Bulleribasidium elongatum Q.M. Wang, F.Y. Bai & A.H. Li, 2020
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.simyco.2020.01.002 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10474814 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03DF87BD-5555-FFB4-53E3-3D7EFBF7FDA8 |
|
treatment provided by |
Jonas |
|
scientific name |
Bulleribasidium elongatum Q.M. Wang, F.Y. Bai & A.H. Li |
| status |
sp. nov. |
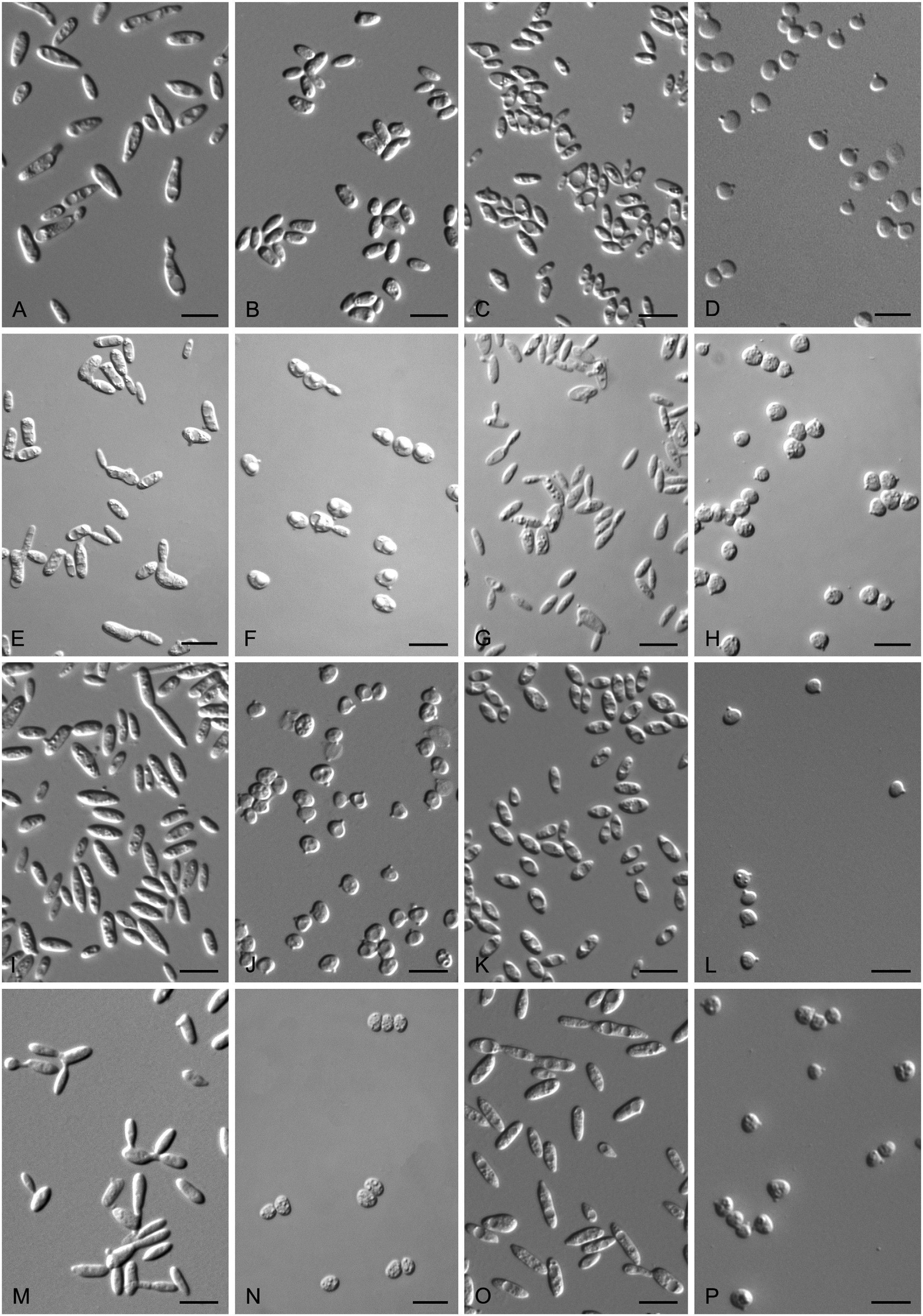
Bulleribasidium elongatum Q.M. Wang, F.Y. Bai & A.H. Li View in CoL sp. nov. MycoBank MB828769. Fig. 9A View Fig .
Etymology: the specific epithet elongatum refers to the elongate vegetative cells of the type strain.
Culture characteristics: In YM broth, after 7 d at 17 °C, cells are ellipsoidal and cylindrical, 2.7–4.1 × 6.8– 12.5 μm and single, budding is polar ( Fig. 9A View Fig ), a sediment is present. On YM agar, after 1 mo at 17 °C, the streak culture is cream, butyrous, wrinkled and dull. The margin is entire. In Dalmau plate culture on corn meal agar, pseudohyphae are formed. Sexual structures are not observed on YM, PDA, V8 and CM agar. Ballistoconidia are not produced.
Physiological and biochemical characteristics: Glucose fermentation is absent. Glucose, galactose, sucrose, maltose, cellobiose, trehalose, melibiose, raffinose, melezitose, D-xylose, Larabinose (delayed and weak), D-arabinose (delayed and weak), D-ribose (delayed and weak), L-rhamnose (delayed and weak), D-glucosamine (delayed and weak), ribitol (delayed and weak) and galactitol are assimilated as sole carbon sources. L-sorbose, lactose, inulin, soluble starch, methanol, ethanol, glycerol, erythritol, D-mannitol, D-glucitol, Methyl-α- D-glucoside, salicin, DL-lactate, succinate, citrate, myo-inositol and hexadecane are not assimilated. Ammonium sulfate, sodium nitrite (delayed and weak), L-lysine, ethylamine hydrochloride and cadaverine dihydrochloride are assimilated as sole nitrogen sources. Potassium nitrate is not assimilated. Maximum growth temperature is 28 °C. Growth in vitamin-free medium is negative. Starch-like substances are not produced. Growth on 50 % (w/w) glucose-yeast extract agar is negative. Urease activity is positive. Diazonium Blue B reaction is positive.
Physiologically, Bu. elongatum differs from its closely related species, Bu. phyllophilum , Bu. foliicola and Bu. hainanense , in its inability to assimilate D-mannitol and its ability to assimilate cadaverine ( Table S1.10 View Table 1 ).
Typus: China, Taiwan province, obtained from a leaf of an unidentified plant, Aug. 2009, Q.-M. Wang (holotype CGMCC 2.4428 T preserved in a metabolically inactive state, ex-type CBS 12489 = TW1.1F-019).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |