Coeligetes borneensis MohamedSaId, 1994
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4085.4.3 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:39DEC898-B737-4ABC-A03C-BEF9DE2E4FC6 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6086514 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03D9D645-FFC7-FF89-FF33-FB5BFEDFF929 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Coeligetes borneensis MohamedSaId, 1994 |
| status |
|
Coeligetes borneensis MohamedSaId, 1994
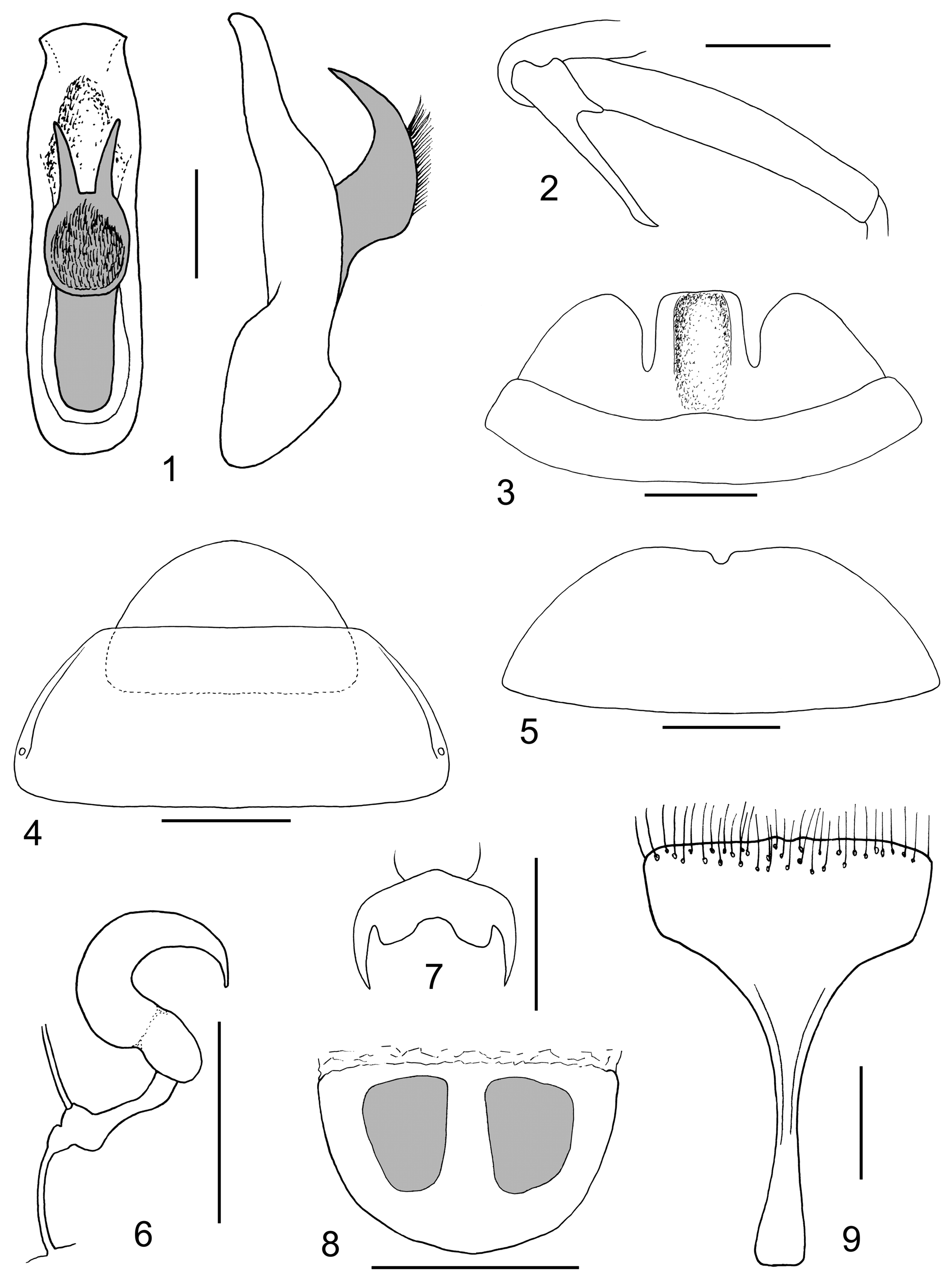
( Figs 1–9 View FIGURES 1 – 9 , 20–21 View FIGURES 20 – 23 )
Coeligetes borneensis Mohamedsaid, 1994: 87 (original description); Mohamedsaid, 1999b: 122; Mohamedsaid & Holloway, 1999: 165; Mohamedsaid, 2004: 101 (catalogue); Mohamedsaid, 2010: 260 (stridulation); Mohamedsaid & Furth, 2011: 21 (photo of legs).
Type locality. “ Malaysia, Sabah, Taman Kinabalu ”.
Type material. Not examined.
Additional material examined. 15 specimens — MALAYSIA: Sabah: 1 ♂, Tambunan , 7.v.2014, Y.- T. Wang leg. ( TARI) ; 1 ♂, same data, 8.v.2014 ( TARI) ; 1 ♀, same data, 9.v.2014 ( TARI) ; 2 ♂, same data, 24.ix.2014 ( TARI) ; 1 ♂, same data, 26.ix.2014 ( TARI) ; 1 ♂, 1 ♀, Tambunan , 18.–26.iv.2010, B. Makovský leg. ( JBCB) ; 1 ♀, Gunung Emas , 6°00 ' N 116°33 ' E, 1600–2000 m, 28.v.–4.vi.2000, P Kalač leg. ( NMPC) GoogleMaps ; 1 ♀, Mount Kinabalu , headquarter, 24.iv.1993, Hoffmann leg. ( RBCN) ; 2 ♂ 2 ♀, Crocker Range, 16 km NW of Tambunan , 5°48 ' 39 '' N 116°20 ' 17 '' E, 1660 m, 14.iv.2013, P. Romantsov leg. ( PRCS) GoogleMaps ; 1 ♀, Crocker Range, 16 km NW of Tambunan , 5°48 ' 47 '' N 116°20 ' 16 '' E, 1660 m, 1.–4.vi.2013, A. Klimenko leg. ( PRCS) GoogleMaps .
Redescription. Measurements. Males: 8.7–11.5 mm, females: 12.4–13.5 mm.
Head reddish with distinctly darkened vertex, antennae reddish with last one or two antennomeres infuscate, pronotum and ventral side of body reddish, legs reddish with outer sides of tibiae darkened, scutellum black, elytra metallic blue or green.
Male ( Fig. 20 View FIGURES 20 – 23 ). Labrum trapezoidal, twice as wide as long, anterior margin nearly straight, lateral margins divergent anteriorly, anterior angles rounded, surface subopaque, with 8 pale setae in transverse row. Anterior part of head impunctate, lustrous, with several long pale setae along anterior margin and lateraly along antennal insertions. Interantennal space as wide as transverse diameter of antennal socket. Eyes large, interocular space narrow, 1.21 time as wide as transverse diameter of eye. Frontal tubercles subquadrangular, transverse, with anterior tips divergent, surface impunctate, lustrous. Vertex distinctly impressed behind frontal tubercles, surface glabrous, covered with distinct punctures, medially with narrow impunctate line. One setigerous pore with long pale seta placed behind inner posterior eye margin. Antennae thin, 0.80 times as long as body, length ratio of antennomeres equals 18-7-12-17-17 -18-18-18-18-17-19.
Pronotum transverse, 2.35 times as broad as long, lustrous, moderately convex, widest in posterior half, sparsely covered with distinct punctures. Anterior margin widely concave, lateral margins parallel in posterior half, convergent and rounded anteriorly, posterior margin widely rounded. All margins distinctly bordered. Surface lateraly with distinct impressed line parallel to lateral margin. All angles swollen, with setigerous pores bearing long pale seta, additional short setae visible on lateral margins of pronotum. Scutellum subtriangular, with rounded tip, glabrous, covered with microsulpture and fine punctures.
