Macrostomus limbipennis
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.281632 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6179134 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03E59A56-FF90-FF85-FF7B-FE796618AA57 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Macrostomus limbipennis |
| status |
|
Macrostomus limbipennis View in CoL species-group
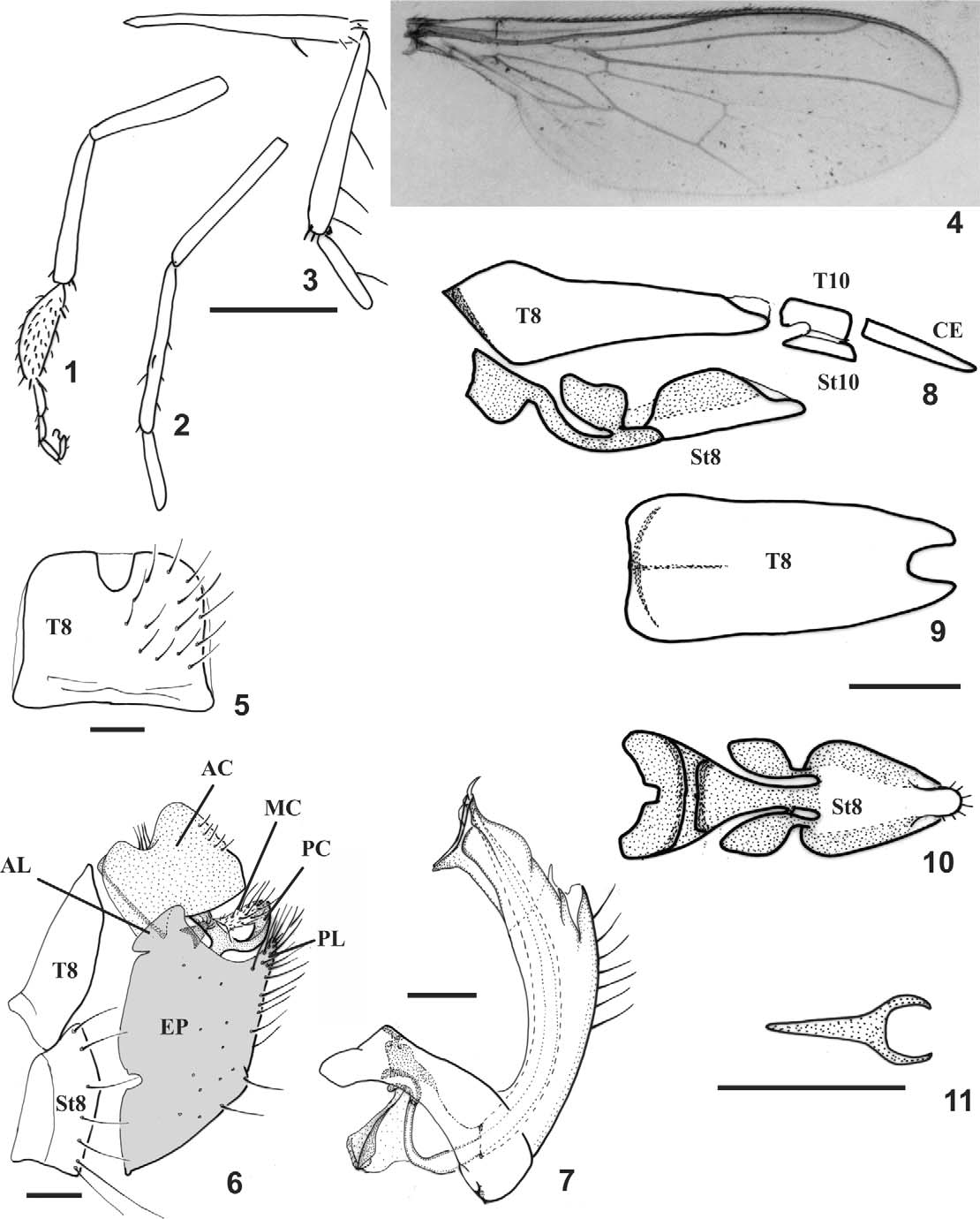
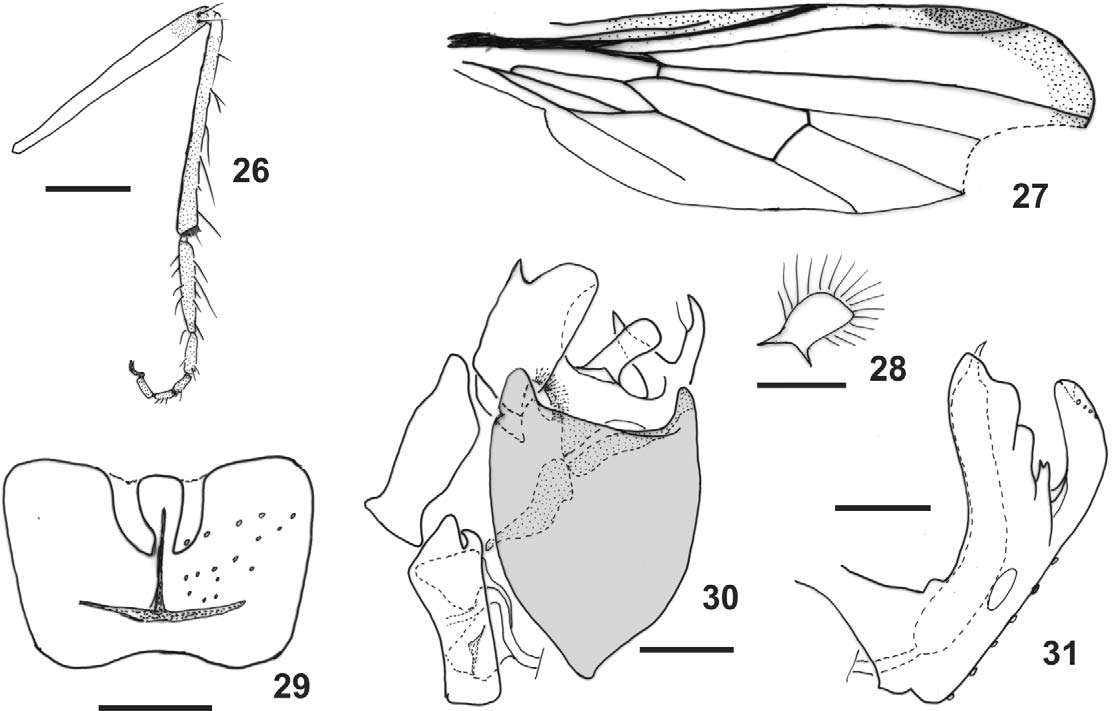
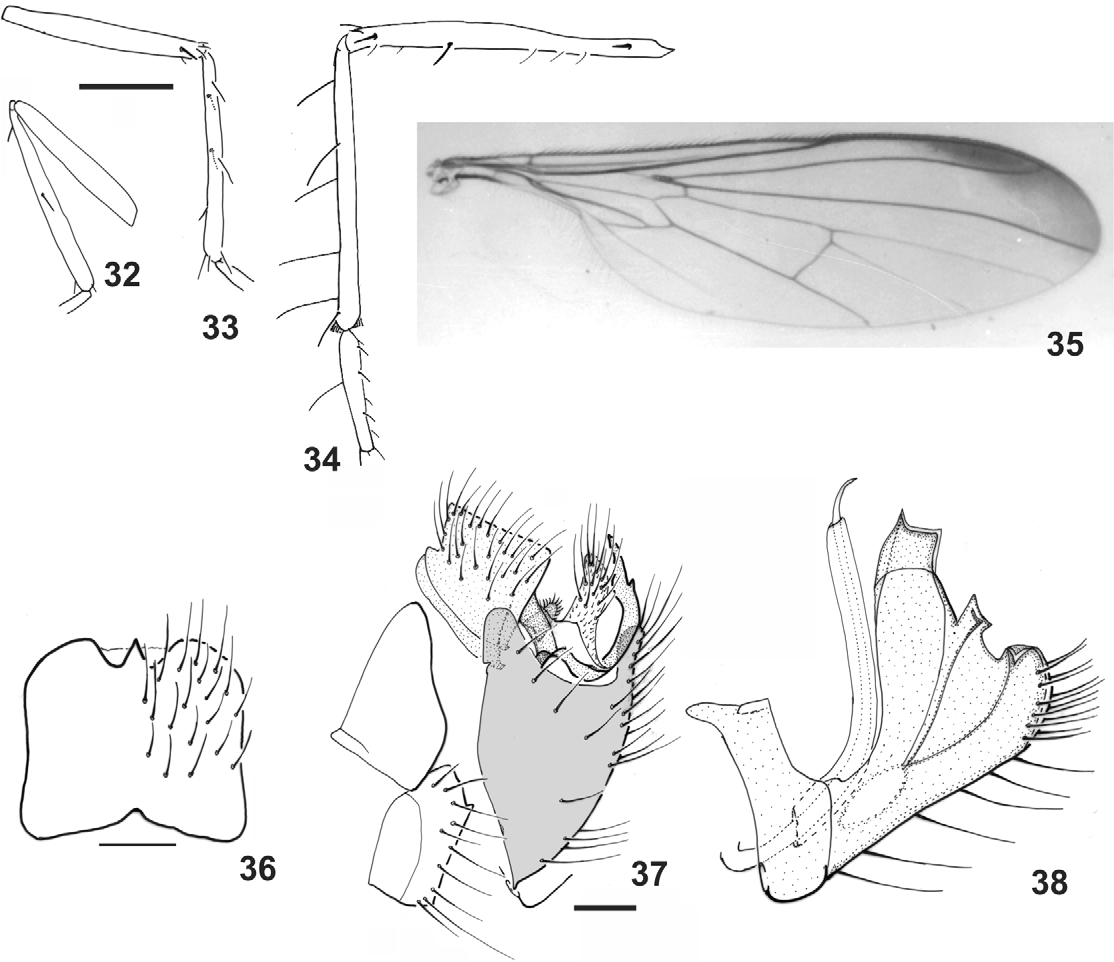
Description. Male. Head dichoptic; frons shining black, as wide as or slightly wider than anterior ocellus width; face as broad as frons, slightly gray pruinose at apex; one or two pairs of ocellar setae, posterior pair weaker when present; postgena sometimes with setae as strong as dorsal thoracic setae; flagellum with 1 or 3 flagellomeres. Thoracic chaetotaxy: 3 pairs of dorsocentrals; 1 postpronotal stout and 1–3 minute; 1 supra–alar presutural; 1 supra–alar postsutural; 1 postalar strong and 1 minute; 2 notopleurals, posterior stout; 2 pairs of scutellars, outer pair weaker; 2–4 antepronotals; 1–4 proepisternals weak or as strong as dorsal thoracic