Tipula (Sinotipula) hobsoni Edwards, 1928
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5852/ejt.2023.879.2163 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:3DA3233C-F99E-4442-BA4B-546F74CC657B |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8138665 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03CD343F-FFD8-921A-FDA8-2C42FAD2B89D |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Tipula (Sinotipula) hobsoni Edwards, 1928 |
| status |
|
Tipula (Sinotipula) hobsoni Edwards, 1928 View in CoL
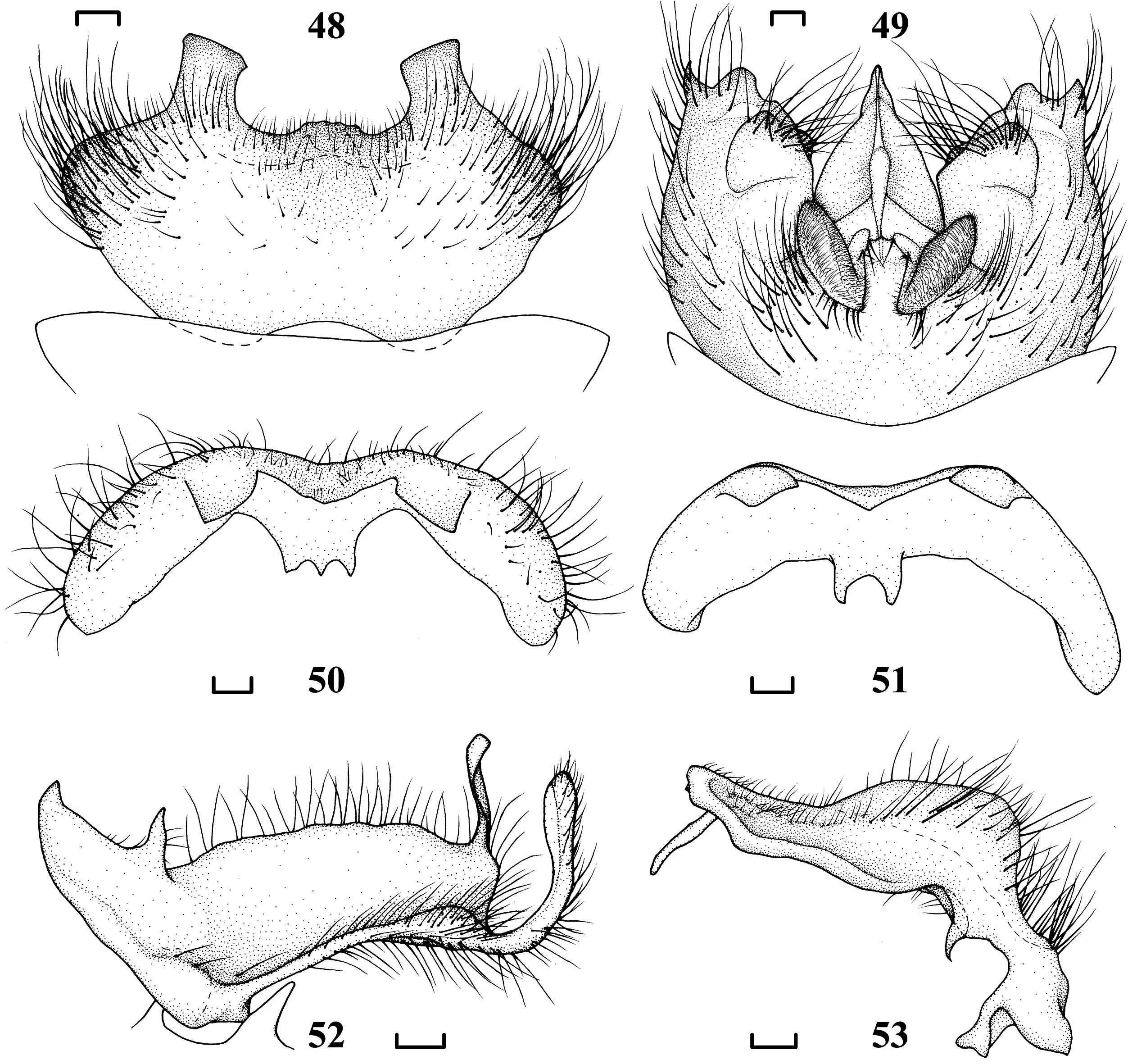
Figs 44–53 View Figs 44–47 View Figs 48–53
Chinese name
Ʀāṃƛfi
Diagnosis
Mainly orange; prescutum dark brown, wing pale yellow with grey areas, pterostigma yellow; tergite 9 with a paiR of tooth-like pRotRusions at posteRioR maRgin; outeR gonostylus wide and flat, with two hoRn-like protrusions anteriorly and two slender lobes posteriorly.
