Cenopalpus spinosus ( Donnadieu, 1875 )
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.24349/acarologia/20184255 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:AABAF96C-DA66-4BF7-BE62-9596C4FFE347 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03C58795-7539-FF9D-D3FE-FDD6FB5DA0E6 |
|
treatment provided by |
Marcus |
|
scientific name |
Cenopalpus spinosus ( Donnadieu, 1875 ) |
| status |
|
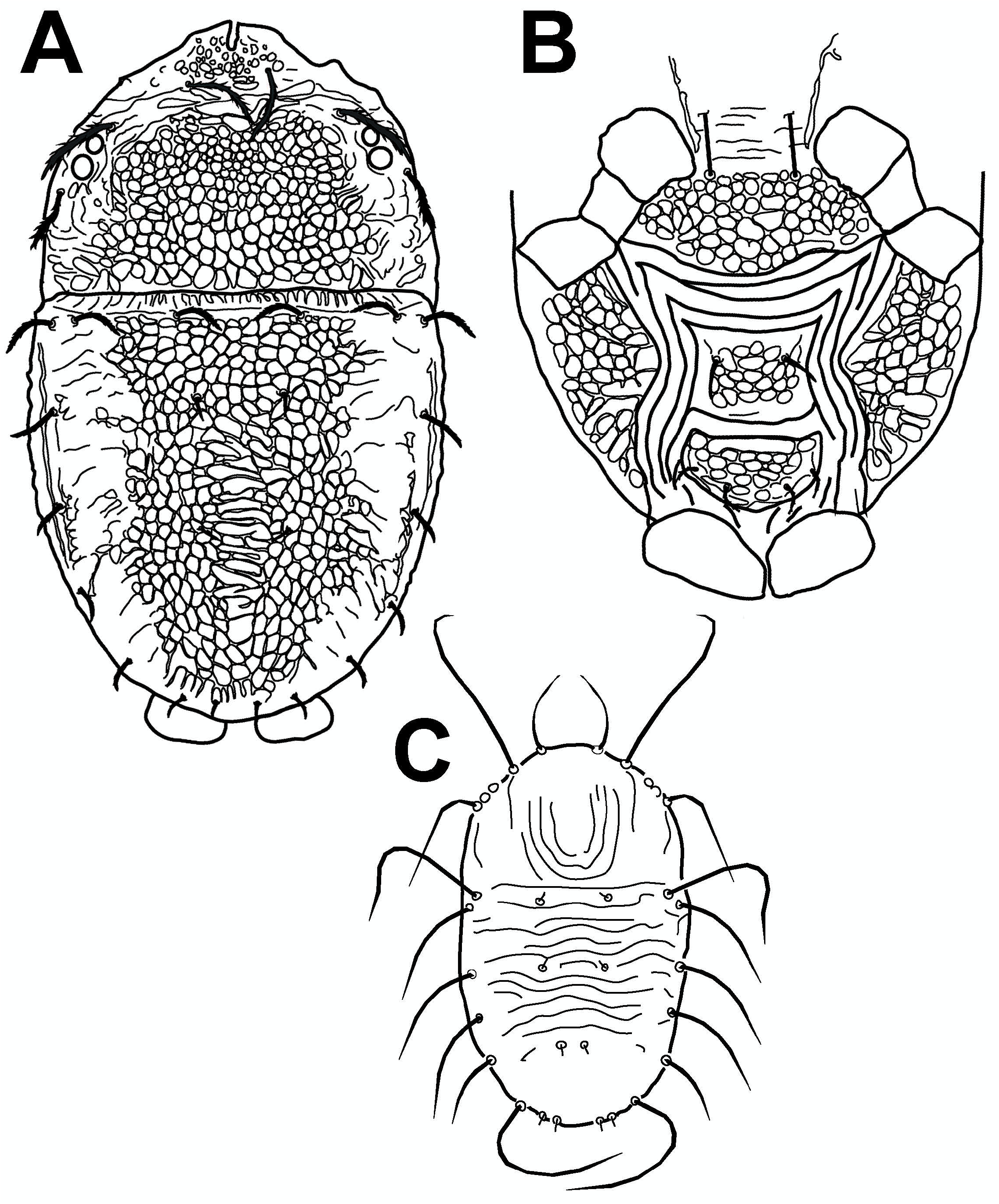
Cenopalpus spinosus ( Donnadieu, 1875) View in CoL ( Figure 17 View Figure 17 )
Diagnosis (Female) — Prodorsum with 3 pairs of long, strongly barbed setae, longer than opisthosomal setae, most also strongly barbed, evenly reticulate with small to medium cells, opisthosoma with f2 present and cuticle with large irregular cells between c1-d1, between d1-h1 reticulation becoming series of short transverse folds, mediolaterally with even reticulation of small cells ( Fig 17A View Figure 17 ); tarsus II with one solenidion distally; rostrum reaching to middle of genu I, palp tibia with 2 setae. Opisthogaster with cuticle between 3a -3a smooth but with fine striae, between 4a -4a with weak transverse bands, ventral and genital shields with medium to large rounded cells and genital shield ( Fig 17B View Figure 17 ).
Deutonymph — Opisthosomal setae c1, d1, e1, h1 and h2 minute, rest of setae long ( Fig 17C View Figure 17 ).
Hosts and localities — Hosts mainly of the Rosaceae family from: Algeria, France,
Germany, Greece, India, Iran, Israel, Morocco (Beard et al. 2013; Hatzinikolis et al., 1999;
Hatzinikolis & Emmanouel, 1987; Khanjani et al., 2012; Pritchard & Baker, 1958).
Symptoms — This species prefers the underside of host leaves and causes yellow to dark spots when feeding on roses ( Hatzinikolis & Emmanouel, 1987).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.