Elytra 1.80 times as long as wide and 0.73 times as long as body, almost glabrous, with several short setae visible on lateral and apical slopes, covered with dense confused punctures. Humeral calli wel developer. Epipleura wide basally, gradually narrowing posteriorly and disappearing before apex.
Anterior coxal cavities nearly closed posteriorly. Posterior coxae with long, thin and sharp process, ca 0.5 time as long as posterior femora ( Fig. 2 View FIGURES 1 – 9 ). Last ventrite with two narrow deep incisions, median lobe with elongate oval impression, penultimate ventrite with slightly concave middle of posterior margin ( Fig. 3 View FIGURES 1 – 9 ). Protarsomeres I and II subtriangular, protarsomere I 1.66 times as long as wide, length ratio of protarsomeres I–IV equals 10-7-8-12. Metatarsomere I long and narrow, length ratio of metatarsomeres I–IV equals 18-8-8-13. Claws appendiculate ( Fig. 7 View FIGURES 1 – 9 ).
Aedeagus small, apex broad, widely rounded, lateraly pointed, subapically slightly constricted. Dorsal process with two sharp, slightly divergent tips, lateraly hook-like ( Fig. 1 View FIGURES 1 – 9 ).
Female ( Fig. 21 View FIGURES 20 – 23 ). Eyes smaller, interocular space wider, 2.22 time as wide as transverse diameter of eye. Antennae filiform, slightly thinner, shorter than in male, 0.61 times as long as body. Posterior coxae without process. Last ventrite with posterior margin slightly concave and with small semicircular incision in middle ( Fig. 5 View FIGURES 1 – 9 ). Pygidium transverse, with posterior margin straight, tergite VIII regularly rounded ( Fig. 4 View FIGURES 1 – 9 ). Sternite VIII with posterior margin nearly straight with two indistinct prominences in middle, with short pale setae cummulated along posterior margin, tignum twice longer than sternite VIII, narrowest in middle ( Fig. 9 View FIGURES 1 – 9 ). Vaginal sclerite semicircular with two darker patches ( Fig. 8 View FIGURES 1 – 9 ). Spermatheca as in Fig. 6 View FIGURES 1 – 9 .
Distribution. Malaysia: Sabah ( Mohamedsaid 1994, 1999b).
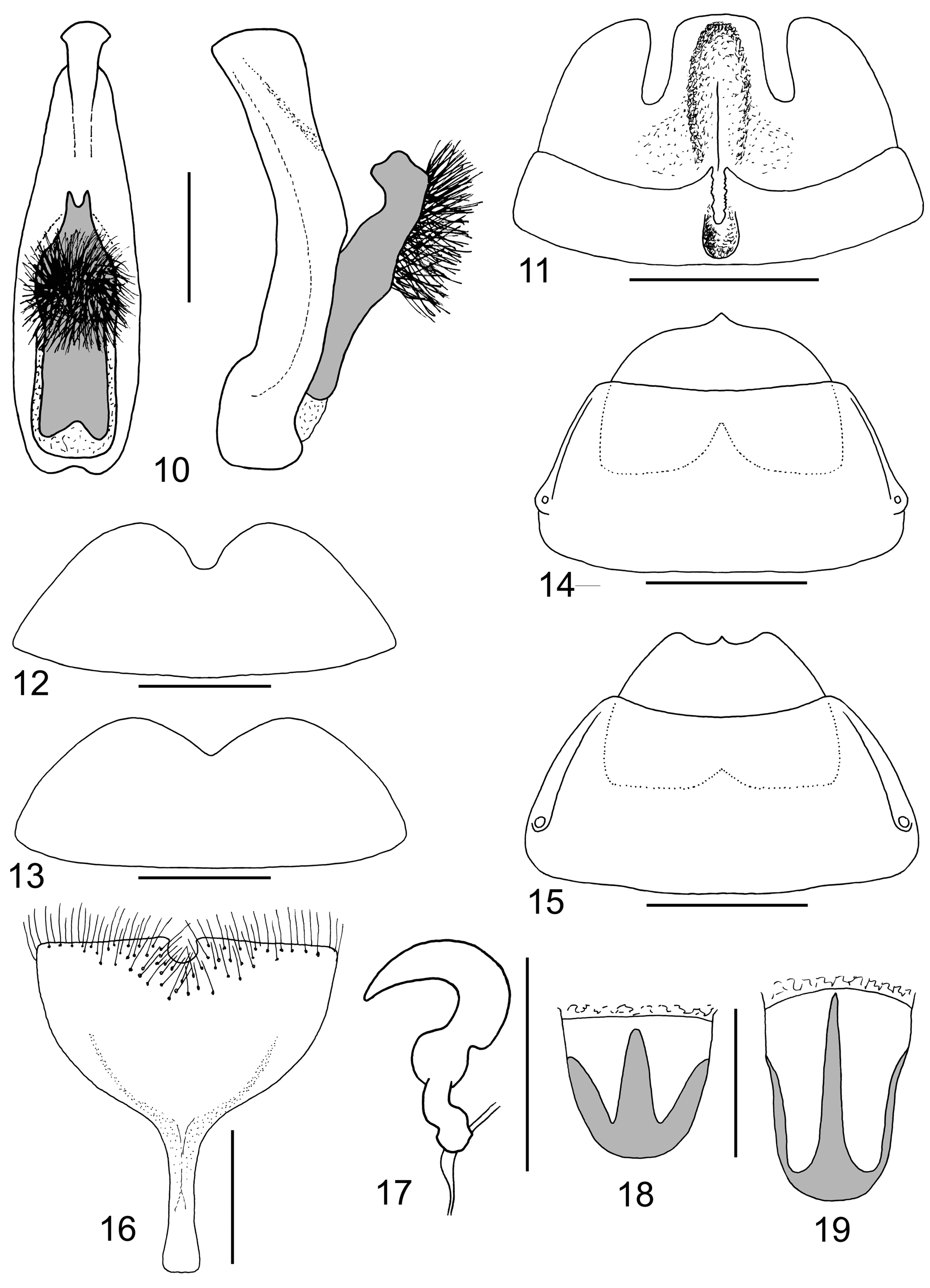
Differential diagnosis. Having metallic blue or green elytra, C. borneensis can be compared only with metallic forms of C. submetallica . Coeligetes borneensis can be distinguished as follows: vertex and scutellum usually dark (often orange in C. submetallica ) (cf. Figs 20, 21, 23 View FIGURES 20 – 23 ), males have a long thin spine on posterior trochanters ( Fig. 2 View FIGURES 1 – 9 ) (absent in males of C. submetallica ), apex of aedeagus is wider and the dorsal process has two long teeth apically (apex of aedeagus is narrower and the dorsal process has two short teeth apically in C. submetallica ) ( Figs 1 View FIGURES 1 – 9 , 10 View FIGURES 10 – 19 ), penultimate abdominal ventrite is not modified (distinctly incised and cavitous in C. submetallica ) ( Figs 3 View FIGURES 1 – 9 , 11 View FIGURES 10 – 19 ), female last ventrite with small incision in the middle of posterior margin (widely Vshaped in C. submetallica ) ( Figs 5 View FIGURES 1 – 9 , 13 View FIGURES 10 – 19 ), posterior margin of sternite VIII almost straight with two indistinct teeth in the middle (almost straight and with small semicircular incision in the middle in C. submetallica ) ( Figs 9 View FIGURES 1 – 9 , 16 View FIGURES 10 – 19 ), vaginal sclerite semicircular with two darker patches (more elongate with dark trifurcate pattern in C. submetallica ) ( Figs 8 View FIGURES 1 – 9 , 18 View FIGURES 10 – 19 ).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Galerucinae |
|
Genus |
Coeligetes borneensis MohamedSaId, 1994
| Bezděk, Jan 2016 |
Coeligetes borneensis Mohamedsaid, 1994 : 87
| Mohamedsaid 2011: 21 |
| Mohamedsaid 2010: 260 |
| Mohamedsaid 2004: 101 |
| Mohamedsaid 1999: 122 |
| Mohamedsaid 1999: 165 |
| Mohamedsaid 1994: 87 |