Ologamasidae
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.168445 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5200654 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03EF1D76-C879-9603-FF2F-E035FA040E67 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Ologamasidae |
| status |
|
Key to genera of Ologamasidae View in CoL (adult females)
1. Podonotal and opisthonotal shields completely separated...................................................... 2
- Podonotal and opisthonotal shields fused to form a holonotal shield, line of fusion may or may not be visible............ 22
2. Epistome with club-shaped anterocentral extension; peritrematal and exopodal shields fused by a narrow connection posterior
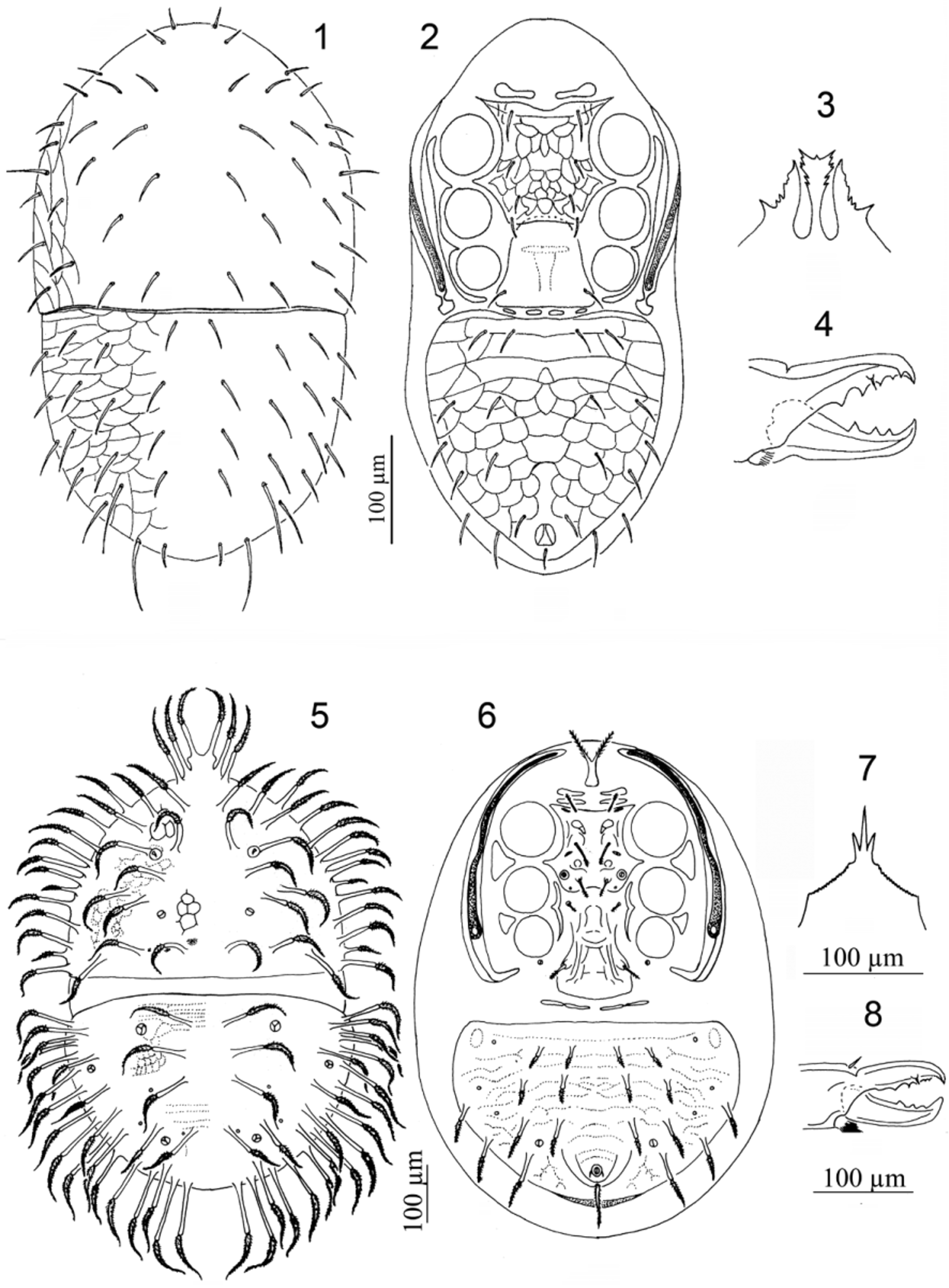
to stigma..................................................................... Geogamasus View in CoL (part) ( Figs 1–4 View FIGURES 1 – 8. 1 – 4 ) - Epistome without club-shaped anterocentral extension; peritrematal shield not fused to exopodal shield, or fused to exopodal shield posterior to stigma by a connection wider than width of peritreme......................................... 3
3. Dorsal shield setae inserted on long stalks............................................... Oriflammella View in CoL ( Figs 5–8 View FIGURES 1 – 8. 1 – 4 )
- Dorsal shield setae not inserted on stalks.................................................................. 4
4. Opisthonotal and ventrianal shields fused.................................................................. 5
- Opisthonotal and ventrianal shields not fused ................................................................ 9
5. Presternal plates absent; pretarsus I absent................................................ Euepicrius View in CoL ( Figs 9–12 View FIGURES 9 – 16. 9 – 12 )
- Presternal plates present; pretarsus I present................................................................ 6
6. With one pair of presternal plates.................................................... Gamaselliphis View in CoL ( Figs 13–16 View FIGURES 9 – 16. 9 – 12 )
- With two pairs of presternal plates....................................................................... 7
7. Opisthogastric region without latero-diagonal fissure; peritreme extending anteriorly to anterior margin of coxa II............................................................................................ Hiniphis View in CoL ( Figs 17–20 View FIGURES 17 – 24. 17 – 20 )
- Opisthogastric region with a distinct latero-diagonal fissure; peritreme extending anteriorly to region of coxa I........... 8
8. Peritrematal shield fused only to exopodal shield near coxa IV.............................. Desectophis View in CoL ( Figs 21–24 View FIGURES 17 – 24. 17 – 20 )
- Peritrematal shield fused to exopodal shield near coxa IV and ventrianal shield..................... Acuphis View in CoL ( Figs 25–28 View FIGURES 25 – 32. 25 – 28 )
9. Podosomal section of dorsum with 28 or more pairs of setae................................................... 10
- Podosomal section of dorsum with fewer than 25 pairs of setae............................................... 12
10. Opisthosomal section of dorsum with more than 30 pairs of setae................................ Pilellus View in CoL ( Figs 29–32 View FIGURES 25 – 32. 25 – 28 )
- Opisthosomal section of dorsum with fewer than 21 pairs of setae............................................. 11
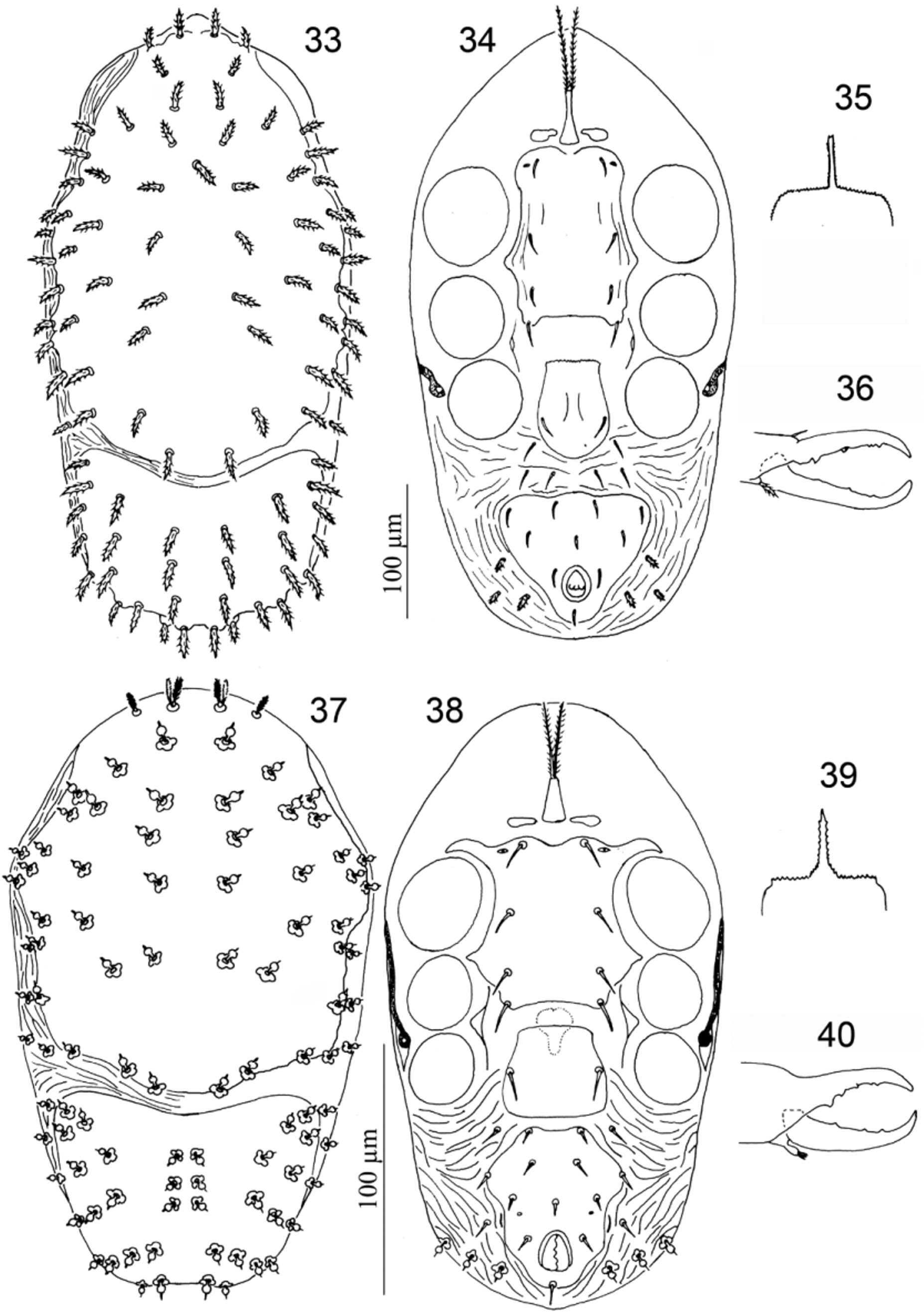
11. Podosomal section of dorsum with 32 pairs of setae and a medial unpaired seta; trochanter IV with six setae, genu III with ten setae and tibia III with nine setae.................................................. Notogamasellus View in CoL ( Figs 33–36 View FIGURES 33 – 40. 33 – 36 )
- Podosomal section of dorsum with 28 pairs of setae; trochanter IV with five setae, genu III with nine setae and tibia III with eight setae................................................................ Podonotogamasellus View in CoL ( Figs 37–40 View FIGURES 33 – 40. 33 – 36 )
