Rhynchonema dighaensis, Datta, Tridip Kumar, Navarrete, Alberto De Jesus & Mohapatra, Anil, 2015
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.3905.3.3 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:7564C962-B1E5-4BAE-B837-58BFB28BF6CF |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5690226 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03F187E6-FFEF-DC0F-FF1A-A9958DCC679F |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Rhynchonema dighaensis |
| status |
|
Key to valid species of Rhynchonema
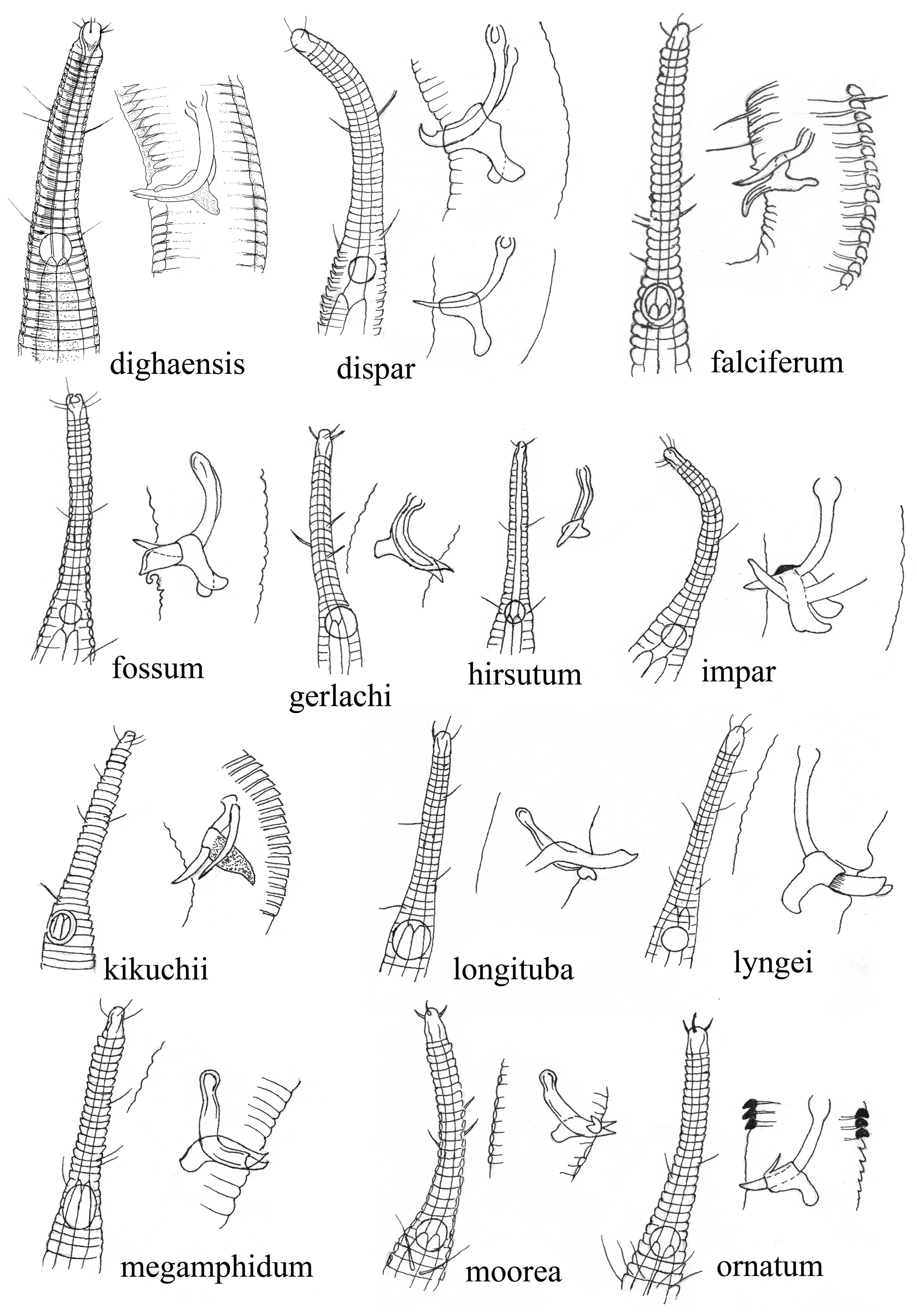
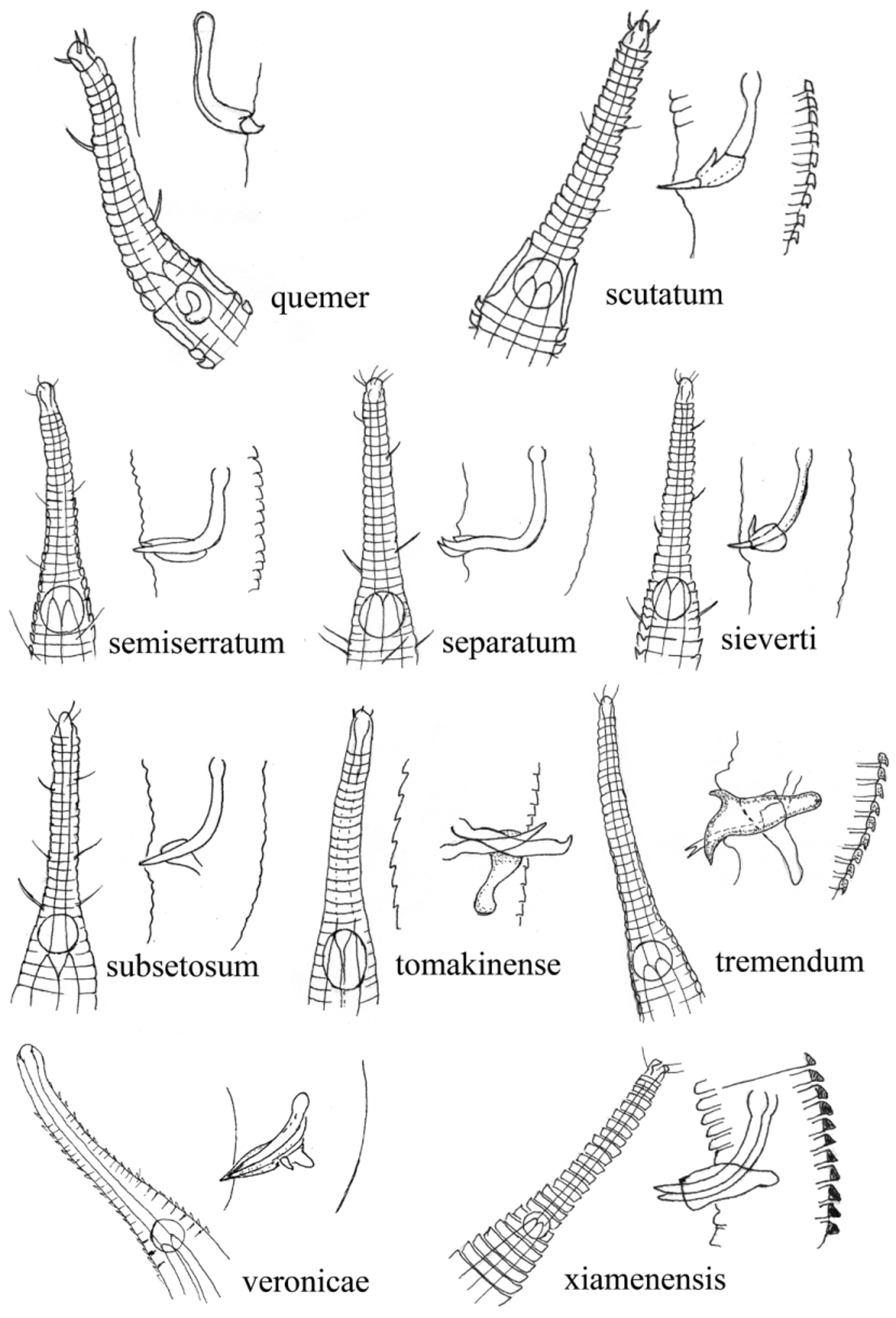
Illustrated guides for Rhynchonema spp . are presented in Figs 5 View FIGURE 5 , 6 View FIGURE 6 & 7 View FIGURE 7 . Morphometric comparison of all valid species of Rhynchonema is given in the Table 2. All species of the genus in the illustrated guide or Table 2 are based on published work, with the exception of R. dighaensis sp. nov. The guide comprises a set of simplified images of the anterior part showing the shape and position of the amphid, the shape of both spicules and the gubernaculum. However, the emphasis here is on the dichotomous key and the illustrated guide is provided for further verification of Rhynchonema spp . Cobb (1920) illustrated only the anterior part of R. cinctum and hence only that is shown in the guide.
1 Spicules sharply curved, “L” shaped..................................................................... 2
- Spicules arcuate..................................................................................... 3
2 Distal end of the spicules sharp and oriented upward; a = 28–30, b =3.4-4.0, c =7.1–7.8, spicules=24–25 µm... R. separatum
- Distal end of the spicule not sharp; a =28–30, b =3.2, c =8.6, spicule=19 µm........................... R. semiserratum
3 Distal end of spicule not pointed........................................................................ 4
- Distal end of spicule pointed........................................................................... 9
4 Distal end of spicule bifid............................................................................. 5
- Distal end of spicule claw-like.......................................................................... 6
5 Spicule converged beak-like; a =25.7, b =4.6, c =9.1, spicules=21 µm.................................... R. gerlachi
- Spicules diverged beak-like; distal part of gubernaculum equipped with two bifid elongations; a =26, b =4.6, c =9.5, spicules=22 µm......................................................................................... R. moorea
6 Gubernaculum with dorsal apophysis; buccal cavity 49–53 µm long; 29–33 annules present anterior to amphid; a =25.8–27.7, b =2.9–3.3, c =7.4–7.7, spicules= 16–18 µm................................................... R. megamphidum
- Gubernaculum without dorsal apophysis.................................................................. 7
7 Amphid spans several annules; 32–35 present anterior to amphid; buccal cavity 39–46 µm long; a =25.3, b =3.6, c =7.2, spic- ules= 23 µm............................................................................ R. ambianorum
- Amphid spans single annule............................................................................ 8
8 Buccal cavity 50–56 µm; spicules one fold of abd, 16 µm in length; a =26.9, b =3.2–3.3; c =7.0–7.9.......... R. deconincki
- Buccal cavity 47 µm; spicules 1.5 fold of abd; a =28.6, b =3.8, c =8.8..................................... R. quemer
9 Gubernaculum with dorsal hook....................................................................... 10
- Gubernaculum plate-like without dorsal hook............................................................. 13
10 Gubernaculum with dorsal apophysis................................................................... 11
- Gubernaculum without dorsal apophysis................................................................. 12
11 Distal end of spicule with median depression; buccal cavity 65–67 µm long; amphid 100% of corresponding body diameter; 35–43 annules present anterior to amphid; a =25–32, b =3.4–3.8, c =7.9–9.3, spicules= 27 µm............... R. longituba
- Distal end of spicule has no median depression; buccal cavity 65–69 µm long; amphid 90% of corresponding body diameter; 35–37 annules present anterior to amphid; a = 24.2–26.1, b =2.8–2.95, c =7.3–7.5, spicule=14–15 µm........ R. falciferum
12 Buccal cavity 27–33 µm long; 18 annules present anterior to amphid; amphid 55% of corresponding body diameter; a =26–35, b =3.9–4.3, c =7.4–8.2, spicules= 22 µm.......................................................... R. brevituba
- Buccal cavity 48–54 µm long; 20–21 annules present anterior to amphid; amphid 73–89% of corresponding body diameter; a =24.9–27.1, b =3.2–3.7, c =3.2–3.7, spicules=23.5–25.5 µm........................................ R. ceramotos
13 Spicules equal...................................................................................... 14
- Spicules unequal.................................................................................... 24
14 Gubernaculum with a median piece directed upward....................................................... 15
- Gubernaculum without any median piece................................................................ 18
15 Gubernaculum with prominent dorsal apophysis........................................................... 16
- Gubernaculum without (or with poorly developed) dorsal apophysis........................................... 17
16 Buccal cavity 50–57 µm long; 26–28 annules present anterior to amphid; a =25.8–28.6, b =3.4–3.5, c =6.2–6.8, spicules=27–30 µm.................................................................................... R. amakusanum
- Buccal cavity 50–52 µm long; 33 annules present anterior to amphid; a = 27–32, b =3.9–4.2, c =7.0–7.4, spicules= 22µm................................................................................................. R. ornatum
17 Preanal papillae (five) present; buccal cavity 57 µm long; amphid size sexually dimorphic; a =29.3–30.3, b =3.3–3.7, c =7.7–8.6, spicules=18–20 µm.................................................................. R. sieverti
- Preanal papillae absent; spicule 19.5 µm long; a =30, b =3.2, c =6.9.................................... R. scutatum
18 Amphid posterior to buccal cavity...................................................................... 19
- Amphid at the level of buccal cavity.................................................................... 21
19 Buccal cavity 52–60 µm long; 42–43 annules present anterior to amphid; a =15.2, b =3.5, c =7, spicules=32 µm.... R. lyngei
- Buccal cavity <50 µm long........................................................................... 20
20 Buccal cavity 36–47 µm long; 31–32 annules present anterior to amphid; a =24.5–32.6, b =4.3–4.7, c =6.6–7.3, spicules=23–33 µm.......................................................................................... R. cemae
- Buccal cavity 36–37 µm long; 30–35 annules present anterior to amphid; a =27, b =3.6, c =7.2, spicules=21 µm.. R. cinctum
21 Buccal cavity 53–55 µm long; a =21.3, b =4.1, c =6.7, spicules=26 µm................................... R. hirsutum
- Buccal cavity <50 µm long........................................................................... 22
22 Gubernaculum relatively larger with small dorsal apophysis; a =26–30, b =3.3–4.0, c =6.7–7.3, spicules= 19.2 µm................................................................................................... R. xiamenensis
- Gubernaculum comparatively small..................................................................... 23
23 Buccal cavity 38–45 µm long; 46–54 annules present anterior to amphid; a =26–32, b =3.3–3.5, c =6.6–7.3, spicules=12 µm............................................................................................ R. chiloense
- Buccal cavity 43 µm long; a genital papilloid supplement present one abd anterior to cloacal opening; a =24.9–32.8, b =4.2–4.8, c =7.9–8.3............................................................................... R. subsetosum
24 Distal end of spicule having median depression or projected piece............................................ 25
- Distal end of spicule having no depression or projected piece................................................ 26
25 Tip of the right spicule has median cleft, left spicule simple; buccal cavity 45–54 µm long; a =22.0–23.6, b =3.0–3.3, c =6.0–6.5, spicules=14–15 (12–13) µm...................................................................... R. dispar
– Both spicules having projected piece posterior to tip; buccal cavity 45–55 µm long; a =24–28, b =3.4–3.9, c =6.8–7.5, spicules=20–21 (18–20) µm.................................................................. R. tremendum
26 Dorsal apophysis with sharp distal ending; 32–37 annules present anterior to amphid; a =18.6–29.8, b =3.5–3.6, c =6.3–6.6, spicules=20–22 (14–16) µm.................................................................... R. kikuchii
- Distal end of dorsal apophyses not sharp but of various shapes............................................... 27
27 Amphid spans a single annule; buccal cavity 38–53 µm long; tail 3.6–4.7 abd; a =22–34, b =3.6–4.0, c =6.2–7.7, spic- ules=16.2–18.7(12.8–13.7) µm.................................................................. R. collare
- Amphid spans several annules......................................................................... 28
28 Spicules lacking strong curvature...................................................................... 29
- Spicules having strong curvature....................................................................... 30
29 Spicules cephalated and turned upward; buccal cavity 44–57 µm long; tail 3.1–4.3 abd; a =22–25, b =4.1–4.7, c =7.1–8.8, spicules slightly unequal, ranges from 11–19 µm................................................... R. tomakinense
- Distal end of spicule is arrow shaped; buccal cavity 38–48.8 µm long; tail 4.0–4.7 abd; a =27–31.7, b =4.0–4.4, c =6.7–7.3............................................................................................. R. veronicae
30 Left spicule longer than the right spicule; symmetrical dorsal apophysis; buccal cavity 37–43 µm; a =33.6–40.6, b =5.1–6.1, c = 6.8–8.5, spicules= 18.7–29.2 (16.1–24.1) µm............................................. R. dighaensis sp. nov.
- Left spicule always shorter than the right; buccal cavity <50 µm long; asymmetric dorsal apophysis.................. 31
31 Distal end of right spicule is broader; cross-section of Right spicule is U-shaped; buccal cavity 53–54 µm long; a = 24–25, b =3.3–3.4, c =6.8–7.2, spicules= 21–22 (15.5–17) µm; Vulva is covered by a thin skin flap................... R. fossum
- Distal end of right spicule is slender; Right spicule is shaped differently than the left; Buccal cavity 62–69 µm; a =24–27, b =3.0–3.1, c =7.5, spicules=21–22 (17–18) µm; vulva not covered by a skin flap............................ R. impar
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |