Syringophiloidus petronicus, Skoracki, 2011
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.2840.1.1 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03DC87DB-FFA0-FF90-70B5-FF0EFA25F8C1 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Syringophiloidus petronicus |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Syringophiloidus petronicus View in CoL sp. nov.
( Figs. 26–28 View FIGURE 26 View FIGURE 27 View FIGURE 28 )
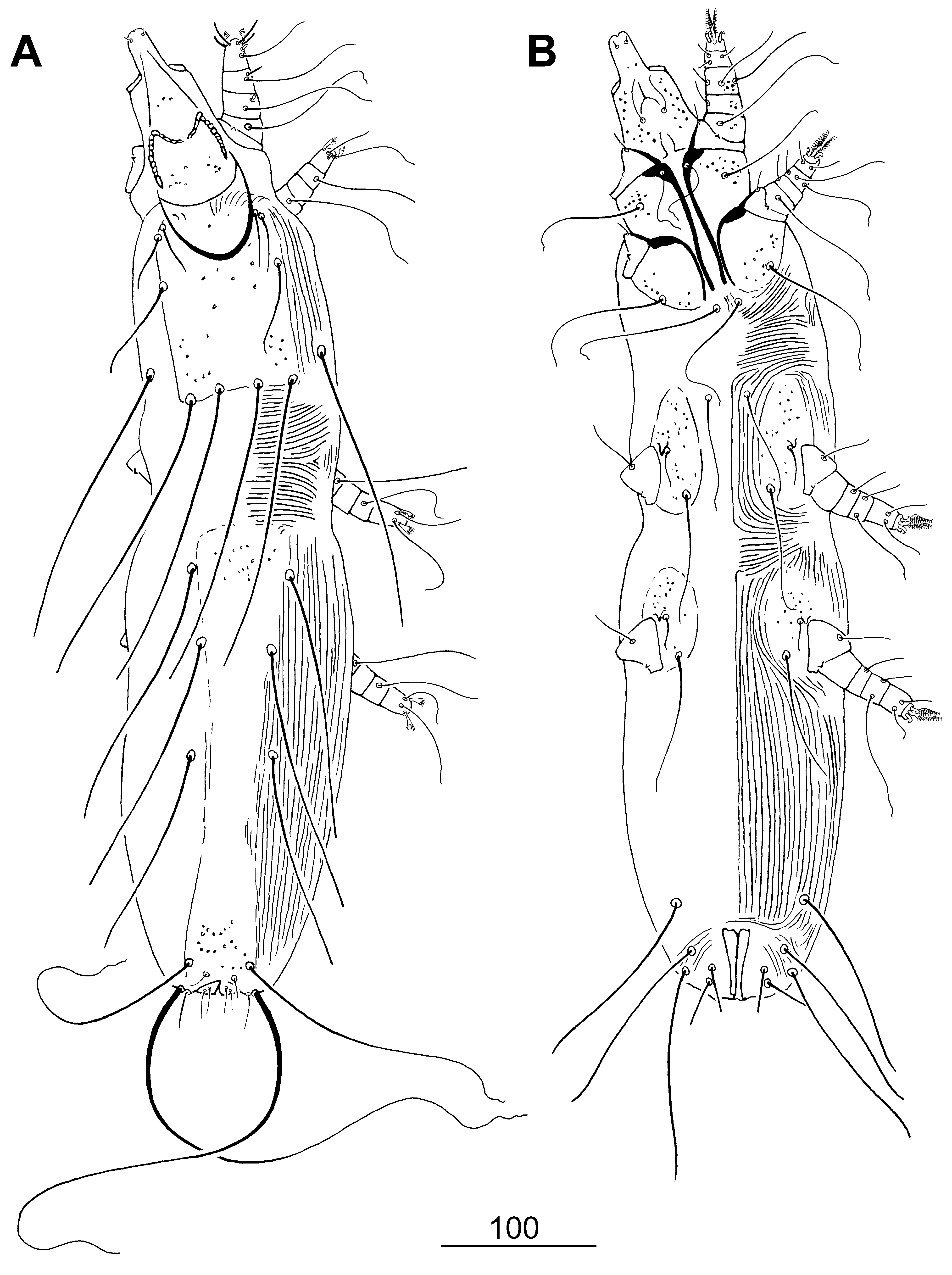
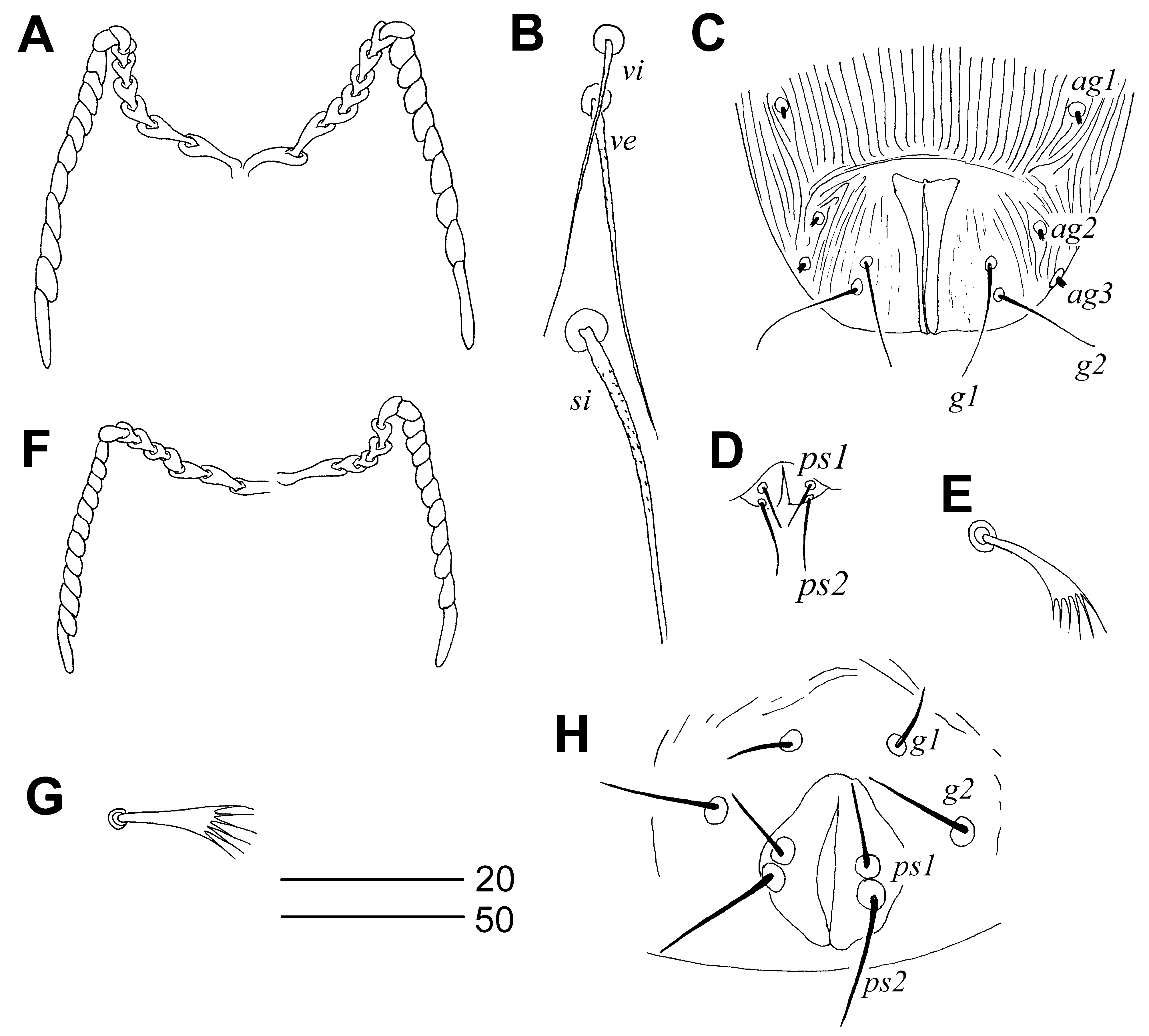
Type host: Petronia petronia (Linnaeus) ( Passeriformes : Passeridae ). Type locality: Italy. Description. FEMALE (holotype). Total body length 665 (605–680 in 5 paratypes). Gnathosoma . Infracapitulum densely punctate. Each medial branch of peritremes with 7–8 chambers, each lateral branch with 10–12 chambers. Stylophore punctate, 160 (155–165) long. Movable cheliceral digit 120 (120–125) long. Idiosoma . Propodonotal shield punctate. Length ratio of setae vi: ve: si 1:1–1.3:2–2.3. All propodonotal setae ornamented. Hysteronotal shield fused to pygidial shield, anterior and posterior part of this fused shield punctate. Setae d2 slightly longer (1.2–1.3 times) than e2. Setae h1 about twice as long as f1. Length ratio ag1: ag2: ag3 1:1:1.0–1.3. Genital plate absent. Setae ps2 1.4–1.6 times longer than ps1. Both pairs of genital setae subequal in length. All coxal fields punctate. Setae 3c 2.7–2.9 longer than 3b. Legs. Fan-like setae p’ and p” of legs III and IV with 5–6 tines. Length ratio of setae tc’III–IV: tc”III–IV 1:1.6–1.7. Lengths of setae: vi 30 (30), ve 35 (35–40), si 60 (60–75), se 200 (170– 205), c1 185 (185–205), c2 170 (160–180), d1 (140–155), d2 180 (150–180), e2 130 (125–135), f1 15 (20–25), f2 155 (140–160), h1 30 (40–50), h2 (315–355), ps1 15 (15), ps2 20 (20), g1 and g2 30 (25–35), ag1 130 (130–135), ag2 130 (125–135), ag3 150 (130–150), tc’III–IV 50 (40–50), tc”III–IV 80 (75–85), 3b 30 (30–35), 3c (80–100), l’RIII (40–45), l’RIV 30 (30–35).
MALE. Total body length 405 in 1 paratype. Gnathosoma . Infracapitulum sparsely punctate. Each medial branch of peritremes with 6–7 chambers, each lateral branch with 11–13 chambers. Stylophore apunctate, 140 long. Movable cheliceral digit 115 long. Idiosoma . Propodonotal shield sparsely punctate, weakly sclerotized in anterior and posterior parts, bearing bases of setae vi, ve, si and c1. Length ratio of setae vi: ve: si 1:1.5:1.5. Hysteronotal shield absent. Pygidial shield restricted to genito-anal region. Setae d2 about 3 times longer than d1 and e2. Setae h2 6.5 times longer than f2. Aggenital setae ag1 and ag2 subequal in length. Setae ps2 1.7 times longer than ps1. Genital setae g1 situated anterior to level of setae g2, setae g2 1.6 times longer than g1. Coxal fields I–IV punctate. Setae 3c twice as long as 3b. Legs. Fan-like setae p’ and p” of legs III and IV with 5–6 tines. Setae tc”III–IV twice as long as tc’III–IV. Lengths of setae: vi 20, ve 30, si 30, se 135, c1 125, c2 130, d1 20, d2 60, e2 20, f2 220, h2 130, ag1 55, ag2 55, tc’III–IV 25, tc”III–IV 50, 3b 25, 3c 50, l’RIII 20.
Type material. Petronia petronia (Linnaeus) ( Passeriformes : Passeridae ): female holotype and paratypes: 11 females, 1 male and 1 nymph ( AMU –SYR.190) (sec.); ITALY, 1911, no other data.
Type material deposition. All type material deposited in the AMU, except 2 female paratypes in the ZISP and 1 female paratypes in the ZSM. Host specimen deposited in the MNHW .
Host range and habitat. Monoxenos species inhabiting quills of secondary feathers of Petronia petronia .
Distribution. Italy.
Etymology. The name petronicus refers to the generic name of the host.
Differential diagnosis. This new species is morphologically similar to Syringophiloidus minor . In females of both species each medial branch of the peritremes has more than 5 chambers; the hysteronotal shield is fused to the pygidial shield; setae si are shorter than 100; dorsal setae are thin and ornemented. Females of S. petronicus are distinguished from S. minor as follow: in females of S. petronicus , the length ratio of aggenital setae ag1: ag2: ag3 is 1:1:1.0–1.3; setae d2 (150–180) are longer than e2 (105–130); setae h1 are twice as long as f1; in males the hysteronotal shield is absent and setae d2 are 3 times longer than d1 and e2. In females of S. minor , the length ratio of aggenital setae ag1: ag2: ag3 is 1:1–1.2:1.5–1.7; setae d2 and e2 are subequal in the length; setae h1 and f1 are subequal in the length; in males the hysteronotal shield is present and setae d1, d2 and e2 are subequal in the length.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.