Eligmodontia dunaris, Spotorno et al., 2013
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.6707142 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6728263 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03F06D13-FF5E-2096-089E-1C730BDEFEB5 |
|
treatment provided by |
Carolina |
|
scientific name |
Eligmodontia dunaris |
| status |
|
718. View Plate 30: Cricetidae
Dune Gerbil Mouse
Eligmodontia dunaris View in CoL
French: Eligmodonte des dunes / German: Diinen-Hochlandwiistenmaus / Spanish: Raton colilargo de dunas
Other common names: Dune Laucha
Taxonomy. Eligmodontia dunaris Spotorno et al., 2013 View in CoL , Sector Playa Los Choros, Coquimbo, Chile.
This species is monotypic.
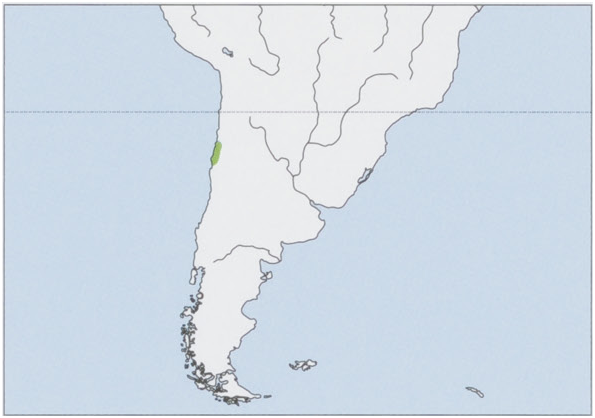
Distribution. N Chile, restricted to Atacama Desert. View Figure
Descriptive notes. Head-body 64-77 mm, tail 57-76 mm, ear 10-18 mm, hindfoot 17-20 mm; weight 9-4-15-5 g. See general characters of the genus under the Hairyfooted Gerbil Mouse ( E. hirtipes ) account.
The Dune Gerbil Mouse is the smallest species in Eligmodontia . Dorsum is very pale yellowish brownish gray; head has slightly darkish band extending from nose to between ears. Venter is immaculately white, sharply demarcated from dorsum by fulvous lateral line. Ears have whitish preauricular tufts, reaching proximal part of pinna. Hindfeet are white above; hypothenar pad is absent. Tail is short (¢.95% of head-body length), bicolored, whitish above and below with slight differentiation, and tip lacks terminal pencil. Chromosomal complement is 2n = 50, FN = 48.
Habitat. Coastal dune belts with xerophytic low matorral (shrubland), scarce small shrubs, and herbs; plant cover includes Cristaria glaucophylla ( Malvaceae ), Tetragonia maritima (Aizoaceae) , Frankenia chilensis (Frankeniaceae) , and Nolana divaricata (Solanaceae) .
Food and Feeding. The Dune Gerbil Mouse is granivorous/omnivorous. One stomach contained pieces of herbs, grains, and insects; captive animals ate grains from commercial bird foods and cat food.
Breeding. In July, a captive female gave birth to four young after three weeks, and in August, another female gave birth to three young. Wild females were pregnant with two, four, and five embryos in September and March.
Activity patterns. The Dune Gerbil Mouse is terrestrial.
Movements, Home range and Social organization. The Dune Gerbil Mouse constructs galleries in sandy soils.
Status and Conservation. Not assessed on The [UCN Red Last.
Bibliography. Lanzone et al. (2015), Spotorno et al. (2013), Valladares et al. (2016).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
SubOrder |
Myomorpha |
|
SuperFamily |
Muroidea |
|
Family |
|
|
Tribe |
Euneomyini |
|
Genus |
Eligmodontia dunaris
| Don E. Wilson, Russell A. Mittermeier & Thomas E. Lacher, Jr 2017 |
Eligmodontia dunaris
| Spotorno et al. 2013 |