12. Peritreme extending anteriorly at most to median region of coxa III....................... Allogamasellus View in CoL ( Figs 41–44 View FIGURES 41 – 48. 41 – 44 )
- Peritreme extending anteriorly at least to median region of coxa II.............................................. 13
13. Setae av2, pv2 on tibia I long, thick, spine-like............................................................ 14
- Setae av2, pv2 on tibia I unmodified...................................................................... 15
14. Tarsus I with a small pair of claws; dorsal shield setae j 1 not on prominent protuberance; on genu I av2 spine-like, al1 unmod- ified......................................................................... Heterogamasus View in CoL ( Figs 45–48 View FIGURES 41 – 48. 41 – 44 )
- Tarsus I without claws; dorsal shield setae j 1 on prominent protuberance; on genu I al1 spine-like, av2 unmodified......................................................................................... Evanssellus View in CoL ( Figs 49–52 View FIGURES 49 – 56. 49 – 52 )
15. Presternal plates absent............................................................. Cyrtolaelaps View in CoL ( Figs 53–56 View FIGURES 49 – 56. 49 – 52 )
- Presternal plates present............................................................................... 16
16. With one pair of presternal plates; if with two pairs (in Rhodacaroides aegypticus ), peritrematal shield not fused with exopodal shield near coxa IV.................................................................................. 17
- With 2–5 pairs of presternal shields; if with two pairs, peritrematal shield fused with exopodal shield near coxa IV....... 19
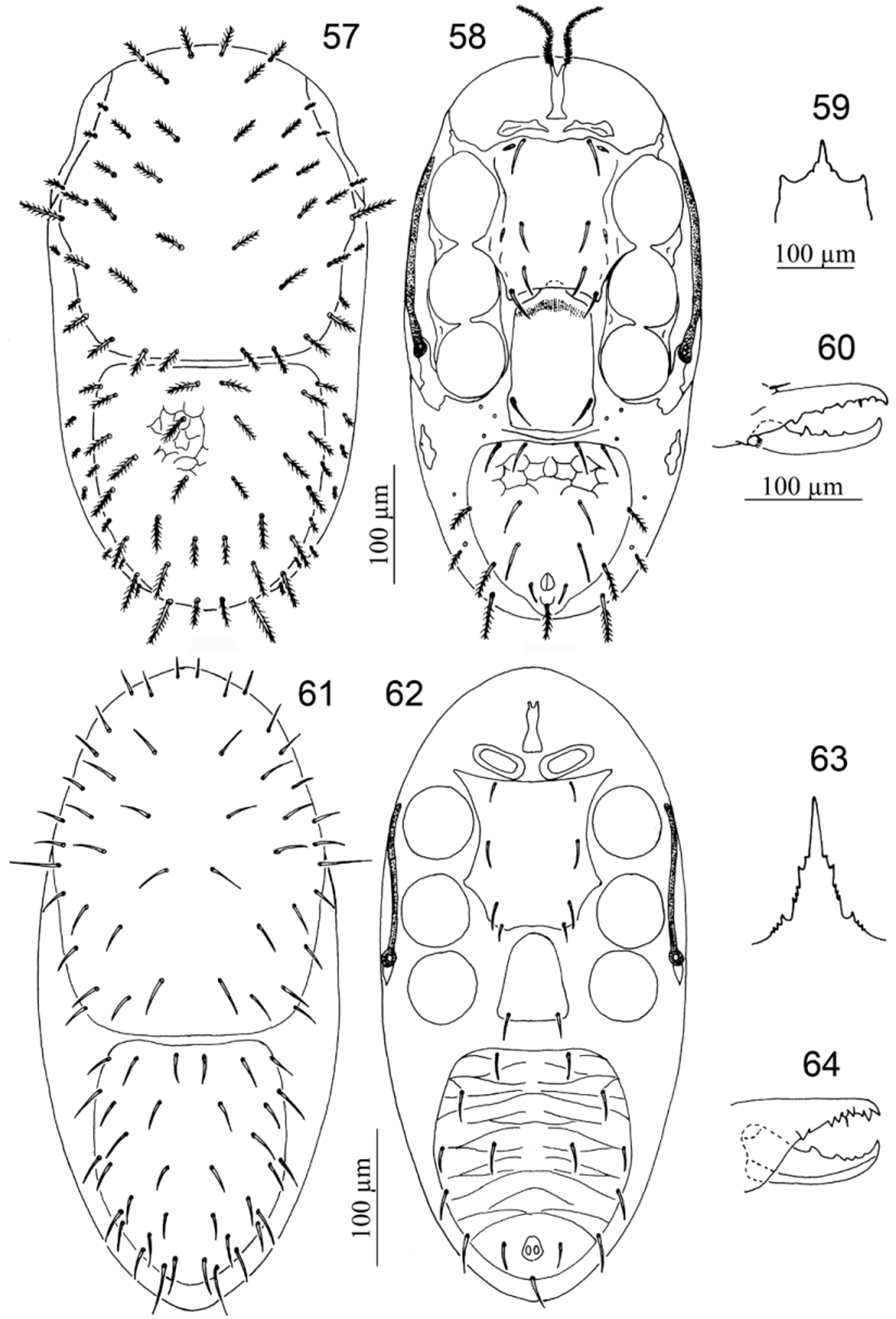
17. Dorsal shields with some setae pilose and/or spatulate.................................... Acugamasus View in CoL ( Figs 57–60 View FIGURES 57 – 64. 57 – 60 )
