Stenochironomus impendens Borkent, 1984
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4117.1.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:4274F17E-D096-4B30-8FD2-E66769F49708 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6073938 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03E32D35-511B-321A-FF04-CF73F74AFE5C |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Stenochironomus impendens Borkent, 1984 |
| status |
|
Stenochironomus impendens Borkent, 1984 View in CoL
( Figs. 15–17 View FIGURE 15 View FIGURE 16 View FIGURE 17 )
Material examined. Brazil, Amazonas: Manaus, Reserva Florestal Adolfo Ducke, Igarapé Bolívia, 02º 59' 14.5" S, 59º 56'30.5" W, in decayed leaves, G.P.S. Dantas ( INPA): 1 male with pupal and larval exuviae, 11.iii.2009; 1 male with pupal and larval exuviae, 17.iii.2009. Itacoatiara, Madeireira Mil, 02º 47’32.3’’ S, 058º 37’42.5’’ W, in decayed leaves, G.P.S. Dantas ( INPA): 1 male with pupal exuviae, 02.iv.2009; 1 female with pupal exuviae, 11.iv.2009.
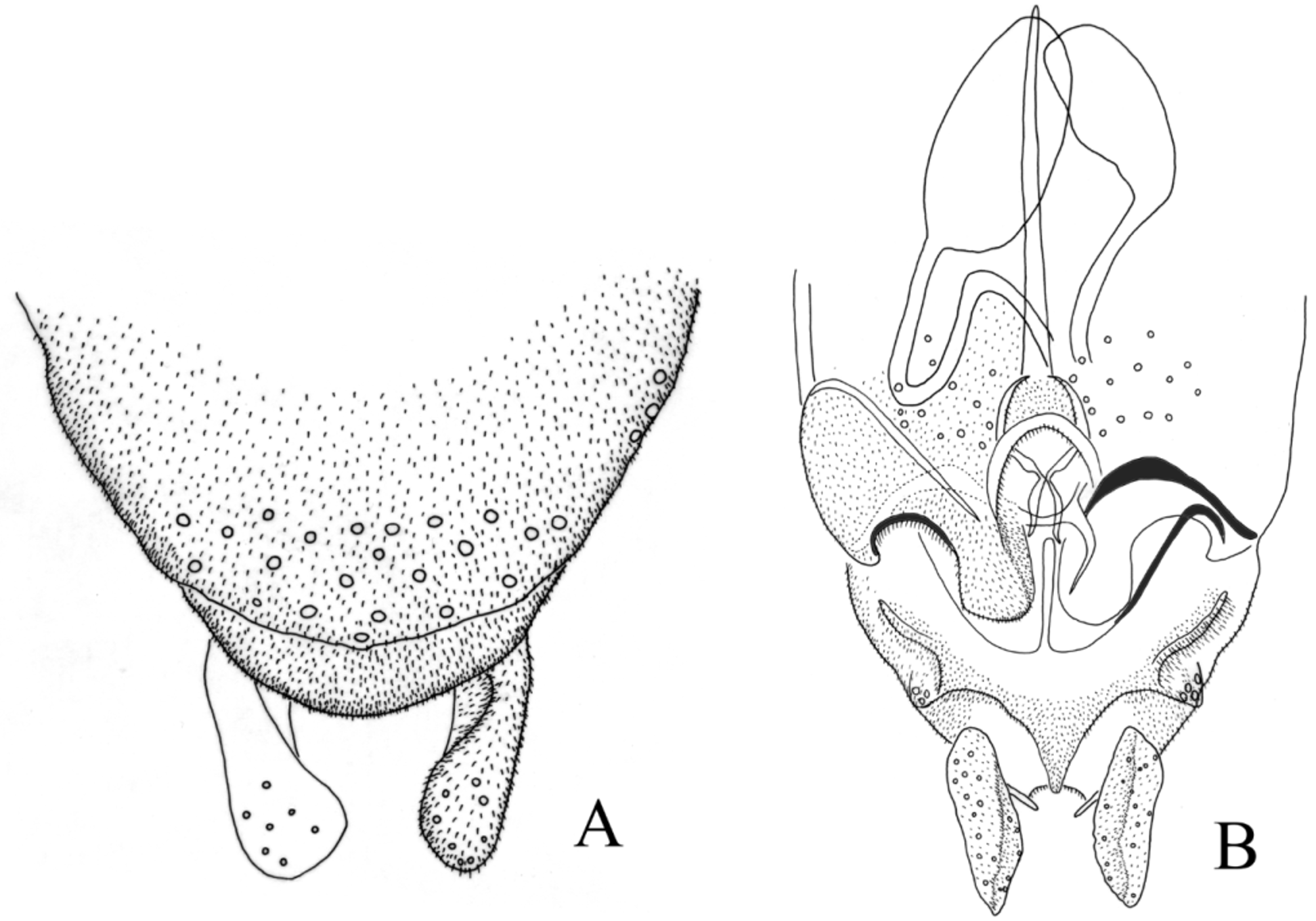
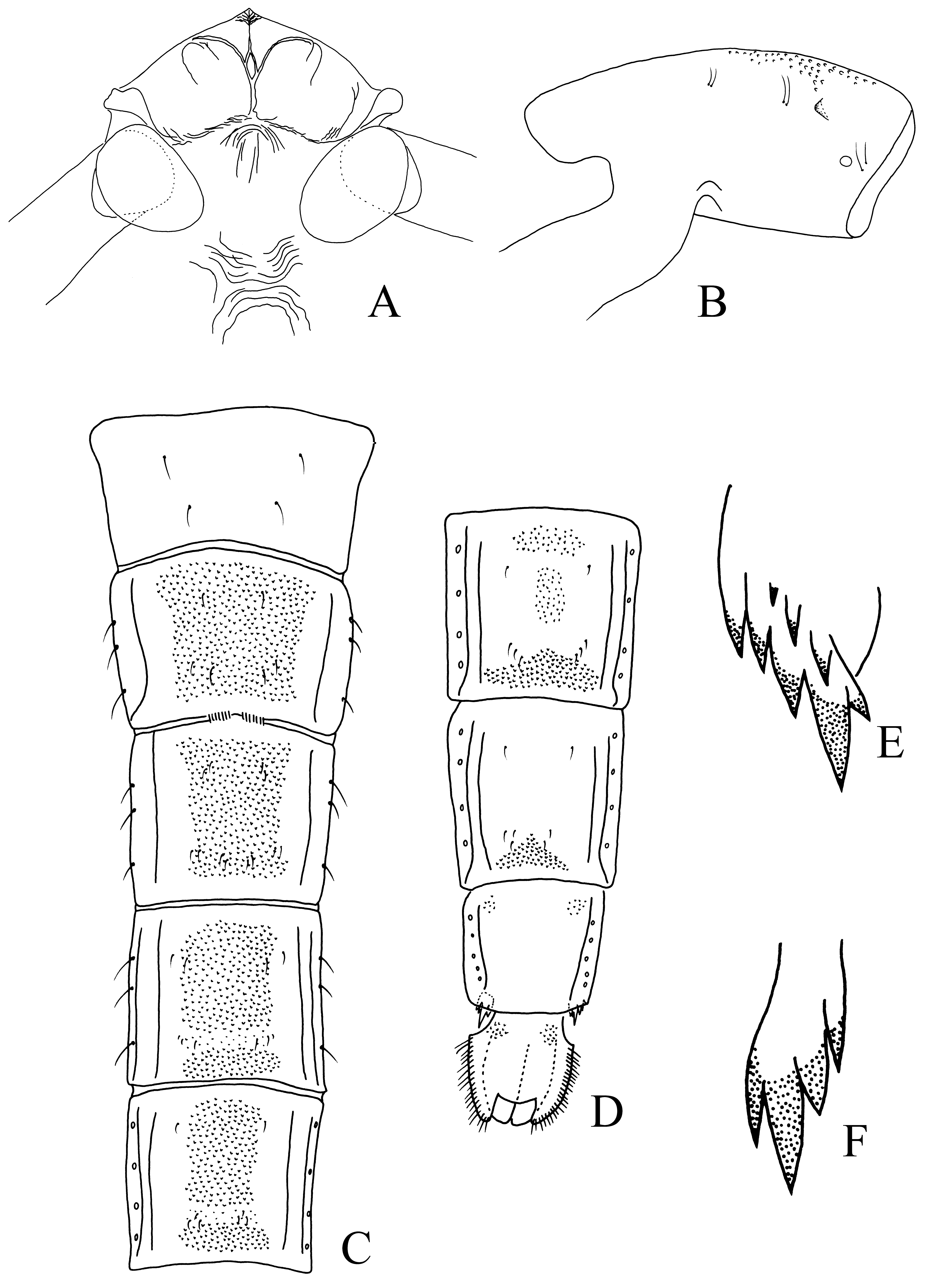
Diagnostic characters. Male: thorax with dark circular patches; dorsal patch of setae on T IX with posterior setae on posteriorly projecting lobe. Female: Thorax light brown, with dark circular patches on each side and a light brown stripe on preepisternum; tergite IX with about 24 setae; post-genital plate slightly triangular in shape. Pupa: frontal apotome not elongated; cephalothorax with tubercle anterior to Dc1, anal lobe with a fringe of about 20 filaments. Larvae: SI, SII, SIII simple; ventromental plate with a concavity near mentum; labiohypopharynx with rounded lobes and cleft between them widening posteriorly.
Female (n = 1). Total length 2.33 mm. Wing length 1.37 mm. Total length/wing length 1.70. Wing length/ length of profemur 1.48.
General coloration brownish. Thorax: very light brown, with dark circular patches on each side and a light brown stripe on preepisternum (it is difficult to see on mounted specimens). Legs: fore coxa brown, fore femur, tibia and tarsus brownish; mid and hind legs pale, with apex of femur and base of tibia light brownish. Wing and antenna brownish. Abdomen: yellowish.
Head. Flagellomere lengths (in µm): 71; 74; 78; 75; 132. Longest seta 427 µm long. AR 0.44. Temporals 11 in single row. Clypeus with 10 setae. Tentorium 103 µm long; 18 µm wide at sieve pore; 9 µm wide at posterior tentorial pit. Stipes 99 µm long, 7 µm wide. Palpomere lengths (in µm): 28; 45; 101; 70; 138.
Thorax. Acrostichals 7; dorsocentrals 13 in single row; prealars 4–5 in two rows. Scutellum with 6 setae in single row.
Wing. VR 1.25. Brachiolum with 2 setae. R with 38 setae; R1 with 28 setae; R4+5 with 57 setae; RM with 3 setae; M with 5 setae; remaining veins bare . Squama with 5 setae.
Legs. Scale of front tibia 41 µm long; spurs of middle tibia 22 µm and 32 µm long; spurs of hind tibia 22 µm and 35 µm long. Apex of fore tibia 50 µm wide, of mid tibia 48 µm wide, of hind tibia 51 µm wide. Lengths (µm) and proportions of legs as in Table 5 View TABLE 5 .
Genitalia ( Figs. 15 View FIGURE 15 A, 15B). Tergite IX with 24 setae; gonocoxite IX with 4 setae. Cercus 82 µm long. Notum 196 µm long. Coxosternapodeme IX 80 µm long. Post-genital plate slightly triangular in shape.
Pupa (n = 3, except when otherwise stated). Total length 3.07–3.24 mm.
Coloration: abdomen and cephalothorax transparent; abdomen with lateral margin from distal half of TV to TVIII brownish.
Cephalothorax ( Figs. 16 View FIGURE 16 A, 16B). Frontal apotome not elongated ( Fig. 16 View FIGURE 16 A). Precorneal setae 2; 53–59 µm long. Dorsocentrals (Dc) 27–32 µm long. Distance between Dc1 and Dc2 4 µm; between Dc2 and Dc3 140–142 µm; between Dc3 and Dc4 4 µm. A laterodorsal tubercle anterior to Dc1 ( Fig. 16 View FIGURE 16 B). Median suture granulose.
Abdomen ( Figs. 16 View FIGURE 16 C, 16D). T I bare ; T II–III with large field of shagreen; T IV–V with two fields of shagreen separated by a bare area; T VI with three fields of shagreen, one anterior, one median and one posterior, separated by bare areas, the posterior field extending laterally while others not. T VII with a small field of shagreen in posterior margin; T VIII with fine shagreen restricted to anterolateral margin; anal segment with anterior pair of shagreen patches. TII with posterior row of hooklets not extending to lateral margin of tergite, divided medially into two groups. Abdominal setation: S I without L setae; S II–IV with 3 L setae; S V–VII with 4 LS setae; S VIII with 5 LS setae. Pedes spurii B absent on II segment. Spur on S VIII with 4–5 transparent to grayish teeth, the largest being 22–24 µm long; there may be small basal denticles ( Figs. 16 View FIGURE 16 E, 16F). Genital sac 170 (1) µm long, overreaching the posterior margin of the anal lobe by 48–50 µm; anal lobe 160 (1) µm, rounded at apex, with fringe of about 20 filaments.
Fourth-instar larva (n = 2 except when otherwise stated). Total length 8.56 (1) mm. Head capsule 531 (1) µm long.
Head. Antenna as in Figure 17 View FIGURE 17 A; lengths of antennal segments (in µm): 62; 20; 12; 10; 4 (1). Blade 21 (1) µm long. Labrum as in Figure 14 View FIGURE 14 B. Labral lamella with two conical-shaped teeth; spicules of pecten epipharyngis simple, arranged in a row ( Fig. 17 View FIGURE 17 B). S1 simple, 21–25 µm long; S2 simple, 21–26 µm long; S3 simple, 15–17 µm long. Premandible 64 (1) µm long. Mandible ( Fig. 17 View FIGURE 17 C) 176–180 µm long, with 4 inner teeth; setae submenti short, drop-like. Mentum concave ( Fig. 17 View FIGURE 17 E), 121–128 µm wide, with 10 blackish teeth; ventromental plate with a concavity near mentum. Base of dorsolateral strip originating near the base of dorsomedian strip. Labiohypopharynx ( Fig. 17 View FIGURE 17 D) with ligular lobes rounded, cleft between lobes widening posteriorly.
Abdomen. Procercus with 4 filaments; associated setae of equal size. The longest anal hook 50 (1) µm long. Systematic remarks. The pupa of S. impendens is quite distinct from the other Neotropical species, with few filaments present on anal lobe and a considerable variation in shape and number of teeth of the spur on S VIII. Previously, a concavity on the ventromental plate near to the mentum was used to distinguish the larvae of S. bacrionis from other species in the genus, but the larva of S. impendens described here also has this feature. The larvae of these two species can be differentiated by the structure of the labrum and labiohypopharynx. The larval exuvia of S. impendens is compacted and completely free of the pupa.
Notes on biology of the species. The adults were reared from larva which had been mining leaves in small, fast flowing, black-water streams. Until now, this species had been recorded only in the type locality, Rio Paru in Pará State.
| INPA |
Instituto Nacional de Pesquisas da Amazonia |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |