Diognetus bagmaticus, Yasunaga & Schwartz & Chérot, 2023
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.37520/aemnp.2023.001 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:3F2C90B1-6EA1-4B38-A218-C314D09F6E00 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/E5B6F7C1-934F-4056-A22A-0D1DC15478A7 |
|
taxon LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:act:E5B6F7C1-934F-4056-A22A-0D1DC15478A7 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Diognetus bagmaticus |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Diognetus bagmaticus sp. nov.
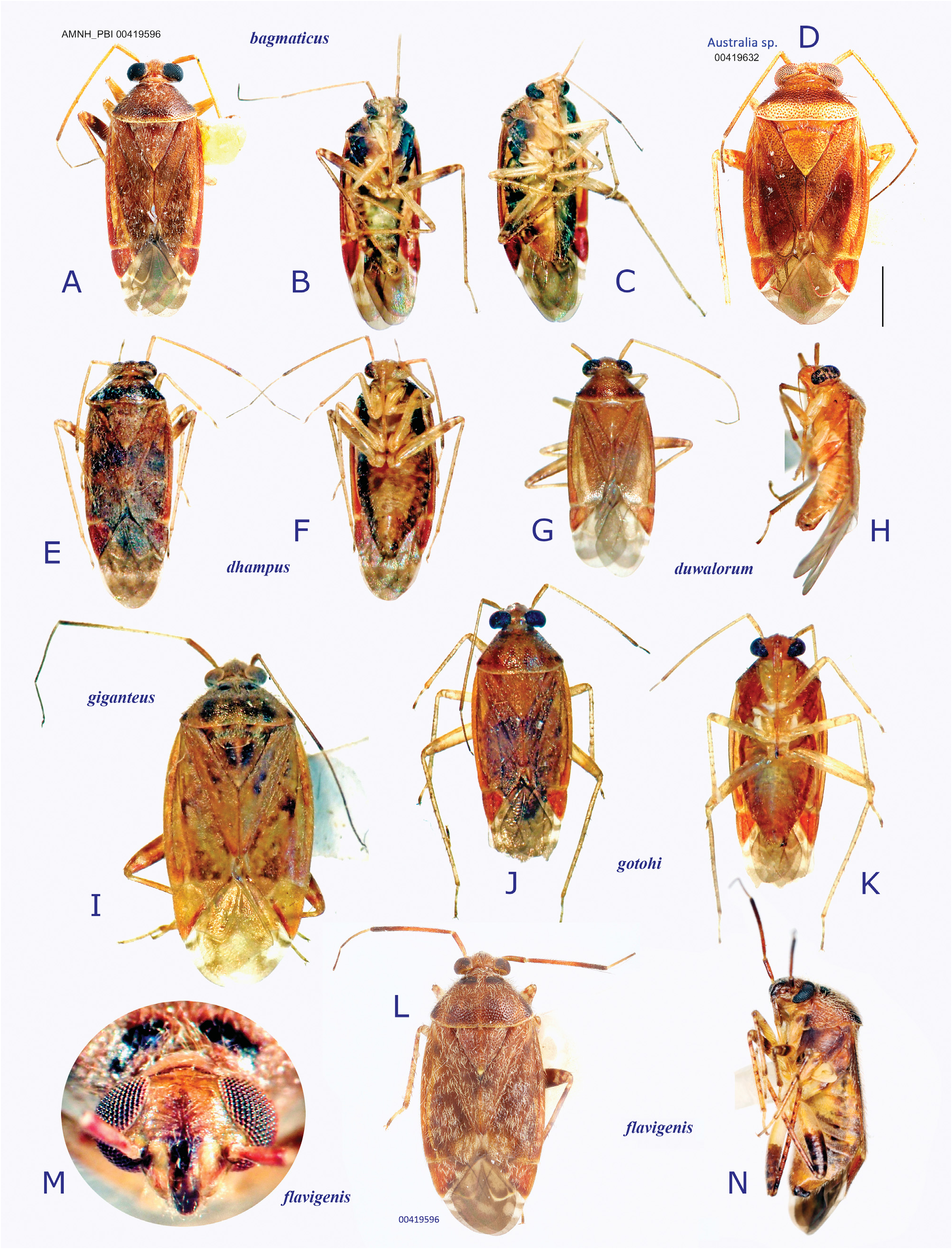
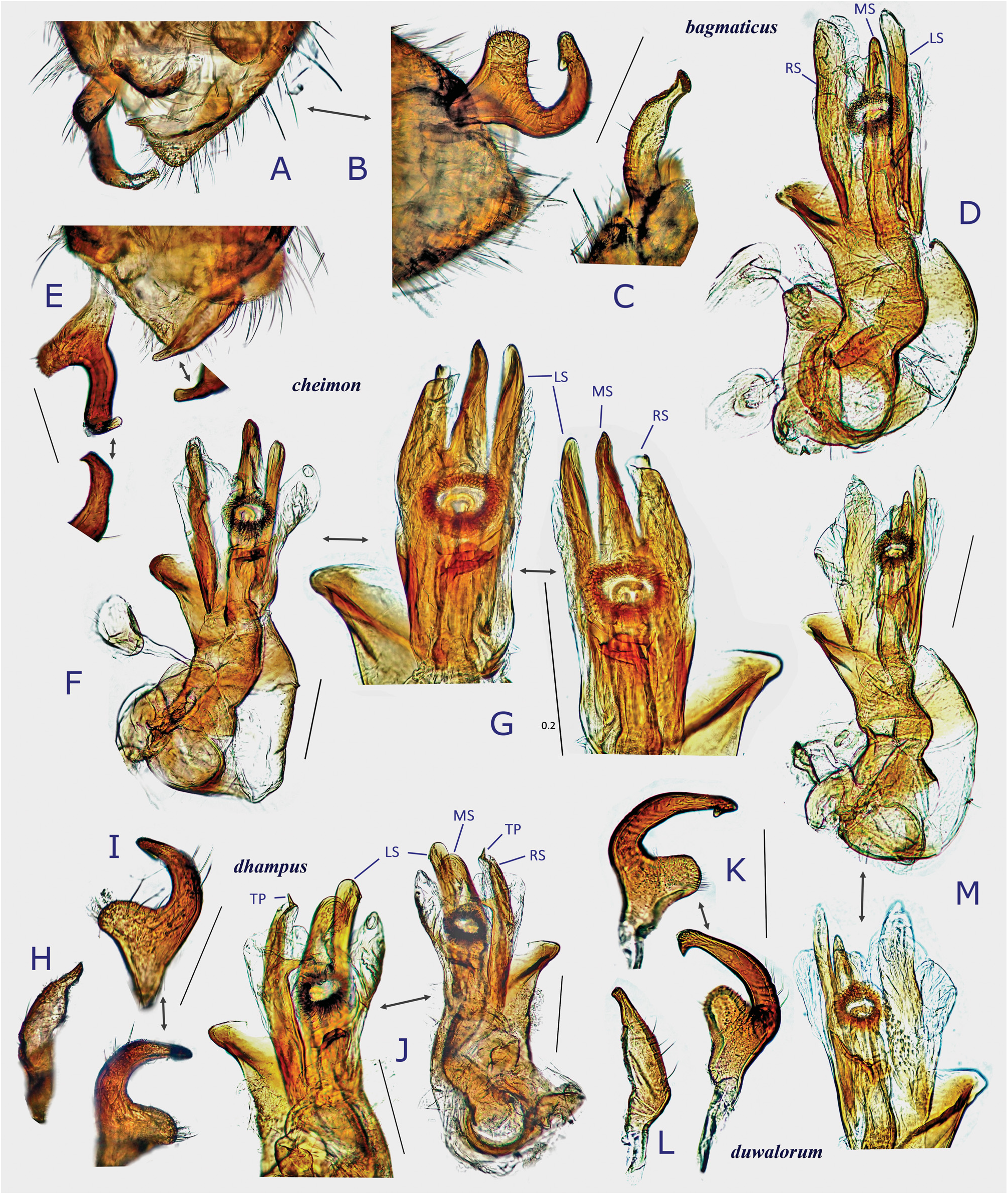
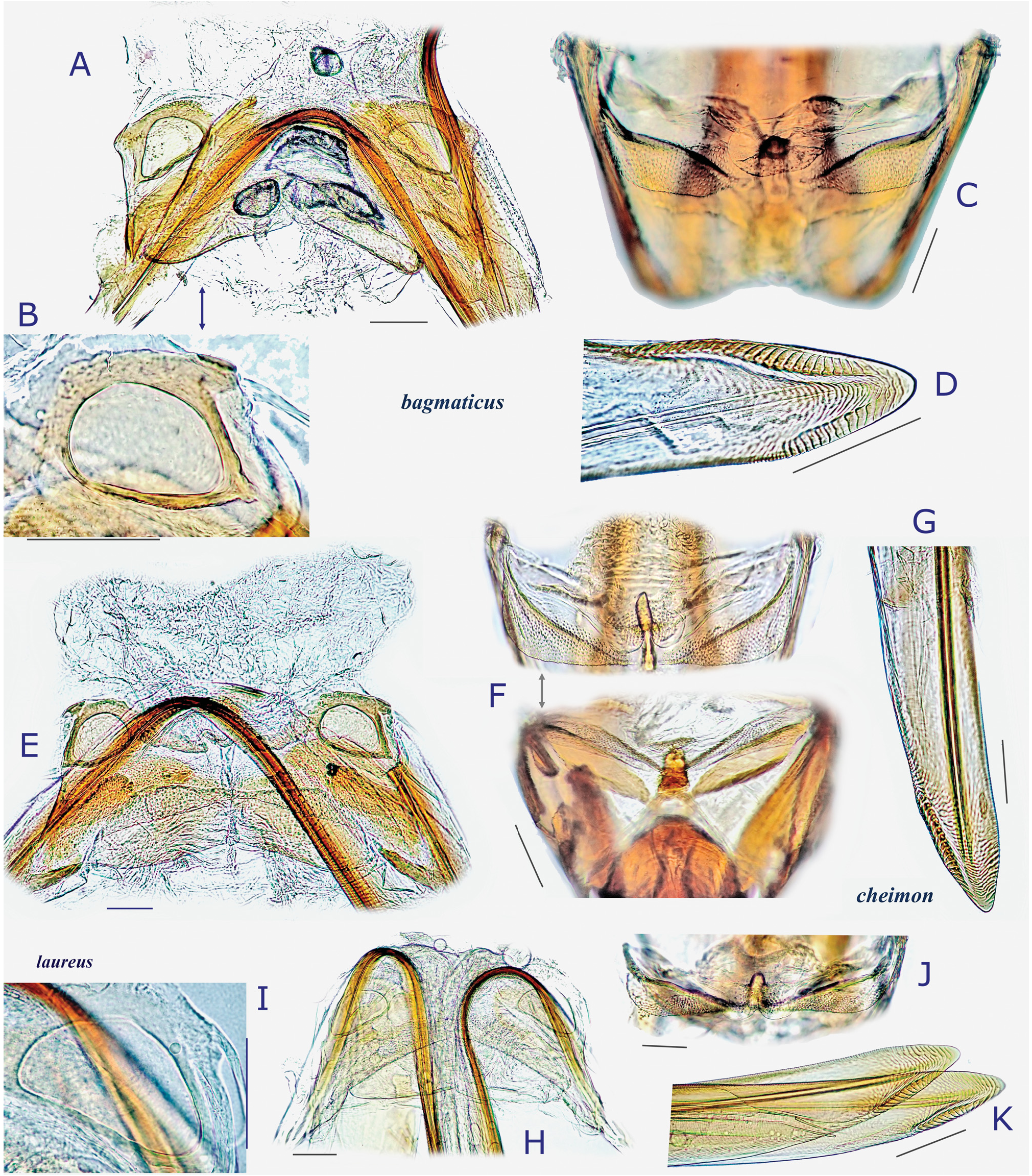
( Figs 1G View Fig , 2A− C View Fig , 7A− C View Fig , 8A− D View Fig , 9A− B View Fig , 10A− D View Fig , 25A− P View Fig )
Type material. HOLOTYPE: J, NEPAL: BAGMATI ZONE: Kathmandu, Tripureshwor , 27.693555, 85.316545, UV lighting, 29 Oct 2006, T.Yasunaga ( AMNH _ PBI 00380744 ) ( NMTU) GoogleMaps . PARATYPES: NEPAL: Kathmandu,same data as for holotype, 1 J 1 ♀ ( TYCN); Kathmandu, Gongabu-Samakhusi, 27.731066, 85.313088, UV lighting, 31 Jun2005, T.Yasunaga,1J ( TYCN); Kathmandu District,Nagarjun,27.7483,85.2519, 1,700 m ( 5,577 ft),flowers of Quercus semecarpifolia , 16 May 2005, T. Yasunaga, 1 J ( AMNH _ PBI 00419516) ( CNC), 1 J without USIs ( TYCN); Kathmandu District, Patibhanjyang, pastures, 27.84678, 85.45931, 1,829 m ( 6,000 ft), 20 Jun 1967, Can. Nepal Exped.,6JJ 7♀♀ ( CNC)(00419583–00419595);Lalitpur District, Godawari [Godavari], 27.59339, 85.39727, 1,829 m ( 6,000 ft), 14–23 Jul 1967, Can. Nepal Exped., 3JJ 16 ♀♀ ( CNC) (00419596–00419611); Laritpur,Godawari,Taukhel, 27.5999, 85.3555,flowers of Schima wallichii , 16 Jun 2006, R.K.Duwal,4JJ 1♀ ( AMNH, TYCN). RASUWA: Langtang Himal National Park, Dhunche,28.112073,85.297022, 1,950 m, at FL light of lodge balcony, 8–9 Jun 2006, T.Yasunaga, 1 ♀ ( TYCN).
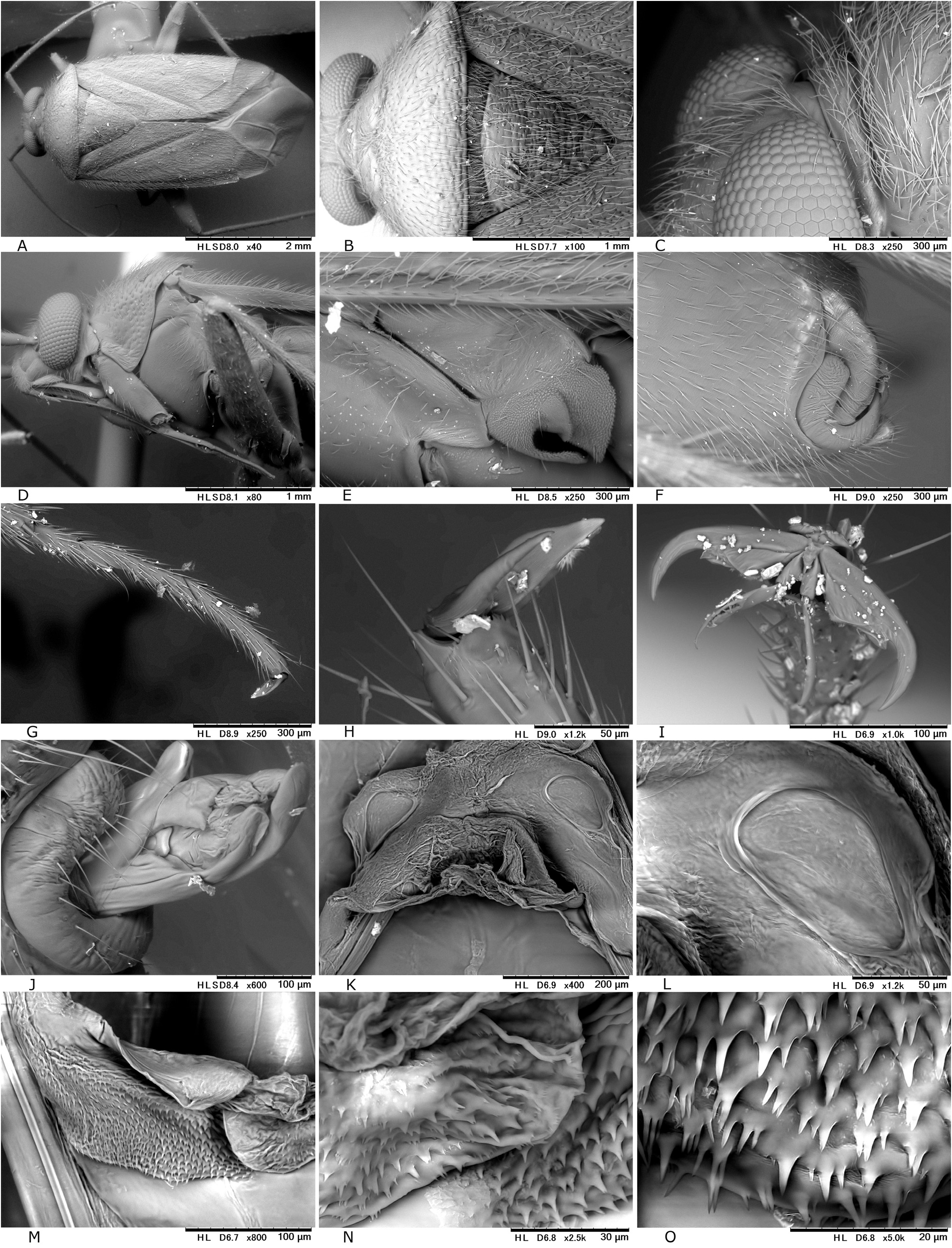
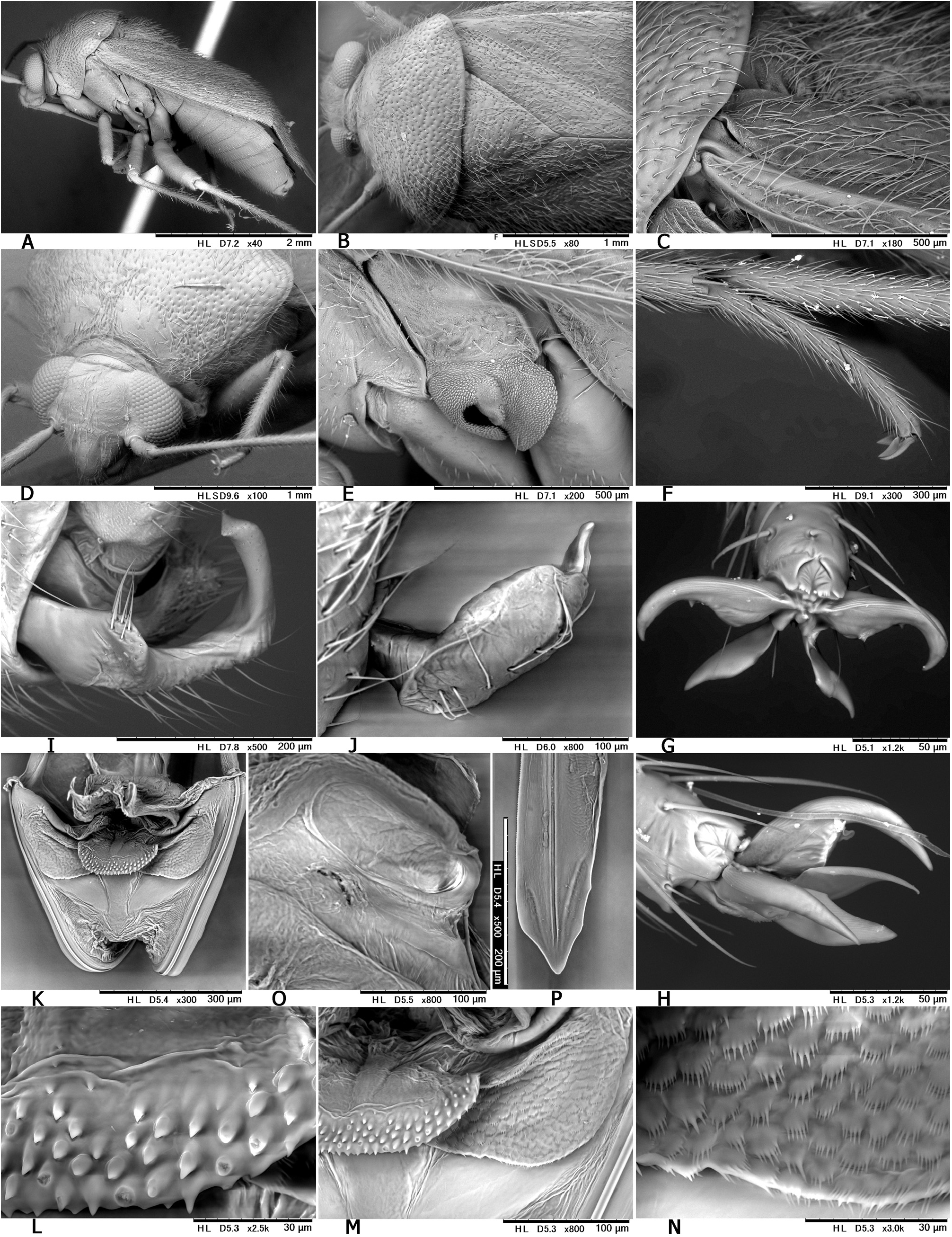
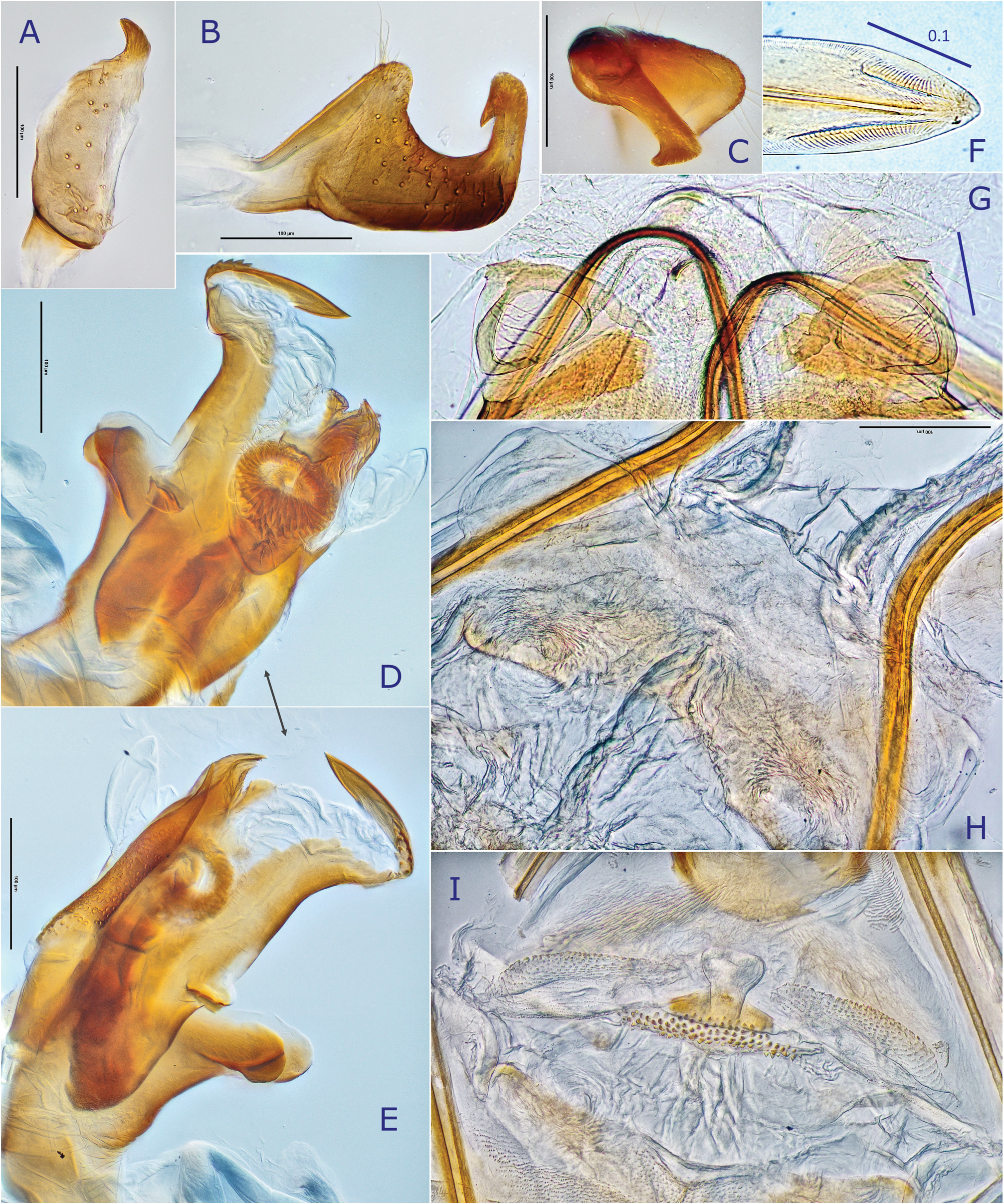
Description. Body elongate ovoid, relatively large in size, 5.1–5.8 mm ( Figs 2A− C View Fig , 7A View Fig ). COLORATION: Dorsum varying from reddish-brown ( Figs 2B View Fig , 7A View Fig ) to chocolate brown ( Fig. 2A View Fig ), usually with mottled pattern ( Figs 2A− C View Fig ). Antennae pale reddish-brown; apex of segment II, segment III (except for pale extreme base) and segment IV dark brown. Labium pale brown, partly tinged with red. Pronotum reddish-brown, with calli and posterior half sometimes darkened ( Fig. 2A View Fig ) and posterior margin narrowly pale; pleura broadly fuscous; scent efferent system creamy yellow. Hemelytron reddish-brown, usually speckled with dark maculae; apices of exocorium (embolium) and cuneus narrowly pale; membrane smoky brown, with yellowish veins. Coxae and legs yellowish brown; mesofemur with two faint dark rings subapically; apical 1/3 of metafemur dark brown, with two pale rings subapically. Ventral surface of abdomen pale brown (somewhat greenish when alive); with more or less darkened lateral margins ( Figs 7B− C View Fig ). SURFACE AND VESTITURE: As in generic diagnosis; dorsal surface weakly shining; vestiture on thoracic pleura relatively sparse; hemelytron rather matte. STRUCTURE: Vertex narrow, with a basal transverse carina, weakly arched ( Figs 25B− C View Fig ). Antennal segment I about as thick as pronotal collar, longer than segment IV. Labium slightly exceeding apex of mesocoxa but not reaching apex of metacoxa ( Fig. 25D View Fig ). Scutellum rather flat, shallowly and sparsely punctate, with transverse wrinkles. Metathoracic scent efferent system as in Fig. 25E View Fig . Metatarsomere I short, about half as long as III; pretarsal structure as in Figs 28H− I View Fig ; parempodia rather long. MALE GENITALIA ( Figs 8A− D View Fig , 25F, J View Fig ): Left paramere with squared, developed sensory lobe and rather broad hypophysis that is hooked at apex ( Figs 8B View Fig , 25F View Fig ). Vesica with short, branched MS and smooth LS, lacking noticeable TP ( Figs 8D View Fig , 25J View Fig ). FEMALE GENITALIA (9A− B, 10A− D, 25K− O): Sclerotized ring with thickened anterior rim ( Figs 11B View Fig , 28L View Fig ); sclerotized ring with thickened anterior margin ( Figs 10A− B View Fig ); posterior wall ( Figs 9A View Fig , 10C View Fig , 25M− O View Fig ) with narrow dorsal structure and moderate-sized interramal lobe.
Measurements. See Table 1.
Differential diagnosis. Recognized by its relatively elongate, large body and shape of the male and female genitalic structures described above. Most similar in overall appearance to D. dhampus sp. nov., which was also found in Nepal and sympatric in some areas; distinguished by shorter antennal segment IV that is ( ♀) as long as / (J) slightly shorter than segment I, sensory lobe of left paramere more strongly produced, somewhat squared; apex (hypophysis) of right paramere flattened; and vesica with shorter, branched MS, lacking TP.
Etymology. Named for the type locality, Bagmati Zone in Nepal; latinized as an adjective.
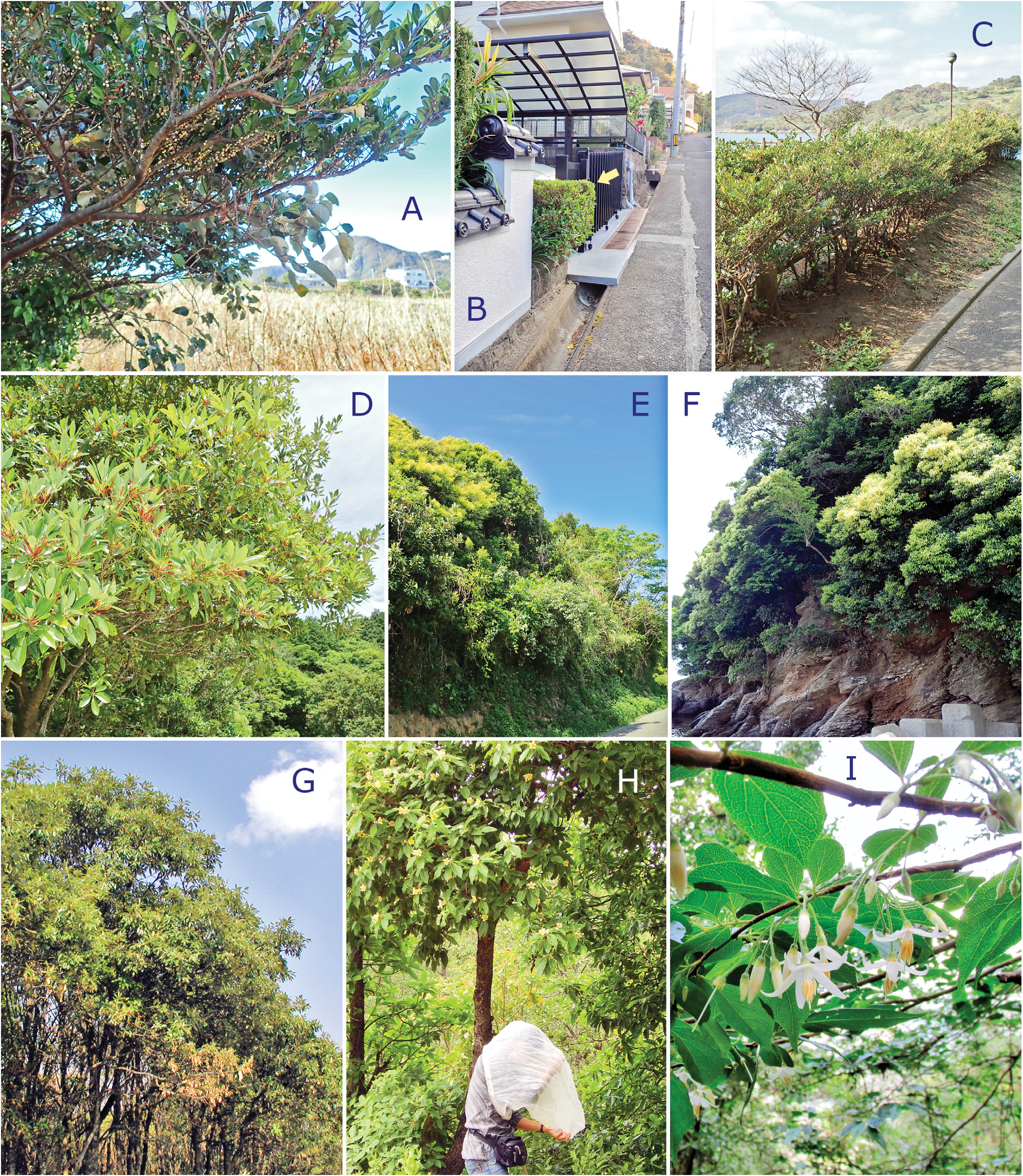
Biology. Many of available individuals were collected by UV lighting method. Like as D. cheimon sp. nov., this species may utilize garden plants or landscaping trees as breeding hosts, since some specimens were collected at downtown area of Kathmandu. Several specimens were yielded by sweeping inflorescence of Quercus semecarpifolia Sm. (Fagaceae) ( Fig. 1G View Fig ) and Schima wallichii (DC.) Korth. (Theaceae) ( Fig. 1H View Fig ). Collection records suggest D. bagmaticus has a bivoltine life cycle; the adults were found in June and October.
Distribution. Nepal ( Bagmati Zone, Rasuwa District).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.