Stichillus species
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5352.3.3 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:858051C8-824F-4A01-A700-8AA7F58A59BD |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8411509 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03EB87EB-FF88-F80B-808A-FA49CB80C2BB |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Stichillus species |
| status |
|
A key to males of ten Stichillus species from East Asia
(except Mongolia and North Korea, modified after Liu & Chou 1996; Liu 2001; Nakayama & Shima 2004)
1. Hind tibia with two dorsal longitudinal setal palisades; ventral membrane of aedeagus kidney-shaped (see Liu 2001: 194, figs. 84, 85)......................................................................... S. tuberculosus Liu & Chou View in CoL
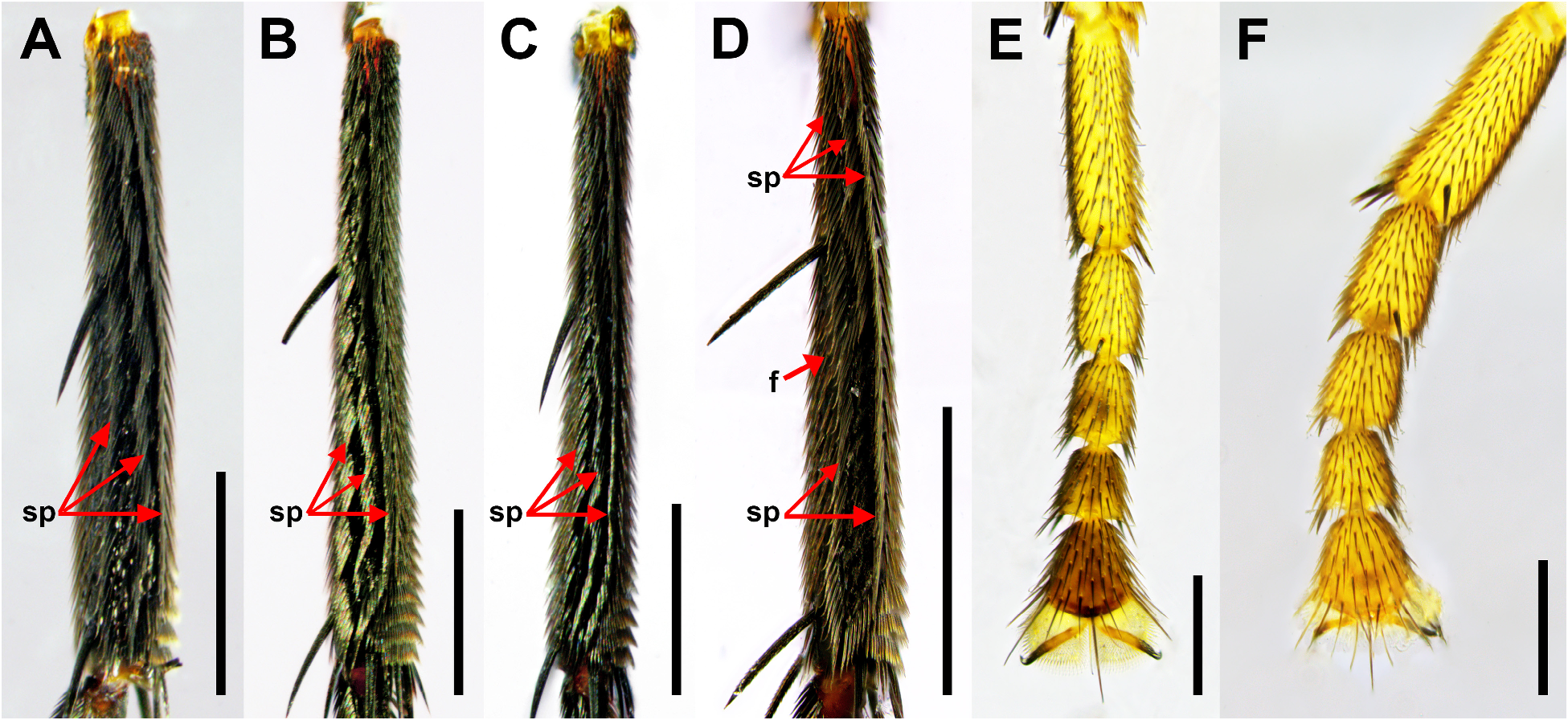
- Hind tibia with three dorsal longitudinal setal palisades ( Fig. 4A View FIGURE 4 ); ventral membrane of aedeagus not as above........... 2
2. Anterior and middle dorsal setal palisades of hind tibia fused apically ( Fig. 4D View FIGURE 4 ); dorsal plate of aedeagus without any strong pointed process at basal portion ( Fig. 9D View FIGURE 9 ).................................................................. 3
- Anterior and middle dorsal setal palisades of hind tibia not fused apically (hind tibia with three setal palisades along its whole length) ( Fig. 4A View FIGURE 4 ); dorsal plate of aedeagus with strong pointed process on dorsal or right side of basal portion ( Figs. 7E View FIGURE 7 )... 7
3. Middle arc of ocellar region distinctly larger than lateral arc; anterior and middle dorsal setal palisades of hind tibia fused at apical 1/5 or 1/4; dorsal plate of aedeagus nearly straight (see Liu 2001: 191, figs. 68, 76)............................ 4
- Middle arc of ocellar region not distinctly larger than lateral arc; anterior and middle dorsal setal palisades of hind tibia fused at apical half ( Fig. 4D View FIGURE 4 ); dorsal plate of aedeagus curved upward ( Fig. 9D View FIGURE 9 )........................................ 5
4. Middle arc of ocellar region greatly extended anteriorly; anterior and middle dorsal setal palisades of hind tibia fused at apical 1/5; epandrial lobe covered with short hairs (see Liu 2001: 191, figs. 68, 76)....................... S. suspectus (Brues) View in CoL
- Middle arc of ocellar region not distinctly extended anteriorly; anterior and middle dorsal setal palisades of hind tibia fused at apical 1/4; epandrial lobe covered with long hairs (see Liu 2001: 193, figs. 75, 80)........... S. polychaetous Liu & Chou View in CoL
5. Space between arcs of three-looped ocellar region wide ( Fig. 2F View FIGURE 2 ; see Liu 2001: 191, fig. 69)........... S. sinuosus Schmitz Space View in CoL between arcs of three-looped ocellar region narrow ( Fig. 2H View FIGURE 2 )............................................. 6
6. Dorsal plate of aedeagus without well-developed dorsobasal ridge; with numerous minute spinules on right surface of apical portion; without short pointed process apically ( Fig. 9E View FIGURE 9 ).................................... S. spinosus Liu & Chou View in CoL
- Dorsal plate of aedeagus with well-developed dorsobasal ridge; without numerous minute spinules on right surface of apical portion; with short pointed process apically (see Liu 2001: 194, figs. 86, 87).................. S. orbiculatus Liu & Chou View in CoL
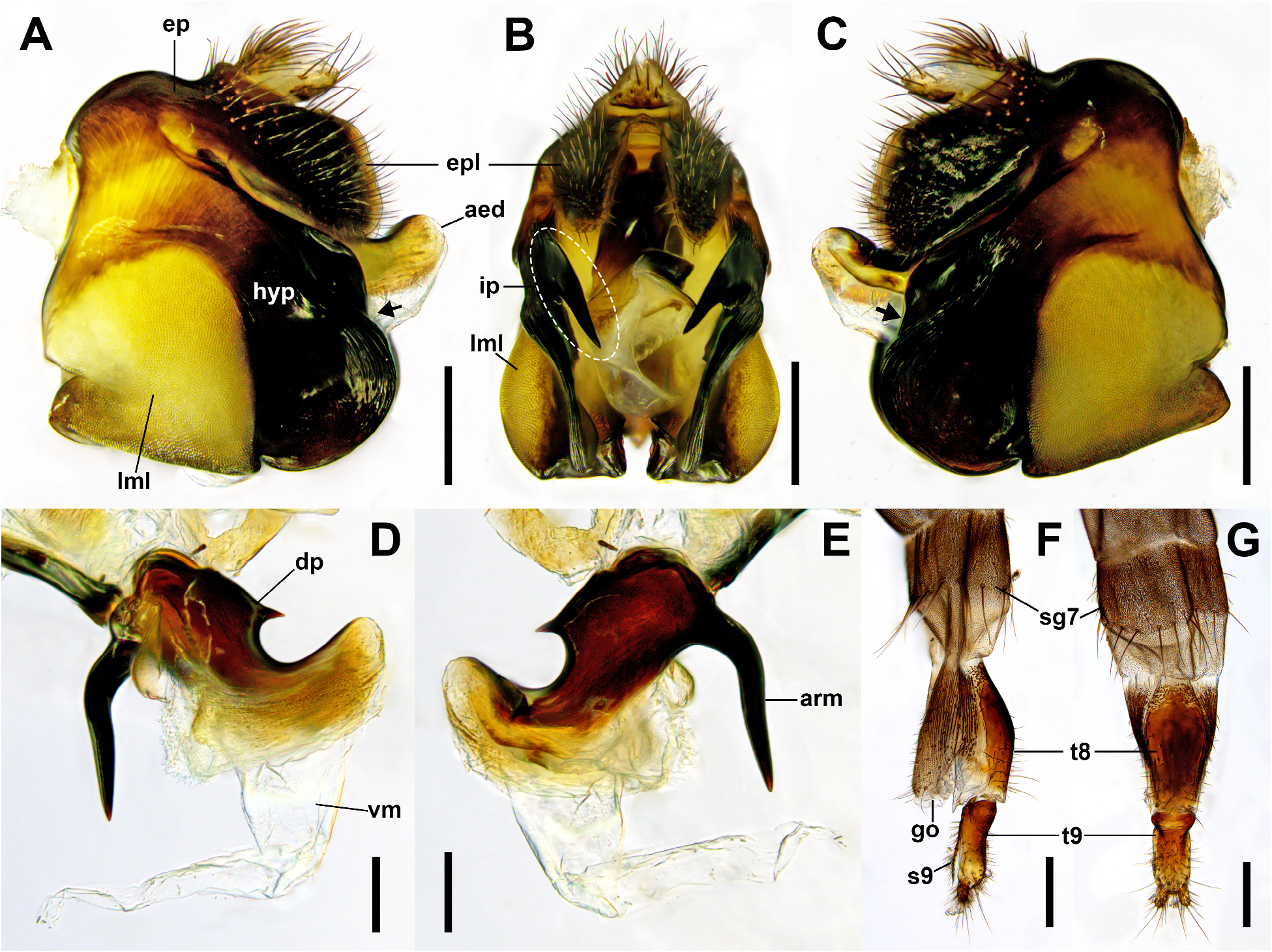
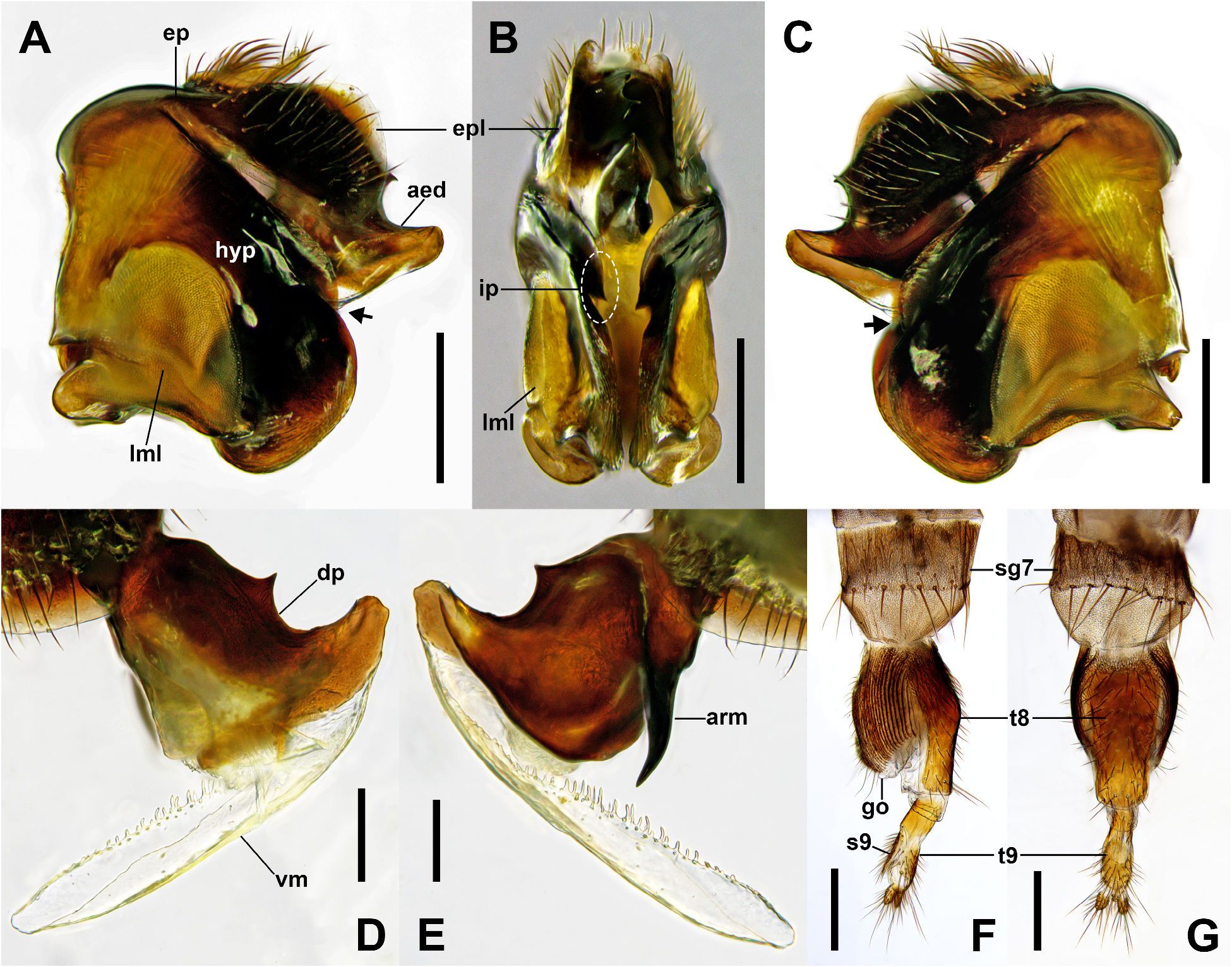
7. Tip of inner projection on posterior margin of hypandrium situated below bottom level of lateral membranous lobe of hypandrium ( Fig. 6B View FIGURE 6 ); dorsal plate of aedeagus without pointed dorsal process, with hooked apex ( Fig. 6D View FIGURE 6 )................................................................................................ S. cylindratus Nakayama & Shima View in CoL
- Tip of inner projection on posterior margin of hypandrium situated above bottom level of lateral membranous lobe of hypandrium ( Fig. 7B View FIGURE 7 ); dorsal plate of aedeagus with pointed dorsal process, apex not hooked ( Fig. 7D View FIGURE 7 )........................... 8
8. Epandrial lobe not greatly enlarged apically ( Fig. 7A View FIGURE 7 ); tip of inner projection on posterior margin of hypandrium long ( Fig. 7B View FIGURE 7 ); dorsal plate of aedeagus with single robust arm curved forming obtuse-angle on right side of basal portion ( Fig. 7E View FIGURE 7 )....................................................................................... S. japonicus (Matsumura) View in CoL
- Epandrial lobe enlarged apically ( Fig. 8A View FIGURE 8 ); tip of inner projection on posterior margin of hypandrium short ( Fig. 8B View FIGURE 8 ); dorsal plate of aedeagus with or without single robust arm on right side of basal portion (presence of robust arm uncertain in S. acuminatus View in CoL ); if present, slightly curved, not forming distinct obtuse-angle ( Fig. 8E View FIGURE 8 )................................. 9
9. First flagellomere of antenna orange red; posterodorsal margin of epandrial lobe nearly straight; dorsal plate of aedeagus curved with angle less than 90°, with apex pointed (see Liu 2001: 192, figs. 78, 79)................... S. acuminatus Liu & Chou View in CoL
- First flagellomere of antenna dark reddish brown ( Fig. 1E View FIGURE 1 ); posterodorsal margin of epandrial lobe rounded ( Fig. 8A View FIGURE 8 ); dorsal plate of aedeagus curved with angle more than 90°, with apex blunt ( Fig. 8D View FIGURE 8 )...................... S. koreanus sp. nov.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.