- Dorsal shields without pilose or spatulate setae............................................................ 18
18. Peritrematal shield not fused with exopodal shield near coxa IV........................... Rhodacaroides View in CoL ( Figs 61–64 View FIGURES 57 – 64. 57 – 60 )
- Peritrematal shield fused with exopodal shield near coxa IV.............................. Euryparasitus View in CoL ( Figs 65–68 View FIGURES 65 – 72. 65 – 68 )
19. Peritrematal and ventrianal shields fused.................................................. Periseius View in CoL ( Figs 69–72 View FIGURES 65 – 72. 65 – 68 )
- Peritrematal and ventrianal shields not fused............................................................... 20
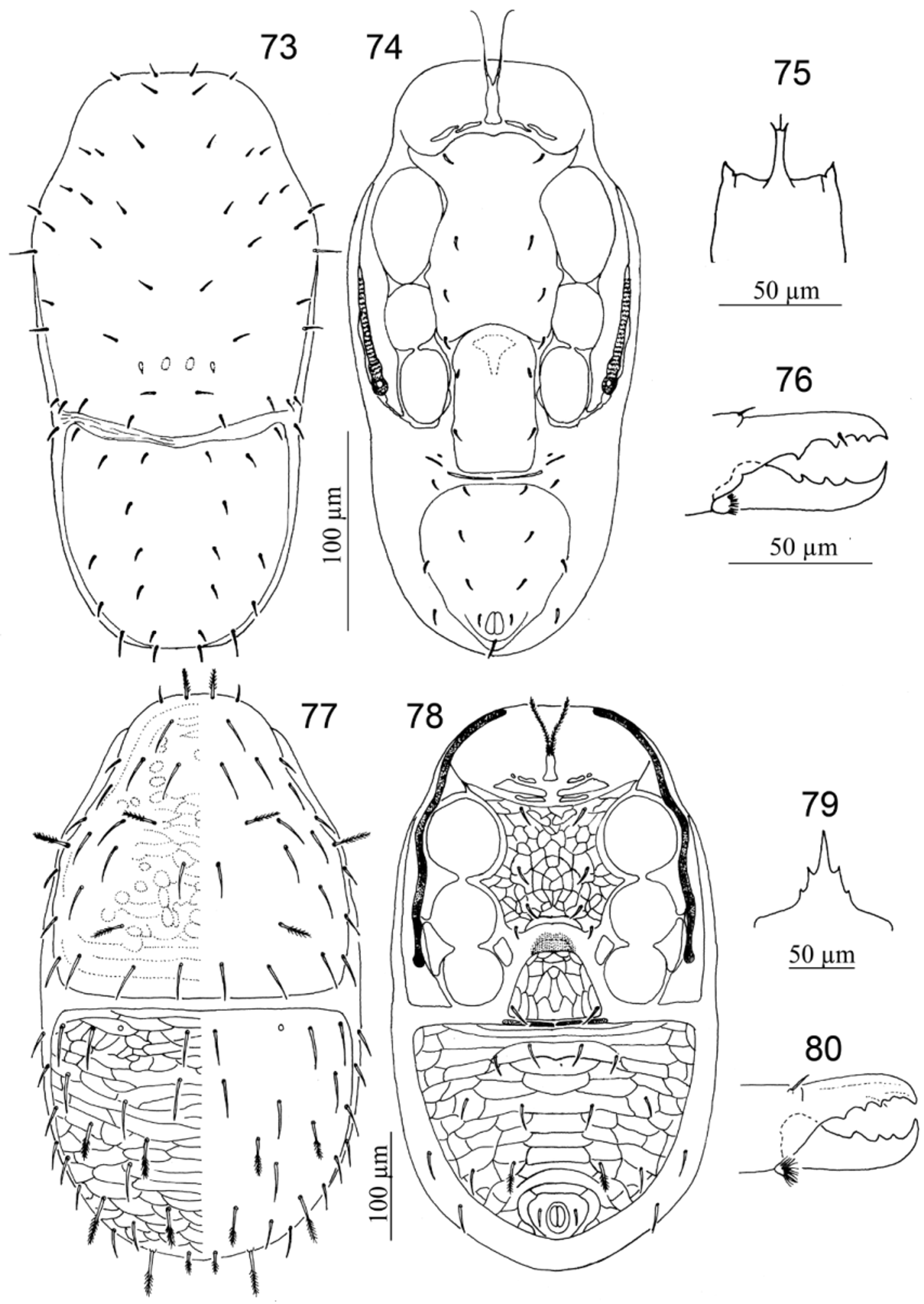
20. Opisthonotal section of dorsal shield with 12 pairs of setae................................ Solugamasus View in CoL ( Figs 73–76 View FIGURES 73 – 80. 73 – 76 )
- Opisthonotal section of dorsal shield with more than 12 pairs of setae........................................... 21
21. With two or three pairs of presternal plates............................................... Gamasellus View in CoL ( Figs 77–80 View FIGURES 73 – 80. 73 – 76 )
- With five pairs of presternal plates.................................................... Litogamasus View in CoL ( Figs 81–84 View FIGURES 81 – 88. 81 – 84 )
22. Line of fusion between podonotal and opisthonotal shields distinctly visible, straight or U-shaped.................... 23
- Line of fusion between podonotal and opisthonotal shields indistinct or absent.................................... 24
23. Line of fusion between podonotal and opisthonotal shields straight; peritrematal shield and exopodal shield near coxa IV not fused........................................................................ Gamasellevans View in CoL ( Figs 85–88 View FIGURES 81 – 88. 81 – 84 )
- Line of fusion between podonotal and opisthonotal shields U-shaped; peritrematal shield and exopodal shield near coxa IV fused.............................................................................. Rykellus View in CoL ( Figs 89–92 View FIGURES 89 – 96. 89 – 92 )
24. Dorsal shield fused with ventrianal shield................................................................ 25
- Dorsal shield not fused with ventrianal shield.............................................................. 34
25. Opisthogaster with incisions behind coxa IV directed almost transversely; dorsal shield setae fine, smooth and pointed except j 1 aciculate, z 4, z 5 and r 3 distally pilose................................................... Pyriphis View in CoL ( Figs 93–96 View FIGURES 89 – 96. 89 – 92 )
- Opisthogaster with incisions behind coxa IV directed strongly posteriorly, if transversely then most dorsal shield setae acicu- late or pilose....................................................................................... 26
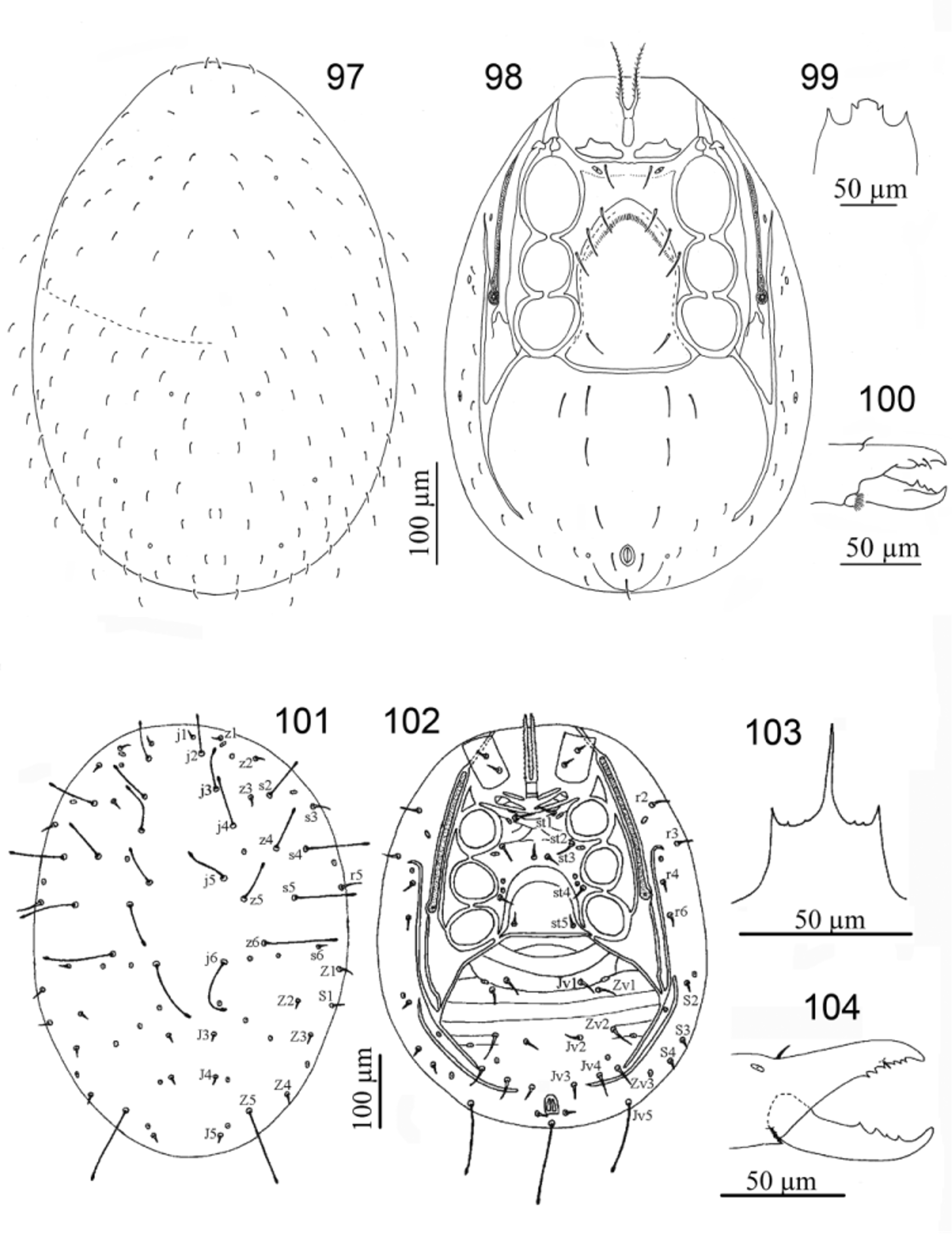
26. Dorsal shield with 50 or more pairs of setae............................................... Caliphis View in CoL ( Figs 97–100 View FIGURES 97 – 104. 97 – 100 )
- Dorsal shield with 45 or fewer pairs of setae.............................................................. 27
27. Sternal shield fused with endopodal shield near coxa IV..................................................... 28
- Sternal shield not fused or fused only by a narrow strip to endopodal shield near coxa IV.......................... 30
28. Exopodal shields near coxae II–III–III fused; with 0–3 pairs of presternal plates.............. Gamasiphis View in CoL ( Figs 101–104 View FIGURES 97 – 104. 97 – 100 )
- Exopodal shields near coxae II–III–III divided at median level of coxa III; with one pair of presternal plates........... 29
29. Dorsal and ventrianal shields with some pilose setae....................................... Cymiphis View in CoL ( Figs 105–108 View FIGURES 105 – 112. 105 – 108 )
- Dorsal and ventrianal shields with all setae smooth..................................... Heydeniella View in CoL ( Figs 109–112 View FIGURES 105 – 112. 105 – 108 )
30. Peritrematal shield fused with exopodal shield near coxa IV.................................................. 31
- Peritrematal shield not fused with exopodal shield near coxa IV............................................... 33
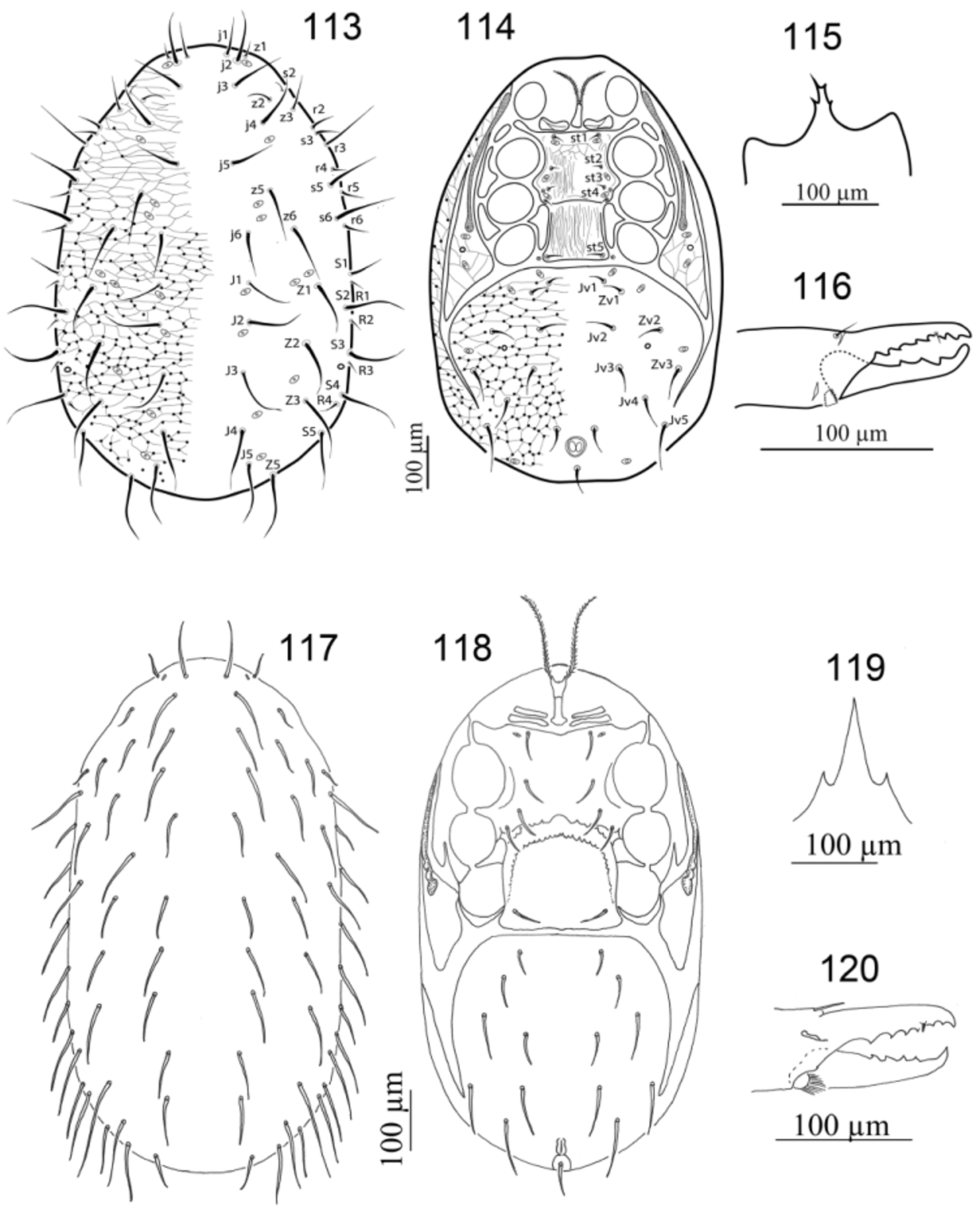
31. With one pair of presternal plates................................................... Ologamasus View in CoL ( Figs 113–116 View FIGURES 113 – 120. 113 – 116 )
- With two pairs of presternal plates....................................................................... 32
32. Setae st 1– st 4 in longitudinal line or st 4 slightly laterad to imaginary line between st 1– st 3; tibia IV with nine setae..................................................................................... Hydrogamasus View in CoL ( Figs 117–120 View FIGURES 113 – 120. 113 – 116 )
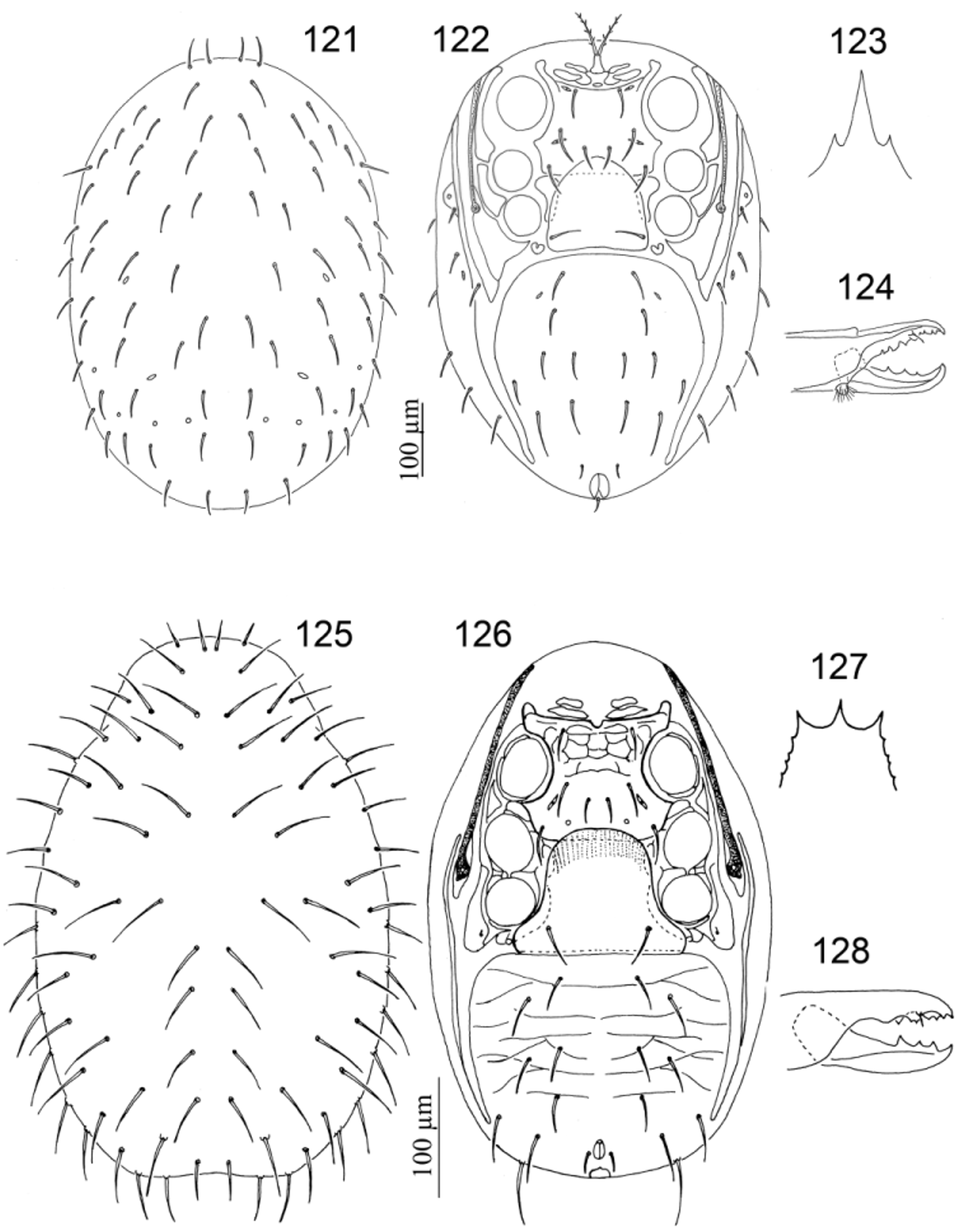
- Seta st 3 mediad to imaginary line between st 1, st 2 and st 4; tibia IV with ten setae.... .. Gamasiphoides View in CoL (part) ( Figs 121–124 View FIGURES 121 – 128. 121 – 124 )
33. With two pairs of presternal plates; peritreme extending anteriorly to region of coxa I......... Laelaptiella View in CoL ( Figs 125–128 View FIGURES 121 – 128. 121 – 124 )
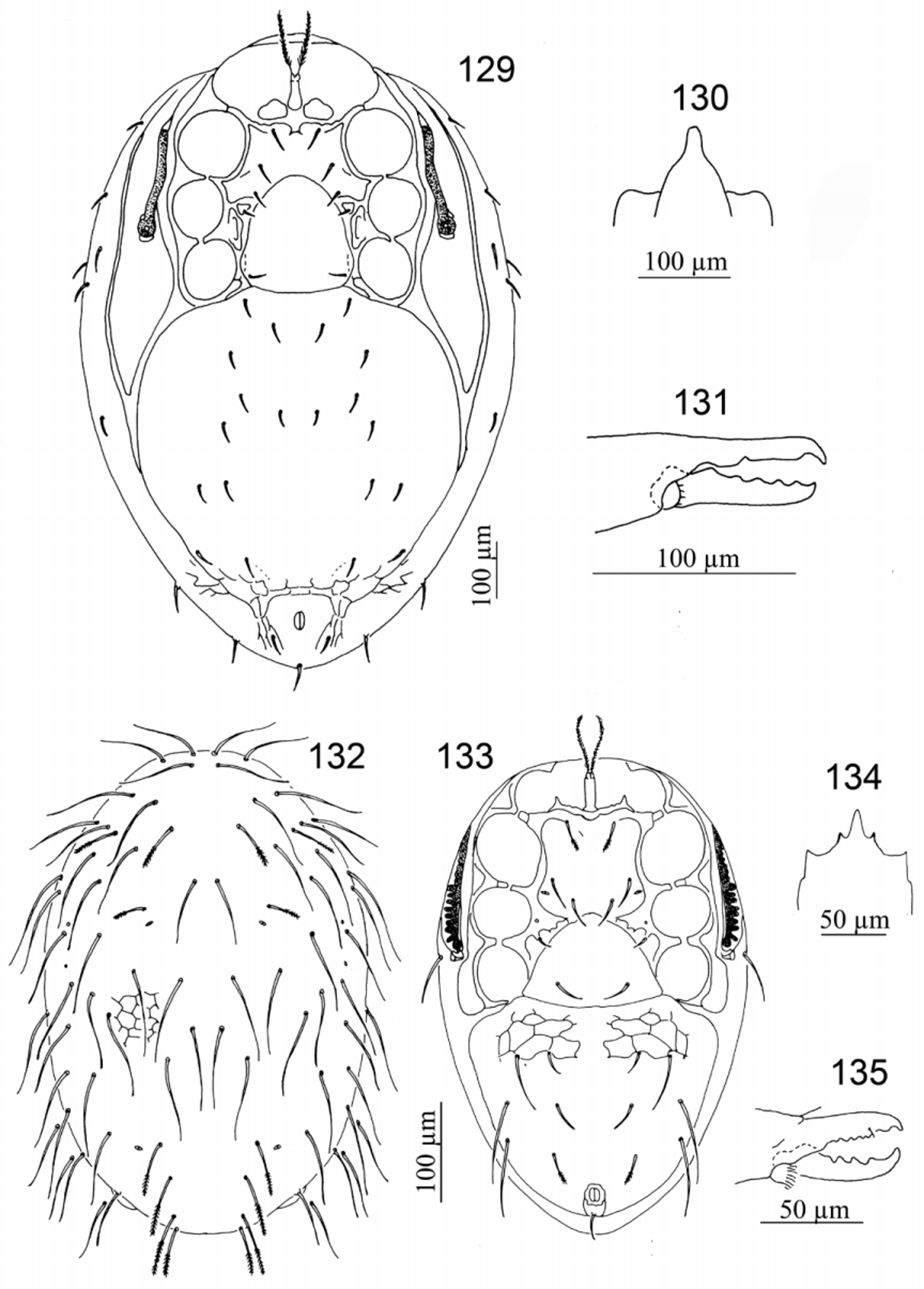
- With one pair of presternal plates; peritreme extending anteriorly to median region of coxa II.... Stylochirus View in CoL ( Figs 129–131 View FIGURES 129 – 135. 129 – 131 )
34. Outer margin of peritreme crenated............................................... Antennolaelaps View in CoL ( Figs 132–135 View FIGURES 129 – 135. 129 – 131 )
- Outer margin of peritreme straight...................................................................... 35
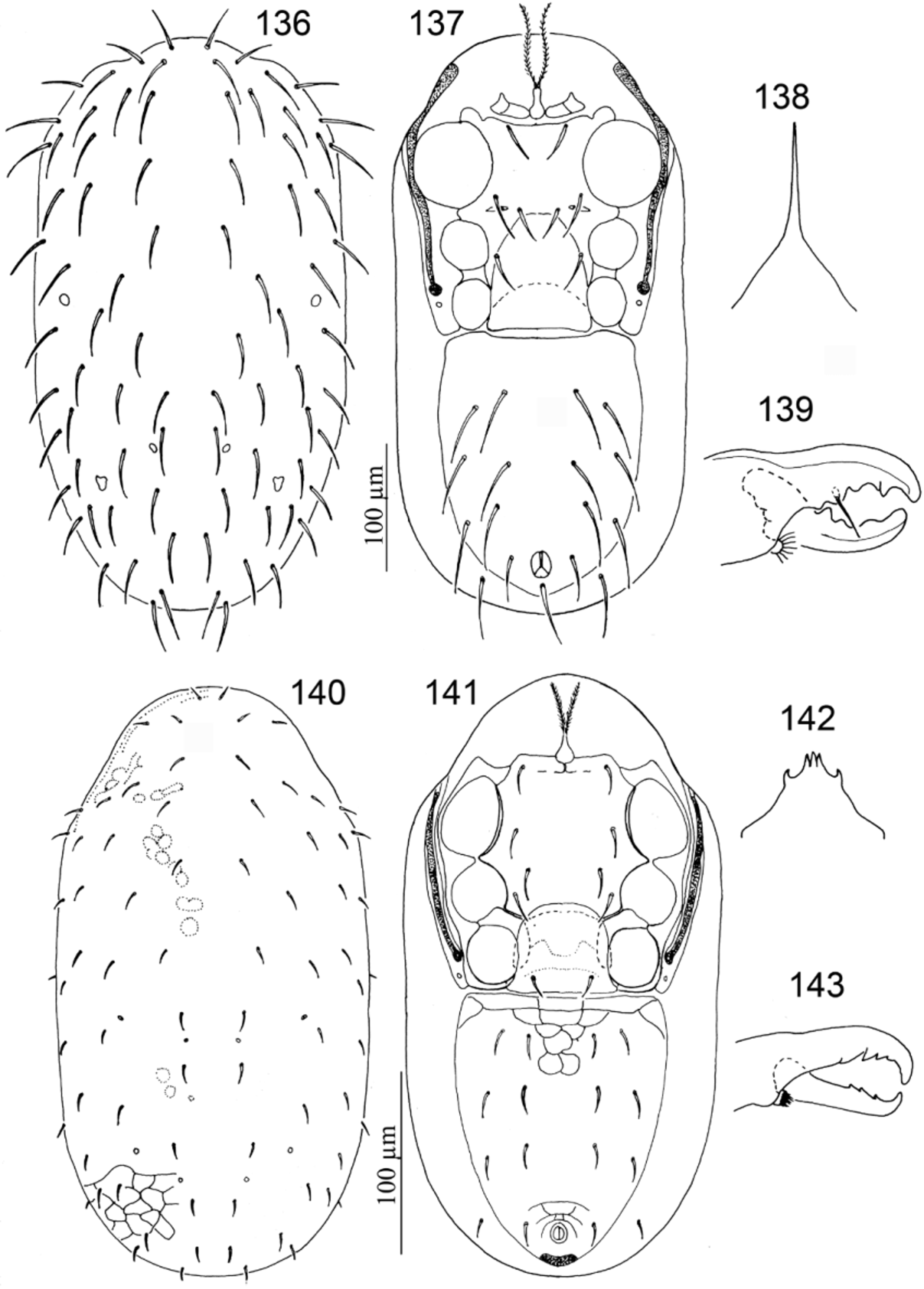
35. Leg II greatly enlarged, tarsus and tibia II with cuticular apophyses and with some setae very heavy, thickened and spur-like............................................................................. Pachymasiphis View in CoL ( Figs 136–139 View FIGURES 136 – 143. 136 – 139 )
- Leg II not greatly enlarged, tarsus and tibia II without very heavy, thickened and spur-like setae...................... 36
36. Genu I with 12 setae (two ventral setae)............................................ Gamasellopsis View in CoL ( Figs 140–143 View FIGURES 136 – 143. 136 – 139 )
- Genu I with 13 setae (three ventral setae)................................................................. 37
37. Peritrematal shield not fused with exopodal shield.......................................................... 38
- Peritrematal shield fused with exopodal shield............................................................. 41
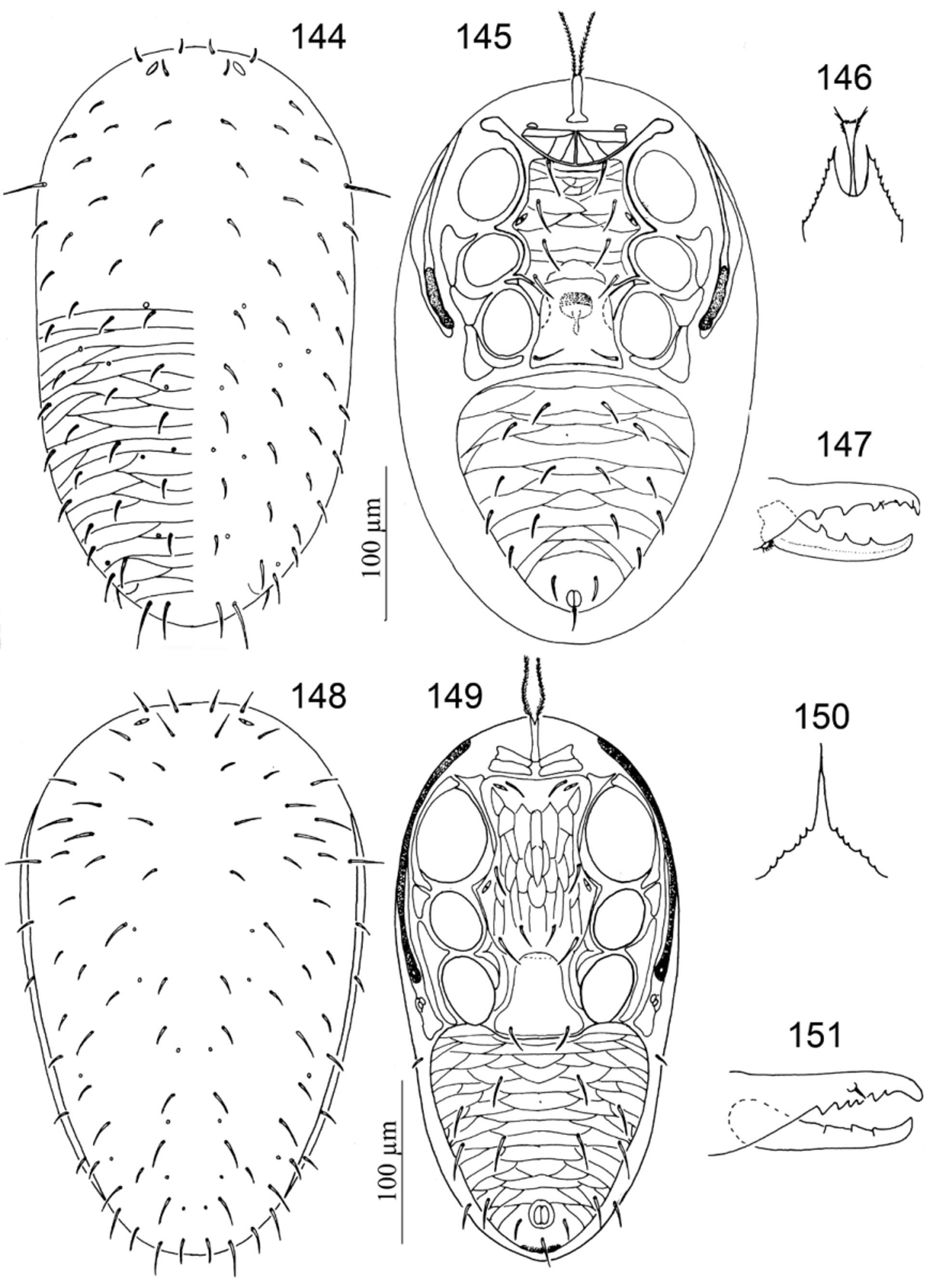
38. Sternal shield not fused with endopodal shield near coxa IV; epistome with a club-shaped anterocentral extension................................................................................... Neogamasellevans View in CoL ( Figs 144–147 View FIGURES 144 – 151. 144 – 147 )
- Sternal shield fused with endopodal shield near coxa IV shield; epistome without a club-shaped anterocentral extension... 39
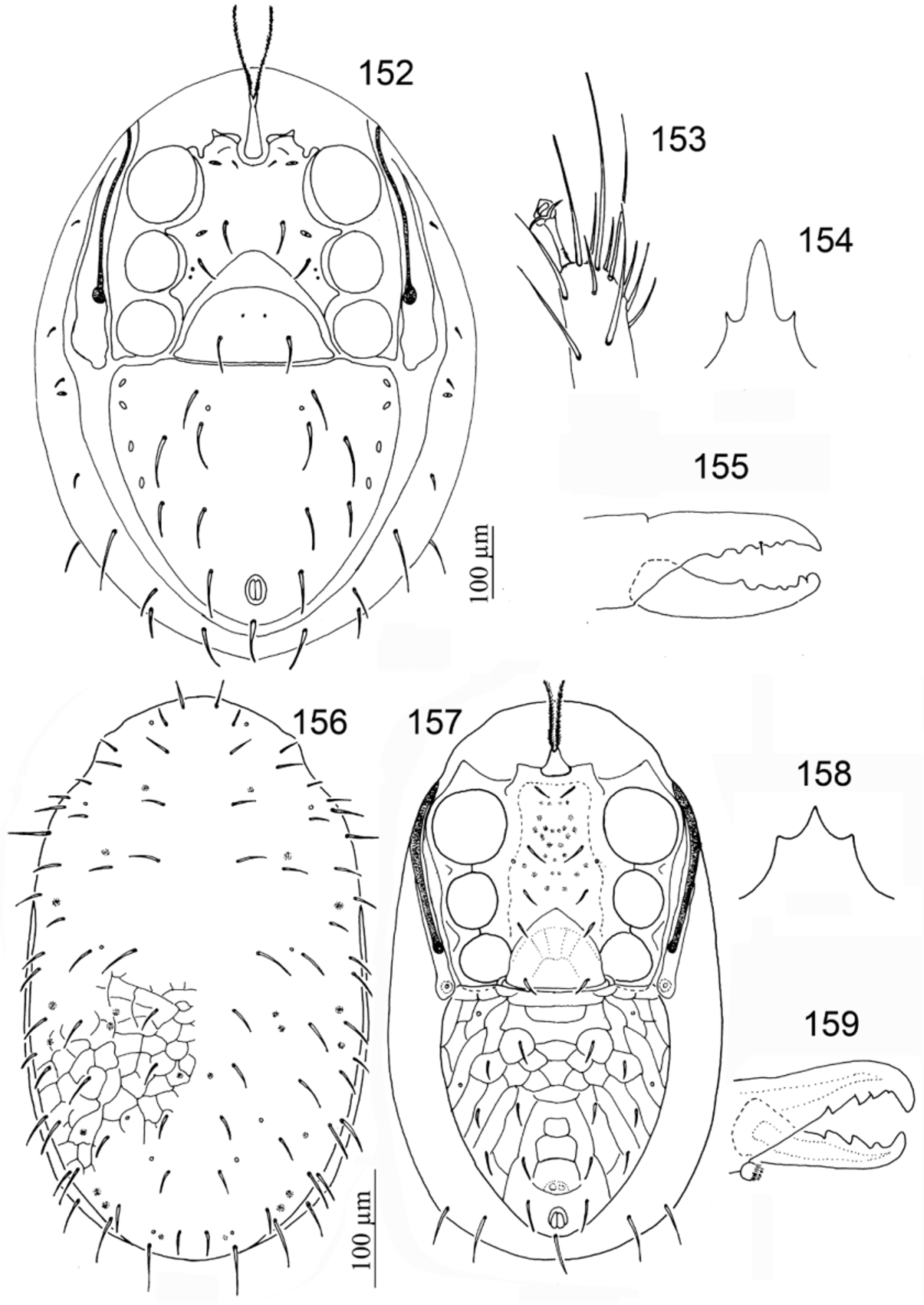
39. Pretarsus I sessile................................................................ Sessiluncus View in CoL ( Figs 156–159 View FIGURES 152 – 159. 152 – 155 )
- Pretarsus I pedunculate............................................................................... 40
40. Genu III with nine setae (two ventral setae) and genu IV with ten setae (five dorsal and two ventral setae)............................................................................................ Onchogamasus View in CoL ( Figs 148–151 View FIGURES 144 – 151. 144 – 147 )
- Genu III with eight setae (one ventral seta) and genu IV with eight or nine setae (four or five dorsal and one ventral setae)................................................................................... Gamasitus View in CoL ( Figs 152–155 View FIGURES 152 – 159. 152 – 155 )
41. With two pairs of presternal plates........................................... Gamasiphoides View in CoL (part) ( Figs 160–163 View FIGURES 160 – 167. 160 – 163 )
- With one pair of presternal plates, partially fused or not fused to sternal shield................................... 42
42. Sternal shield fused with endopodal shield near coxa IV......................... Queenslandolaelaps View in CoL ( Figs 164–167 View FIGURES 160 – 167. 160 – 163 )
- Sternal shield not fused with endopodal shield near coxa IV.................................................. 43
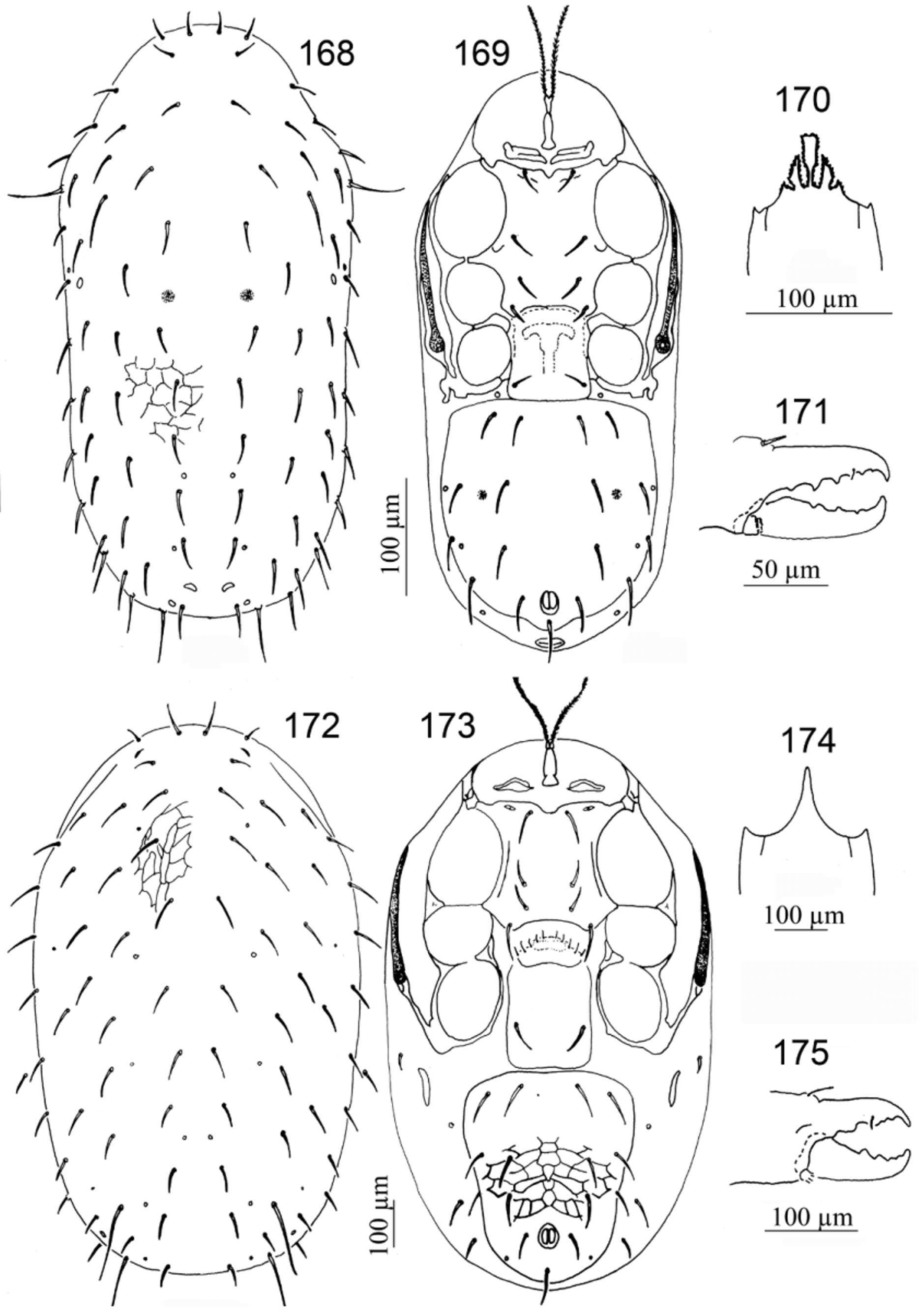
43. Epistome with a club-shaped anteromedian extension; connection between peritrematal and exopodal shields behind stigma narrower than peritreme..................................................... Geogamasus View in CoL (part) ( Figs 168–171 View FIGURES 168 – 175. 168 – 171 )
- Epistome without a club-shaped anteromedian extension; connection between peritrematal and exopodal shields behind stigma wider or narrower than peritreme....................................................................... 44
44. Pretarsus I not pedunculate and subequal to other pretarsi............................... Parasitiphis View in CoL ( Figs 172–175 View FIGURES 168 – 175. 168 – 171 )
- Pretarsus I pedunculate and smaller than other pretarsi....................................................... 45
45. Insemination pore located on trochanter III............................................. Athiasella View in CoL ( Figs 176–179 View FIGURES 176 – 183. 176 – 179 )
- Insemination pore located on coxa III........................................... Hydrogamasellus View in CoL ( Figs 180–183 View FIGURES 176 – 183. 176 – 179 )
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |