Rhagomys rufescens (Thomas, 1886)
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.6707142 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6727501 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03F06D13-FF60-20A9-0D99-1E720191FBED |
|
treatment provided by |
Carolina |
|
scientific name |
Rhagomys rufescens |
| status |
|
597. View Plate 27: Cricetidae
Brazilian Arboreal Mouse
Rhagomys rufescens View in CoL
French: Rhagomys du Brésil / German: Brasilianische Baummaus / Spanish: Raton arboricola de Brasil
Other common names: Rufescent Rhagomys
Taxonomy. Hesperomys rufescens Thomas, 1886 , Rio deJaneiro, Rio deJaneiro, Brazil.
An Amazonian record from northern Mato Grosso, Brazil, points to a possible third undescribed species of Rhagomys . Monotypic.
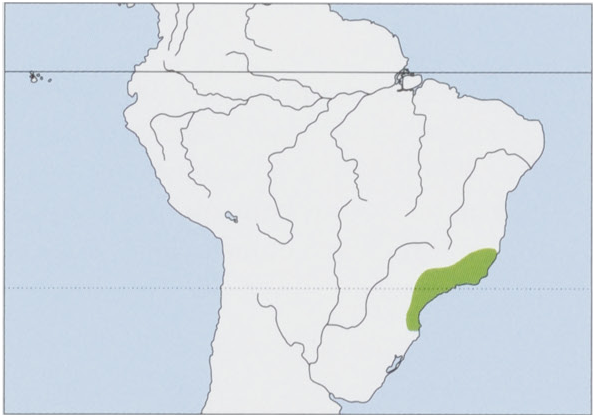
Distribution. Known from a few localities in SE & S Brazil (Espiritu Santo, Minas Gerais, Rio de Janeiro, Sao Paulo, and Santa Catarina states). View Figure
Descriptive notes. Head-body 82-98 mm, tail 85—107 mm, ear 10-15 mm, hindfoot 18-22 mm; weight 16-32 g. The Brazilian Arboreal Mouse is similar to the Longtongued Arboreal Mouse ( R. longilingua ) but differs from it by having soft and lax rather than spiny fur. Back ofthe Brazilian Arboreal Mouse is reddish to yellowish brown (i.e. honey yellow and oak brown), head is cinnamon brown, snout is brownish orange (Pompeian yellow), sides are yellowish brown, and venter is reddish gray to brownish orange. Tail is unicolored brownish, with small scales, covered with blackish hair becoming progressively longer toward tip, which ends in small tuft of brown hair. Pes is short and broad, c.24% of head-body length, with short hallux. Third and fourth digits on manus are nearly equal in length, both completely distinctive in length from others. There are three pairs of mammae: one inguinal, one abdominal, and one postaxial. Chromosomal complement is 2n = 36 and FN = 50.
Habitat. Atlantic Forest environments including second growth semideciduous tropical forest and transitional formations of coastal vegetation and tropical forest from sea level to elevations of ¢.1700 m. A Brazilian Arboreal Mouse was captured in the interior of a forest fragment, with a canopy of 18-25 m high, more than 40 m from nearest edge.
Food and Feeding. Little is known, but stomach of one Brazilian Arboreal Mouse had three unidentified species ofants.
Breeding. No information.
Activity patterns. The Brazilian Arboreal Mouse is terrestrial. Anatomicaltraits suggest arboreal and scansorial habits.
Movements, Home range and Social organization. No information.
Status and Conservation. Classified as Near Threatened on The IUCN Red List. The Brazilian Arboreal Mouse occurs in area larger than 20,000 km?, but it occupies forest fragments that are declining due to deforestation.
Bibliography. Braga & Pires (2012), Geise, Percequillo & Bergallo (2008), Luna (2015), Luna & Patterson (2003), Pacheco (2003), Passamani et al. (2011), Percequillo, Goncalves & Oliveira (2004), Percequillo, Tirelli et al. (2011), Pinheiro et al. (2004), Steiner-Souza et al. (2008), Testoni et al. (2010), Thomas (18864).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.