setae; 3–10 katatergitals. Fore and mid tibiae with some setae slightly stronger, sometimes absent on fore tibia; hind femur with anterior setae at base and apex, or absent and 1–2 longer anteroventral setae at distal third; hind tibia with 3–5 longer dorsal setae; hind tarsomere 1 with 1 longer dorsal seta. Wing brown infuscated on costal and distal margin to almost entirely hyaline; pterostigma slightly darker; cell dm elongate, slightly acute to truncate; veins M1, M2 and apex of A1 evanescent or somewhat distinct. Abdomen shining black. Terminalia with tergite 8 somewhat short with distal sinus ( Figs. 5 View FIGURES 1 – 11 , 17 View FIGURES 12 – 19 , 29 View FIGURES 26 – 31 , 36 View FIGURES 32 – 38 ). Epandrium with anterodorsal and posterodorsal lobes of same height ( Figs. 6 View FIGURES 1 – 11 , 18 View FIGURES 12 – 19 , 30 View FIGURES 26 – 31 , 37 View FIGURES 32 – 38 ). Hypandrium with variable setae, with apex narrow ( Figs. 7 View FIGURES 1 – 11 , 19 View FIGURES 12 – 19 ) or wide ( Figs. 31 View FIGURES 26 – 31 , 38 View FIGURES 32 – 38 ). Cercus divided into two lobes (see Rafael & Cumming 2004) and an additional distinct median membranous lobe between them ( Fig. 6 View FIGURES 1 – 11 ); anterior cercus wide or narrow, connected anteriorly and medially by large flat cercal expansion; posterior cercus elongated. Phallus ( Figs. 7 View FIGURES 1 – 11 , 19 View FIGURES 12 – 19 , 31 View FIGURES 26 – 31 , 38 View FIGURES 32 – 38 ) as long as hypandrium, with apical portion of endophallus slightly projected beyond sheath ( Fig. 38 View FIGURES 32 – 38 ). Ejaculatory apodeme tetralamelar ( Fig. 7 View FIGURES 1 – 11 ).
Female. Head dichoptic; frons wider than anterior ocellus width; face narrower than frons, approximately half of anterior ocellus width. Legs with no pinnate scales; hind tarsomere 1 with one dorsal setae. Wing slightly wider than in male, usually more infuscated at costal and distal margin. Terminalia less shining and more gray pruinose than preabdomen. Tergite 8 elongate. Sternite 8 usually with median large sinus, laterally with ventral constriction. Genital fork with short to indistinct lateral arms. Spermatheca ( Fig. 25 View FIGURES 20 – 25 ) with long duct and rounded receptacle.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Empidinae |
|
Genus |