Gonioctena ( Brachyphytodecta ) kangdingensis, Cho, Hee-Wook, 2017
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4272.3.10 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:2B08F09C-BACA-4737-A49A-78BB195E0761 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6003773 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03D08784-FFB2-483E-FF2C-C22DFD5FF88B |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Gonioctena ( Brachyphytodecta ) kangdingensis |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Gonioctena ( Brachyphytodecta) kangdingensis sp. nov.
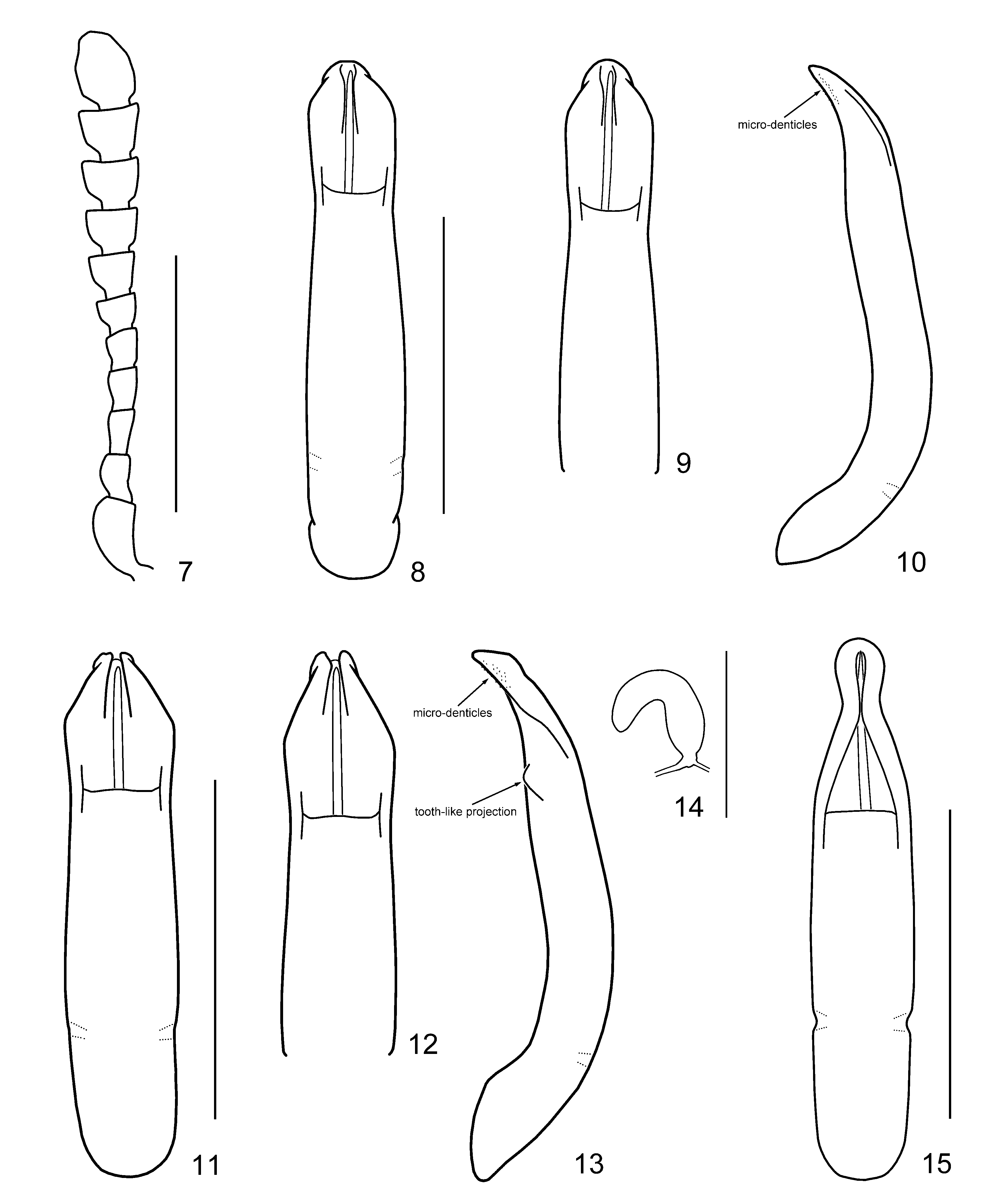
( Figs 3–4 View FIGURES 1 – 6. 1 – 2 , 11–14 View FIGURES 7 – 15. 7 – 10 , 16 View FIGURE 16 )
Type material. Holotype: male, ‘Ta-tsien-Lou [= Kangding], Chasseurs Thibetains 1896 // HOLOTYPUS Gonioctena ( B.) kangdingensis sp. n. Cho & Borowiec 2014’ (MNHN). Paratypes: 2 females ( MNHN), same data as holotype.
