Endonura asiatica, Smolis, Adrian, Deharveng, Louis & Kaprus’, Ighor J., 2011
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.278475 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5630249 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03C9E776-FFD8-FFB9-BCAB-FC96A4A9FF72 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Endonura asiatica |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Endonura asiatica sp. nov.
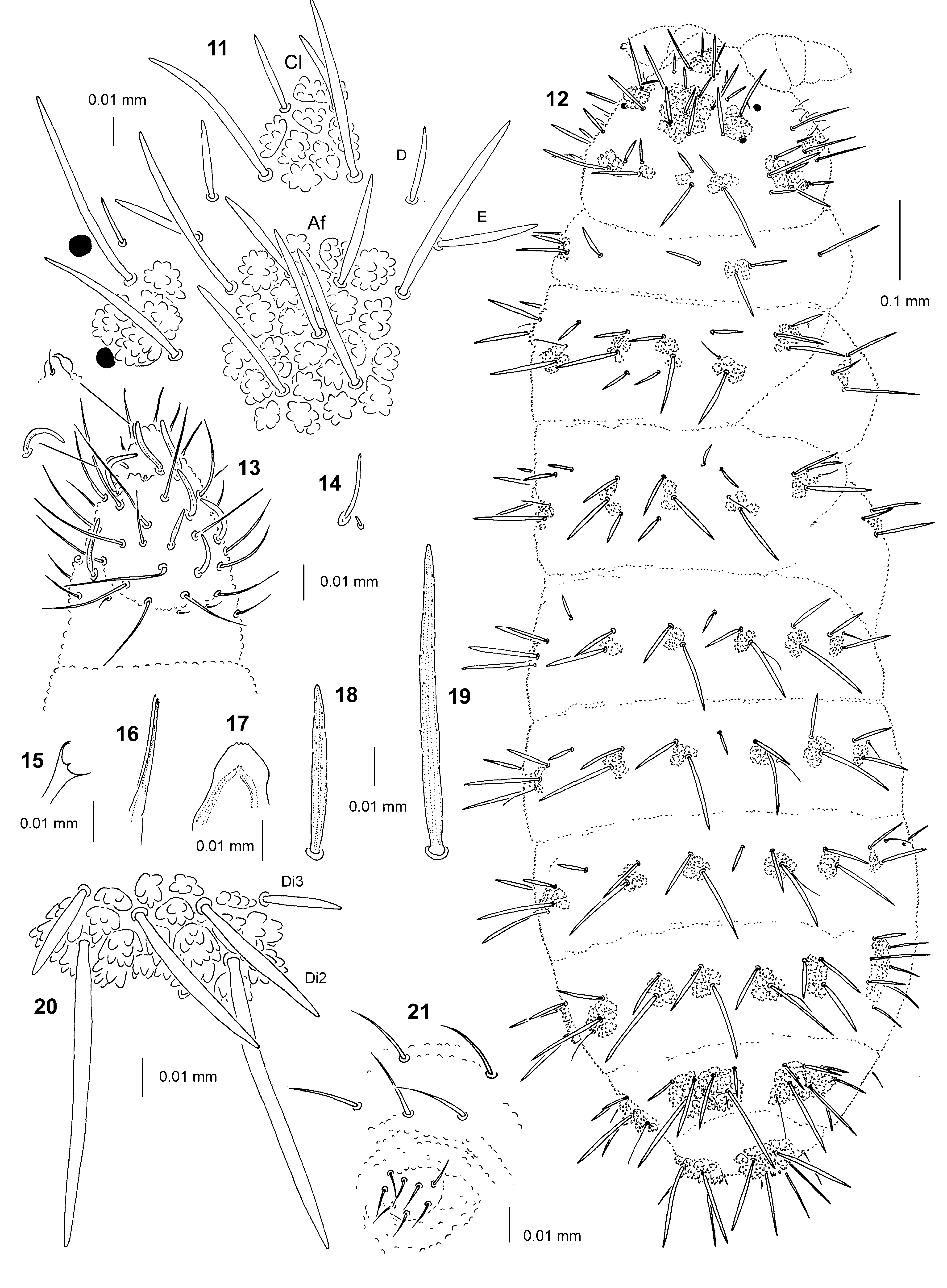
Figs 11–21 View FIGURES 11 – 21 , Tab. 2 View TABLE 2
Type material. Holotype: adult female on slide: Kyrgystan: Issyk-kul district, Griegorievskoye Uschel’ye, near Bozteri, under the bark of rooting log of the sorb, spruce forest, 9.vi.2006. leg. R. J. Pomorski. Paratypes: 3 females and 5 males, same data as holotype, 5, 2 and 1 paratypes in ZIWU, MNHNP and MNHL respectively.
Other material. 1 female on slide: Kyrgystan: Issyk-kul district, Karakol area, Dzhety Oguz, under the bark of spruce, 25.vii.2005, leg. R. J. Pomorski, ZIWU.
Etymology. The species name refers to its terra typica.
Diagnosis. Habitus typical of the genus Endonura . Dorsal tubercles present and well developed, except tubercles Di on th. I. 2 +2 eyes dark pigmented. Buccal cone rather short. Head with chaetae A, B, C, D and E. Chaeta O present. Tubercles Dl and (L+So) on head with 6 and 10 chaetae respectively. Tubercles De on th. II and III with 3 and 4 chaetae respectively. Tubercles L on abd. III and IV with 4 and 7 chaetae respectively. Abd. IV and V with 8 and 3 tubercles respectively. Claw without inner tooth. Tibiotarsi with chaetae B4 and B5 short.
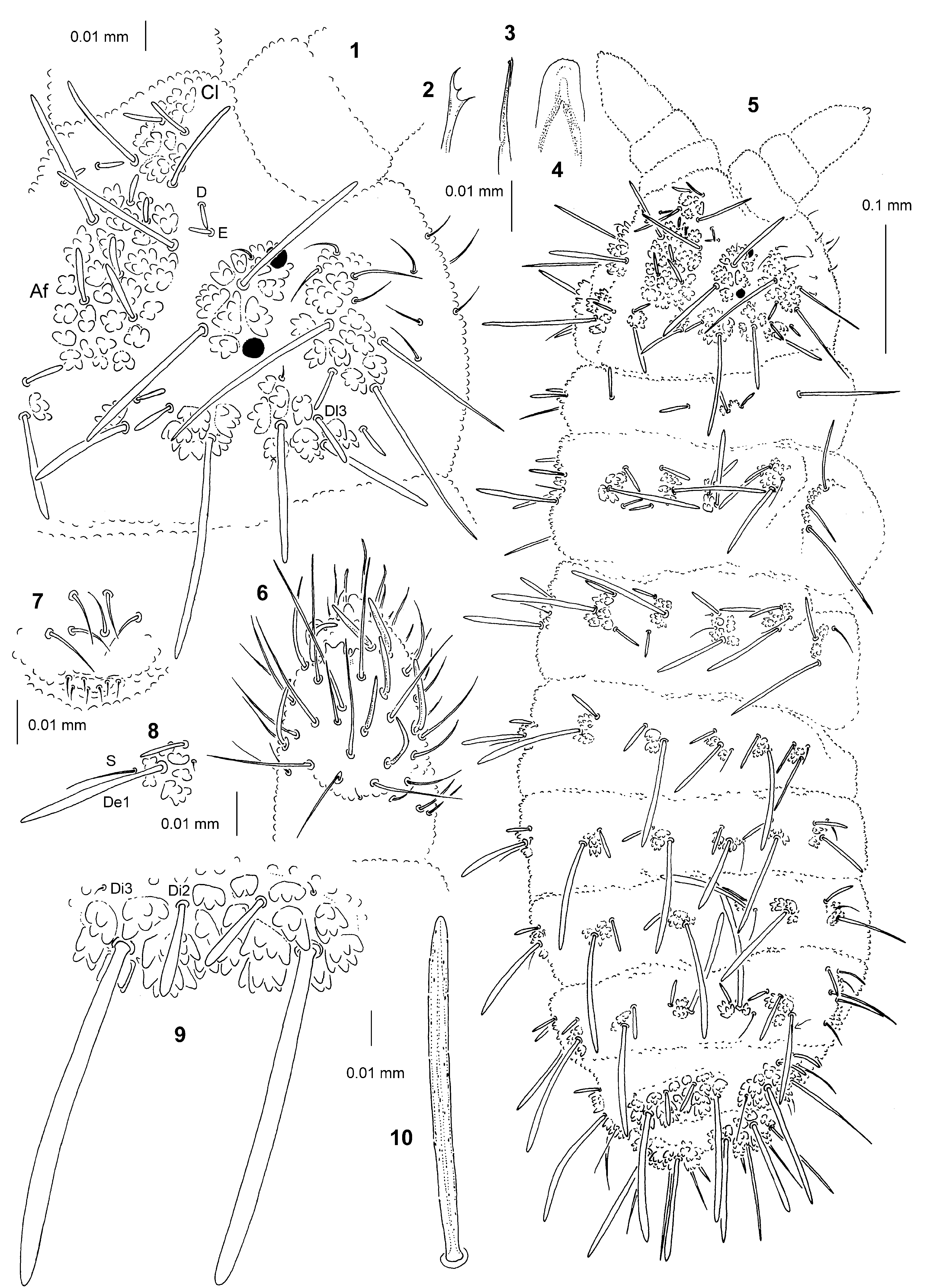
Description. Habitus typical of the genus. Body length (without antennae): 0.86–1.45 mm (holotype: 1.38 mm). Colour of the body bluish grey. 2+2 medium dark-pigmented eyes ( Fig. 1 View FIGURES 1 – 10 ).
Types of dorsal ordinary chaetae. Macrochaetae Ml rather long, thickened, tapered, fusiform, straight or slightly arc-like, narrowly sheathed, feebly serrated, apically rounded or pointed ( Figs 11–12, 18–21 View FIGURES 11 – 21 ); macrochaetae Mc and Mcc thickened, fusiform, straight or slightly arc-like, apically rounded or pointed; mesochaetae and microchaetae short, thin, feebly serrated and pointed.
Head. Buccal cone short. Labrum rounded, with ventral sclerifications as in Fig. 17 View FIGURES 11 – 21 . Labrum chaetotaxy 2–4/2, 4, sometimes median prelabral chaetae absent. Labium with four basal, three distal and four lateral chaetae, papillae x absent. Maxilla styliform ( Fig. 16 View FIGURES 11 – 21 ), mandible thin with two basal and two apical teeth ( Fig. 15 View FIGURES 11 – 21 ). Chaetotaxy of antennae as in Tab. 2 View TABLE 2 c and in Figs 13–14 View FIGURES 11 – 21 . Apical vesicle distinct, trilobed ( Fig. 13 View FIGURES 11 – 21 ). S–chaetae of ant.IV of medium length and moderately thickened, S3 slightly thinner than others ( Fig. 13 View FIGURES 11 – 21 ). Chaetotaxy of head as in Tab. 2 View TABLE 2 a, b, and Figs 11–12 View FIGURES 11 – 21 . Tubercles Cl and Af separate ( Fig. 11 View FIGURES 11 – 21 ). Chaeta O present. Chaetae D and E free. Anterior eye located outside tubercle Oc ( Fig. 11 View FIGURES 11 – 21 ). Tubercle Dl with 6 chaetae, chaeta Dl3 present. Tubercle (L+So) with 10 chaetae, chaetae So3 and L3 present. Elementary tubercle BE absent. Chaeta A shorter than B.
Thorax, abdomen, legs. Body s-chaetae thin and smooth, shorter than nearby macrochaetae ( Fig. 12 View FIGURES 11 – 21 ). Chaetotaxy of th. and abd. as in Tab. 2 View TABLE 2 d and in Figs 12, 18–21 View FIGURES 11 – 21 . Tubercles Di on th.I not differentiated. Chaetae De3 on th. III and abd. I–III as Mcc or Mc. Chaetae De2 on th. II–III and De3 on th. III free. Chaetae De3 on abd. I–III free ( Fig. 12 View FIGURES 11 – 21 ). The line of chaetae De1–chaeta s no perpendicular to the dorsomedian line on abd. I–IV. Tubercle L on abd. III and IV with 4 and 7 chaetae respectively ( Fig. 12 View FIGURES 11 – 21 ). Furca rudimentary with 8 microchaetae ( Fig. 21 View FIGURES 11 – 21 ).Tubercles Di on abd. V fused, with chaetae Di2 and Di3 as Mc ( Figs 18–20 View FIGURES 11 – 21 ). Chaetae L' and Vl on abd. V present. No cryptopygy. Chaetotaxy of legs as in Tab. 2 View TABLE 2 d. Tibiotarsi with chaetae B4 and B5 short. Claw without inner tooth.
Discussion. E. asiatica differs from all other members of the genus in having its anterior eye located outside the tubercle Oc on head ( Fig. 11 View FIGURES 11 – 21 ). Morphologically E. asiatica is most similar to E. quadriseta Cassagnau & Péja, 1979 and E. reticulata ( Axelson, 1905) from which it may be distinguished by the shape of long dorsal macrochaetae (in asiatica fusiform, in quadriseta and reticulata subcylindrical or cylindrical), the number of chaetae on head tubercle (L+So) (in asiatica and reticulata 10; in quadriseta 9, chaeta So2 absent), the presence/absence of male ventral organ on abdomen (in asiatica and reticulata absent, in quadriseta present), the presence/absence of microchaetae on furca rudimentary (in asiatica present, in quadriseta and reticulata absent), the presence/absence of free chaeta L on abd. IV (in asiatica and reticulata absent, in quadriseta present).
a) Cephalic chaetotaxy––dorsal side b) Cephalic chaetotaxy––ventral side
Group Number of chaetae Vi 6 Vea 4 Vem 3 Vep 4 Labium 11, 0x
c) Chaetotaxy of antennae d) Postcephalic chaetotaxy
TABLE 2. Chaetotaxy of Endonura asiatica sp. nov.:
| Tubercle | Number of chaetae | Types of chaetae | Names of chaetae |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cl | 4 | Ml Mc | F G |
| Af | 11 | Ml Mc | A, B C, D, E, O |
| Oc | 3 | Ml Mcc or mi | Ocm, Ocp Oca |
| Di | 2 | Ml Mc | Di1 Di2 |
| De | 2 | Ml Mc | De1 De2 |
| Dl | 6 | Ml Mc | Dl1, Dl5 Dl2, Dl3, Dl4, Dl6 |
| (L+So) | 10 | Ml Mc Mcc or mi Mcc or me me | L1, L4, So1 L2 So2 L3 So3–6 |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |