Seminemacheilus ahmeti Sungur, Jalili, Eagderi & Çiçek 2018
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4802.3.5 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:CEAB7B85-E24D-4E30-B501-1302005C6D0C |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10564429 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03C57553-FFBB-FFB6-57AA-036FF7C18FD0 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Seminemacheilus ahmeti Sungur, Jalili, Eagderi & Çiçek 2018 |
| status |
|
Seminemacheilus ahmeti Sungur, Jalili, Eagderi & Çiçek 2018
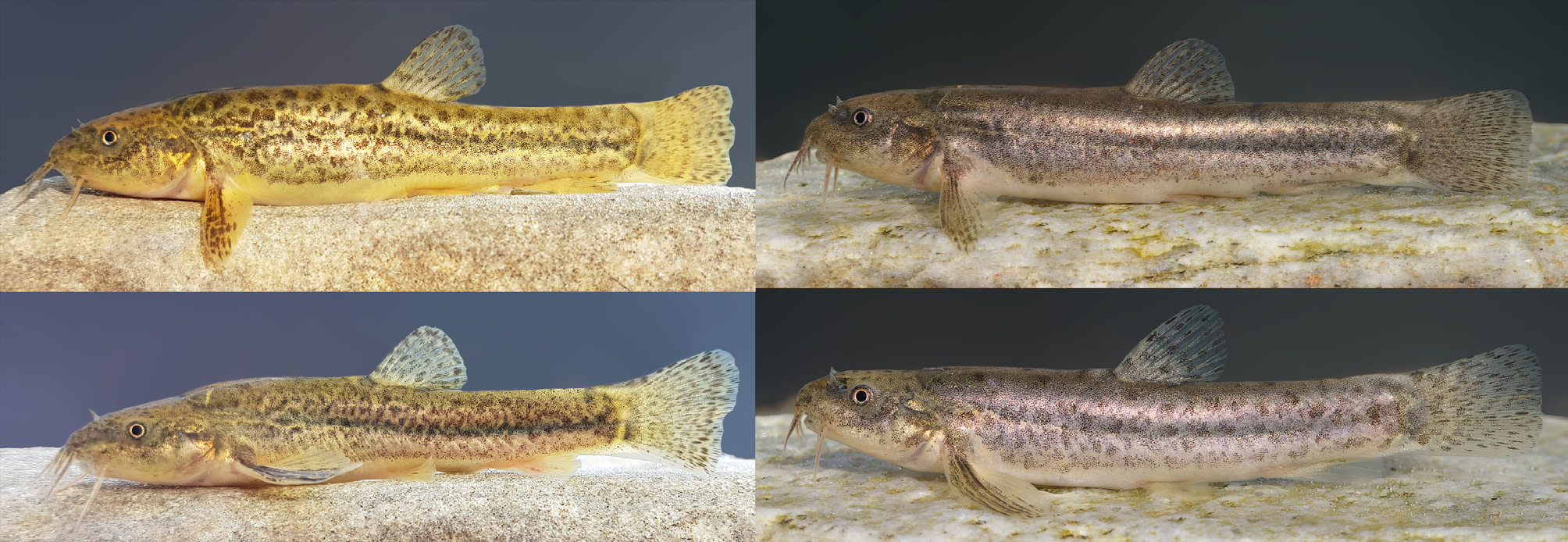
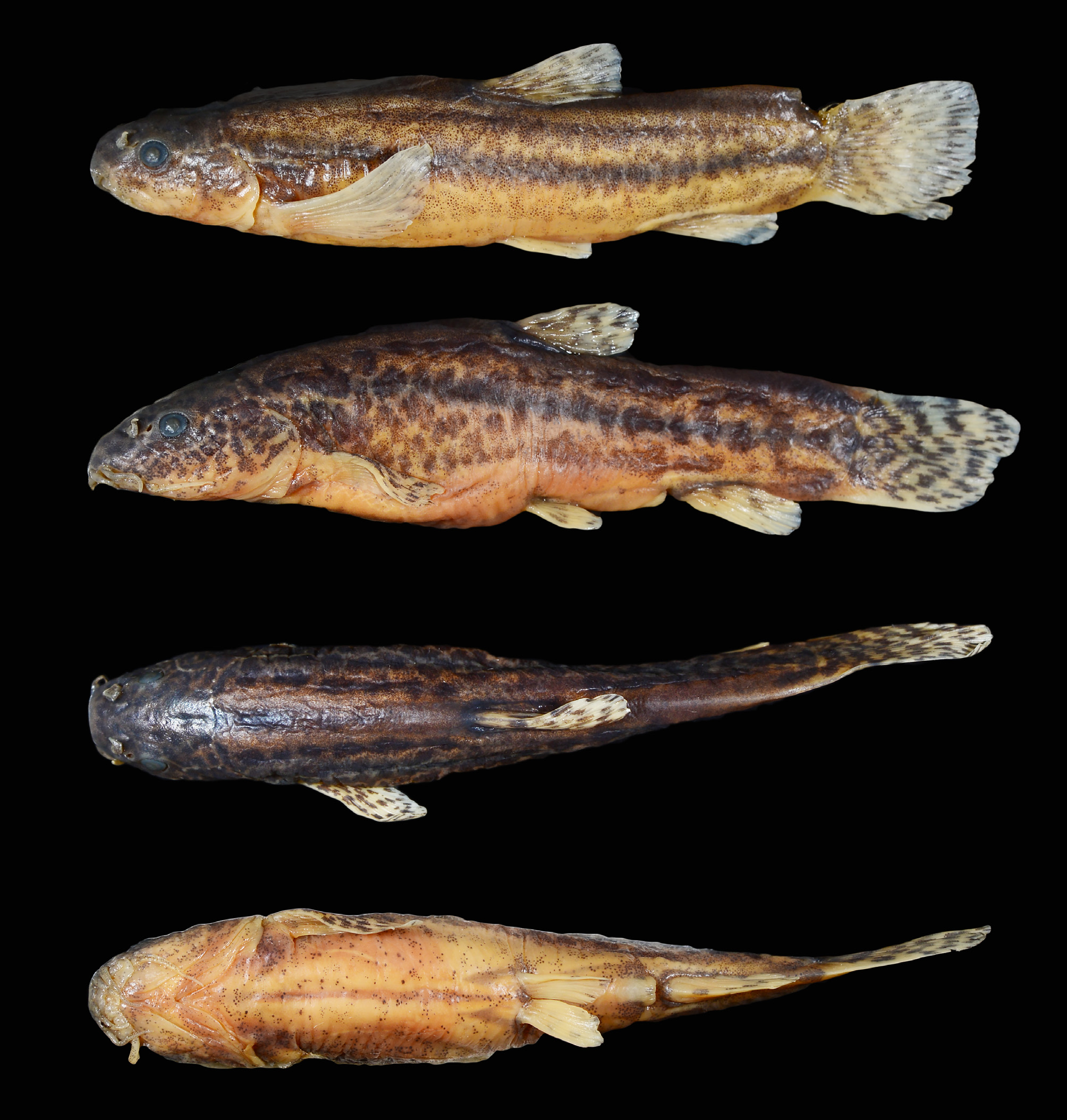
( Figs. 7–8 View FIGURE 7 View FIGURE 8 )
Seminemacheilus ahmeti Sungur, Jalili, Eagderi & Çiçek, 2018:467 , Figs. 1–4 View FIGURE 1 View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 View FIGURE 4 , 5b View FIGURE 5 , 6b View FIGURE 6 , 7b View FIGURE 7 ( type locality: Sultan Sazlığı GoogleMaps near Yeşilova Village, Kızılırmak Basin, Kayseri Province, Turkey, 38.2014, 35.2221)
Material examined. FFR 15562 , 4, 47–57 mm SL; FSJF 2604, 20, 33–54 mm SL; Turkey: Kayseri prov.: spring Soysallı west of Soysallı , 38.3902, 35.3656 GoogleMaps .— FSJF 2501 , 4, 32–38 mm SL; Turkey: Kayseri prov.: canal north of Senir at road to Sultan Sazlığı National Park , 38.2013, 35.2525 GoogleMaps .
Material used in molecular genetic analysis. FSJF DNA-986 ; Turkey: Kayseri prov.: canal north of Senir at road to Sultan Sazlığı National Park , 38.2013, 35.2525. (GenBank accession numbers: MT077012 View Materials , MT077013 View Materials ) GoogleMaps .— FSJF DNA-956 ; Turkey: Kayseri prov.: spring Soysallı west of Soysallı , 38.3902, 35.3656. (GenBank accession numbers: KJ554681 View Materials , KJ554757 View Materials , MT077014 View Materials , MT077015 View Materials ) GoogleMaps .
Diagnosis. Seminemacheilus ahmeti is distinguished from all other species of Seminemacheilus by having many small black or brown dots or blotches on the belly (vs. absent) and the posterior naris reaching to the anterior eye margin when folded backward (vs. not reaching). It is further distinguished by a combination of characters. Seminemacheilus ahmeti is distinguished from S. ispartensis by lacking scales (vs. having deeply embedded scales on the caudal peduncle), having a roundish caudal fin (vs. truncate in S. lendlii and S. ispartensis ), a long head (head length 24–27% SL vs. 21–24 in S. isparaensis ), and 2–5 supraorbital head pores (vs. 5–8 in S. lendlii ; 6–10 in S. ispartensis ).
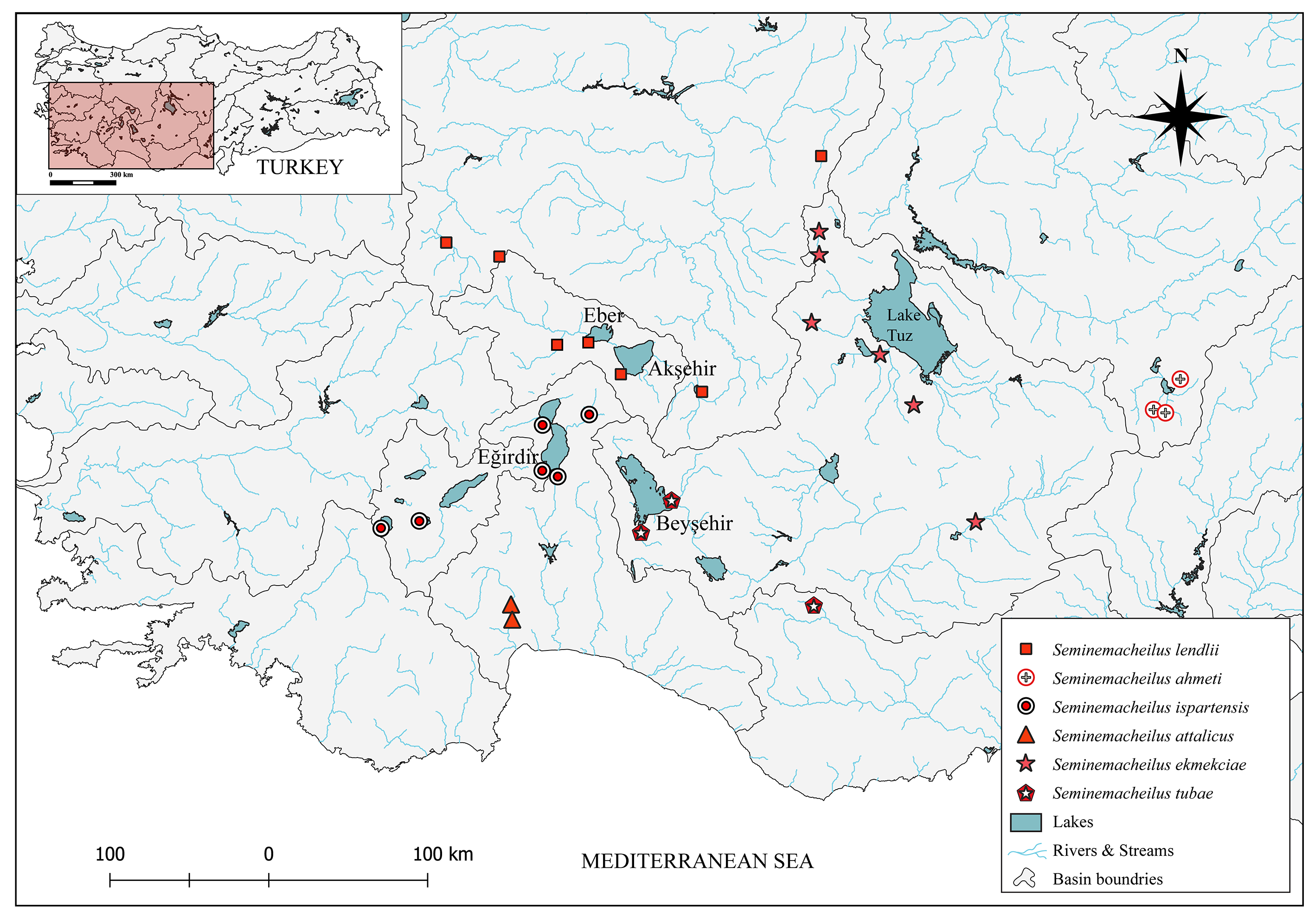
Distribution. Seminemacheilus ahmeti is endemic to Sultan Sazlığı, an endorheic basin in Central Anatolia.
Remarks. Based on DNA barcoding, S. ahmeti is well separated from all other studied Seminemacheilus species, and by a minimum K2P distance of 2.4% to S. ekmekciae , its closest relative. It is supported as a distinct species by the PTP approach, but not by the mPTP delimitation. Seminemacheilus ahmeti is one of five fish ( Aphanius danfordii, Pseudophoxinus elizavetae, Oxynoemacheilus ciceki and Cobitis joergbohleni ) endemic to Sultan Sazlığı ( Freyhof et al., 2018). All these species are now restricted to very small habitat patches, since the wetland has been drained and dried out in recent decades. This case triggers a high threat category for all the fish in Sultan Sazlığı, including S. ahmeti , making this small wetland a place of major importance for conservation.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Seminemacheilus ahmeti Sungur, Jalili, Eagderi & Çiçek 2018
| Yoğurtçuoğlu, Baran, Kaya, Cüneyt, Geiger, Matthias F. & Freyhof, Jörg 2020 |
Seminemacheilus ahmeti Sungur, Jalili, Eagderi & Çiçek, 2018:467
| Sungur, Jalili, Eagderi & Cicek 2018: 467 |