Diagnosis. Gonioctena kangdingensis sp. nov. is almost identical with G. davidi sp. nov. in the body shape and coloration, however it can be distinguished by the thicker aedeagus with a pair of tooth-like lateral projections at apical 1/4 (thinner aedeagus without tooth-like lateral projections before apex in G. davidi in sp. nov.). Gonioctena flavipennis (Jacoby) is also very similar ( Figs 5–6 View FIGURES 1 – 6. 1 – 2 ), but differs in the narrow and rounded apical process of aedeagus ( Fig. 15 View FIGURES 7 – 15. 7 – 10 ).
Description. Measurements in mm: length of body: 5.20–5.90 (mean 5.47); width of body: 3.60–4.20 (mean 3.82); height of body: 2.40–2.80 (mean 2.55); width of head: 1.55–1.70 (mean 1.63); interocular distance: 1.10– 1.20 (mean 1.14); width of apex of pronotum: 1.72–1.95 (mean 1.82); width of base of pronotum: 3.20–3.55 (mean 3.32); length of pronotum along midline: 1.50–1.65 (mean 1.57); length of elytra along suture: 3.80–4.40 (mean 4.05).
Body oval and strongly convex ( Fig. 3 View FIGURES 1 – 6. 1 – 2 ). Head reddish-brown, with apex of mandibles black. Antennomeres 1– 2 yellowish-brown, 3–11 lost. Pronotum reddish-brown, basal margin black. Scutellum and elytra reddish-brown. Venter reddish-brown, partially black. Legs blackish-brown to black.
Head. Vertex weakly convex, covered with sparse punctures, becoming coarser and denser toward sides. Frontal suture V-shaped, reaching anterior margin, coronal suture weak. Frons flat, strongly depressed at anterior margin, covered with dense punctures. Clypeus very narrow and trapezoidal. Anterior margin of labrum almost straight. Mandibles with 2 sharp apical teeth and a large excavation for maxillary palp on outer side. Maxillary palp 4-segmented, with apical palpomere slightly widened, truncate apically.
Pronotum. Lateral sides widest at base, roundly strongly narrowed anteriorly, anterior angles strongly produced ( Fig. 4 View FIGURES 1 – 6. 1 – 2 ). Anterior and lateral margins bordered, lateral margins invisible in dorsal view. Trichobothria absent on both anterior and posterior angles. Disc covered with sparse punctures; lateral sides covered with much larger and denser punctures; interspaces covered with fine and sparse punctures. Scutellum slightly wider than long, narrowed posteriorly.
Elytra. Lateral sides very slightly widened posteriorly, widest before middle, thence roundly narrowed posteriorly. Humeral calli well developed. Disc covered with 11 regular rows of large punctures, including a short scutellar row; interspaces covered with fine and sparse punctures. Epipleura visible except near base in lateral view. Hind wings well developed.
Venter. Hypomera weakly rugose, with a few punctures near anterolateral corners of prosternum. Prosternum covered with coarse and dense punctures bearing long setae; prosternal process enlarged apically, bordered laterally, with sparse punctures. Metasternum covered with small and sparse punctures in median region, large and dense punctures in lateral region. Abdominal ventrites covered with sparse or dense punctures bearing short setae.
Legs. Moderately robust. Tibiae widened apically, with a tooth-like projection. Fore legs with tarsomere 1 slightly narrower than 3 in both sexes. Tarsal claws appendiculate.
Genitalia. Aedeagus rather thick, weakly sinuate, distinctly narrowed from apical 1/10 to incised apex in dorsal view ( Figs 11–12 View FIGURES 7 – 15. 7 – 10 ); moderately curved with many micro-denticles on apicolateral surface and a pair of toothlike projections at apical 1/ 4 in lateral view ( Fig. 13 View FIGURES 7 – 15. 7 – 10 ). Spermatheca C-shaped, swollen and apex rounded ( Fig. 14 View FIGURES 7 – 15. 7 – 10 ).
Etymology. The species is named after the type locality, Kangding in China.
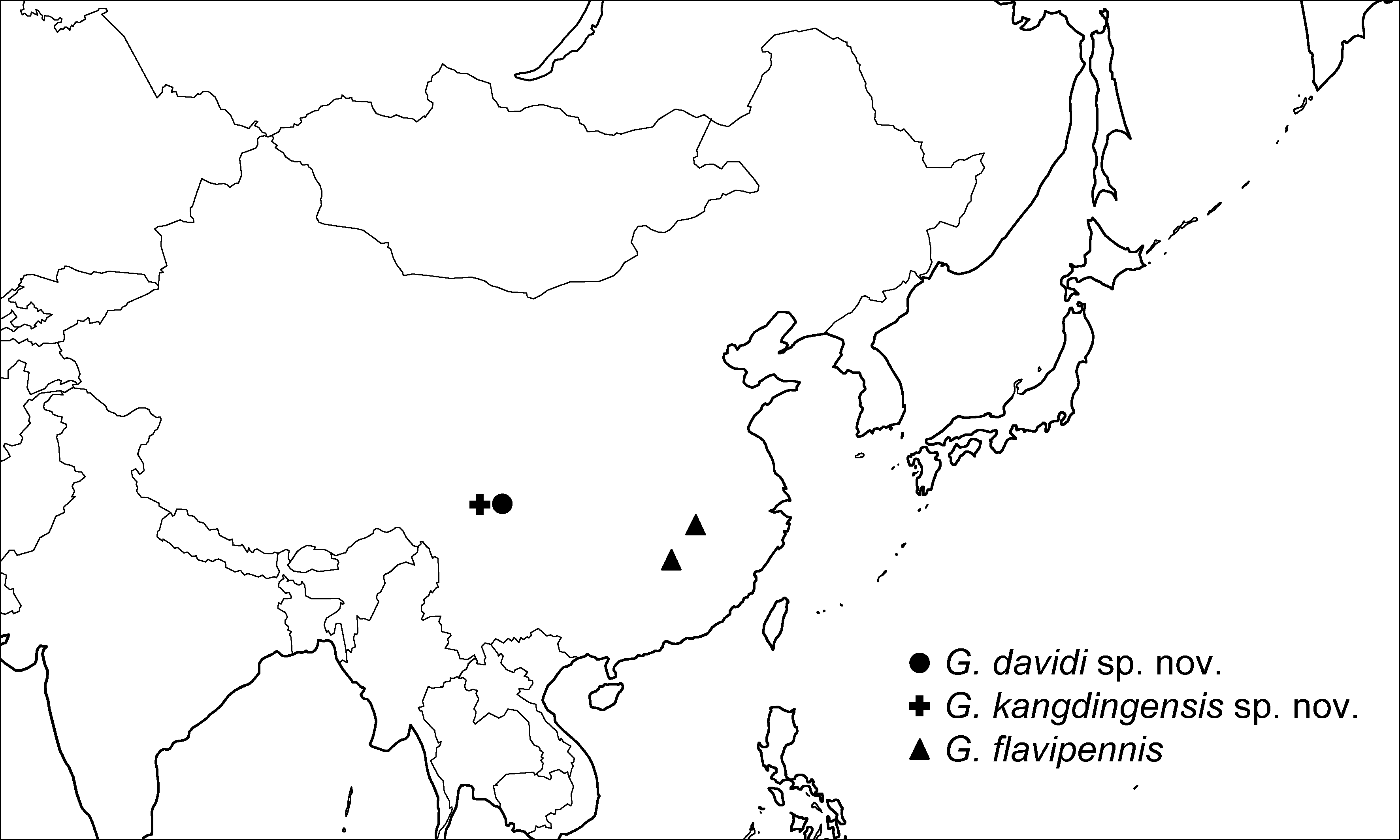
Distribution. China: Sichuan ( Fig. 16 View FIGURE 16 ).
| MNHN |
Museum National d'Histoire Naturelle |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |