Exomis deqinensis, Wang & Zhou, 2020
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4748.2.7 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:1110012B-A68A-449D-BA03-AEB0DE911BFB |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3705092 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03FA3308-FFC9-323F-1ABE-20B2FD8025D5 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Exomis deqinensis |
| status |
sp. nov. |
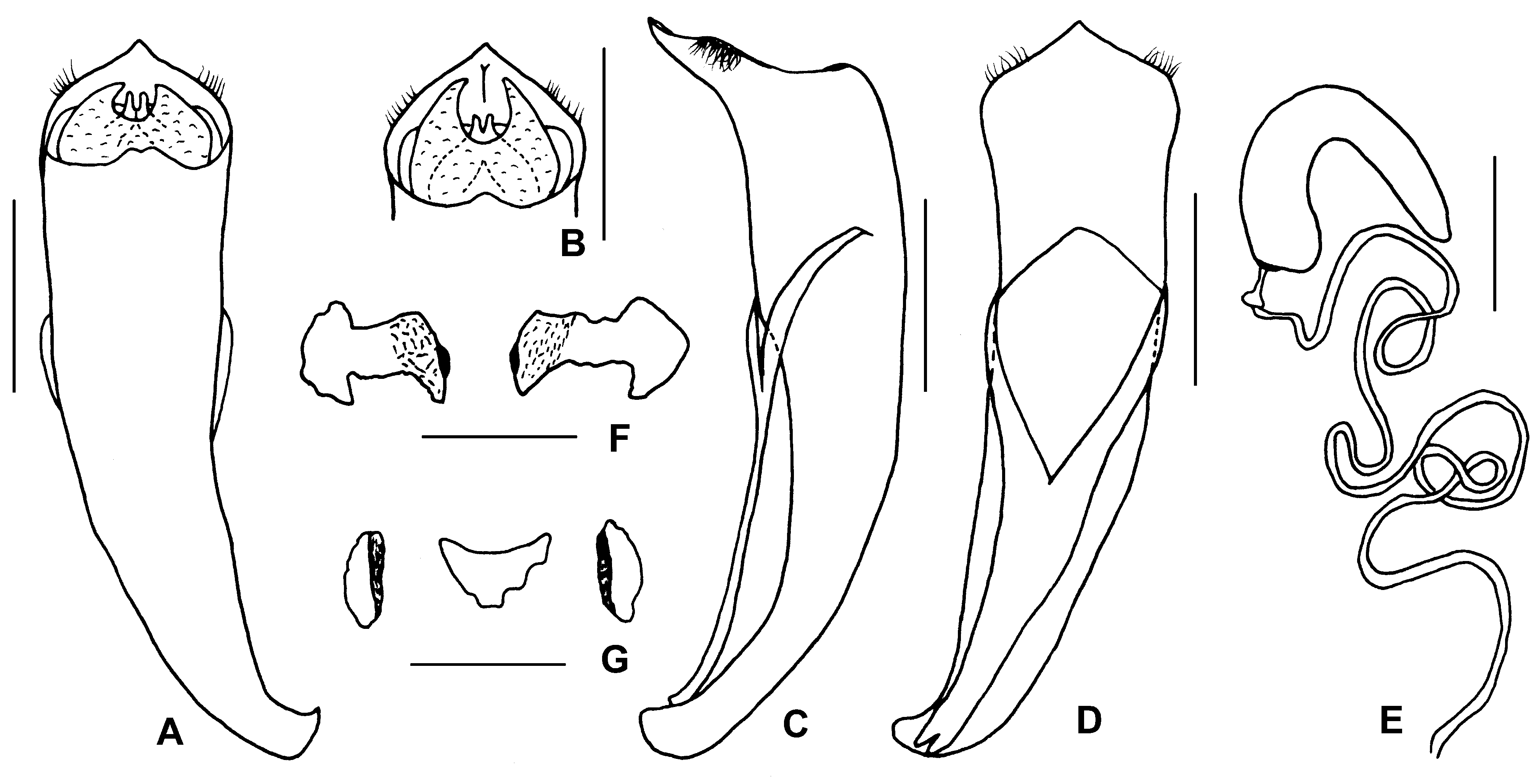
1. Exomis deqinensis sp. nov.
( Figs 1 View FIGURE 1 A–G, 9A)
Types. HOLOTYPE: male, CHINA: Yunnan: Deqin, Benzilan , 1982.VII.13, leg. Shuyong Wang ( IZ-CAS) ; PARATYPES: Yunnan: 14 males, 22 females, same data as holotype ( IZ-CAS) ; 7 males, 4 females, Deqin, Benzilan , 1981.VIII.23, leg. Shuyong Wang ( IZ-CAS) .
Measurements. Males: 3.7–5.1 mm, females: 3.9–5.3 mm.
Description. Body elongate. Head black, labrum blackish brown, underside of mouthparts brown; basal four antennomeres fulvous, others blackish brown. Pronotum orange. Scutellum black. Elytra fulvous, in darker specimens, spot at humerus indistinct. Ventral side of body black, prothoracic hypomeron fulvous. Legs black, apical 2/3 of femora fulvous.
Head densely covered with white pubescence. Mandibles short, slightly incised at anterior margin, with sparse pubescence; clypeus uneven and shining, with tiny punctures, anterior margin widely “V”-shaped incised; frons covered with dense wrinkles and coarse punctures, medially with a small fovea; vertex slightly convex, with sparse punctures. Antennae robust, extending to base of prothorax, pubescent, 1 st antennomere strongly swollen, 2 nd small and round, 3 rd oval, even smaller than second, 4 th widely triangular, 5 th – 10 th serrate, last segment long and conical.
Prothorax transverse, width 1.93 times of length, moderately convex; anterior margin slightly concave, lateral margins slightly arcuate, convergent anteriad, posterior margin sinuate; anterior angles rectangular, posteriorly broadly rounded, lateral margins narrowly bordered; surface shining, basal lobed area with few sparse punctures. Scutellum triangular, covered with indistinct punctures, basally with pubescence, apex slightly elevated over elytral surface.
Elytra cylindrical, 1.61 times as long as wide at humeri, slightly narrower than prothorax; surface covered with shallow but distinct punctures, interstices 0.3–2x puncture diameters; epipleura with sparse and short pubescence.
Underside and legs thickly clothed with long silvery pubescence; apex of pygidium arcuate. Legs robust, tarsi short, length ratio of protarsomeres 1.4:1.1:0.2:1.7.
Aedeagus long, bent ventrally, basal 2/3 paler and less sclerotized than apical 1/3; apico-ventral with two short fringes of sparse short setae.
Female. Body more robust; anterior margin of clypeus shallowly incised; prothorax narrower than elytra at humeri; apex of pygidium truncate; legs almost black except for anterior 2/3 of femora fulvous, or completely black; spermatheca falcate, spermathecal duct pale, about the same thickness throughout, nearly uncoiled; ventral rectal sclerites large, more sclerotized towards middle, dorsal central sclerite sub-triangular; inner margins of lateral sclerites more sclerotized.
Distribution: China (Yunnan).
Etymology. The species is named after the name of the type locality, Deqin.
Diagnosis. Exomis deqinensis sp. nov. is characterized by the following characters: small body size, fulvous dorsal pattern and specific genitalia.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |