Caridina appendiculata Jalihal & Shenoy, 1998
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.176586 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6249875 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03CB87FF-0017-FFF3-3B88-C22EFB89FCD1 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Caridina appendiculata Jalihal & Shenoy, 1998 |
| status |
|
Caridina appendiculata Jalihal & Shenoy, 1998 View in CoL
Caridina gracilirostris De Man, 1892: 399 View in CoL (part); Holthuis, 1978: 35 (part). Caridina appendiculata Jalihal & Shenoy, 1998: 128 View in CoL .
Material examined: 3 males cl 3.1–3.7 mm, 1 female cl 3.6 mm, 1 ovigerous female cl 4.9 mm ( MZB Cru 1567) Indonesia, Central Sulawesi, Luwuk Peninsula, freshwater spring in Malontong, west of Ampana, brackish water pool; 0°53.125’S 121°31.371’E (Loc. 70-05); coll. M. Glaubrecht, T. von Rintelen & K. Zitzler, May 27, 2005; 4 males cl 2.9–3.5 mm, 3 ovigerous females cl 4.2–5.3 mm ( ZMB 29000), same locality as above.
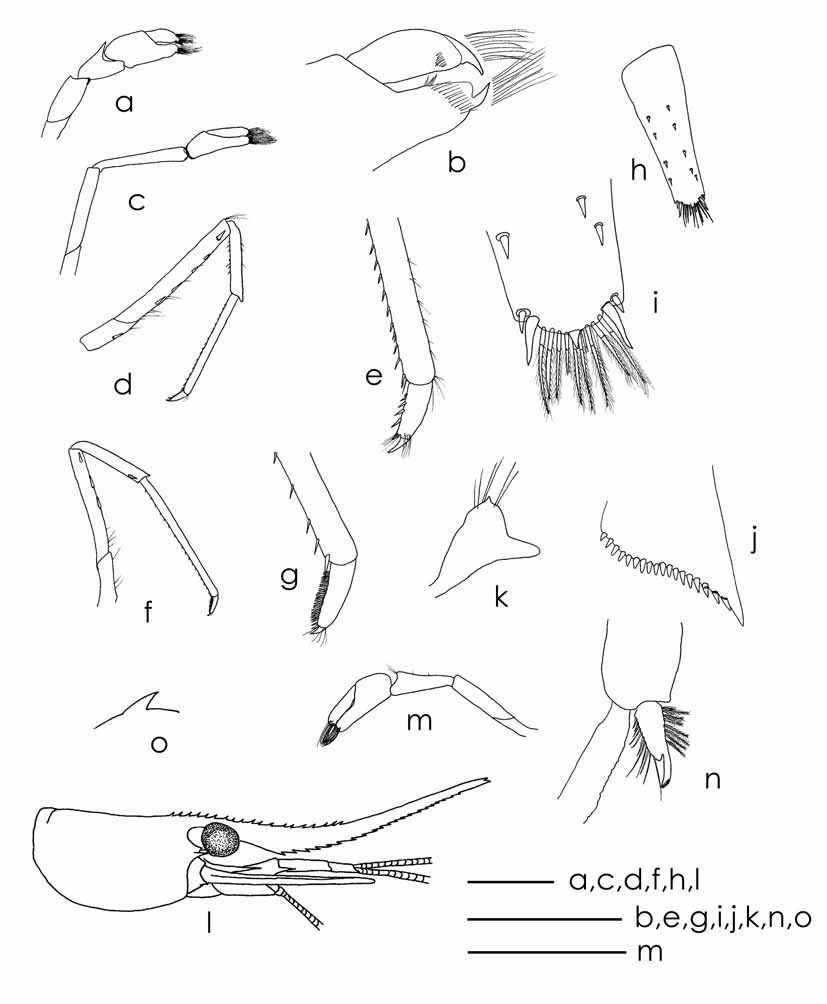
Description: Rostrum ( Fig.3 View FIGURE 3 l) long 1.4–2.2 as long as carapace in males, 1.3–1.4 as long in females, curved up distally, reaching well beyond scaphocerite. Dorsal teeth somewhat irregular spaced, unarmed in distal half except for 1–3 subapical teeth. Teeth on ventral margin more closely set. Rostrum formula 2–3 + 7– 17 +1–3 / 13–29.
Eyes ( Fig.3 View FIGURE 3 l): well developed with cornea globular.
Carapace ( Fig.3 View FIGURE 3 l): Smooth, glabrous with sharp antennal spine placed slightly below orbital angle. Pterygostomial margin blunt, no teeth.
Antennule ( Fig 2 View FIGURE 2 k): Peduncle 0.9–1.2 times cl, three-segmented; anterolateral process of proximal antennular segment long and sharp; all segments with submarginal plumose setae; stylocerite sharp, long, reaching to about 80–90% of first peduncle.
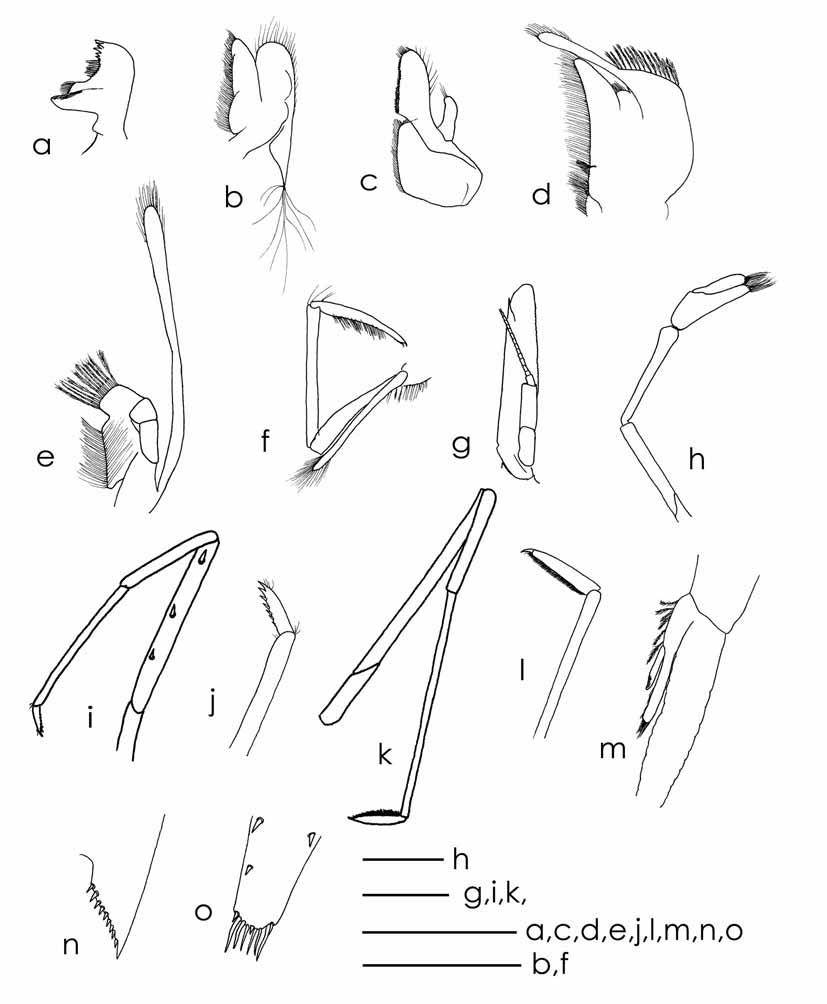
Scaphocerite ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 g): Longer than antennular peduncle, length 3.7–4.5 times width, inner and anterior margins with long plumose setae.
Mouthparts as figured in Fig.4 View FIGURE 4 . Mandibels ( Fig.4 View FIGURE 4 a): Incisior process of mandibels ending in irregular teeth, molar process truncated. Upper lacinia of maxillule ( Fig.4 View FIGURE 4 c) elongated with numerous small teeth on inner margin, palp slender with few plumose stetae at tip, lower lacinia broadly rounded. Upper endites of maxilla ( Fig.4 View FIGURE 4 b) subdividet, palp fingerlike, scaphognatite tapering posteriorly with long hairs at distal end.
First maxilliped ( Fig.4 View FIGURE 4 d): With palp truncate, ending in an indistinct fingerlike tip.
Second maxilliped ( Fig.4 View FIGURE 4 e) as typical for the genus.
Third maxilliped ( Fig.4 View FIGURE 4 f): With exopod, penultimate segment of endopod longer than proximal and distal segment.
First pereiopod ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 m): Slender, chela about 1.8–2.6 times as long as wide, dactylus 0.9–1.6 times as long as palm. Fingertips without prominent claws. Carpus 1.8–3.2 times as long as wide, somewhat excavated distally.
Second pereiopod ( Fig.4 View FIGURE 4 h): More slender and longer than first pereiopod Chela 2.0–2.9 times as long as wide, dactylus 1.1–1.5 times as long as palm. Carpus 5.0–7.7 times as long as wide.
Third pereiopod ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 i): Slender, dactylus ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 j) with 6–8 spines on flexor margin in addition to the terminal spine, propodus 4.5–7.1 as long as dactylus.
Fifth pereiopod ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 k): Dactylus ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 l) with about 37 spines, propodus very slender, 16.0–26.7 times long as distal width, 4.5–6.0 times as long as dactylus.
Well developed epipods on first to fourth pereiopods.
First pleopod: Endopod ( Fig.3 View FIGURE 3 n) leaf-like with a long appendix interna in males.
Second pleopod: With appendix masculina ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 m) slender, rod-shaped in males.
Abdomen: Glabrous, sixth abdominal segment 0.76–0.89 times cl in males, 0.65–0.72 times cl in females.
Preanal carina ( Fig.3 View FIGURE 3 o) with a prominent fingerlike backward striking tooth.
Telson ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 o) 0.71–0.96 times cl, 3.55–3.82 times as long as proximal width, ending in a median point, 3 pairs of distal spines, lateral pair longer than intermediate.
Uropodal diaeresis ( Fig.4 View FIGURE 4 n) with 9–13 spinules.
Egg size 0.41–0.46 x 0.16–0.26 mm, fully developed eggs from one female 0.43 x 0.26 mm
Remarks: With the long, upcurved rostrum and the prominent tooth on the preanal carina our specimens resemble C. gracilirostris De Man, 1892 . From “typical” C. gracilirostris as described by De Man (1892) our shrimps differ by a larger number of teeth on the dorsal margin of the rostrum (9–19 vs. 8–10, subapical teeth excluded) which also seem to be somewhat more densely spaced than in typical specimens, a lower number of ventral teeth (13–29 vs. 24–37 in C. gracilirostris ) and more slender first pereiopods (dactylus 0.9–1.6 times as long as palm vs. as long as palm or shorter in C. gracilirostris ), carpus 2.2–3.2 times as long as wide (1.8 times in one female) vs. 1.7 times as pictured by De Man (1892). In preview to an ongoing revision Cai & Shokita (2006) pointed out that those specimens of C. gracilirostris with a well developed appendix interna on male first pleopod should rather be assigned to C. appendiculata . The description of this species by Jalihal & Shenoy (1998) is only rather cursory, but our specimens agree well with an extended description of this species (Cai, pers. comm.). We tentatively assign our specimens from Malontong to C. appendiculata , thus. The latter also resembles C. brevidactyla Roux, 1919 , particularly the form and dimension of the pereiopods. C. appendiculata only differs from C. brevidactyla in a lower number of teeth on the proximal part of the dorsal margin of the rostrum (9–19 vs. 9–30 -mostly 17–24- as described by Roux, 1919, for C. brevidactyla ), a slightly lower number of spines on the dactylus of the fifth pereiopods (about 37 vs. 50–63 in C. brevidactayla ) and by possessing a prominent tooth on the preanal carina (which is absent in C. brevidactyla , according to the description of a sample from Halmahera, Indonesia by Cai & Ng (2001). De Man also reported 3 specimens of C. gracilirostris from Luwuk Peninsula and some more from Flores which differ from his “typical” form from Balangnipa, Sulawesi, in having the same slender first and second pereiopods as our specimens, thus pointing towards conspecificity of these specimens to the present species.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Caridina appendiculata Jalihal & Shenoy, 1998
| Rintelen, Von 2007 |
Caridina gracilirostris De Man , 1892 : 399
| Jalihal 1998: 128 |
| Holthuis 1978: 35 |
| De 1892: 399 |