Stichillus koreanus, Lee & Kim, 2023
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5352.3.3 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:858051C8-824F-4A01-A700-8AA7F58A59BD |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8407456 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03EB87EB-FF80-F810-808A-FEA9CED9C71D |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Stichillus koreanus |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Stichillus koreanus sp. nov.
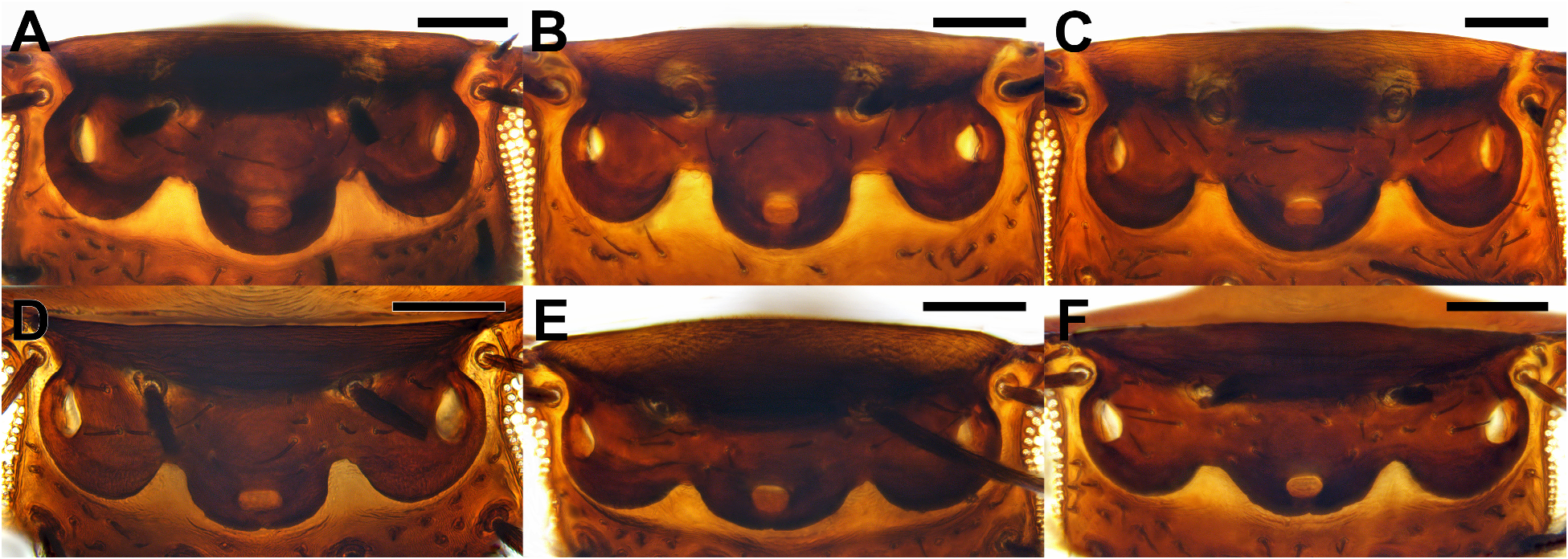
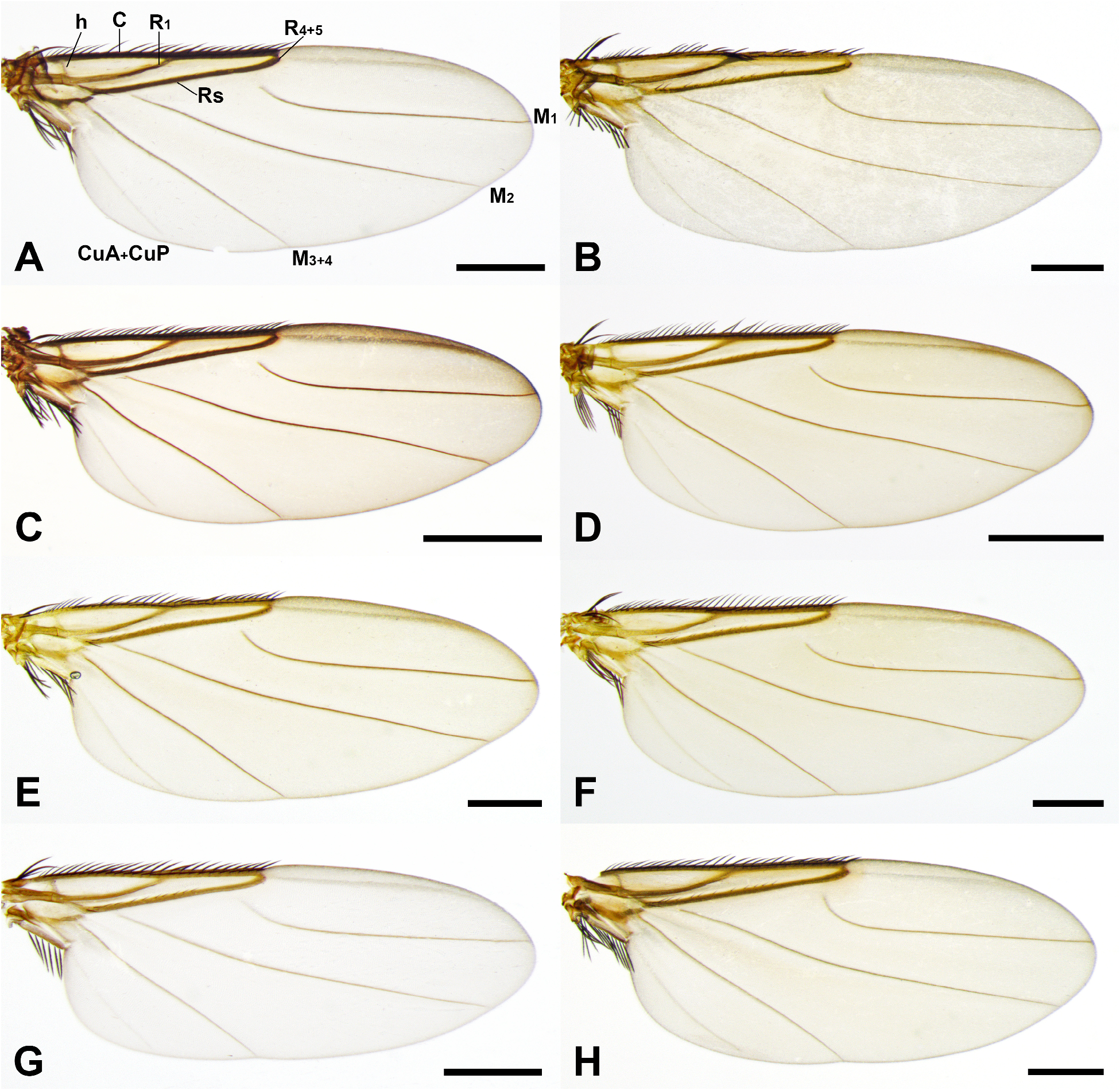
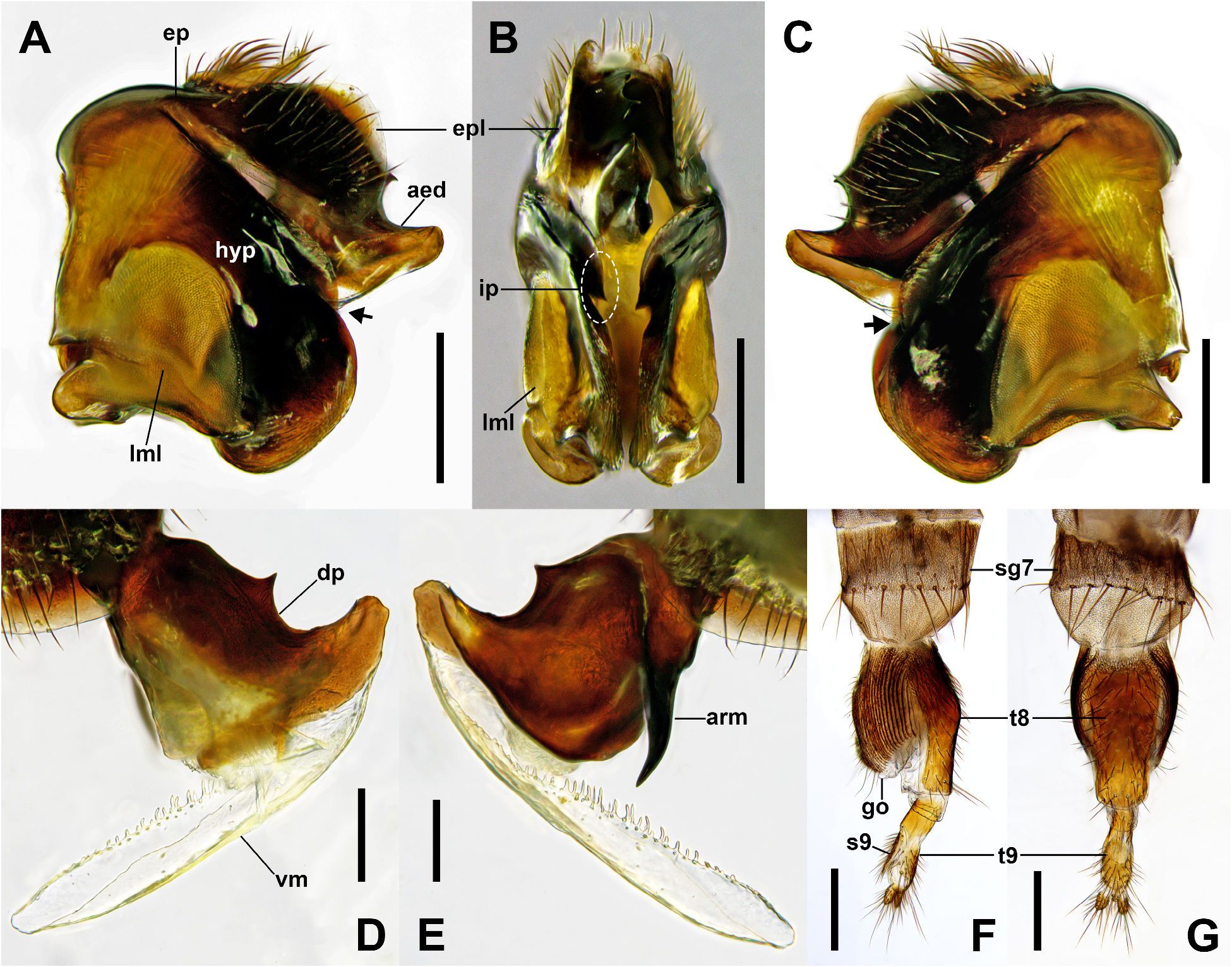
( Figs. 1E, 1F View FIGURE 1 , 2E, 2F View FIGURE 2 , 3A–C View FIGURE 3 , 4C, 4F View FIGURE 4 , 5E, 5F View FIGURE 5 , 8 View FIGURE 8 , 11 View FIGURE 11 )
Diagnosis. This species can be distinguished from other Stichillus species by the combination of the following characteristics: male epandrial lobe distinctly enlarged dorsoapically; inner projection on posterior margin of hypandrium small, apically pointed; dorsal plate of aedeagus with short pointed dorsal process and single robust, gently curved, pointed arm on right side of ventrobasal portion; female tergite 9 moderately elongated, covering only posterior half.
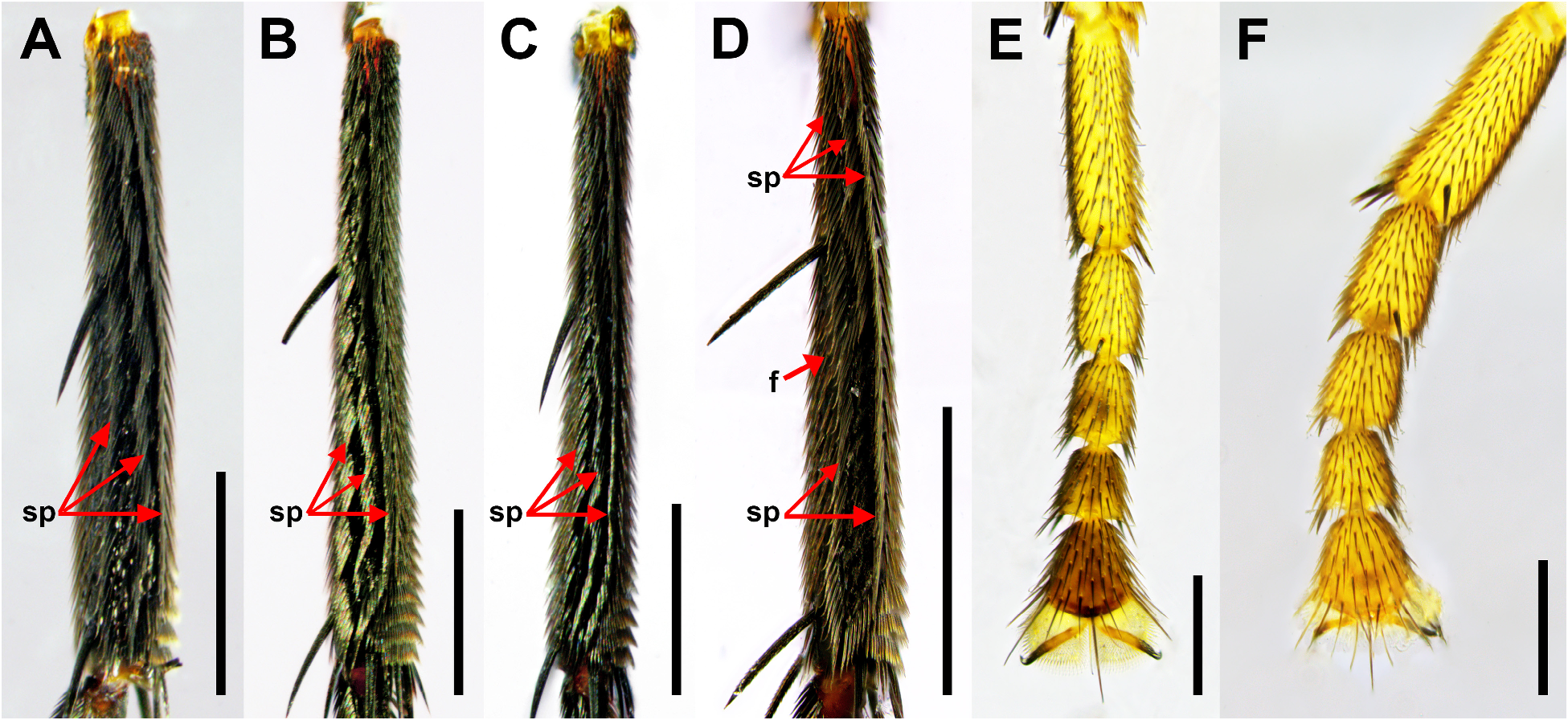
Description. Male. Body length 3.76–4.34 mm (n=10). Head ( Figs. 1E View FIGURE 1 , 2E View FIGURE 2 , 3A–C View FIGURE 3 ). Frons black, shiny, with three transverse rows of four long bristles and sparsely covered fine hairs; supra-antennal bristle absent; middle row of bristles slightly procurved. Ocellar region as in figures 2E, 3A–C. First flagellomere dark reddish brown, pyriform, twice longer than wide; arista brown, located subapically. Palpus yellowish brown, with single long bristle on apex and some shorter bristles on near apex to ventral margin. Labrum and labella yellow, short. Thorax ( Fig. 1E View FIGURE 1 ). Scutum and scutellum black. Posterior margin of scutum with two pairs of strong prescutellar bristles; inner pair of bristles distantly spaced with each other. Scutellum with anterior pair of long narrow bristles and posterior pair of strong bristles distinctly longer than anterior bristles. Pleuron dark reddish brown; upper half of anepisternum covered with short setae. Legs ( Figs. 1E View FIGURE 1 , 4C, F View FIGURE 4 ). Black except fore tibia and tarsus yellowish brown. Fore tibia with one strong dorsal bristle on basal half and single longitudinal row of short dorsal setulae on entire length. Fore tarsomere 5 widened, with enlarged pulvilli ( Fig. 4F View FIGURE 4 ). Midtibia with two dorsal longitudinal setal palisades on basal half, which fused together from middle to apical half, and with one pair of bristles on basal quarter (one dorsal and the other anterodorsal), one long anteroventral preapical bristle, two short dorsal preapical setae, and one long posteroventral apical spur. Hind tibia ( Fig. 4C View FIGURE 4 ) with three dorsal longitudinal setal palisades along its whole length, one anterodorsal strong bristle on basal third, one anterodorsal preapical bristle, one dorsal and three ventral long apical spurs, and some posterior—posteroventral apical short setae. Wing ( Fig. 5E View FIGURE 5 ). 3.27–3.73 mm long (n=10). Costal index 0.5–0.54. Mean costal ratio 1.02:1; range 0.95–1.08:1. Costal setae of costal section II 0.09–0.12 mm long. Vein Rs with single row of short, fine hairs on dorsal face except apical end. Vein R 2+3 absent. Vein M 1 slightly curved basally and nearly straight apically. Veins brown, membrane hyaline with yellow tinge. 6–8 alular setae present, 0.17–0.22 mm long. Halter black. Abdomen ( Fig. 1E View FIGURE 1 ). Tergites black, shiny, extended posteromedially; tergite 2 elongated, approximately twice longer than tergite 1. Venter of abdomen blackish brown, with single pair of oval, weakly developed sternite 6. Hypopygium ( Fig. 8A–C View FIGURE 8 ). Epandrium nearly symmetrical, dark brown; epandrial lobe elongated posteroventrally, covered with some short hairs, with rounded apex distinctly enlarged dorsoapically. Hypandrium large, dark brown; lateral membranous lobe triangular, densely spinulose; inner projection on posterior margin of hypandrium small, pointed, protruded ventrally ( Fig. 8B View FIGURE 8 ); tip of inner projection situated far above bottom level of lateral membranous lobe. Cercus and hypoproct short, with some short hairs. Aedeagus ( Fig. 8D, E View FIGURE 8 ). Dorsal plate dark brown, with short pointed dorsal process directing posteriorly; ventrobasal portion of dorsal plate with single robust, slightly curved, pointed arm on right side ( Fig. 8E View FIGURE 8 ). Ventral membrane usually twisted at base and elongated ventrally, hyaline, approximately twice as long as maximum width of basal portion, tapering apically, serrated on single side.
Female. Body length 3.92–5.45 mm (n=10). Head ( Figs. 1F View FIGURE 1 , 2F View FIGURE 2 ). Similar to male, except first flagellomere smaller, globose, orange. Ocellar region as in figure 2F. Thorax ( Fig. 1F View FIGURE 1 ). Similar to male. Legs ( Fig. 1F View FIGURE 1 ). Similar to male, except fore apical tarsomere not widened, pulvilli not enlarged. Wing ( Fig. 5F View FIGURE 5 ). Similar to male, 3.39– 4.18 mm long (n=10). Costal index 0.49–0.54. Mean costal ratio 0.92:1; range 0.87–0.99:1. Costal setae of costal section II 0.09–0.13 mm long. 6–8 alular setae present, 0.19–0.23 mm long. Halter black. Abdomen ( Figs. 1F View FIGURE 1 , 8F, G View FIGURE 8 ). Tergites 1–6 well developed, black. Tergite 2 elongated as male. Tergite 7 absent ( Fig. 8F–G View FIGURE 8 ). Tergite 8 ( Fig. 8G View FIGURE 8 ) nearly rectangular, dark brown, 2.5× longer than wide, anterior portion slightly swollen dorsally ( Fig. 8F View FIGURE 8 ). Tergite 9 ( Fig. 8F–G View FIGURE 8 ) approximately 4× as long as anterior width, brown; anterior half cylindrical with dorsal face unsclerotized; posterior half with only dorsal face sclerotized; posterior margin with two pairs of long hairs and some short hairs. Venter of abdomen blackish brown, with only sternite 9 discernable. Genital opening enlarged posteriorly ( Fig. 8F View FIGURE 8 ). Cercus oval, apically with some long and short hairs.
Etymology. The specific epithet refers to the country of origin, Korea.
Type specimens. Holotype, ♂, Korea: Gangwon-do , Pyeongchang-gun , Yongpyeong-myeon , Nodong-ri, on rock surfaces covered with moss in Nodong valley, 37°41′50.4″N, 128°28′34.1″E, ca. 783 m, 16.viii.2021, hand collecting, J. H. Lee leg. [KNU-PHO 2023-0584] ( NIBR) GoogleMaps . Paratypes, 1♀, same data as holotype, J. H. Lee leg. [KNU-PHO 2023-0585] ( KNU) GoogleMaps ; 5♂ 2♀, Korea: Gangwon-do, Yangyang-gun, Seo-myeon , Osaek-ri , Mt. Seoraksan , 38°06′12.8″N, 128°27′22.5″E, 1004 m, 27.viii–7.ix.2017, pitfall trap, T. S. Kwon et al. leg. [KNU-PHO 2022-0224] ( KNU) GoogleMaps ; 1♂, Gangwon-do, Pyeongchang-gun, Jinbu-myeon , Dongsan-ri , Mt. Odaesan , streamside near Sangwonsa temple, 37°47′03.9″N, 128°33′45.2″E, ca. 934 m, 15.vii–14.viii.2020, Malaise trap, J. H. Lee et al. leg. [KNU-PHO 2023-0583] ( KNU) GoogleMaps ; 2♀, Chungcheongbuk-do, Danyang-gun, Daegang-myeon, Yongbuwon-ri , Mt. Sobaeksan , Yeonhwabong Peak , 36°56′06″N, 128°27′32″E, ca. 1337 m, 16.vii.2021, hand collecting, J. H. Lee leg. [KNU-PHO 2023-0587] ( KNU) GoogleMaps ; 1♀, Gyeongsangbuk-do, Cheongdo-gun, Unmun-myeon, Sinwon-ri , streamside in Unmunsan National Recreational Forest , 35°39′05″N, 129°01′28″E, ca. 440 m, 27.viii.2022, hand collecting, J. H. Lee leg. [KNU-PHO 2023-0588] ( KNU) GoogleMaps .
Other specimens examined. Korea: 2♂, Gangwon-do, Jeongseon-gun, Gohan-eup, Gohan-ri, Mt. Jeongamsan, near Bugeumgyo bridge, 37°11′19.1″N, 128°52′38″E, 781 m, 19–29.vii.2017, pitfall trap, T.S. Kwon et al. leg.( KNU); 1♂, Gangwon-do, Pyeongchang-gun, Daehwa-myeon, Haanmi-ri, Mt. Gariwangsan, 37°28′32.2″N, 128°30′09.2″E, 1004 m, 18–28.viii.2017, pitfall trap, T. S. Kwon et al. leg. ( KNU); 1♂, ditto, 37°28′37.8″N, 128°31′17.7″E, 1200 m; 2♂, Gangwon-do, Pyeongchang-gun, Mitan-myeon, Hoedong-ri, Mt. Gariwangsan, 37°27′41.5″N, 128°33′48.2″E, 1562 m, 18–28.viii.2017, pitfall trap, T. S. Kwon et al. leg. ( KNU); 1♀, Gangwon-do, Yangyang-gun, Seo-myeon, Osaek-ri, Mt. Seoraksan, 38°05′41.9″N, 128°27′01″E, 820 m, 27.viii–7.ix.2017, pitfall trap, T. S. Kwon et al. leg. ( KNU); 2♂ 3♀, ditto, 38°06′42.1″N, 128°27′39.7″E, 1401 m; 1♂, ditto, 38°06′59.6″N, 128°27′50.4″E, 1596 m; 1♂, Gyeongsangnam-do, Sancheong-gun, Sicheon-myeon, Jungsan-ri, Mt. Jirisan, 35°19′08.5″N, 127°45′16.8″E, 884 m, 5–18.viii.2018, pitfall trap, T. S. Kwon et al. leg. ( KNU); 43♂ 9♀, ditto, 35°19′34.9″N, 127°45′08.9″E, 998 m; 2♂, ditto, 35°19′40.8″N, 127°44′29.7″E, 1223 m; 8♂, ditto, 35°19′40.2″N, 127°44′07.3″E, 1392 m; 31♂ 6♀, ditto, 35°19′53.8″N, 127°44′02.8″E, 1597 m; 3♂, ditto, 35°20′04.9″N, 127°43′50.8″E, 1799 m; 2♂, Gyeongsangnam-do, Hapcheon-gun, Gaya-myeon, Chiin-ri, Mt. Gayasan, 35°48′55.6″N, 128°06′45.2″E, 1000 m, 6–19.viii.2018, pitfall trap, T. S. Kwon et al. leg. ( KNU); 16♂ 1♀, ditto, 35°49′14.2″N, 128°06′59.3″E, 1214 m; 1♂, ditto, 35°49′23.6″N, 128°07′17″E, 1399 m; 1♂, Jeollabuk-do, Muju-gun, Seolcheon-myeon, Samgong-ri, Mt. Deokyusan, 35°51′58.4″N, 127°44′51.2″E, 1377 m, 4–14.ix.2019, pitfall trap, T. S. Kwon et al. leg.( KNU); 1♂, Gangwon-do, Pyeongchang-gun, Jinbu-myeon, Dongsan-ri, Mt. Odaesan, streamside near Sangwonsa temple, 37°47′03.9″N, 128°33′45.2″E, ca. 934 m, 14.viii–18.ix.2020, Malaise trap, J. H. Lee et al. leg. ( KNU); 1♀, Gangwon-do, Chuncheon-si, Dongsan-myeon, Bongmyeong-ri, streamside in Kangwon National University Experimental Forest, 37°46′49.9″N, 127°49′05.4″E, ca. 270 m, 28.vii.2021, sweeping, J. H. Lee leg. ( KNU); 2♀, Chungcheongbuk-do, Danyang-gun, Daegang-myeon, Yongbuwon-ri, Mt. Sobaeksan, near second Yeonhwabong Peak, 36°55′44″N, 128°26′49″E, 1253 m, 19.viii.2021, hand collecting, J. H. Lee leg. ( KNU); 2♂, Gangwon-do, Jeongseon-gun, Gohan-eup, Gohan-ri, Mt. Hambaeksan, near Changokbong Peak, 37°09′03″N, 128°54′37″E, 1330 m, 31.vii.2023, hand collecting, S. K. Kim leg. ( KNU).
Ecology. This species was collected in mountainous area of relatively low to high altitude, about range of 200– 1900 m above sea level in South Korea, similarly with S. japonicus but altitudinal distribution range was broader than the latter. Adults can be found on leaves of wood fern or broadleaf shrubs in deep forest or rock surfaces covered with moss in streamside showing wandering or feeding behavior ( Fig. 11 View FIGURE 11 ). Detailed ecological information including larval feeding habits is largely unknown.
Remarks. This species is somewhat similar to S. japonicus but can be readily distinguished from the latter by characteristics of fore apical tarsomere, male hypopygium and female postabdomen (see remarks of S. japonicus above). The hypopygium of S. koreanus sp. nov. is also similar to Chinese species S. acuminatus but can be readily distinguished from the latter by the following characteristics: posterodorsal margin of epandrial lobe rounded (nearly straight in S. acuminatus ); dorsal plate of aedeagus curved with angle more than 90°, with blunt apex (curved with angle less than 90°, with pointed apex in S. acuminatus ) (characteristics of S. acuminatus were referred to the illustrations and description of Liu 2001: 192, figs. 78, 79).
Distributions. Korea (Gangwon-do, Chungcheongbuk-do, Jeollabuk-do, Gyeongsangbuk-do, Gyeongsangnam-do).
| NIBR |
National Institute of Biological Resources |
| KNU |
Kyungpook National University |
| T |
Tavera, Department of Geology and Geophysics |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Phorinae |
|
Genus |