Fuminana Freytag, 1989
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5219.5.5 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:D071CC26-8080-4983-B56C-9CAB7C334978 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7432393 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03D1532E-FC07-FFA4-52A2-FBB8FC2019CA |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Fuminana Freytag, 1989 |
| status |
|
Fuminana Freytag, 1989 View in CoL
Fuminana Freytag, 1989: 1 View in CoL .
Type-species: Clinonaria ingula DeLong & Freytag, 1969: 166 View in CoL .
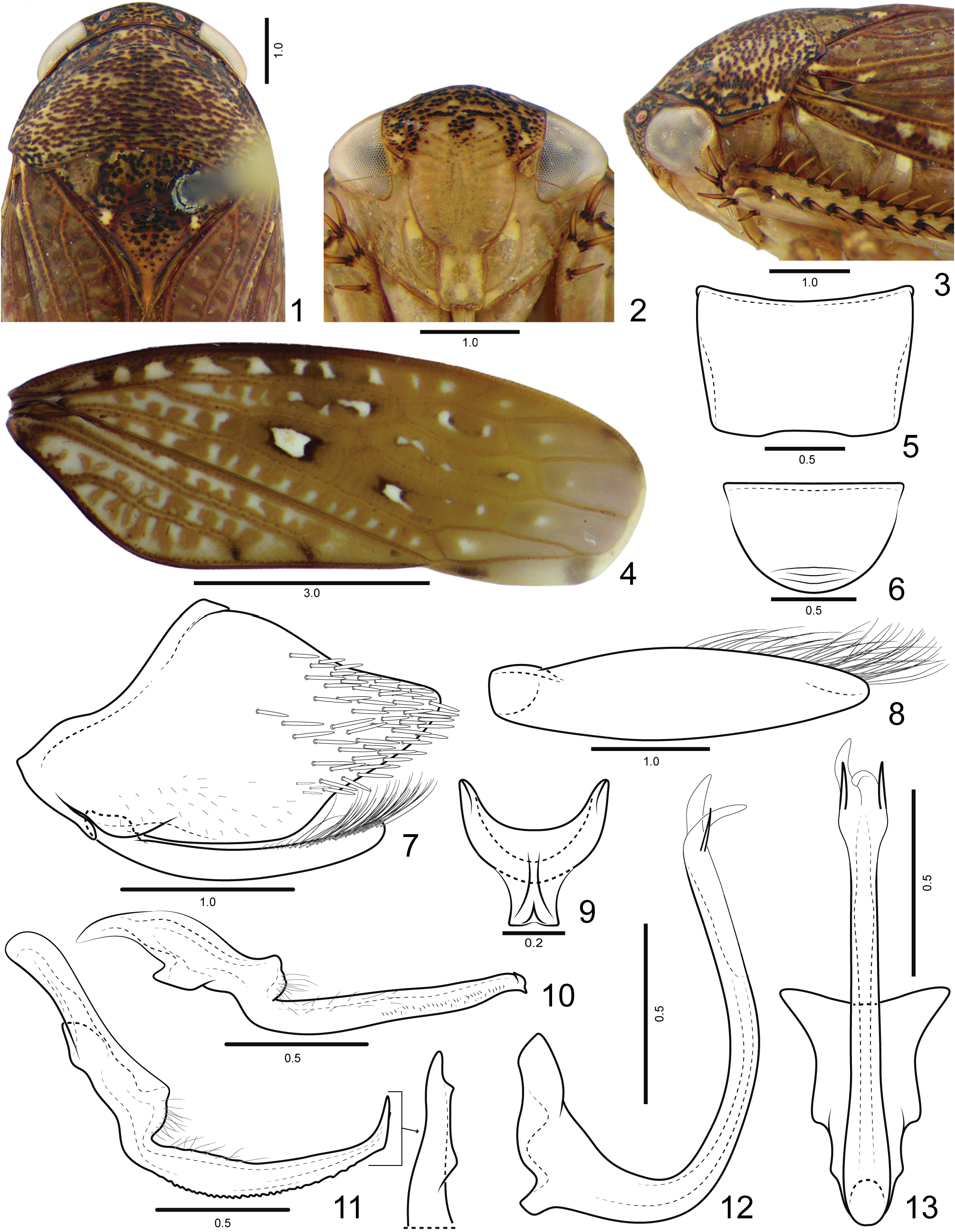
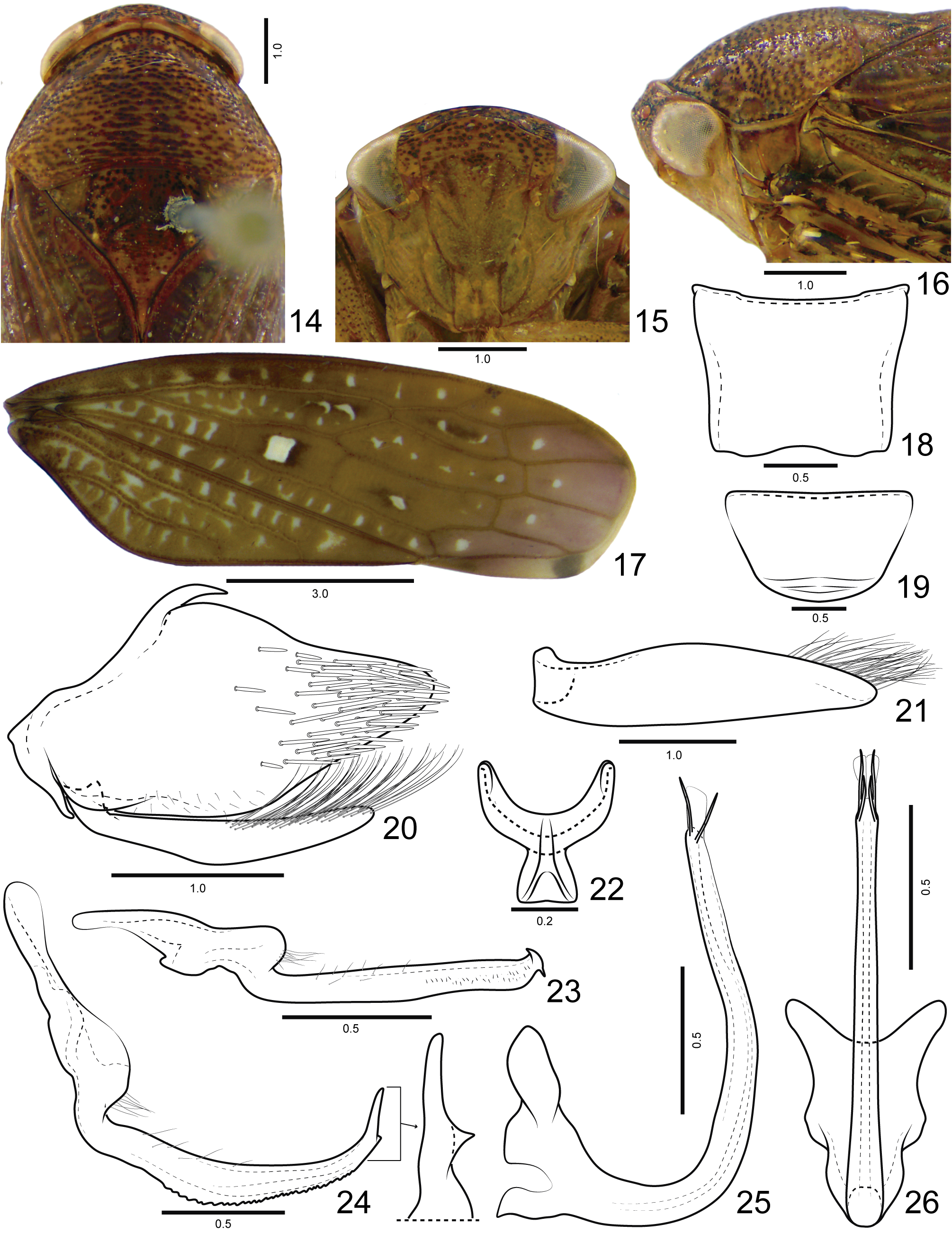
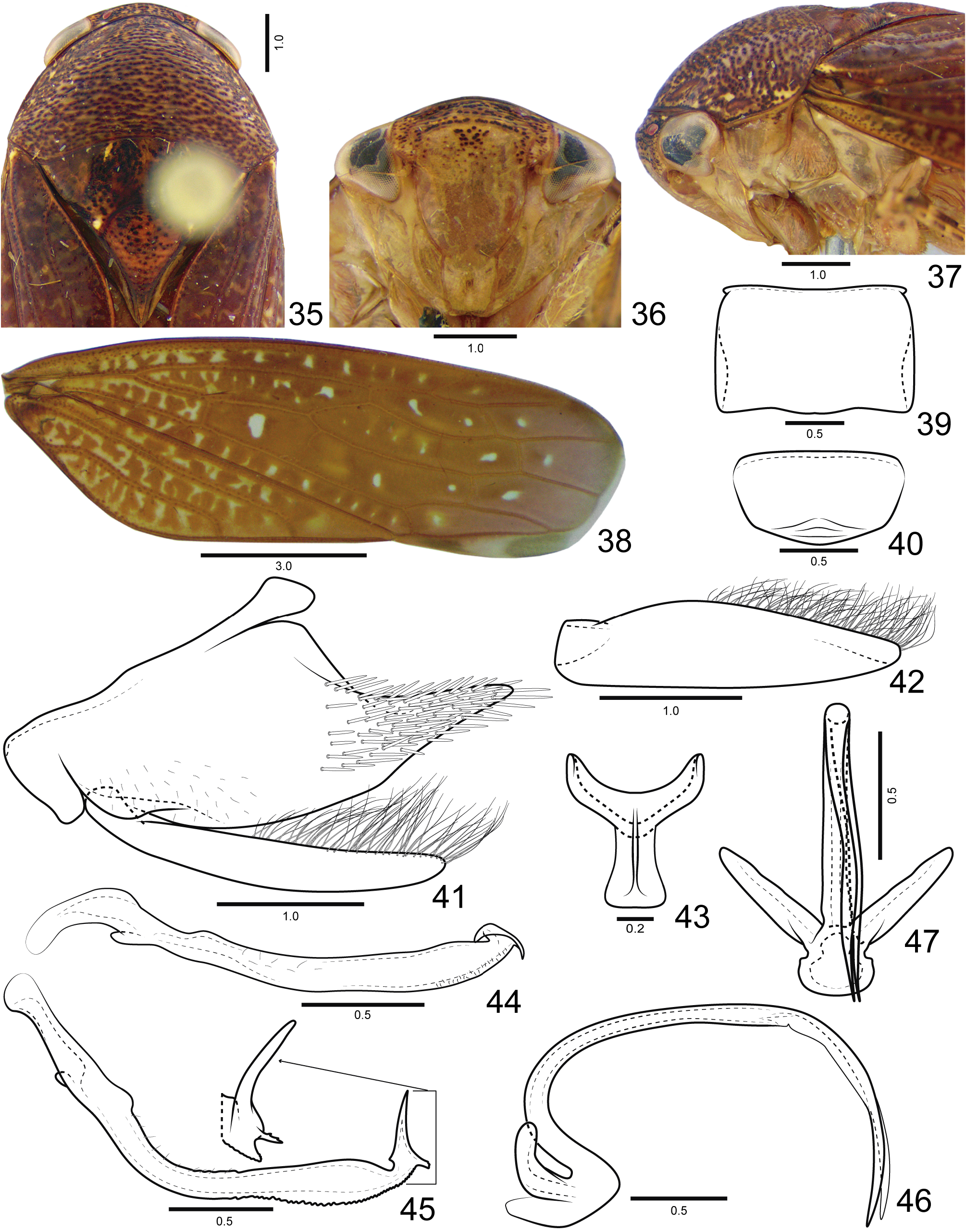
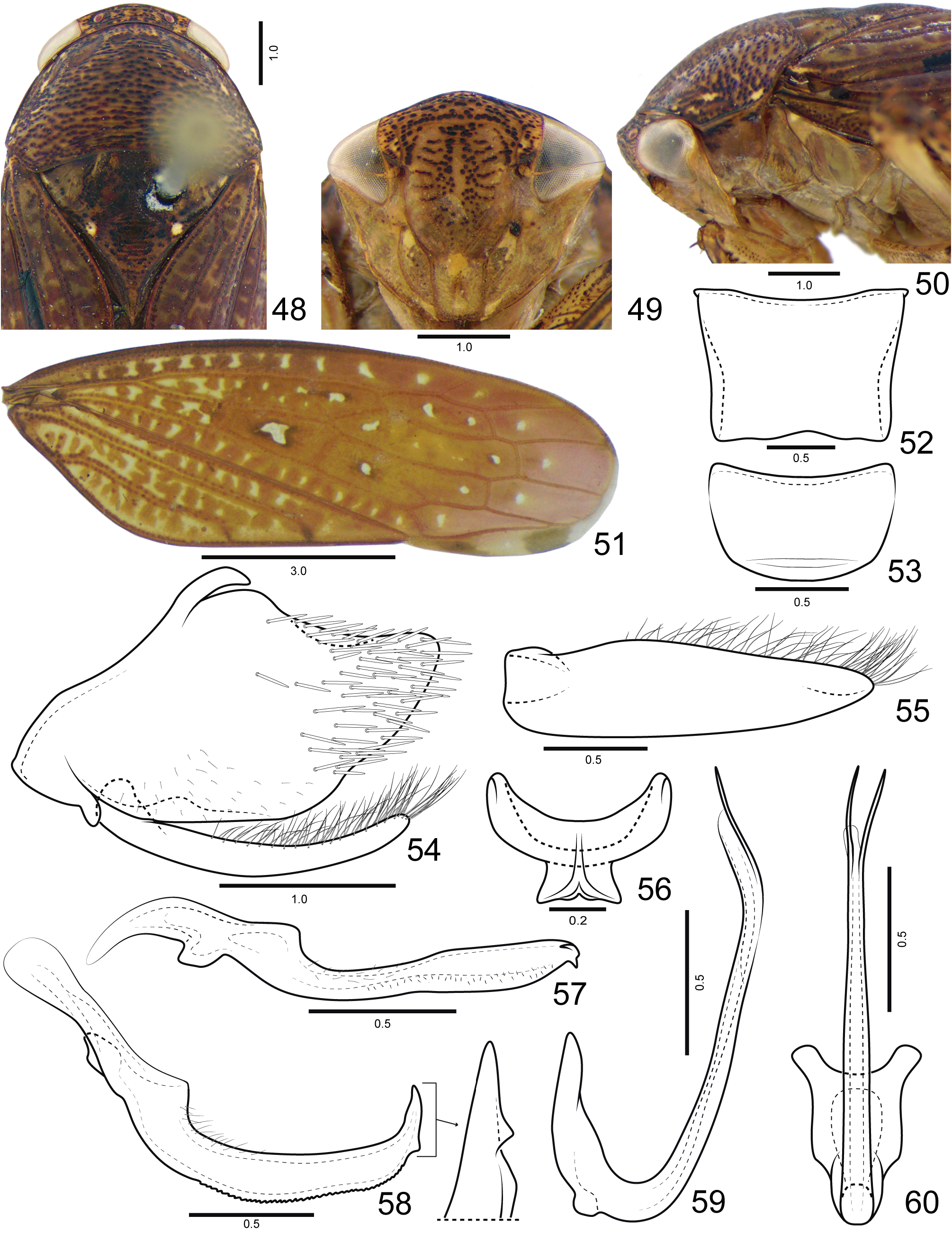
Diagnosis. Medium to large-sized and robust leafhoppers ( Figs 74 View FIGURES 74 –83). Coloration ( Figs 1 View FIGURES 1 –4, 74–83) reddishbrown, with black punctures on head and thorax, forewing with creamy spots, being the largest at middle of inner discal cell. Head ( Figs 1 View FIGURES 1 , 3) short and rounded in profile. Posterodorsal corner of pro and mesotibiae with two longitudinal carinae and setae of PD row placed between the carinae. Metatibia AD row without intercalary setae between macrosetae. Subgenital plate (Figs 8, 21) with filiform setae on dorsal surface, near outer lateral margin and apex, ventral surface without filiform setae.
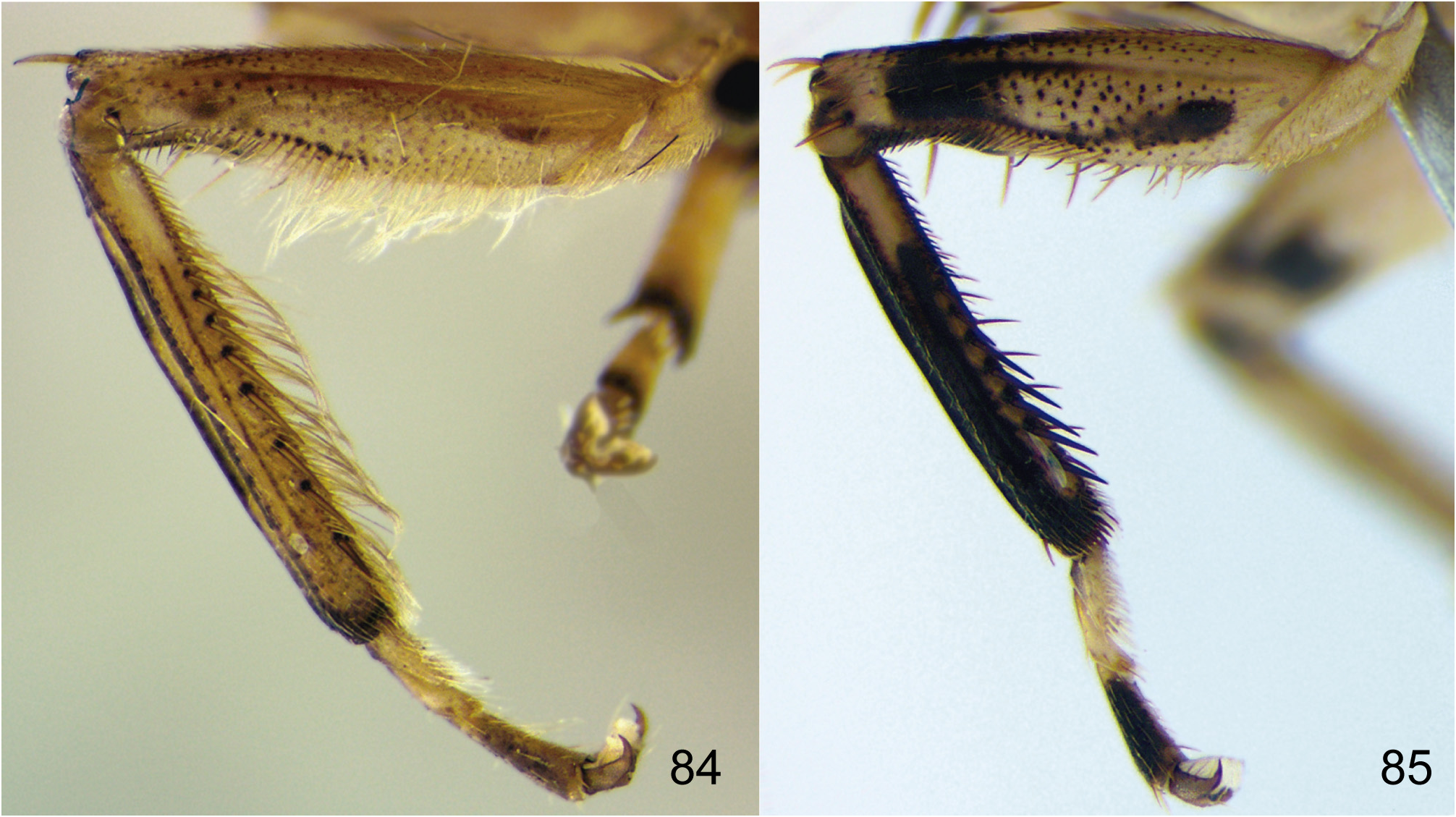
Coloration. Head and thorax ( Figs 1 View FIGURES 1 , 14 View FIGURES 14 ) background yellowish. Ocelli red. Crown and transition crown-face ( Figs 1 View FIGURES 1 , 2) with black punctures. Face (Figs 2, 49) yellow, sometimes with few punctures present on frons; lorum commonly with light-yellow spot on dorsal portion; clypeus frequently with light-yellow laterally maculae near epistomal suture, lateral margins and apex. Pronotum, mesonotum and scutellum ( Figs 35 View FIGURES 35 , 48 View FIGURES 48 ) with many brown or black punctures; mesonotum with two pairs of small light-yellow spots near anterior margin and pair of larger spots adjacent to scutoscutelar suture. Forewing (Figs 4, 16) reddish-brown with several small creamy spots variable in size, quantity and shape, but the largest one always present at middle of inner discal cell. Legs (Figs 75, 77, 84, 85) yellow with black maculae mainly on anterior surface of pro and mesofemur, dorsal surface of pro and mesotibia, and bases of macrosetae and apex of metatibia.
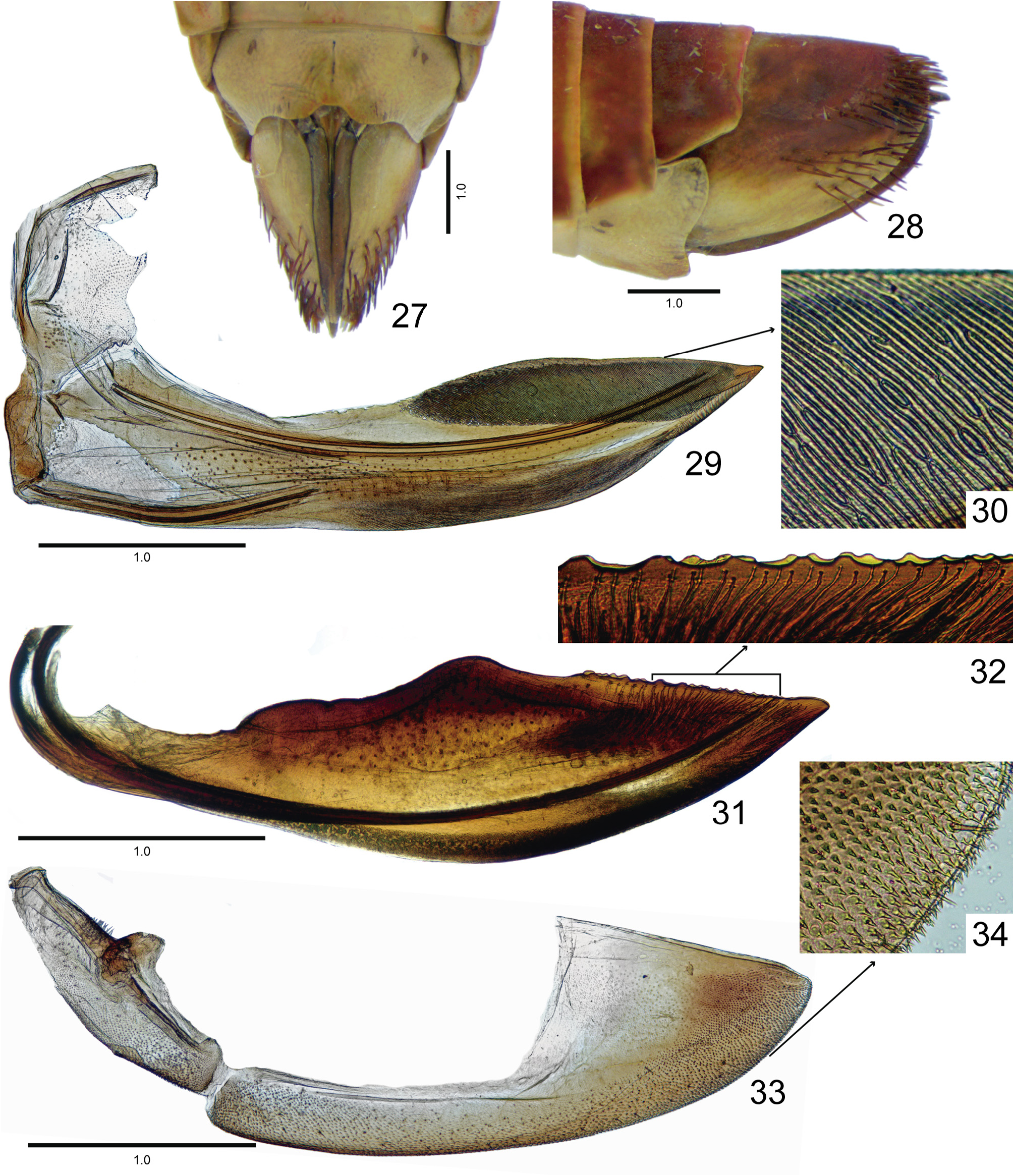
External morphology. Robust, medium to large-sized leafhoppers, 9.8–15.0 mm in length. Head ( Figs 1 View FIGURES 1 , 35 View FIGURES 35 ), in dorsal view, not produced, short, distinctly narrower than the pronotum width; median length 1/4 as long as interocular width; transocular width ca. 8/10 of maximum pronotum width; anterior and posterior margins approximately parallel, anterior margin not produced over margin of eye; crown with few transverse irregular striae, surface slightly concave between ocellus and eye. Ocellus large, convex, closer to eye than to median line and almost adjacent to anterior margin of crown. Head (Figs 2, 49), in ventral view, with face slightly wider than long; frontogenal suture distant from eye margins by half width of clypeus and surpassing antennal ledge, by long distance, extending to anterior margin of crown; antennal ledge carinate and slightly arched, extending over frons by short distance; frons ca. 1.1x longer than wide, surface with texture shagreen, not excavated below anterior margin of crown and bearing few transverse irregular striae on upper portion; lorum extending dorsally nearly to ventral third of frons; epistomal suture indistinct medially; maxillary plate produced ventrally as far as clypeus apex; gena with ventrolateral margin rounded, not excavated below eye margin; clypeus ca. 1.2x longer than wide, lateral margins straight, weakly convergent towards apex, apex carinate, weakly emarginated. Head (Figs 3, 16), in lateral view, with crown-face transition weakly defined, rounded and with transverse irregular striae; frons flattened medially and declivous near lateral margins; clypeus weakly inflated. Pronotum ( Figs 1 View FIGURES 1 , 48 View FIGURES 48 ), in dorsal view, with transverse striae on disc and posterior third, lateral margins convergent anterad, longer than eye length; in lateral view (Figs 3, 37), convex and declivous anterad. Forewing (Figs 4, 17) wide, ca. 3x longer than wide; venation distinct, anal veins and CuA with many veinlets; section of vein M between R+M fork and crossvein m-cu 1 3x longer than the length of m-cu 1; inner discal cell as long as half length of outer discal cell; 3 subapical cells and 5 apical cells (R1 vein present); appendix developed, slightly narrower than maximum width of first apical cell and bordering first, second and third apical cells; apex broad, subtruncated. Profemur ( Figs 84 View FIGURES 84 , 85) elongated, ca. 4x longer than wide; AD, AM, and PD rows reduced and poorly defined, with exception of apical setae AD 1, AM 1 and PD 1 respectively; AV and PV rows with more than 7 well developed setae or formed by group of long filiform setae. Protibia ( Figs 84 View FIGURES 84 , 85), in cross-section, more or less cylindrical, posterodorsal corner with two longitudinal carina, one anterior and one posterior of PD row; AV row formed by setae gradually increasing in thickness and length towards apex, longer setae only as long as diameter of protibia; AD row formed by undifferentiated setae; PD row with 3–4 long setae; dorsal surface with apical setae AD 1 absent and PD 1 developed; PV row with undifferentiated setae and 8–12 long setae; ventral surface with or without long filiform setae. Mesotibia posterodorsal corner with two longitudinal carina, one anterior and one posterior to PD row. Metafemur setal formula 2:2:1. Metatibia rows PD, AD, and AV with 24–26, 14–15, and 17–20 macrosetae, respectively; AD row without intercalary setae between macrosetae; PV row with setae of apical half formed by sequence of 1 thicker and 3–4 thinner macrosetae, ending with a single short and thin seta after the last macroseta. Metatarsomere I with pair of well developed dorsoapical setae; inner row of plantar surface with 7–9 short noncucullate setae, outer row absent or with few inconspicuous setae; apex with 6 patellae flanked by tapered lateral setae. Metarsomere II pecten with 3–4 platellae flanked by 2 tapered lateral setae on inner and 1 on external corner.
Male terminalia. Sternite VIII (Figs 5, 18) strongly convex; posterior margin nearly straight. Valve (Figs 6, 19) integument thickening present only on anterior margin; inner surface with transverse rugae near posterior margin; posterior margin not excavated, rounded. Pygofer (Figs 7, 20) sometimes with small basodorsal process; short scattered filiform setae dispersed near ventral margin; many macrosetae dispersed on apical third; apical portion without processes.Anal tube without processes, more pigmented and sclerotized on lateroventral margins and apically. Subgenital plate (Figs 7, 8, 20, 21), in lateral view, not surpassing pygofer apex; elongate and ligulate, bearing long filiform setae on dorsal surface, near outer lateral margin and apex, but not on ventral surface. Connective (Figs 9, 22) Y-shaped, stem present; dorsal median keel moderately developed, forked apically. Style (Figs 24, 71) with short filiform setae on outer lobe and external surface of blade; blade long with ventral margin serrated; apex with a toothlike process directed inward or serrations. Aedeagus (Figs 12, 13, 25, 26) preatrium not developed; dorsal apodeme moderately developed, without apodemal processes; dorsal margin excavated; shaft long, cylindrical; apical portion frequently less sclerotized, with apical and/or subapical processes; gonopore apical.
Female terminalia. Sternite VII ( Figs 27 View FIGURES 27 , 28) posterolateral angles rounded more produced than posterior margin. Internal sternite VIII membranous. Pygofer (Fig. 28) macrosetae distributed on posterodorsal third and posteroventral half; apex rounded. First valvifer (Fig. 29) trapezoidal, higher than long; posterior margin weakly sclerotized. First valvula (Fig. 29) slightly curved dorsally; wider near apical third; ventral interlocking device short, extending over basal 2/5; dorsal sculptured area (Fig. 30) strigate and extending to ventral margin at apex; apex tapered and acute. Second valvula (Fig. 31) distinctly wider at mid-length, dorsal protuberance well developed and rounded; apical third (Fig. 32) with small irregular teeth; apex tapered and subacute, without denticles on ventral margin. Gonoplac (Fig. 33) ca. 2.5x longer than wide; dorsoapical margin straight, with 2/5 length of gonoplac; ventral margin and apical portion (Fig. 34) with dentiform cuticular projections and few short setae; apex rounded.
Distribution. Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, French Guiana, Guyana, Paraguay, Peru and Venezuela.
Species of Fuminana
F. abana Freytag, 1989: 3 View in CoL . Venezuela.
F. astra ( DeLong & Freytag, 1969) : 167 ( Clinonaria ). Brazil ( new record): Mato Grosso; Peru.
F. callida ( DeLong & Freytag, 1969) : 176 ( Clinonaria ). Brazil: Mato Grosso, Distrito Federal ( new record), Goiás ( new record), Maranhão ( new record), Piauí ( new record).
F. conspicua ( DeLong & Freytag, 1969) : 179 ( Clinonaria ). Brazil ( new record): Mato Grosso, Tocantins, Distrito Federal, Goiás, Mato Grosso do Sul, Mato Grosso, Minas Gerais; Peru.
F. curra ( DeLong & Freytag, 1969) : 166 ( Clinonaria ). Bolivia; Brazil ( new record): Rondônia; Peru.
F. diaphana sp. nov. Brazil: Maranhão, Piauí.
F. extata Freytag, 1989: 3 . Brazil ( new record): Roraima, Mato Grosso; Venezuela.
F. falcifera Freytag, 1989: 3 . Venezuela.
F. guaricica sp. nov. Brazil: Paraná.
F. incurvata sp. nov. Brazil: Rondônia.
F. ingula ( DeLong & Freytag, 1969) : 166 ( Clinonaria ). Brazil: Pará; Ecuador; Peru; Venezuela.
F.jaculum ( DeLong&Freytag,1969) :164( Clinonaria ). Brazil ( new record): Rondônia, Mato Grosso; Colombia; Peru.
F. lira ( DeLong & Freytag, 1969) : 167 ( Clinonaria ). Bolivia; Brazil:Amazonas, Rondônia ( new record); Colombia; Ecuador;? Paraguay?; Peru.
F. marita ( DeLong & Freytag, 1969) : 168 ( Clinonaria ). Brazil: Mato Grosso,? Rio de Janeiro?.
F. metra ( Freytag & DeLong, 1982) : 6 ( Scaris ). Guyana.
F. niluga sp. nov. Brazil: Acre, Pará, Rondônia, Mato Grosso.
F. retorta sp. nov. Brazil: Rondônia.
F. saga ( Freytag & DeLong, 1982) : 6 ( Scaris ). French Guiana.
F. serosa ( DeLong & Freytag, 1969) : 178 ( Clinonaria ). Bolivia, Peru.
F. setigera ( DeLong & Freytag, 1969) : 179 ( Clinonaria ). Brazil: Amazonas; Colombia.
F. setosa ( DeLong & Freytag, 1969) : 172 ( Clinonaria ). Brazil: Pará, Mato Grosso ( new record), Distrito Federal ( new record), Maranhão ( new record), Tocantins ( new record).
F. signa ( DeLong & Freytag, 1969) : 167 ( Clinonaria ). Brazil ( new record): Rondônia, Mato Grosso; Bolivia.
F. superba ( DeLong & Freytag, 1969) : 178 ( Clinonaria ). Brazil ( new record): Rondônia; Colombia; Peru.
F. taenia ( Freytag & DeLong, 1982) : 7 ( Scaris ). Brazil: Pará; French Guiana.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Tribe |
Gyponini |
Fuminana Freytag, 1989
| Domahovski, Alexandre Cruz & Cavichioli, Rodney Ramiro 2022 |
Fuminana
| Freytag, P. H. 1989: 1 |
F. abana
| Freytag, P. H. 1989: 3 |