Cephennula gombakiana, Jałoszyński, Paweł, 2011
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.279337 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6185255 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03DF87B0-1F51-8E0B-86C5-FB232318FB15 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Cephennula gombakiana |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Cephennula gombakiana View in CoL sp. n.
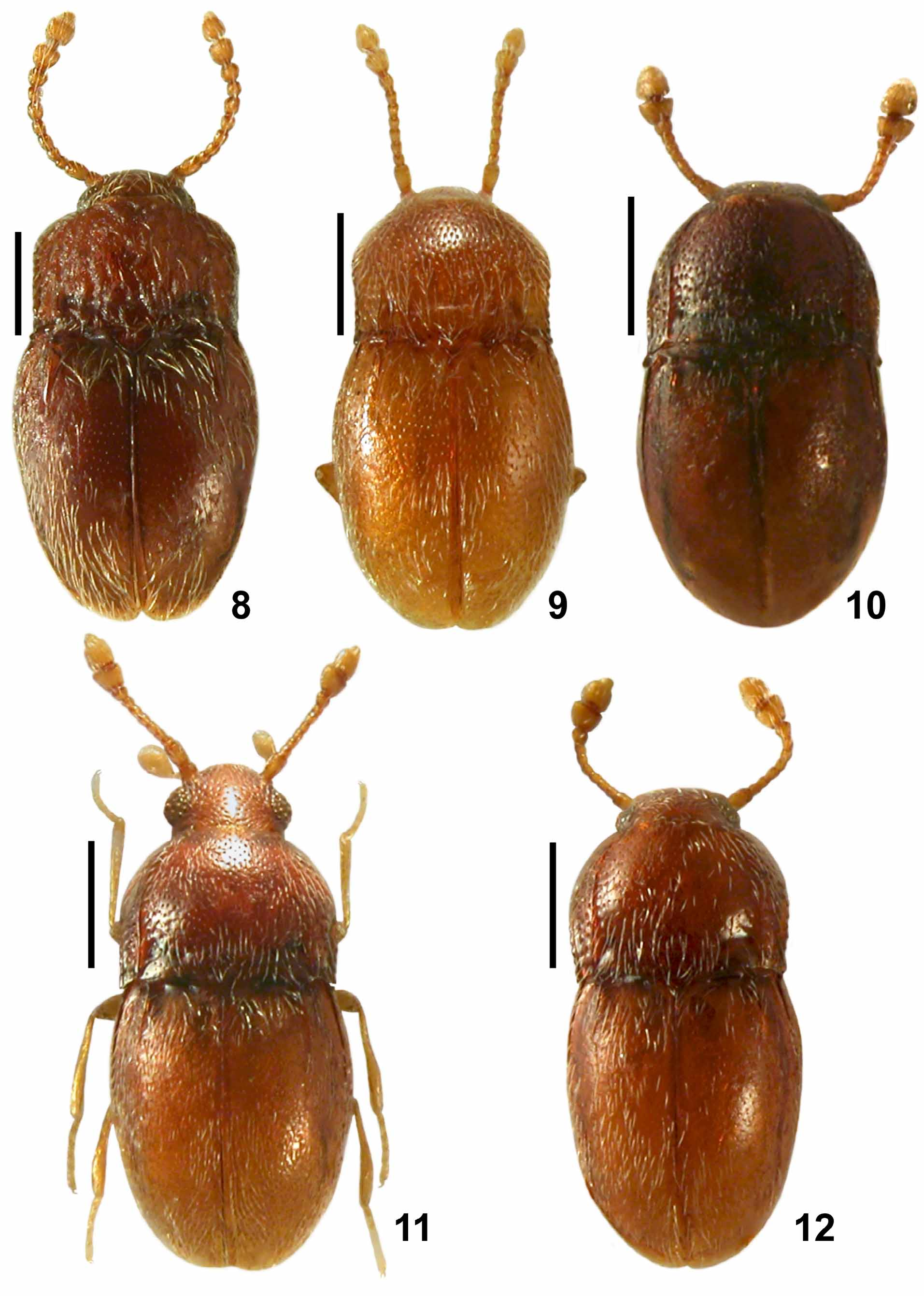
( Figs. 11 View FIGURES 8 – 12 , 29, 30 View FIGURES 25 – 32 )
Holotype: E MALAYSIA: 3, two labels: " Malaisie. Selangor \ Gombak. 29.VIII.72 \ 13 miles Kuala Lumpur \ T. Jaccoud" [white, handwritten in black ink]; " CEPHENNULA \ gombakiana m. \ det. P. Jałoszyński, 2011 \ HOLO- TYPUS " [red, printed] ( MHNG).
Diagnosis. Body between 0.7 and 0.8 mm in length; antennal club strongly flattened and compact; head unevenly covered with large and deep punctures, vertex with very small median impunctate area, punctures on sides of vertex and frons dense, those on median part of frons and on clypeus sparser; median part of pronotum with small, shallow and dense punctures; sublateral pronotal carinae as long as pronotum; ante-basal transverse groove with median fovea; subhumeral carinae slightly longer than 1/ 3x EL and much longer than humeral carinae; aedeagus in ventral view approximately bottle-shaped with slightly broadened apex and broadly arcuate apical margin; endophallus lightly pigmented, composed of median bell-shaped structure.
Description. Body of male ( Fig. 11 View FIGURES 8 – 12 ) strongly convex, elongate, with barely marked constriction between pronotum and elytra, moderately glossy, light brown, covered with yellowish vestiture, legs and antennae slightly lighter. BL 0.76 mm.
Head broadest at large, coarsely faceted and strongly convex eyes, HL 0.09 mm, HW 0.20 mm; vertex and frontoclypeal area convex; supraantennal tubercles barely marked. Punctures on dorsum of head unevenly distributed, large and deep, on sides of vertex and frons dense, median part of frons and clypeus with sparser punctures, small median area on vertex impunctate; setae short and sparse, suberect. Antennae with strongly enlarged, strongly flattened and compactly assembled antennomeres X–XI and moderately enlarged antennomere IX, so that club appears two-segmented, AnL 0.28 mm; antennomere I about 1.2x as long as broad; II 2x as long as broad; III about as long as broad; IV–VI subequal in length and width, each about 1.2x as long as broad; VII slightly longer than VI, 1.3x as long as broad; VIII distinctly shorter and hardly noticeably broader than VII, about as long as broad; IX distinctly broader and slightly longer than VIII, slightly transverse; X much longer and broader than IX, strongly transverse; XI slightly narrower than X, 1.4x as long as broad.
Pronotum approximately semielliptical, broadest slightly anterior to middle; PL 0.23 mm, PW 0.35 mm, anterior margin weakly rounded; lateral margins distinctly microserrate, strongly rounded in anterior half, nearly straight in posterior half and slightly convergent towards sharp and acute hind angles; posterior margin very weakly bisinuate; sublateral carinae as long as pronotum. Transverse ante-basal groove shallow but sharply marked and slightly arcuate, with small but distinct median fovea; sublateral ante-basal foveae small and shallow; lateral antebasal foveae distinctly deeper and larger. Punctures on median part of pronotum slightly smaller and shallower than those on head but distinct and dense, punctures between sublateral pronotal carinae and lateral margins of pronotum much larger and denser than those in middle, nearly adjacent to each other and coarse; setae sparse, moderately long, suberect.
Elytra strongly convex, oval, broadest between middle and anterior 1/3; EL 0.45 mm, EW 0.38 mm, EI 1.20; base of each elytron with rudimentary basal fovea located slightly closer to scutellum than to base of humeral carina; subhumeral carinae distinct, slightly longer than 1/ 3x EL; humeral carinae indistinct and very short, shorter than 1/ 5x EL. Punctures on elytra much smaller than those on head and pronotum, very fine and shallow but relatively distinct, sparse; setae similar as those on pronotum but slightly less suberect.
Legs moderately long and slender; protibiae nearly straight, meso- and metatibiae slightly curved.
Aedeagus ( Figs. 29, 30 View FIGURES 25 – 32 ) in ventral view approximately bottle-shaped with broad, subrectangular and slightly broadened apex and broadly, regularly arcuate apical margin; AeL 0.10 mm. Endophallus lightly pigmented, with median bell-shaped structure; parameres slender, very short, each bearing single apical seta.
Female. Unknown.
Distribution. West Malaysia (Selangor).
Etymology. Locotypical, after the district Gombak of the Selangor State of Malaysia.
Remarks. The aedeagus of this species is very similar to that of C. secunda , also known to occur in Selangor ( Jałoszyński 2008). Cephennula gombakiana differs in having an additional, median ante-basal fovea on the pronotum (in middle of the ante-basal groove) and the length of the humeral elytral carinae, which in this species are shorter than 1/ 5x EL, while in C. secunda the humeral carinae are as long as 1/ 3x EL.
| MHNG |
Museum d'Histoire Naturelle |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Scydmaeninae |
|
Genus |