Aphelocerus scutellaris (Chevrolat)
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.1206/0003-0090(2005)293<0001:CNHAEO>2.0.CO;2 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03E787FE-9958-113A-FC9D-FEB3FD59FE1D |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Aphelocerus scutellaris (Chevrolat) |
| status |
|
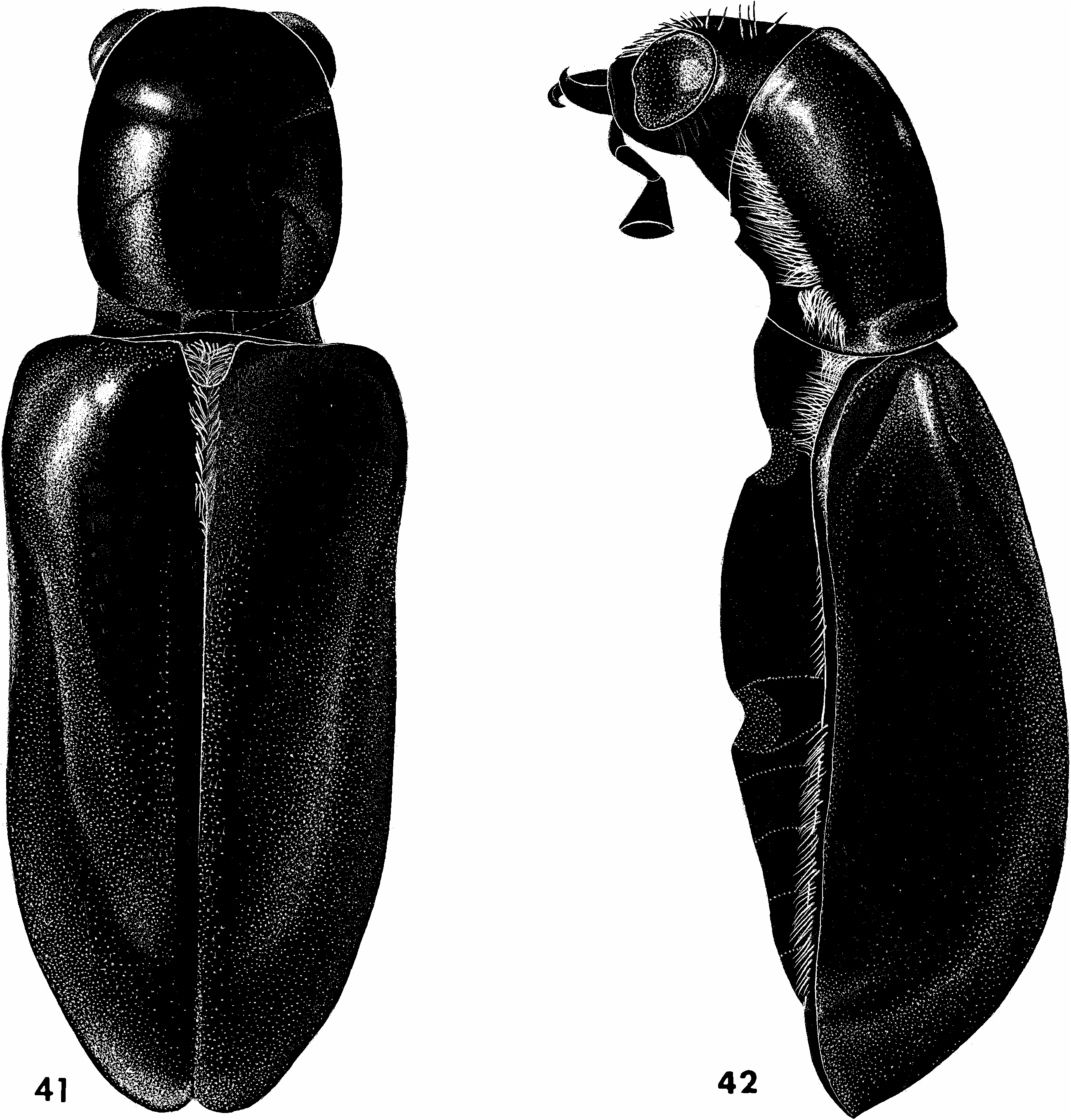
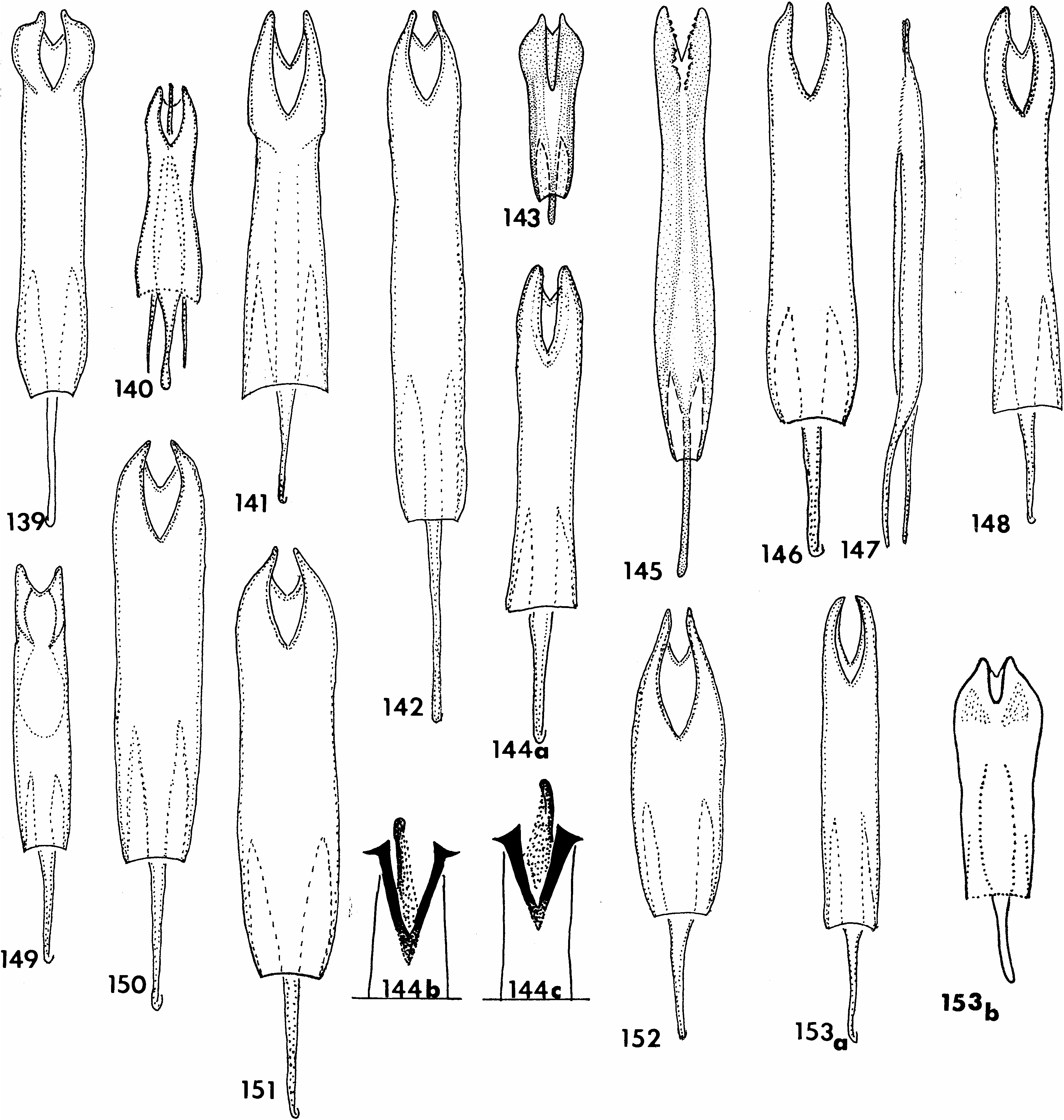
SCUTELLARIS GROUP Aphelocerus scutellaris (Chevrolat) Figures 41, 42 View Figs , 84 View Figs , 145 View Figs ; map 21
Clerus scutellaris Chevrolat, 1874: 296 . Lectotype: Male. Here selected. Mexico, Orizaba (MNHN). (Specimen point mounted, sex label affixed to paper point, white, machine printed; support card, white, with lines; identificationlocality label, green, mounted on white card, cursive; identification label, beige, cursive; Paris Museum repository label, white with green mark, machine printed; identification label, white, machine printed; the lectotype is marked by an elytral puncture resulting from the original pinning). Chevrolat, 1876: 15; Gorham, 1882: 162; Corporraal, 1950: 147; Barr, 1976: 18.
Adelphoclerus nitidus Wolcott, 1910: 357 .
Adelphoclerus fulgidus Wolcott, 1927: 73 (new name for Adelphoclerus nitidus Wolcott ).
HOLOTYPE: Mexico, Jalapa , Smith ( FMNH). (Specimen point mounted; locality label, beige, machine printed; H. F. Wickham Collection label; type label, red, machine and hand printed; identification label, beige, cursive; type label, white and bordered by two red lines, hand printed; identification label, white, machine printed.) NEW SYNONYMY. One paratype with the same data as holotype ( USNM).
DIAGNOSIS: In A. scutellaris (Chevrolat) specimens, the largest specimens in this species group (8 mm), the elytra are conspicuously compressed laterally. There is an acute posthumeral lateral deflection that sharpens the humeral angle and gives the dorsal fascies of the elytra a subtrigonal appearance (figs. 41, 42).
DESCRIPTION: Size: Length 7.4–8.6 mm; width 2.4–4.4 mm. Integument: Black, antennal apex testaceous, tarsi piceous. Vestiture: Frontal, pronotal, metepisternal tufts well developed, epipleural tuft moderately developed, sutural tuft short but prominent; mesocutellum matted with white setae, elytral apical region in pale setae, remainder of dorsum sparsely vested with erect black setae; anterior fascies and apex of profemur vested with long, black setae, tarsi vested with black setae, pterothorax and abdomen vested with pale setae. Head: Gena and epicranium expanded; interocular depression and frontal umbo indistinct; frons, epicranium, and gena finely and sparsely punctate; eye subspherical, moderately convex; width across eyes slightly narrower than width across pronotum (60:63); antenna (fig. 84) elongate, nearly as long as length of pronotum (70:75). Thorax: Pronotum elongate (75: 63), disc finely wrinkled transversely in posterior region, finely punctate in remainder, side margins feebly arcuate, anterior transverse depression faintly indicated at sides, considerably narrower than width of elytra across humeri (63:85); elytra boldly convex and conspicuously compressed laterally especially behind the humerus, humeral angle pronounced, with 10 rows of very fine setiferous punctations, rows of punctations seem to coincide in position with faintly indicated longitudinal carinae, depth at humerus 30, greatest depth at posterior half 50; legs very prominently elongate, metafemur extended beyond elytral apex. Abdomen: Posterior margin of pygidium evenly arcuate in both sexes, tegmen as in figure 145; inner margins of parameres denticulate.
VARIATION: Elytral coloration varies from black to piceous and the basal half of the pronotal disc varies in the number and structural development of the transverse wrinkles. The antenna apex is less testaceous in some specimens. Also, there is some variation in the prominence of the transverse subapical depression of the pronotum, humerus, posthumeral margin, lateral coompression of the elytra, and longitudinal elevations of the elytral disc.
NATURAL HISTORY: Specimens were captured in June, July, and in September, at altitudes ranging from 914 to 1493 m.
DISTRIBUTION (map 21): These specimens have been most abundantly collected from the Atlantic slopes of the Sierra Madre Oriental, but it is also known from the isthmus of Tehuamtepec.
MATERIAL EXAMINED: I examined 18 specimens from Mexico: Veracruz: 10 km N Fortin , 21–29VII1976, E. Giesbert ; Fortin de Las Flores , 6VII1963, J. Doyen ; Jalapa, Smith: Hidalgo: Chiapas. Specimens are de posited in EMEC, FSCA, JEWC, RHTC, WOPC, and ZMAN .
REMARKS: In 1910, A. B. Wolcott published the name Adelphoclerus nitidus ( Wolcott, 1910: 357) which he later rejected as a secondary homonym of Clerus nitidus ( Chevrolat, 1843: 25) , and replaced it with the Adelphoclerus fulgidus ( Wolcott, 1927: 73) .
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Aphelocerus scutellaris (Chevrolat)
| OPITZ, WESTON 2005 |
Adelphoclerus fulgidus
| Wolcott, A. B. 1927: 73 |
Adelphoclerus nitidus
| Wolcott, A. B. 1910: 357 |
Clerus scutellaris
| Barr, W. F. 1976: 18 |
| Gorham, H. S. 1882: 162 |
| Chevrolat, M. A. 1876: 15 |
| Chevrolat, M. A. 1874: 296 |