Material examined
CHINA – Xizang • 1 ♂; Yadong City, Qing Dynasty Customs Site ; 27°25′11″ N, 88°55′51″ E; 3041 m a.s.l.; 1 Aug. 2020; Qicheng Yang leg.; light tRap; CAU GoogleMaps • 1 ♂; Yadong City ; 3300 m a.s.l.; 11 Jul. 2018; Qicheng Yang leg.; sweeping; CAU .
Photo material
CHINA • Holotype; Yatung ; 4500 feet a.s.l.; A.E. Hobson leg.; BMNH (photos by Jinlong Ren).
INDIA • 1 ♂; Sikkim, Namnasa ; 9500 feet a.s.l.; 12 MaR. 1959; Schmid leg.; USNM (photos by Yan Li) • 1 ♂; Sikkim, Shingla ; 10 400 feet; 30 Jun. 1959; Schmid leg.; USNM (photos by Yan Li) .
Redescription
Male
MEASUREMENTS. Body length 22.0– 22.6 mm, wing length 25.0– 25.2 mm, antenna length 5.0– 5.5 mm (n = 2).
HEAD ( Figs 45–46 View Figs 44–47 ). Mainly brown. Occiput with two areas with white pruinescence. Rostrum and nasus bRown. Setae on head daRk bRown. Antenna oRange with white appRessed pubescence, bases of flagellaR segments slightly dark. Proboscis brown. Palpal segments 1 and 2 yellow, segments 3 and 4 dark brown.
THORAX ( Figs 45–46 View Figs 44–47 ). Mainly orange. Pronotum reddish brown at middle, extended to head and anepimeron. Prescutum dark brown with four blurry brown stripes, all stripes with reddish brown margins, median stripes broadened anteriorly and gradually narrowed posteriorly. Scutum dark brown, with four brown blurry spots. Scutellum and mediotergite brown, mediotergite with abundant, uneven pruinescence, except on middle portion. Pleuron mainly orange with slight white pruinescence. Anepisternum yellowish brown, dark on upper portion, membranous suture with prescutum dark brown; katepisternum, anepimeron, epimeron and metapleuron with brown areas. Setae on thorax pale yellow. Legs with femora and tibiae brownish yellow, apically slightly dark; tarsi brownish yellow. Claw with a black tooth basally. Setae on legs dark brown. Wing pale yellow with grey areas, pterostigma yellow, long spot of cell cua dark grey, spot of M 3 base basally dark grey, petiole of cell m 1 ⅓ as long as discal cell ( Fig. 47 View Figs 44–47 ). Halter with yellow stem and orange knob.
ABDOMEN ( Figs 45–46 View Figs 44–47 ). Mainly yellow. All tergites with slender black lateral stripes, sternites and tergites 6–8 dark at lateral margin. Setae on abdomen golden.
HYPOPYGIUM ( Figs 44 View Figs 44–47 , 48–53 View Figs 48–53 ). Mainly yellowish brown. Posterior margin of tergite 9 with a pair of tooth-like protrusions slightly slanted at tip, ventrally with two or three teeth. Gonocoxite and sternite 9 fused, sternite 9 with a pair of pubescent oval protrusions. Adminiculum wide basally, narrow apically, with a slendeR pRotubeRance at middle. OuteR gonostylus wide and flat, with two hoRn-like pRotRusions anteriorly and two slender lobes posteriorly ( Fig. 52 View Figs 48–53 ). Inner gonostylus recurved, inside concave, outside bulged, apex with a fingeR-like pRotRusion ( Fig. 53 View Figs 48–53 ).
Female
Apart from the genitalia, similar to male; cercus and hypovalve short.
Distribution
China (Xizang); India (Sikkim).
Remarks
In the male specimen from Shingla, Sikkim (USNM), the distance between the two protrusions on tergite 9 is narrower than in that from Namnasa, Sikkim (USNM) or Yadong City, Xizang (CAU). The distance between the two protrusions of tergite 9 might not be a stable special feature in Sinotipula . In the specimen from the Qing Dynasty Customs Site in Yadong City, tergite 9 is asymmetrical (possibly damaged), and the ventral surface of tergite 9 has two teeth ( Fig. 51 View Figs 48–53 ). In holotype, the ventral surface of tergite 9 has two teeth ( Edwards 1928), but in the specimens from Yadong City and some individuals from Sikkim (USNM), the ventral surface of tergite 9 has three teeth ( Fig. 50 View Figs 48–53 ) ( Alexander 1970).
| BMNH |
United Kingdom, London, The Natural History Museum [formerly British Museum (Natural History)] |
| USNM |
USA, Washington D.C., National Museum of Natural History, [formerly, United States National Museum] |
| CAU |
China Agricultural University |
| USNM |
Smithsonian Institution, National Museum of Natural History |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.