 10, g4 10 (9–10) and g5 10 (9–10). Ovipositor 42 long, 28 wide, bearing at least 12 setae (12 to 20 setae) (17 (16–17)). Pseudanal valves bearing 3 pairs of setae, ps3 13, ps2 15 (14–15) and ps1 18 (16–18).
Legs. Lengths of leg I 227 (222–227), leg II 139 (137–139), leg III 156 (145–156), leg IV 193 (191–193). Tibiae II and III each with a stout ventral seta (vm”), II vm” (22–23) obviously stronger and longer than others setae (11–15) on tibiae II, III vm” (23–24) stronger and longer than others setae (12–18) on tibiae III; tibia IV with two long strong setae (23–25). Tarsi II, III and IV each with 5 stout ventral setae. Counts of setae and solenidia on legs I–IV: coxae (including 1a, 2 a, 3a and 4a) 4 + 1 elcp, 4, 4, 4; trochanters 1, 1, 2, 1; basifemora 5, 4, 3, 3; telofemora 5, 5, 4, 5; genua 12 + 1, 5, 5, 5; tibiae 12 + 3, 5 + 1, 5 + 1, 9 + 1; tarsi 18 + 7 + 1, 14 + 2, 11, 11. Lengths of solenidia and famulus, I 7 (6.5–7), 1I 7.5 (7–7.5), 2I 18 (18–19), 3I 7.5 (7–7.5), p 1I 13 (13–14), p 2I 13, p 3I 12 (12–13), p 4I 14 (14–16), m I 8, I 2.5 (2.5–3), 1I 11 (11–12), 2 20 (20–22); II 7 (6–7), 1II 10 (9–10), 2II 10 (9–10), III 5 (5–6), IV 5 (4.5–5).
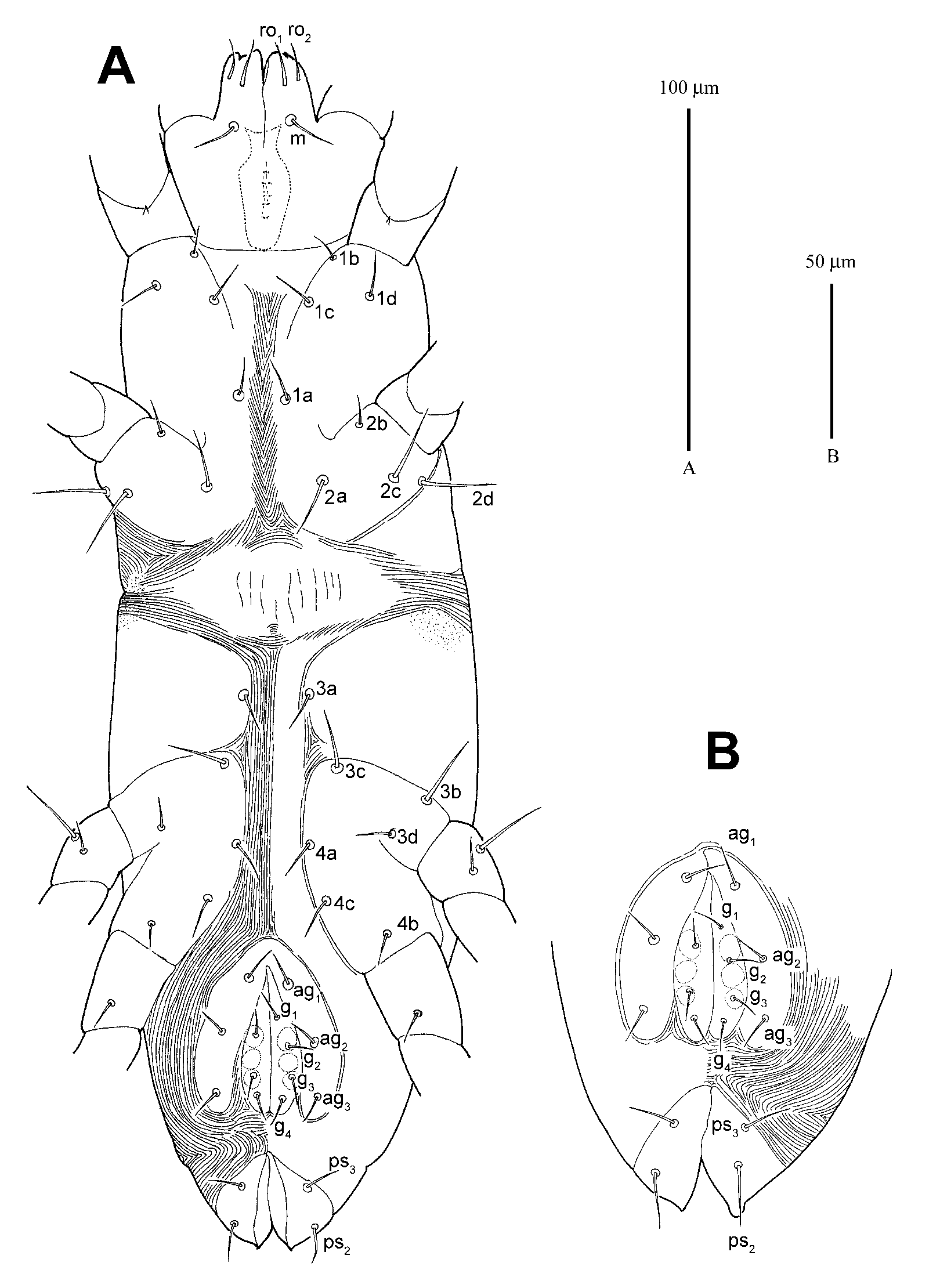
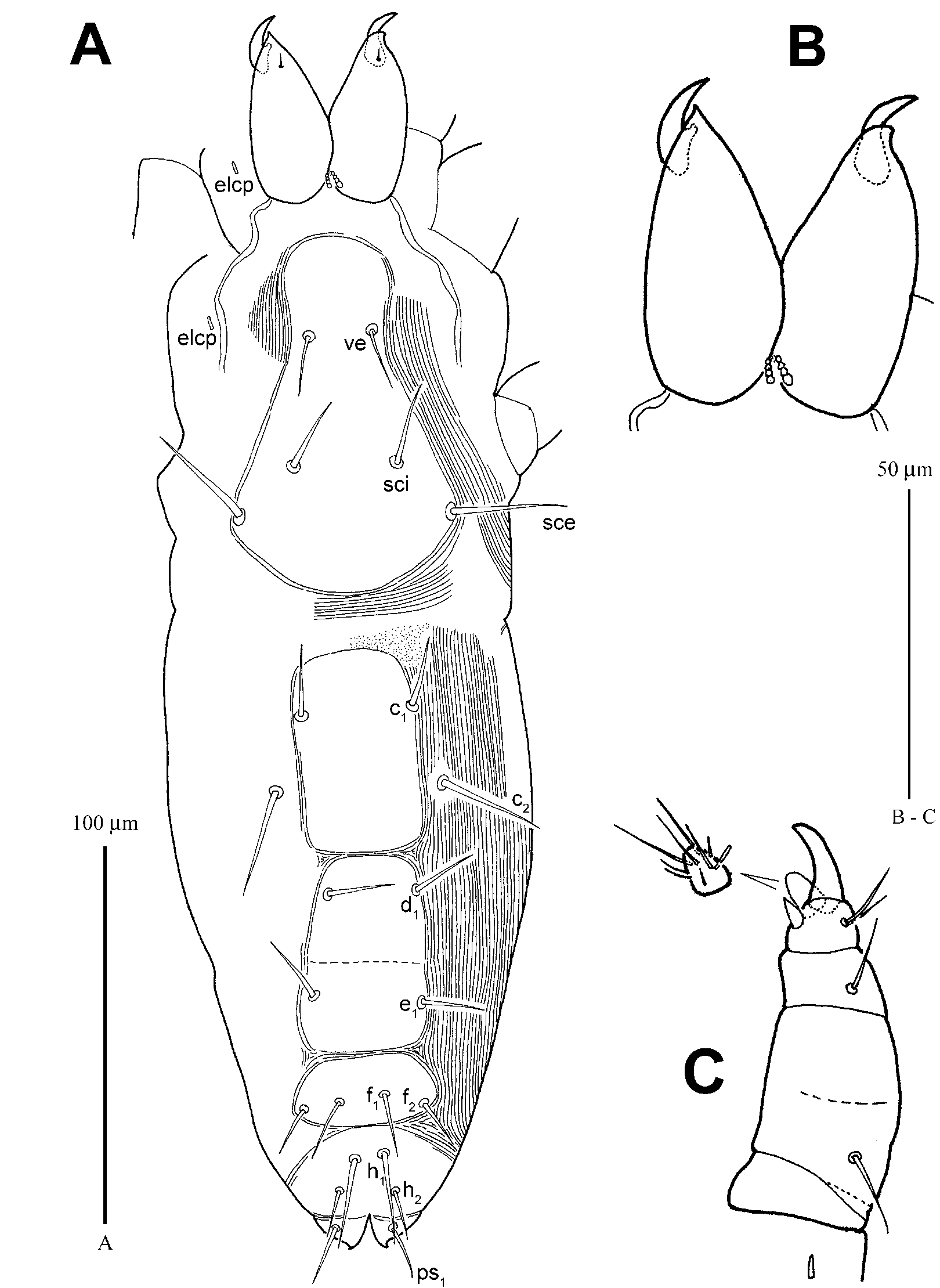
TRITONYMPH ( Figs. 4–6 View FIGURE 4 View FIGURE 5 View FIGURE 6 ; n=4)
Gnathosoma . Chelicerae (61 (60–61)) about 3.8× of movable digits (16 (16–17)). Palp 71 (70–71) long, terminal palptibial claw strong (16 (16–17)), accessory claw conical (5); counts of setae and solenidia as in adult female. Subcapitular setae m (16 (15–16)) about as long as width of m–m (14 (14–17)), rostrum with 2 pairs of setae, ro1 (10) and ro2 (10).
Idiosoma. Narrowly oval in shape (309 (289–309) long, 103 (103–105) wide). All dorsal setae smooth. Prodorsal shield ornamented with a longitudinal refringent ridgelike mark behind setae ve and reticulated between sci, bearing 3 pairs of setae, ve (17), sci (21 (21–22)) and sce (33 (33–34)); distances: ve–ve 19 (19–20), ve–sci 42 (37–42), sci–sci 29 (29–31) and sci–sce 21 (19–21). Hysterosomal shield C longitudinally rectangular, bearing 1 pair of setae, c1 (20 (18–20)), on anterior half part; setae c2 (30 (30–31)) obviously longer than other hysterosomal setae, situating on platelets posterior to c1; shields D and E, nearly square, each bearing 1 pair of setae, d1 (18 (18–20)) and e1 (18); shield F oval, bearing 2 pairs of setae, f1 (16 (16–18)) and f2 (13 (13–14)), f2 widely spaced and slightly posterior to f1; shield H trapeziform, bearing 2 pairs of setae, h1 (20 (19–20)) and h2 (17 (16–17)), h2 obviously posterior to h1; distances c1–c1 32 (31–32), c1–c2 25 (21–25), c1– d1 55 (50–55), d1–d1 25 (25–27), d1–c2 35 (31–35), d1– e 1 30 (28–30), e1– e 1 30 (27–30), e1–f1 30 (29–30), f1–f1 18 (18–20), f1–f2 14 (13–14), f1–h1 11 (11–12), h1–h1 11 (11–12), h1–h2 18 (11–18), h2–h2 15 (14–15).
Ventral setae simple, 1a 13, 2 a 16 (16–18), 3a 12 (12–13) and 4a 11 (11–13). A pair of shields present anterior to coxae III. Aggenital valves bearing 3 pairs of setae, ag1 10, ag2 9 and ag3 9. Genital valves bearing 3 setae on one side and 4 on the other side, g1 8 (8–10), g2 7 (7–9), g3 7 (7–9), g4 8 (8–9). Pseudanal valves bearing 3 pairs of setae, ps3 11, ps2 12 (12–13) and ps1 16 (15–16).
Legs. Lengths of leg I 197 (197–200), leg II 123 (123–125), leg III 139 (139–143), leg IV 167 (167–170). Tibiae II and III each with a stout ventral seta, II vm” (20) obviously longer than others setae (10–14), III vm” (20) longer than others (10–15); tibia IV with two long strong setae, obviously stronger and longer (20–21). Tarsi II, III and IV each with 5 strong ventral setae. Counts of setae and solenidia on legs I–IV: coxae (including 1a, 2a, 3a and 4a) 4 + 1 elcp, 4, 4, 3; trochanters 1, 1, 2, 1; basifemora 5, 4, 3, 3; telofemora 5, 5, 4, 5; genua 11 + 1, 5, 5, 5; tibiae 12 + 3, 5 + 1, 5 + 1, 7 + 1; tarsi 18 + 6 + 1, 14 + 2, 11, 11. Lengths of solenidia and famulus, I 7 (6–7), 1 I 7, 2I 20 (18–20), 3 I 7, p 1I 12, p 2I 12 (11–12), p 3 I 8 (7–8), p 4I 13 (13–14), I 3, 1I 12, 2 20 (19–20); II 5.5 (5–5.5), 1II 18 (10–18), 2 II 8, III 6 (5–6), IV 4.
DEUTONYMPH ( Figs. 7–9 View FIGURE 7 View FIGURE 8 View FIGURE 9 ; n=1)
Gnathosoma . Chelicerae (52) about 3.5× of movable digits (15). Palp 63 long, terminal palptibial claw strong (15), accessory claw conical (5); counts of setae and solenidia as in adult female. Subcapitular setae m (14) slightly shorter than width of m–m (16), rostrum with 2 pairs of setae, ro1 (10) and ro2 (10).
Idiosoma. Narrowly oval in shape (275 long, 99 wide). All dorsal setae smooth. Ridgelike mark of prodorsal shield not observed. Prodorsal shield bearing 3 pairs of setae, ve (17), sci (20) and sce (30); distances: ve–ve 18, ve–sci 35, sci–sci 27 and sci–sce 19. Hysterosomal shield C longitudinally rectangular, bearing 1 pair of setae, c1 (20), on anterior half part; setae c2 (30) obviously longer than other hysterosomal setae, situating on platelets posterior to c1; shields D and E, nearly square, each bearing 1 pair of setae, d1 (18) and e1 (17); shield F nearly trapezoid, bearing 2 pairs of setae, f1 (17) and f2 (14), f2 widely spaced and slightly posterior to f1; shield H trapeziform, bearing 2 pairs of setae, h1 (25) and h2 (15), h2 obviously posterior to h1; distances c1–c1 30, c1–c2 20, c1–d1 48, d1– d1 24, d1–c2 29, d1– e 1 27, e1– e 1 29, e1–f1 29, f1–f1 11, f1–f2 10, f1–h1 9, h1–h1 9, h1–h2 9, h2–h2 13.
Ventral setae simple, 1a 12, 2 a 16, 3 a 13 and 4a 12. A pair of shields present anterior to coxae III. Aggenital valves bearing 2 pairs of setae, ag1 11 and ag2 10. Genital valves bearing 2 pairs of setae, g1 8 and g2 8. Pseudanal valves bearing 3 pairs of setae, ps3 10, ps2 12 and ps1 16.
Legs. Lengths of leg I 183, leg II 115, leg III 131, leg IV 144. Tibiae II and III each with a stout ventral seta, II vm” longer (17) than others (9–11), III vm” longer (18) than others (9–10); tibia IV with two long setae (18). Tarsi II, III and IV each with 5 strong ventral setae. Counts of setae and solenidia on legs I–IV: coxae (including 1a, 3a and 4a) 4 + 1 elcp, 4, 3, 2; trochanters 1, 1, 2, 1; basifemora 5, 3, 3, 1; telofemora 5, 5, 4, 4; genua 8 + 1, 5, 5, 5; tibiae 10 + 2, 5 + 1, 5 + 1, 6 + 1; tarsi 17 + 5 + 1, 14 + 2, 11, 11. Lengths of solenidia and famulus, I 6, 1 I 7, 2I 17, p 1I 12, p 2 I 7, p 3I 11, I 3, 1 I 11, 2 18; II 5, 1 II 8, 2 II 7, III 5, IV 3.
Remarks
Females of P. subterranea sp. n. resemble those of P. benhami Price, 1974 in having similar number of setae and solenidia on leg I–IV except that tarsus I with 18 + 8 intead of 19 + 8. It can also be separated from the latter in that ovipositor with at least 12 pairs of setae instead of less than 10 pairs.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
SubOrder |
Prostigmata |
|
SuperFamily |
Pomerantzioidea |
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |